Introduction
Research Background
In the last decade, different leadership management strategies have been applied within the hospitality industry in the UAE as part of sustaining the competitive advantage. As the demand for quality services increased among customers, hotels within the UAE hospitality industry have developed and implemented a series of leadership sustainability strategies aimed at output and efficiency improvement. In the previous century, the most common leadership process was linear, which is characterized by centralized decision making followed by communication of such actions by an individual or office. However, in the 21st century, the process has changed into an interaction model characterized by a proactive transition of the decision making and implementation processes (Vaccaro, Jansen, Bosch, & Volberda, 2012). Under the interactive model, there is direct interaction between the subjects and the leader in addressing the aspects of efficiency, corporate social responsibility, and sustainable performance among others (Baxter, 2014). Specifically, the need for efficiency in decision making and improved organizational performance necessitated more research into the current leadership styles being applied within the Burj Al Arab and how they affect organizational performance. Therefore, the proposed research will attempt to proactively provide a practical employee motivation framework for the Burj Al Arab as influenced by the leadership approaches in place.
Research Objectives
Considering the role of leadership styles on organizational performance, the proposed research examines the current leadership styles being practiced at the Different leadership approaches being applied at the Burj Al Arab and the degree of their impacts on organizational performance. Thus, the objectives of the case study research are;
- To review the significance of different leadership styles within the Burj Al Arab.
- To explore ways for measuring the level of employee motivation as influenced by the leadership style in practice.
Research Questions
- How effective and sustainable is the current leadership approach within the Burj Al Arab in the management of the level of employee motivation?
- How effective is the function of the current leadership styles in improving organizational performance at the Burj Al Arab?
Literature Review
Leadership Theories
Several leadership theories have been put forward to explain their development and effectiveness in organizational management. For instance, the transformational leadership theory defines organizational management as dependent on employee empowerment, critical problem solving, and strategic commitment (Dasgupta, Suar, & Singh, 2012). Secondly, the leadership expectancy theory states that organizational functionality in decision making should be void of stereotype, prejudices, and emotions. In fact, the theory highlights ethical decision making as part of valence, effort, and outcome performance (De-George, 2013). The incentive theory defines the perception of an employee on the effectiveness of motivational strategies. This means that higher expectations, in terms of motivation, attract better performance when all other factors are held constant (Arslan & Staub, 2013).
The arousal theory functions within the organizational communication structure as defining the expectations, development norms, and guidelines controlling performance. For instance, Huczynski (2012) argues that, “what valence a certain object or activity and partly upon the needs of the state of the person at that time” (p. 273). This position is supported by the Vroom’s expectancy theory, which defines leadership as significantly influenced by the expected rewards and potential future benefits that individual can obtain from an organization. This means that the leadership behavior model should be angled on stages to conceptualize a clear process for decision making and implementation. For instance, the Vroom expectancy model suggests a classification of leadership behavior on the premises of symbols, analytics, and people as interdependent (Arslan & Staub, 2013).
Leadership Styles
In the 21st century, there has been a paradigm shift in roles and responsibilities of business leaders in organizations as the decision environment becomes more dynamic and proactive. According to Baxter (2014), a leadership style refers to the approach applied by a manager or leader in an organization. Among the notable leadership styles being practiced currently are autocratic, democratic, and participatory approaches. However, there are few organizations practicing the laissez faire style.
Autocratic leadership style is defined by decision making process that is based on the management. The decisions made under this style are then communicated to the subordinates without consultation. As per this leadership behavior, it is expected that the subordinates should obey these decisions as the company position on a matter (Vaccaro et al., 2012). In line with the theory Y and theory X, autocratic leadership style functions on direct supervision on the basis of instructions issued to responsible employees (De-George, 2013). This leadership approach has the advantage of promoting proactive employee participation in implementation of different decisions.
The Democratic leadership style is characterized by proactive organizational management through consultative decision making framework involving the management and employees. According to Arslan and Staub (2013), “democratic leadership style means facilitating the conversation, encouraging people to share their ideas, and then synthesizing all the available information into the best possible decision” (p.45). This leadership approach is associated flexible decision making process that is broad and accommodative to different views. However, consensus building may become a challenge and delay decision making in crisis, when fast and radical resolutions should be made.
