Introduction
Kuwait is one of the member states of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). This country has a stable economy due to the availability of different natural resources, including oil. Its leading industries include shipbuilding, petrochemicals, petroleum, cement, construction, and food processing. The report presented below gives a detailed analysis of this country’s economy. It goes further to discuss and examine its banking corporate governance. The information presented in this paper can guide and empower investors planning to do business in Kuwait.
Kuwait Economy
Kuwait is one of the smallest countries in the world with a petroleum-based economy. The country’s financial industry forms an integral part of its non-petroleum sector. A report released by the World Bank in 2016 identified Kuwait as one of the most successful in terms of GDP (Biygautane, Gerber, & Hodge, 2016). The key aspects presented below gives a detailed view of this country’s economy.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
In 2017, Kuwait’s GDP stood at $120.13 billion (“Kuwait GDP,” n.d.). This means that its GDP value represents around 0.2 percent of the global economy (Hassan, Al Shriaan, & Al-Mutairi, 2017). Since the 1960s, the country’s GPD has averaged 44.5 USD (“Kuwait GDP,” n.d.). The highest GPD of 174.2 billion US dollars was recorded in the year 2013 (see Figure 1). The lowest was recorded in the year 1962 at 1.8 US dollars (“Kuwait GDP,” n.d.). These statistics reveal that Kuwait is one of the most stable countries in terms of economy, thereby making it an admirable investment destination for many people from different parts of the world.
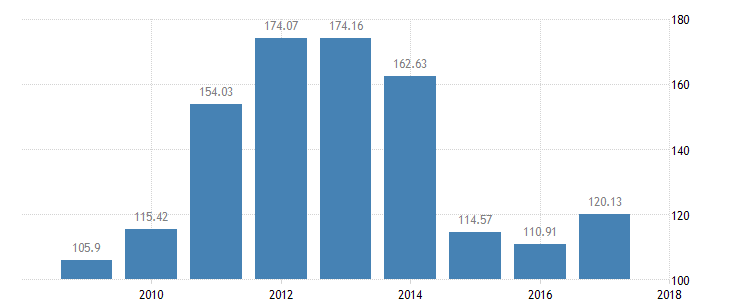
GDP Growth: Ease of Business Investment
Kuwait’s GDP has been growing steadily within the past few years. For example, the rate of growth for 2015 was around 0.6 percent. In 2016, the percentage of GDP growth increased to 3.5. Some of the leading sectors that continue to support economic growth and development in this country, such as agriculture, petrochemical and petroleum industries, and financial services (Hague, Patnaik, & Hashmi, 2017). Due to these indicators and developments, the country has been ranked number 96 when it comes to the ease of doing international business.
Interest Rate
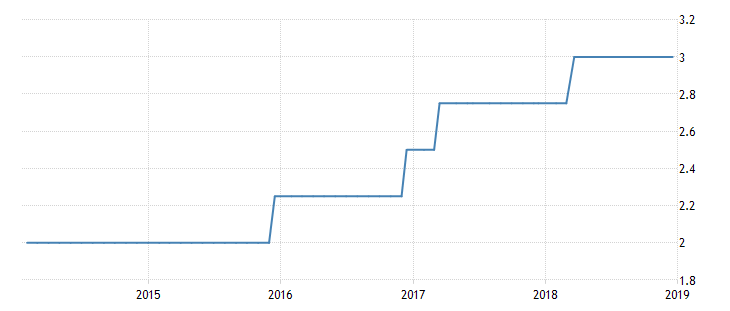
One of the outstanding aspects of Kuwait is that it ensures that its currency is not pegged to the US dollar. Instead, it has linked the dinar to different global currencies (“Kuwait interest rate,” n.d.). From 1999 to 2018, the interest rate has averaged 3.7 percent (see Figure 2). The highest percentage of 7.25 percent was recorded in 2000 while the lowest was in 2012.
