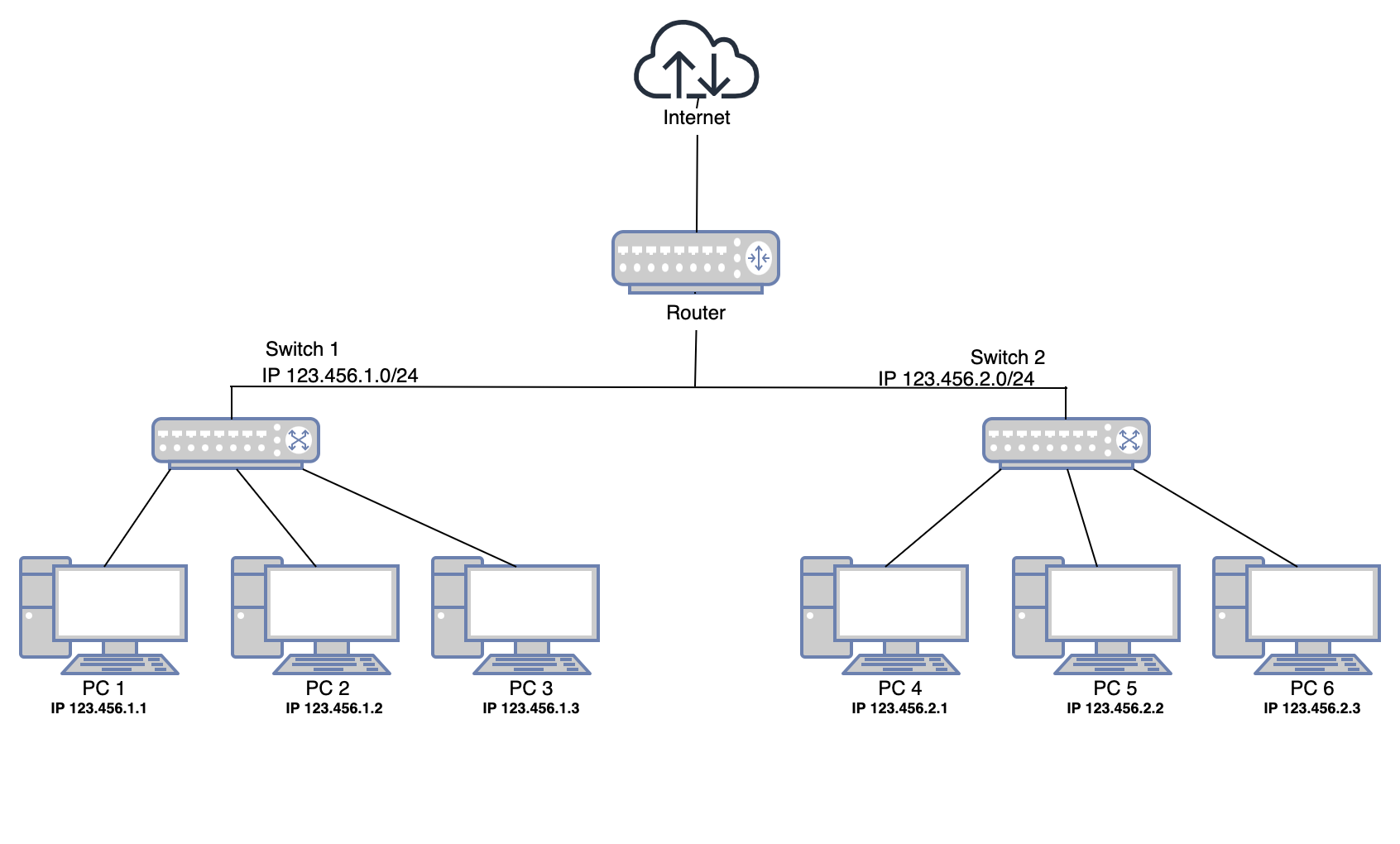
The diagram below represents the Local Area Network that is equipped with six workstations. The twisted-pair cable is used in the given diagram, which is considered the most common type of cabling for LAN. The magnetic fields around the wire interfere with signals on the nearest wires, creating noises. In order to avoid crosstalk and statics, the pairs are twisted, thus forming a circuit for data transmission. In the given Network Diagram, the unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable is used. The cable consists of 4 copper wires that are tightly twisted together. The UTP was used due to technical and safety reasons. It has a smaller diameter because of thin pairs of copper wires and does not require grounding.
The distance between connections is 80-95 m to ensure safety since the standard for any twisted-pair cables is no more than 100 m. The standard of wiring which stipulates the division of twisted pair categories is the American TIA-EIA-568B Standard.