According to Baxter (2014), “participatory leadership is a system in which employees of a business organization take an active role in the decision-making process as it relates to the way the business operates” (p. 34). Participatory leadership style is associated with teamwork, inclusion, and higher level of employee responsibility. In the UAE, participatory leadership style is the most common within the restaurant sector.
Laissez faire style of leadership is characterised by the “manager taking a back seat in proceedings, leaving the staff in charge of their own specific sections or tasks” (Arslan & Staub, 2013). This style of leadership is associated with improved employee morale as they are empowered to make decisions in all cases. Moreover, it promotes creativity and innovative idea creation and implementation. However, this style of leadership is prone to redundancy through abuse of office. For instance, since the manager does not intervene in decision making, employees might lose sense of direction and accountability. Within the UAE restaurant sector, laissez faire leadership style cannot work because of the sensitivity and dynamics of the market forces.
Importance of Leadership in the UAE Restaurant Sector
Different leadership styles are associated with varying operational and decision making models. Specifically, efficient leadership styles facilitate proactive performance through analytical and scientific decision making process. In relation to the UAE restaurant sector, different leadership styles in practice have facilitated improved performance quality through improved employee motivation (Baxter, 2014). As a result of well developed leadership tradition in management of restaurants within the UAE, the highly skilled managers have become the pillars of inspiration and creativity. At present, the city of Dubai has some of the best and most effective restaurants such as the Burj Al Arab.
The managers of these hotels have integrated strategic communication models and constant performance reviews to nurture an ideal operation environment for optimal output. Series of past and current literate suggest that the Dubai restaurant sector has been on an upward growth trend (Huczynski, 2012). In the last ten years, the sector has continued to recruit more employees, improve on production output, and welcome many new entrants and expanding hotels. In order to sustain the competitive advantage matrix, the current breed of restaurant managers within the UAE has incorporated empowerment, critical problem solution, proactive participation, and constant commitment to put the sector on a world map. For instance, the Burj Al Arab is one of the leading seven-star hotels across the globe. These leadership approaches have resulted in improved effectiveness of the hotels within the UAE restaurant sector.
Topic and its Significance
Introduction of Research Topic
The purpose of this research is to explore quantifiable and specific impacts of different leadership styles on the performance of the Burj Al Arab as part of employee motivation. It is necessary to review the impact of these leadership styles on organizational performance within the UAE restaurant industry. Specifically, the researcher concentrates on leadership styles being practiced at the Burj Al Arab hotel. The case study research will examine the best leadership practices within the restaurant and how employees perceive these strategies as affecting their level of motivation and actual performance. Thus, the outcomes of this case study will be instrumental to the management of the Burj Al Arab in improving the scope of employee motivation strategies. In addition, the findings might assist the Burj Al Arab’s management team in implementing the effective leadership styles that are associated with sustainability and efficiency of employee motivation.
Research Justification or Significance
Organizational performance as related to leadership styles in practice is significant in determining the level of efficiency and employee behavior orientation. Apparently, there is no specific research study that has been carried out to quantify the impacts of the current leadership styles on the organizational performance matrix at the Burj Al Arab. Thus, the rationale for the case study will be to establish the possible link between organizational performance and different leadership styles in place.
Research Methodology
Research Approach
The survey study approach was used to address the objectives of the research. Qualitative research was adopted because of the dynamic, subjective, and focused study. The research targeted 30 employees of the Burj Al Arab who were requested to fill questionnaires consisting of twelve close-ended questions about organizational leadership and performance. The questionnaire survey was conducted via a drop-and-pick approach from the survey pool consisting of 10 managers and 20 employees. Each questionnaire was accompanied by a consent letter defining the research scope, rights of respondents, confidentiality of the research and process of withdrawal. Before commencing the study, permission for research was forwarded to the Burj Al Arab management. Validity and reliability in the research were achieved through pre-testing the questionnaire. This was necessary to ensure that comparative research is not compromised. The data collected from the primary data were coded for easy analysis and interpretation. In order to present a clear picture of the findings, figures, tabulation, and charts were incorporated in the analysis.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire consisted of 12 seven-item closed-ended questions. A simple language was used in the design of the questionnaire. The questions were created by the researcher as summarized below.