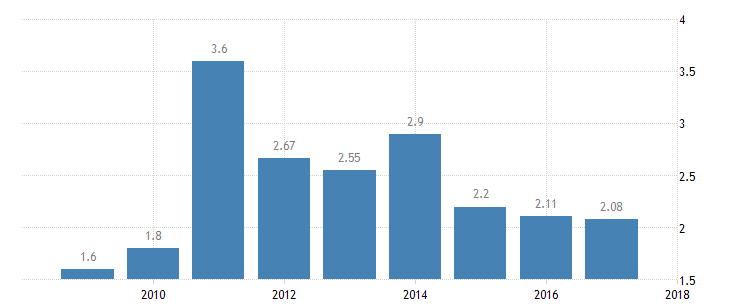
Unemployment Rate
From the year 1983, the rate of unemployment has averaged 1.5 percent. The highest rate of 3.8 percent was recorded in 2011 (see Figure 3). The lowest percentage of 0.50 percent was recorded in 1990. This is a clear indication that the country’s leaders have implemented adequate measures and initiatives to ensure that all citizens have stable sources of income (“Kuwait unemployment rate,” n.d.). This is something critical towards improving or supporting economic development and performance.
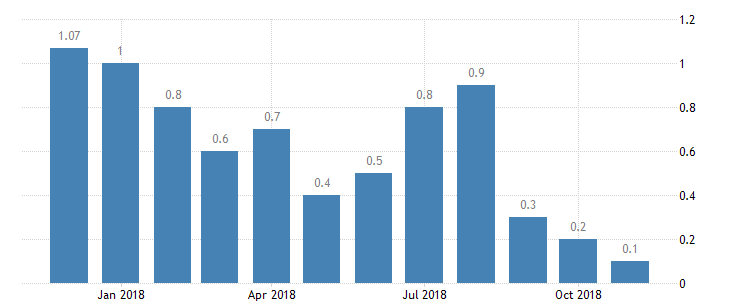
Inflation Rate
Since 2012, Kuwait’s inflation has remained quite low and sustainable. For instance, the highest rate of 3.68 percent was recorded in the year 2015. The graph presented below gives a summary of this country’s infiltration rate for the last twelve months (see Figure 4). Many experts and economists believe that the existing policies and financial measures have continued to support the goals of many investors (“Kuwait inflation rate,” n.d.). Kuwait’s inflation rate is expected to continue promoting economic performance and development.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
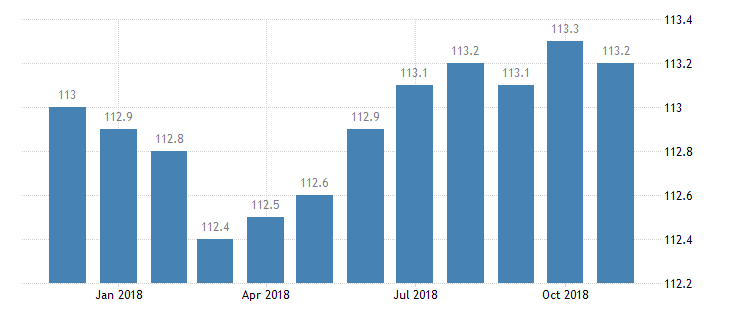
Statistics indicate that the consumer price index has been decreasing steadily with the past few months. For instance, the CPI decreased from 113.30 Index Points in October 2018 to around 113.20 Index Points in November (“Kuwait’s consumer price index,” n.d.). The average consumer price index averaged 88.05 from the year 2000 to 2018 (see Figure 5). The highest index stood at 113.20 in August 2018. The lowest was recorded in May 2001 at 65.30 Index Points.
The above graphs and discussions reveal that Kuwait’s economy has remained stable due to the nature and effectiveness of the existing policies. Such strategies explain why the petroleum-based economy continues to attract and empower different investors. According to the World Bank, the Kuwait dinar remains one of the highest-valued currencies in the world (Hague et al., 2017). The government’s focus on non-petroleum is an approach that has continued to support economic development.
The financial industry has continued to play an integral part in Kuwait’s economy, thereby making it competitive in the global arena. It would, therefore, be appropriate for the government to continue focusing on powerful policies and programs that will support economic development and ensure that the changing needs of the greatest number of citizens are met (Ramadhan & Al-Musallam, 2014). Such initiatives will eventually support all sectors and transform the living standards of different people.
Corporate Governance: Kuwait Banking Sector
Overview
Leadership and management are critical practices that dictate the success of every business organization. Belal and Hamat (2016) define “corporate governance” as a system of processes, rules, and practices by which a specific organization is controlled, operated, or directed. This concept is taken seriously to balance and meet the needs of all stakeholders of a given firm, including key shareholders, financiers, suppliers, customers, community, and government.
