Pyramid of Success and Business
In my opinion, Wooden’s pyramid of success accurately indicates the necessary parts of success. Friendship, alongside with loyalty, will help the leader work on a project that others can find uninteresting (e.g. Sergei Brin and Larry Page). Both of the mentioned owners of Google would not work on the search engine back in the 1990s if they did not have enough enthusiasm for it (Brezina, 2012). At the same time, since both of them were highly educated, their skills allowed them to create one of the first popular search engines that were easy to operate. At last, nowadays, Google’s competitive greatness is in its ability to provide users with everything they need and want before their rivals can do it.
Leadership Style
I am a consultative leader; I believe it is important to know and validate the opinions of others, although my decision remains to be the final one. Therefore, I agree with Wooden on team spirit because only those individuals who place the team above their own self are the ones capable of bringing change into the organization. I also believe that alertness or the ability to learn are crucial for a consultative leader because followers are a major source of new ideas and information that the leader can overlook. However, I cannot agree with Wooden’s view of poise because leaders can often be carried away with their own beliefs and miss important opinions due to this blindness. It is important to be a flexible leader who can be true to him/herself but who can admit his/her beliefs are wrong if it is so. Self-control is an important trait both for leaders and for followers because it mediates the work of a team, allowing it to be more efficient and reducing the number of conflicts. In my personal life, self-control is an anchor that helps me stay confident even during highly stressful events.
Pyramid’s Aspects
Aspects I agree with are the following: cooperation, intentness, and condition. Cooperation is an essential part of any business because it is difficult, if not impossible, to start and run a business project completely alone. As Wooden (2017) accurately notices, cooperation helps “reach your organization’s full potential” (para. 2). Intentness is helpful when a business faces serious problems and the will to quit grows in the leader; without intentness, the promotion of an idea (or products) will fail at once when first difficulties emerge. Condition (mental, moral, and physical) is crucial not only for the leader but followers as well because any disruption in it will compromise teamwork, leading to unfruitful choices, which are often hazardous for the future of the project.
I do not agree with Wooden’s view of industriousness; furthermore, I do not understand why he does not address the importance of creativity. There are thousands of people who are enthusiastic about their job and who work incredibly hard, but their actions do not lead to competitive greatness because they lack creativity and replicate something that already exists (e.g. Samsung smartphones that are unable to beat Apple’s products due to less creative approach to the brand). One should also not forget about the privilege of social status; if Sergey Brin’s family had not immigrated to the USA when he was a child, the question arises whether he would be able to create the new search engine without being educated at Stanford at first.
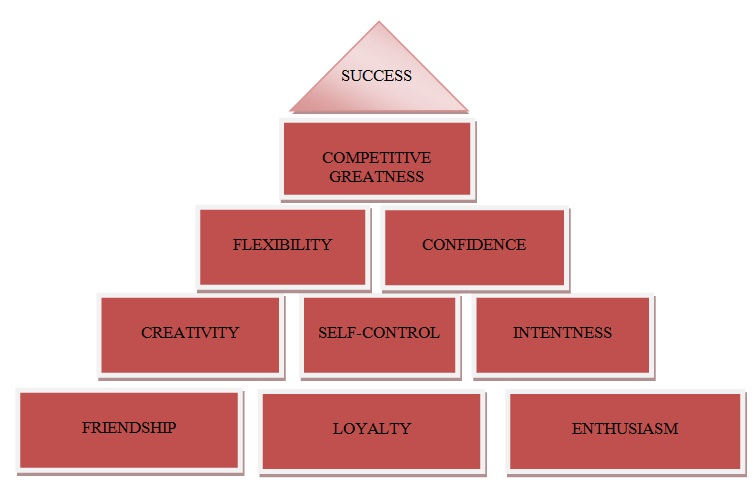
New Pyramid of Success
Friendship and loyalty are the basis of any business project because they encourage collaboration, interaction, and can potentially strengthen business relations (Newman, 2012). Without enthusiasm, the team will be unable to work on the product during the first years when investments are high, and revenues are low. Self-control and intentness are necessary for the team spirit and well-being even during the worst crises; the wish to give up should be controlled by the team’s focus on the goals. Confidence can significantly change the course of the business project, attracting new investors and customers (Passman, 2015). Flexibility allows the leader to be attentive to the opinions of others and admit where his or her choices are rather harmful than helpful. Competitive greatness is of importance during the latest phases when the project is recognized by the target market and has to compete with other strong rivals (see Figure 1).
Step-By-Step Strategy
During a crisis, the team can follow the proposed strategic plan:
- Evaluate the level of loyalty of the team members; additional encouraging might be necessary if it is low.
- Provide followers with clear vision and mission to increase enthusiasm; remind them of the past successful choices.
- Remember your intentions with regard to the project and see whether they have changed significantly. Control your reactions, emotions, and thoughts in the face of a crisis to avoid unnecessary disruptions in teamwork (Hazelton, 2014).
- Do not forget about creative approach; examine what is innovative about your project and what needs to be redone, compare its creativeness to other, more successful projects to understand whether you unintentionally copy any other businesses.
- Be confident in your choices but pay attention to overconfidence (Zaidi & Tauni, 2012). If any issues related to team’s decisions are recognized, be flexible and work on them.
References
Brezina, C. (2012). Sergey Brin, Larry Page, Eric Schmidt, and Google. New York, NY: The Rosen Publishing Group.
Hazelton, S. (2014). Positive emotions boost employee engagement: Making work fun brings individual and organizational success. Human Resource Management International Digest, 22(1), 34-37.
Newman, M. E. (2012). Communities, modules and large-scale structure in networks. Nature Physics, 8(1), 25.
Passman, D. S. (2015). All you need to know about the music business. New York, NY: Simon and Schuster.
Wooden, J. (2017). Cooperation. Web.
Zaidi, F. B., & Tauni, M. Z. (2012). Influence of investor’s personality traits and demographics on overconfidence bias. Institute of Interdisciplinary Business Research, 4(6), 730-746.