Are you aware of leadership styles at the Burj Al Arab?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Are there unique styles being used by the Burj Al Arab management in running the organization?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Do you agree that the common leadership style(s) are promoting organizational efficiency?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Are the leadership styles reflective of the actual performance at the organization?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Do you agree that the success of the current leadership strategy is related to implementation?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
6. Do you believe that the current leadership styles are very effective?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Are you satisfied with the content of the current leadership style(s)?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Do you agree that the current leadership style(s) have been important in merging thoughts and opinion to promote proactive engagement?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Are you aware of other restaurants within Dubai using similar leadership style(s)?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Does the current leadership styles represent the Burj Al Arab’s corporate balance?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Do you think the leadership styles resonate with the dynamics of the UAE restaurant sector?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Do you think the leadership styles are functional and flexible to meet your expectations?
- Strongly Disagree
- Disagree
- Slightly Disagree
- Neither Disagree nor Agree
- Slightly Agree
- Agree
- Strongly Agree
Data Tables and Analysis
The rate of response to the questionnaires was 100 %( as captured in table 1). The repossesses were given on time.
Table 1: Characteristics of the respondents. (Source; Self generated).
The responses to each question was analyzed and cross tabulation generated (as captured in table 2 and figure 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13) to make sense of the actual situation.
Table 2: Summary of the responses in percentage. (Source; self generated).
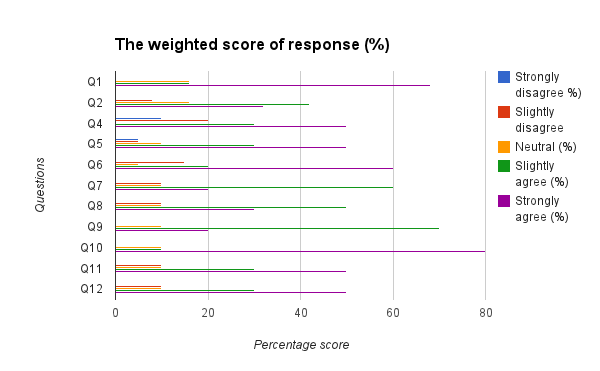
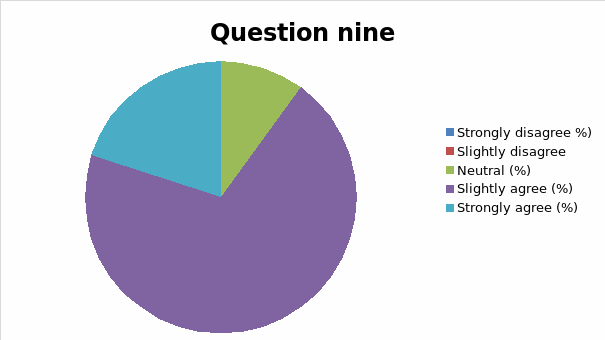
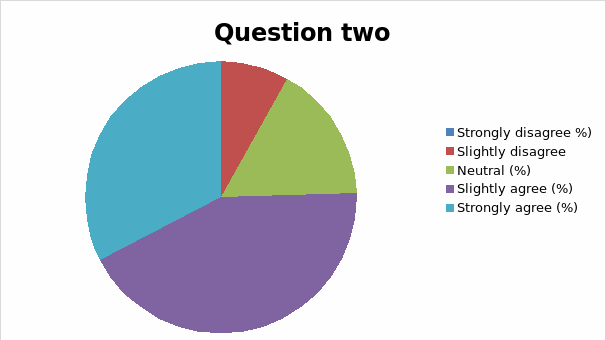
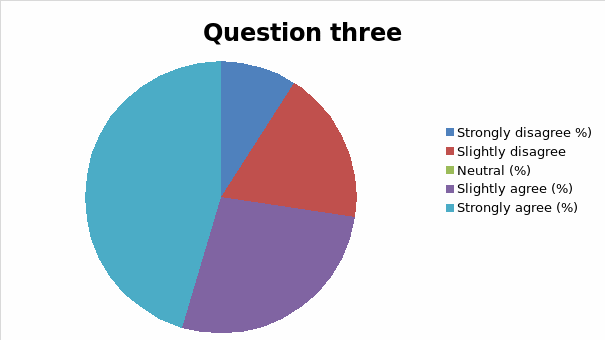
