Introduction
The study concerned with preparing strategic management procedure of “Starbucks”. This analysis would focus on a number of key points regarding the external and internal environments, strategic missions, business, corporate and global strategies, corporate governance programs, organizational structures, innovative features and many other issues of related to the strategic competitiveness to earning more than average income.
“Starbucks” at a glance
The companies was established in 1985 aimed to buy and roast better quality coffee beans and sell them as fresh as Italian style. Several accessories and machines were included to prepare coffees as ready to drink beverages. Starbucks also sells the trademarks and licenses by using a number of channels and retail stores are regarded with specialty. However, the vital goal of the company is gain international recognition with operational specialty and selective distribution channels. Annual report-2008 shows that Starbuck earns total 85% of its revenue from the own operated retail, 11% from licensing and 15% from specialty.
Strategic management process
Starbuck’s overall strategic management process could be designed as following:
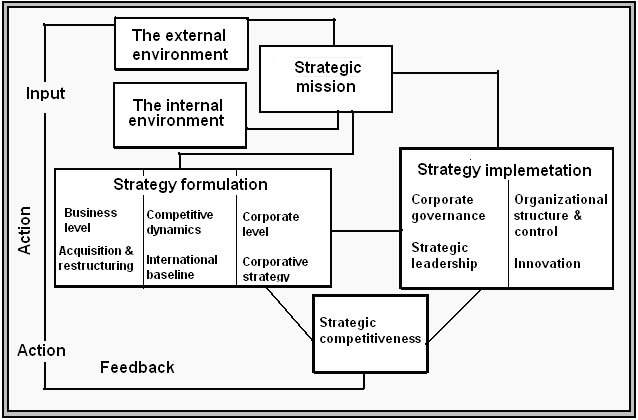
Environmental analysis
Starbuck’s environmental factors could be examined by PEST analysis as following:
- Political factors: Starbuck has ‘gained ground’ regarding the ethics and supplier relation while it is also in a risk of imposition of greater control by China government regarding a minimum level of risks of interpretation, intellectual property enforcement and related laws while there is a chance of being penalized and restriction of launching new stores. David, F., (2008) argued that target markets of developing countries political conditions are causing the similar problems.
- Economic factors: Starbuck scored a high net income of $9.4 billon in 2007. In 2006 it gained $7.8 billion as net revenue. At the same time licensing revenue was $1.0 billion results from the high sales growth rate and the CPG business. The company has also proved its economic excellence by a global revenue of $1.3 billion, sales growth by 8% with others income of $29 million by the year 2006.
- Socio-cultural factors: Kotler, P. (2006) said CSR enables the company to providing social, economic and environmental satisfaction to public with 172000 competent employees.
- Technological factors: Modern technological supported Starbucks card for customer service, convenient central management of products and pricing for international distribution are very significant with technical expertise for production line.
Environmental concern
It includes a number of factors, like- resources, capabilities and core competencies. Those are as following:
- Resources: David, F., (2008) argued that under resource based theory, a company has 6 types of resources. Thus, Starbucks resources are:
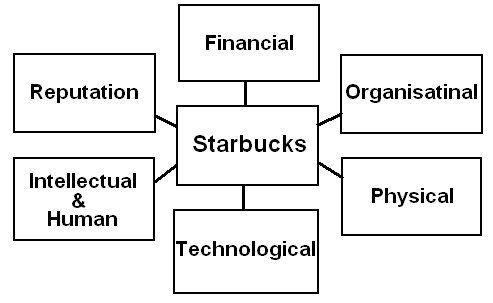
- Financial resources: The comparative financial possession of the company could be presented as:
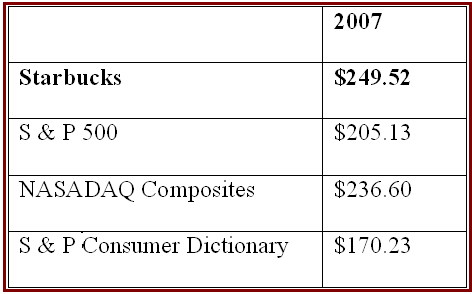
Starbucks is capable to gain high revenue and sales growth and a better EPS all that augmented to meet up the sales target in restaurant and retail sector of USA.
