Introduction
The aim of this report is to analyze macro-environmental factors of Starbucks, assess the liabilities related to PESTEL factors and examine the past position that cause dilemmas with production or cost.
Macro-Environmental Factors of Starbucks
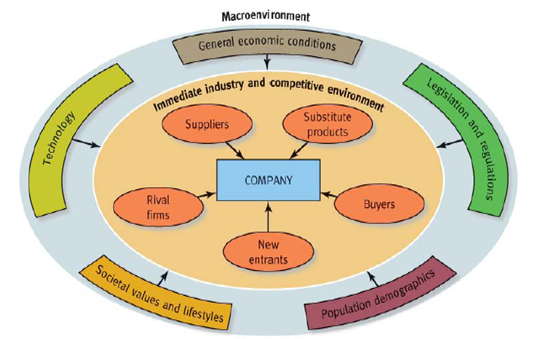
Figure 1: The Components of Starbucks Macro-environment
Source: Brown (16)
Political Factors
According to Brown (19), the coffee industry experiences numerous political pressures in the macro environment; for example, the market players import coffee-beans from different nations, and each of the nations possess respective customs and tariff-regulations; so companies such as Starbucks needs to cautiously observe political disruptions and policy modifications like decision to seize foreign company’s assets
Economic Factors
According to the annual report 2011 of Starbucks, this company faced serious challenge due to global financial crisis in 2008 while yearly profits decreased and operating costs increased significantly.
In addition, there are many other related issues, which adversely impact the business, such as, unfavourable general economic conditions, lack of customer acceptance of new products, lower customer base because of recessionary impact like high unemployment rate, decline consumer demand, and so on.
However, extreme competition in the global market for free trade policy or low cost coffee providers, unstable economic conditions in the local and certain international markets, rise of the price of raw materials, uncertainty about duties due to inflation and fluctuation of currency can influence the business of Starbucks. However, the following figure demonstrates the historical stock price of Starbucks in three stock exchanges –
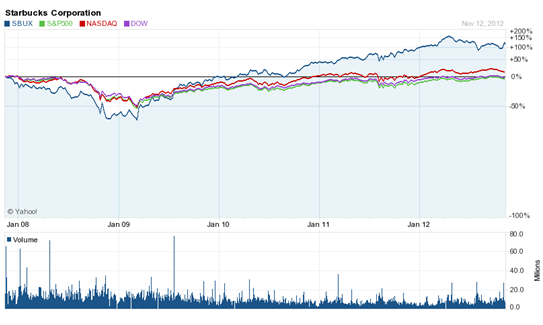
Figure 2: Historical stock price performance of Starbucks from 2008 to 2011
Source: Yahoo Finance (1)
Socio-cultural Factors
Brown (19) argued that socio-cultural factors concentrate on the way in which customers force the industry and how the company responds to this; this company executes a CAFE agenda to deal with concerns regarding the CSR of the industry to enable sustainability of coffee-bean cultivators that may create quality benchmark; moreover, SBUX also buys non-fat-milk to serve health-conscious customers
Technological Factors
Brown (20) stated that implementation of advance technology is one of the most important factors in the coffee industry because it relates to customer interaction to the business, new product development, quality control, marketing and advertisement process; however, Starbucks integrates CRM system to develop communication system as both consumers and employees are the significant issue for the future.
At the same time, technology plays vital role to compete with the competitors, such as, integration of information technology and new equipment like coffee-bean roasters and brewing machines, the use of Wi-Fi internet capability services, and so on.
Environmental Factors
According to Slideshare (1), the company is particularly observant to ascertain eco-friendly production process by focusing on sustainable solutions; these include recycling in outlets, reusing cups, composting of coffee-ground, buying renewable-energy, generating a design to verify retail outlets and outlet archetypes, lessening power utilization by twenty-five percent, executing a climate change policy, concentrating on energy conservation, and so on
Legal Factors
The coffee industry is subjected to numerous laws and regulations; so, being one of the major players of the industry and operating in 61 countries across the world, SBUX needs to obey all rules of the industry.
This company carefully complies with the laws of the countries in which it operates; these include employment legislation (such as working-time and minimal wage-rate), health-safety legislation, customer safety legislation, and so on; therefore, the company is expending further 250m US dollars on health-insurance and expending 225,000 US dollars to resolve Consumer Protection litigation for gift card breaches (Starbucks 15)
Historical background that cause problems with production or cost
- Business plan: In 1992, Schultz made a business plan to attain the projected revenue of $60 million, but it created difficulties in production segment due to lack of experienced and skilled management;
- Self cannibalization: BBC (1) reported that Starbucks expanded its business rapidly (from 84 US stores in 1990 to 1,000 in 1996), but it created image problems and tarnished the exclusive as the customers compared this company with McDonald’s and Burger King;
- Construction costs increased due to implementation of growth strategies in the past decades;
- Volatility of the price of raw materials increased production costs (raised the costs of high-quality Arabica coffee-beans), which influenced the company to offer high price, but the competitors set new pricing strategies to provide services at low cost;
Liabilities of Starbucks towards Their Macro-Environmental Factors
SBUX confronts several liabilities while coping with macro environmental factors as external environment effects the way in which the market players conduct their businesses; for example, the coffee market is extremely competitive and flooded with rival firms and if it fails to extend business outside the US market and discover new customers, then the market share could keep on falling.
Governmental directive is one of the macro environmental factors and a boost in formulating strict laws regarding import, export, or health and safety may mean more investment in ensuring workplace safety or fluctuation in trading costs for Starbucks; conversely, if the supply of high quality coffee-beans fall, the costs of acquiring the supply will increase (Brown, 68).
Works Cited
BBC. Why Starbucks’ sales have gone cold. 2008. Web.
Brown, Harold. External Environmental Analysis of Starbucks and the Coffee Industry. 2011. Web.
Slideshare. Starbucks Coffee Company: Macro-environmental Analysis. 2011. Web.
Starbucks. Annual Report. 2011. Web.
Yahoo Finance. Historical stock price performance of Starbucks. 2012. Web.