In Kuwait, the issue of corporate governance is taken seriously in an attempt to ensure that the banking sector meets that targeted economic development objectives. With proper leadership, it can be possible for banks to achieve their goals and deliver positive results.
Kuwaiti regulatory and regulatory authorities have been pursuing and supporting the idea of effective governance in all companies. Banks have been benefiting significantly from this kind of practice. Such agencies have been keen to support the development of superior regulations and laws that have the potential to confront emerging negative effects. Since the 1960s, the Central Bank of Kuwait (CBK) has been reviewing and issuing updated instructions to all banks operating in this country.
The main reason for doing so has been to ensure that the banking sector adheres to evidence-based managerial and leadership practices (Al-Shammari, 2014). The CBK has also been focusing on relevant international standards and control measures that result in effective corporate governance. This initiative is critical since it can ensure that all banks are capable of supporting performance and ensuring that that the targeted economic goals are realized.
Several issues or aspects dictate the nature of corporate governance in Kuwait’s banking sector. The first one is that top leaders have to support effective internal financial and auditing functions. Such practices should be completed by competent, licensed, and independent professionals. CBK should approve all individuals in charge of all boards of governors. This practice is by Article 68 of the CBK Law (Bashir, Fatima, Sohail, Rasul, & Mehboob, 2018).
The activities and missions of the board members should never be influenced by externally or internally. Another important issue is that of the board’s duties and responsibilities. These individuals are expected to exercise adequate supervision over other members of the executive, set the right organizational culture and structure, monitor internal operations, and lay down the right strategies objectives, and plans (Al-Shammari, 2014). The board in every banking institution is required to manage any form of conflict of interest, ensure that adequate and transparent data is available to all shareholders, and monitor compensation packages.
The executive function revolves around implementing the right policies and plans for financial operations, monitoring organizational activities, and analyzing results of all operations. All members of the executive must remain objective and transparent. They should provide adequate and verifiable reports, abide by all outlined laws, and ensure that the highest levels of professional ethics are maintained by all members of staff (McKenzie, 2016). They should go further to support the development of adequate principles and values.
The CBK also monitors the major initiatives undertaken in an attempt to promote good governance in financial and banking institutions. For instance, they require all banks to develop scientific procedures for identifying and managing risks, combating all forms of money laundering, and implementing adequate instructions to monitor investment procedures (Belal & Hamat, 2016). These attributes of organizational leadership in the Kuwaiti banking sector have continued to deliver positive results, thereby supporting economic sustainability and performance.
Major Amendment in Kuwait Banking Sector Corporate Governance
In 2012, the Central Bank of Kuwait (CBK) introduced new policies and regulations in an attempt to transform the nature of corporate governance and ensure that all banks can compete globally. According to CBK’s governor, the presented changes were essential since they were capable of consolidating trust in the sector at both the local and international levels (Kassem, 2018).
Many stakeholders supported the changes and regulations since they were capable of improving the nature of operating environments for all banks while at the same time maximizing local economic performance (see Table 1). Such laws also amended the major changes that had been supported by previous regulations implemented before the year 2012.
The new directives issued by the CBK in 2012 were mainly aimed at streamlined governance regulations and rules for all Kuwaiti banks. The first area of the amendment was that of the board of governors’ roles (“New rules for corporate governance,” n.d.). The new regulations affirmed that all boards were needed to honor their obligations and support the performance of the targeted institutions. The new amendment redefined several aspects, including strategic goals (Bell & Dent, 2018). The board of every bank should now improve governance practices or standards, be part of managerial practices, protect the interests of all stakeholders, and focus on the best approaches to manage risk. The board could also buttress internal management and monitor external auditing procedures.
The second aspect focused on the issue of the board’s independence. The main requirement was for boards to ensure that all decisions and issues were addressed objectively. This practice would make sure that the demands of minorities were not compromised (Zerban & Ateia, 2016). The board was also expected to promote its confidence and focus on profitability. This role was also expanded to address the needs of depositors and the overall stability of the monetary system (“Kuwait banking system well-positioned for future growth,” 2018). This was a major expansion of the regulations existing before the 2012 regulations.