- Organizational resources: Regarding the organizational structure, Starbucks expanded in the field of retailing and situated with high traffic and visibility areas involving suburban centers, university campuses and situated outside of retails houses with various channels.
- Physical resources: It includes land, buildings, store equipments, leasehold improvements, equipments for roasting, and furniture, fixtures and others resulting total value of $28904330 by the year 2007.
- Technological resources: Starbucks is in top to performing its task by adopting modern technologies. For this purpose, it has implemented card system for customer service with entire process of maintaining restaurant service, retailing and global operations with innovative supports.
- Intellectual and human resources: Starbucks R&D is enriched with scientists, chemists and culinarians who are active for technical installation of foods, beverages and other machineries. It incurs about $7.0 million, $6.5 million and $6.2 for the year 2007, 2006 and 2005 for the R&D costs relative to testing process improvements of products and corporation.
- Reputation resources: Starbucks affords a high brand value and keeps continuous effort develop in future in North America. This reputation is the outcome of consumer perceptions about the quality, trust and ethical factors in every market segment. The generated goodwill for the year 2007 was $127636 in United States, $78289 around the world, $9700 in CPG and a total of $215625 in total.
SWOT analysis Starbucks Corporation
Strengths:
- Starbucks has outstanding brand awareness and quality image which helps to.
- It has websites to cover spread its business all over the world.
- It has skill and efficient employees and administration.
- It has make huge profit from capital lease, in last three years it has made $12.8 million from lease capital.
Weaknesses:
- Pricing and availability for all sorts of customers.
Opportunities:
- Starbucks has strong capital and resources for further expansion.
- Increased consumer interest on new products.
Threats:
- Competitors are the main threats for Starbucks Corporation
- Last year it had failed to meet market expectation
Capabilities
Capabilities enable the company for creation and exploitation of opportunities for the development of sustainable advantages while a utilization of adroitness and insights. The flow of capabilities of the company can be shown as:
- Building of heart relationships with customers by the products.
- Maintenance of community services and strong supply chain with the distributors.
- Sourcing, roasting and improvement in making worldwide famous coffees.
- Committing to the acts of environmental leadership.
- Sharing possible and related information with stakeholders and partners.
- Innovative and diversified adaptive tendency.
- Controlling and evaluating the performance of every project.
- Initiating for co- branding as well as marketing performances.
- Operational swiftness at in store selling.
- Effectiveness in infrastructure of administration.
Core competencies: It indicates Starbucks resources and capabilities which are providing as a modem of competitive advantage, like quality, taste, flavor and diversification that distinguish it competitive and glorify its image and personality.
Formulation of strategies
Thompson, A., argued that strategic options are coordinated and interrelated set of actions that has been designed for exploiting the core capacities and competencies for achieving competitive advantage. So, according to the standard model, Starbucks generate several strategic options through some systematic phases from business- level to co- operative strategy:
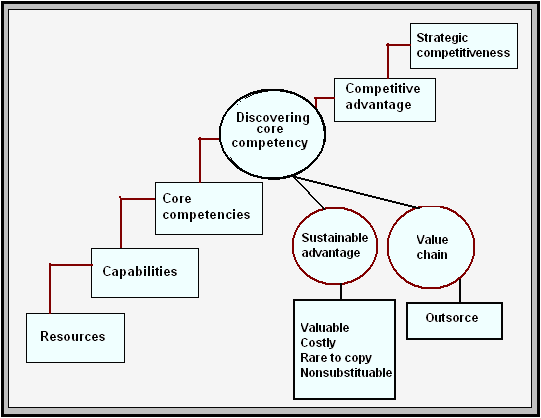
Thus, a number of strategies at this level are as:
Business- level strategy
Starbucks can generate this type of strategy by using Porter’s generic strategy as below:
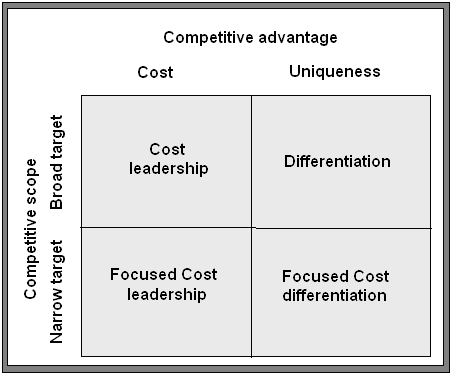
- By following the cost leadership strategy, Starbucks will be able to provide coffee beverages at the lowest costs in relation to other competitors’ like- McDonald’s, KFC, and Pizza Hut.