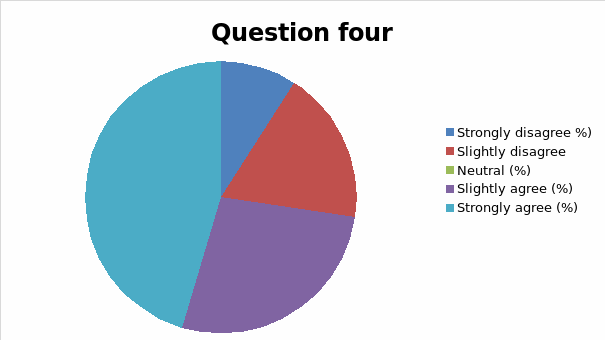
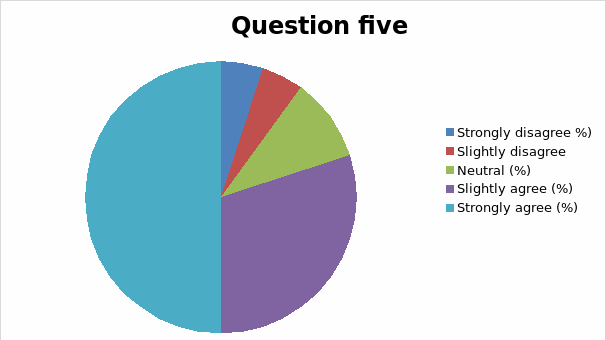
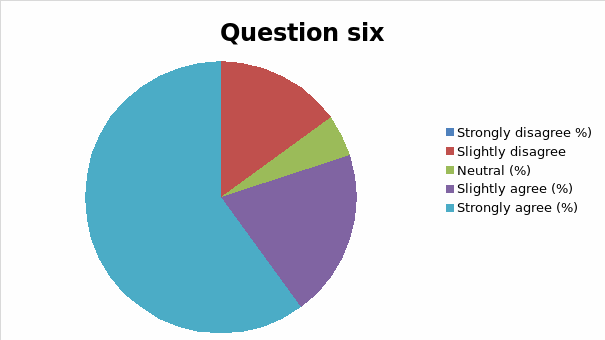
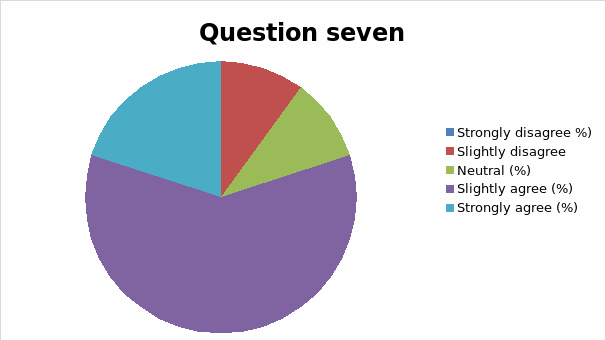
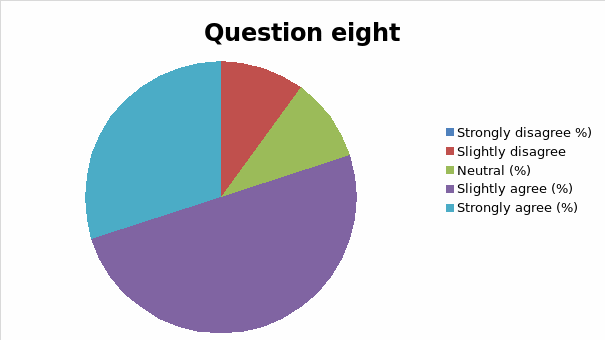
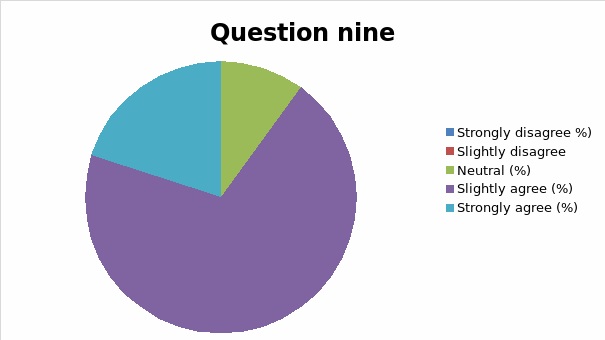
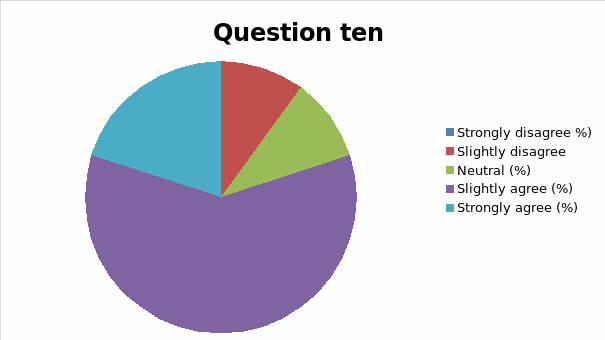
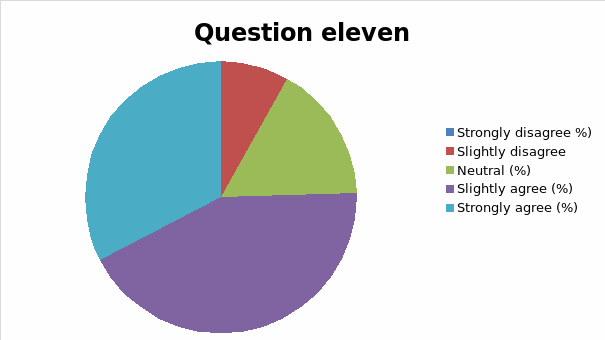
Since the proposed study relates different leadership approaches to organizational performance of the Burj Al Arab, the current and future strategies for sustainable management were examined as part of proactive employee motivation for optimal output. The research study reviewed the current leadership behaviors and how they have impacted the growth and sustainability of the Burj Al Arab’s business model in the dynamic Dubai restaurant sector. The results of the data analysis suggest that the respondents were aware of the leadership application in their organization and its impact on performance. Specifically, for all the close-ended questions, an average of 80% of responses could associate the current successes of the organization to leadership strategy. Among the factors noted by the respondents are contributing to positive impacts include dependability, clarity, visionary approach, and reliability.
Conclusion and Lessons Learned
Conclusion
- As established in the research findings, the Burj Al Arab’s business model is angled on a strong and strategic leadership management system that promote employee participation in fulfillment of different goals and objectives.
- The Burj Al Arab’s management consists of well skilled managers who have been proactive in providing sustainable approaches to running the daily activities at the hotel.
- The employees of the Burj Al Arab are well motivated and aware of the impact of the current leadership system on their motivation and performance.
- The high level of employee satisfaction with the current leadership is an indication of better future for the organization, in terms of performance and business growth.
- However, the Burj Al Arab should improve on the aspect of direct employee engagement in decision making since this element had the least score. This would facilitate improvements of the organizational culture and structure in leadership application.
Lessons from the Project