The supervisory role of the board was widened to include the active supervision of the executive. The proposal was to introduce new committees managed by the board of directors. The ultimate objective was to monitor every sensitive activity or operation undertaken by Kuwaiti banks (Dibra, 2016). This strategy would streamline operations, minimize potential losses, and eventually support the country’s economic performance.
Another issue captured under the new corporate governance framework of 2012 was that of bonuses and allowances. The new role was for boards to assess bonuses and allowances in proportion to the bank’s long-term and short-term risk management. Leaders of boards were also expected to bolster transparency and enhance the announcement of data criteria (Zerban & Ateia, 2016). Such an initiative would promote effectiveness and eventually deliver positive results.
Chief executive officers (CEOs) and leaders of boards were required to focus on critical values and ethics of governance. Such attributes were taken seriously in an attempt to maximize professionalism and improve performance. With these changes, the CBK was keen to undertake new surveys and studies aimed at assessing how certain financial institutions and banks followed such regulations (Kotnal, 2016). The collected information would then be considered to propose new improvements or changes to transform the nature of corporate governance in the country’s banking sector.
Table 1. Comparison of regulations in Kuwaiti corporate governance in the banking sector.
Conclusion
The above discussion has revealed that Kuwait is one of the countries in which the economy is performing positively. The CBK’s ability to implement effective corporate governance procedures for the banking sector is a critical initiative that continues to deliver desirable results. The laws and regulations introduced by the CBK in 2012 streamlined corporate governance in the banking industry, thereby creating a better environment for financial transparency, effectiveness, and economic development. The organization should, therefore, continue to introduce superior amendments and legal improvements to support all stakeholders’ needs and continue making the country a leading competitor in the regional and global markets.
References
Al-Shammari, B. (2014). An investigation of the impact of corporate governance mechanisms on the level of corporate risk disclosure: Evidence from Kuwait. International Journal of Business and Social Research, 4(6), 51-70.
Bashir, U., Fatima, U., Sohail, S., Rasul, F., & Mehboob, R. (2018). Internal corporate governance and financial performance nexus: A case of banks in Pakistan. Journal of Finance and Accounting, 6(1), 11-17. Web.
Belal, Z., & Hamat, M. (2016). An overview of corporate governance practices of selected Islamic banks. TSAQAFAH: Journal Peradaban Islam, 12(1), 1-18. Web.
Bell, O., & Dent, I. (2018). Frontier markets: Banking on further Kuwaiti catalysts. Expert Investor. Web.
Biygautane, M., Gerber, P., & Hodge, G. (2016). The evolution of administrative systems in Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar: The challenge of implementing market based reforms. Digest of Middle East Studies, 26(1), 97-126. Web.
Dibra, R. (2016). The role of corporate governance failure in the banking sector. European Scientific Journal, 12(34), 68-74. Web.
Hague, A., Patnaik, A. K., & Hashmi, S. Z. (2017). Foreign direct investment and growth: A study in the context of Kuwait. International Journal of Financial Research, 8(1), 9-15. Web.
Hassan, M., Al Shriaan, A., & Al-Mutairi, A. (2017). An analysis of Kuwait economy 1995-2015. Asian Social Science, 13(12), 24-34. Web.
Kassem, M. (2018). Kuwait banking system stable as economy grows, Moody’s says. The National. Web.
Kotnal, J. R. (2016). Corporate governance in banking sector: A fine-tuning performance. International Journal of Applied Research, 2(2), 619-624.
Kuwait banking system well-positioned for future growth: Shaikha Al-Bahar. (2018). Kuwait Times. Web.
Kuwait GDP. (n.d.). Web.
Kuwait inflation rate. (n.d.). Web.
Kuwait interest rate. (n.d.). Web.
Kuwait’s consumer price index. (n.d.). Web.
Kuwait unemployment rate. (n.d.). Web.
McKenzie, B. (2016). Recent developments in the banking sector and AML in Kuwait. Lexology. Web.
New rules for corporate governance go into effect in 2014. (n.d.). Web.
Ramadhan, M., & Al-Musallam, M. (2014). The international experience in private sector development: Lessons from Kuwait. Theoretical Economics Letters, 4, 279-288. Web.
Zerban, A. M., & Ateia, W. B. (2016). Corporate governance in the banking sector (empirical study on the effect of separating chairman and chief executive officer (CEO) positions on financial performance. Accounting and Finance Research, 5(3), 37-43.