- Dibb, S. et al (2001) argued that by following the differentiation strategy, the company can deliver unique attributes and features to the target customers. Here, Starbucks can offer the finest whole bean coffees, quality green coffees and other unique items. At the same time providing an effort to catch the customers according to their working, traveling, dinning places as a symbol of offering values at a distinctive way. The formulation of differentiation strategy can be shown as following:
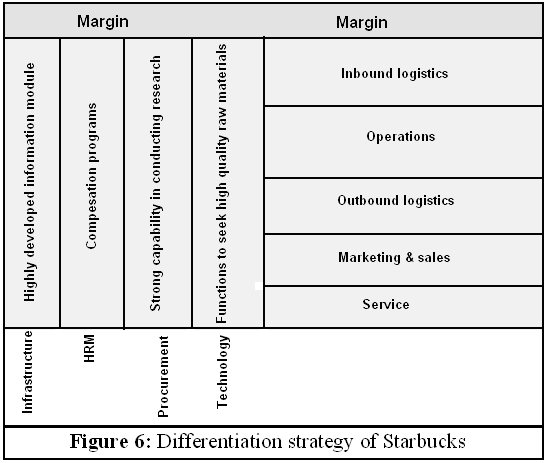
But before running with these options, the company should consider a number of factors as bargaining power of suppliers and customers and suppliers, potential entrants, substitutes etc.
- Griffin, R. W. (2006) mentioned that the company can also adopt focused cost leadership strategy for the purpose of providing the customers with “affordable solutions for better living” by offering the products at a lower price for the particular segment of the market9.
- Focused differentiation strategy will enable the company of offering unique differences to match the significant needs of a small segment of the target market.
Competitive dynamics
At this phase Starbucks can attempt to create competitive dynamics that comes from a series of competitive actions and responses among the competitors within the ready- to- drink beverage industry which may be affected by a number of factors, like- resource similarity, relative size of the firm, innovation, quality etc.
Corporate-level strategy
This concept focuses on diversification that involves the company’s retail segment offers the diversified sales mix of items for the year 2007 as:

Acquisition and restructuring strategies
Through the acquisition strategy, Starbucks will be able to buy a control or 100% interests in other company by using the core competency more effectively through the making of the bought firm a subsidiary in the sole portfolio. So, it can consider that strategy to gain:
- Increasing market power by horizontal, vertical or related acquisition.
- Overcoming entry barriers in newer or less- repudiated segment, like- North America.
- Increasing the speed to market.
- Increasing diversification.
- Reshaping own competitive scope etc.
For such purposes, Starbucks has bought a 90% stake in the licensed operations located in Beijing- China in the first quarter of last year. Because of the lion ownership from that acquisition, it has used the consolidation approach for the relevant data.
Another important aspect of acquisition is licensing of retail stores. Here, it leverages the zonal partners and stocks for the operational and store improvement expertise. Annual report-2008 demonstrated that by the year 2007, there were 3891 licensed stores existed in United States. Additionally, it also has this sort of relationship with Craft Foods, Inc., coffee partnership in North America with a joint partnership with Pepsi in while Starbucks has an equal investment of 50% for the bottled Frappuccino, Double Shot and espresso beverages.
Through restructuring, Starbucks will be able to sustain the fall in acquisition with others by changing the operating sets or financial structure. It can take many forms, like:
- Downsizing for reducing the number of employees and operating units with no changing in business portfolio.
- Downscoping for spinning off or offsetting business which are not related with its core business objectives.
- A leveraged buyout (LBO) for purchasing all the company’s assets for the purpose of privatization.
International strategy
Since Starbucks is operating and distributing services over 15000 stores in 43 countries, to become a successful player in the international market it should consider the following factors:
- Factors of production.
- Demand conditions.
- Related and supporting industries.
- Firm’s strategy, structure and rivalry.