- Apparently, carrying out scientific research requires proper planning, gathering the right information from which a research topic can be created. In the planning stage, it is necessary to review the past documents on the same topic to graps a previous perspective and establish a potential research gap. The research gap forms the significance of the study since rationalization of any new research should be based on the areas ignored by previous studies.
- Carrying out primary research is very demanding, especially at the stage of following up the respondents and waiting for approval permission by the bureaucratic management of the Burj Al Arab restaurant in the city of Dubai.
- Although the findings are scientific, the results may not be relied upon in decision making if other factors promoting effective organizational performance are not integrated.
- Proper leadership orientation in an organization may make the different in performance, especially when the employees feel left behind or not appreciated. This means that any leadership strategy must be accommodative and consultative to capture various views to gurantee acceptance and success.
- The research project was an eye opener in the practical application of leadership, theoretical proposals, and the dynamics steering proper decision making. For instance, in carrying out theoretical perspective analysis, it was interesting to reveal the many theories in place to explain different leadership styles and their application.
References
Arslan, A., & Staub, S. (2013). Theory X and theory Y type leadership behaviour and its impact on organizational performance: Small business owners in the şishane lighting and chandelier district. Procedia-Social and Behavioural Sciences, 75(1), 102-111.
Baxter, J. (2014). Who wants to be the leader? The linguistic construction of emerging leadership in differently gendered teams. International Journal of Business Communication, 3(4), 23-41.
Dasgupta, A., Suar, D., & Singh, S. (2012). Impact of managerial communication styles on employees’ attitudes and behaviours. Employee Relations, 35(2), 173-199.
De-George, R. (2013). Business ethics (7th ed.). New York, NY: Pearson Education Limited.
Huczynski, A. (2012). Management gurus, revised edition. London, UK: Routledge.
Vaccaro, G., Jansen, P., Bosch, J., & Volberda, H. (2012). Management innovation and leadership: Tshe moderating role of organisational size. Journal of Management Studies, 49(1), 28-51.