Hill, C., (2007) argued that its global store base is growing vastly while the company is obtaining contribution of renowned global segments by the investment and the emerging that segment. For example- China, Russia, Brazil. The current segments demand a vast support company regarding the present revenues and operating profits. In 2006, the company earned total net revenues of $1302914 from its international market because of high sales volume of goods as well as lower costs of sales involving vast distribution of fixed costs and low dairy costs which are contributing greatly for the compensation based on stocks.
Co-operative strategies
In the light of the existing plans and situations, Starbuck can develop various types of co- operative strategies as following:
- By composition of strategic alliances, it can combine the resources, capabilities and core competencies with other firms for gaining the mutual interest in designing, distributing and producing goods.
- By joint- ventures it can enjoy benefits by the combination of assets as it is doing now.
Implementation of strategies
The company can implement the above projected and proposed strategies by the following dimensions:
Corporate governance
It dictates the co- relation of all the stakeholders in terms of control and directive performance of Starbucks. These ruling bodies are committed for maintaining the straight and powerful principles of growth. For that issue, Starbucks board of directors has taken rules of governance and committee for charters for directing the activities. This board consists of 9 directors, minimum majorities that face all the flexible demands of NASDAQ as well as the SEC (Securities & Exchange Commission) of United States. Additionally, it has installed an ethical code in respect to the CO, CF, controller and leaders of finance for a “code of ethics” indicated by the SEC rules.
Thus, the corporate governance structure can be presented as following:
- Board of directors: This group is responsible for performing at the owner’s profits by the systematic monitoring and controlling the business. Starbucks board of directors include Howard Schultz, Barbara Bass, Howard Behar, Mellody Hobson, Javier G. Teruel and many others as chairman, president, director, retired vice chairman etc.
- Senior officers: It includes CEO, CFO, president, executive vice president, senior vice president for marketing, global manufacturing operations, partner resources, global logistics, Asia- pacific, global procurement and coffee, Latin America, global coffee of Starbucks, business solution etc.
- Compensation program: The Company’s compensation schedule based on stock has been established according to the SFAS No. 123(R) or “Share- Based Payment Schedule” provision. The Black- School- Merton Model is used for pricing policy according to the subjective guesses that entitles time period for partners and stock price volatility.
Organizational structure and control
The organizational structure of Starbucks is as following:
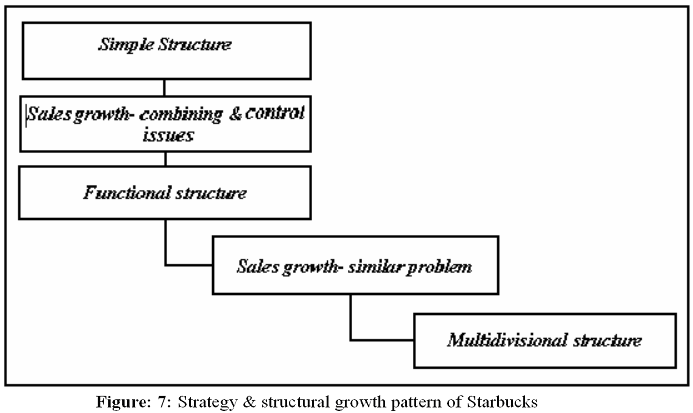
Since Starbucks is highly differentiated in its own industry, it basically follows the following functional structure:
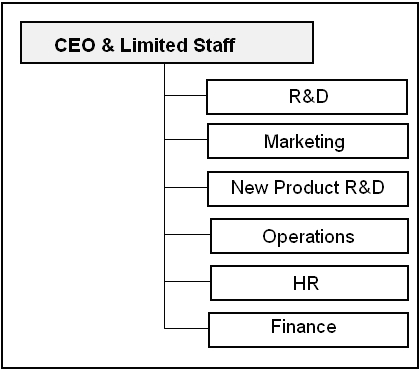
Additionally, the company operates the controlling function for assurance of material data according to the SEC’s references for the timely decision making.
Strategic leadership
Starbucks maintains such issue for anticipation, envision and flexibility of the entire planning as:
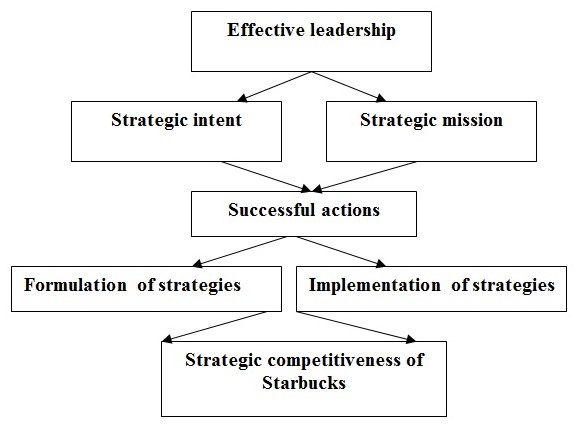
Corporate entrepreneurship and innovation: It includes about 170000 committed employees, efficient operating team, management capability and experienced R&D of which all are responsible for the company’s handsome revenues, net income and global goodwill. The company proves its environmental concern by utilizing and selling environmentally healthy goods, taking the social concern as value of the company, and other affairs.
Recommendations
To become more effective and efficient, Starbucks should concentrate on the following issues:
- It should be alert about the expectation of market since there exist a chance of reducing the stock price at an extensive and sharp rate.
- Should be concerned about war, terrorism or political fluctuation.
- At present the company has to compete against the qualified restaurants in U.S.A and the established companies are offering a great threat for Starbucks.
Since the company’s another lion revenues come for international sector, it should take in mind about some risk factors:
- Fluctuated rate of currencies.
- Uncertain economic, social and political factors.
- Interception of rigidity of laws etc.
- Richer prospect and flexible contract with China government as there the company is facing a major entry barrier for laws and regulations.
- Conducting campaigns and other efforts to remove public thoughts about the negative effects of coffee on health by illness and other fatal impacts.
Though the company typically faces all of those challenges, it is somewhat possible to handle it with an exact strategic and appropriate strategic planning and a proper management of it.
Conclusion
Starbucks, a core coffee company is managing the strategic process in a quite well structured way with adequate amount of resources, capabilities, core competencies, social responsibilities, innovative approach, worldwide distribution network, and many other factors for which in the previous year it has experienced targeted opening of new centers, in- store sales growth and consumers pressure in retail and restaurant business which converted into 21% of net revenues and 16% increase in earnings during that year although the company faced a number of major challenges.
Bibliography
Chernev, A., (2007), Strategic Marketing Analysis, 2nd edition, Brightstar Media, ISBN: 978-0979003912.
David, F., (2008), Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases, 12th edition, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 978-0136015703.
Dess, G., and Lumpkin, G.T. (2008), Strategic Management: Text and Cases, 4th edition, McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 978-0073404981.
Doyle P. D, (2004), Adding value to marketing: the role of marketing in today’s profit-driven organization, 2nd Editions, London: Kogan Page, ISBN: 9780749421755.
Dibb, S. Simkin, L. Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O.C. (2001), Marketing Concepts and Strategies, 4th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Mifflin.
Griffin, R. W. (2006), Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South- Western Thosmson Learning, Singapore.
Hill, C., and Jones, G., (2007) Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach, 8th edition, South-Western College, ISBN: 978-0618894697.
Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2006), Exporing Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases, 8th edition, London: FT Prentrice Hall.
Kotler, P., Armstrong, G. (2006), Principles of Marketing, 11th Edition, Prentice-Hall of IndiaPrivate Limited, New Delhi, ISBN: 81-203-2825-6.
Kotler, P. (2006), Marketing Management, 11th edition., Prentice Hall, NJ, ISBN: 0-13-0336297.
Kotler Marketing Group (2008), Dr. Philip Kotler Answers Your Questions on Marketing, Web.
Porter, M. E. (2004), Competitive Strategy, Export Edition, New York: The Free Press, ISBN-10: 0743260880.
Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., Gilbert, D. R. (2006), Management, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, ISBN: 81-203-0981-2.
Starbucks Corporation (2008), Corporate Governance Principles and Practices for the Board of Directors, Web.
Starbucks Corporation (2008), Code of Ethics for CEO and Finance Leaders, Web.
Saloner, G., Shepard, A., and Podolny, J., (2001), Strategic Management, 2nd edition, John Wiley, ISBN: 9780471380719.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission (2008), Form 10-K, Starbucks Corp – SBUX, Annual Report. Web.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission (2007), Starbucks Corporation – SBUX, Annual Report. Web.
Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.