Executive Summary
Effective brand management is critical in organizations’ pursuit of competitive advantage in any market. Companies’ performance in the international market is not only dependent on how effective the marketing strategies are formulated. On the contrary, the firms’ management team must ensure that ethical and regulatory principles are observed. Nestle has identified the UAE as an attractive market for its infant formula product, NAN. Nevertheless, the advertising strategy that the firm has adopted through collusion with healthcare facilities in the UAE to increase its sales revenue of the NAN infant formula product is unlawful and unethical. The study’s findings illustrate that Nestle has developed a remarkable reputation in the international market. However, its failure to apply ethical principles in its advertising process in the UAE might affect its achievements. Based on the research findings, the study recommends Nestle adjust its approach to marketing by investing in marketing research, brand management, training its employees, and adhering to ethical marketing practices.
Introduction
Marketing is a vital strategic management component that influences the enterprises’ long-term competitiveness (Langen, Grebitus, & Hartmann, 2013). Different companies are progressively entrenching cross-border market expansion to generate high sales revenue and profits. Sele (2006) posits that multinational corporations [MNCs] are progressively identifying viable market opportunities outside their domestic market. The BRIC countries [Brazil, India, and China] and countries in the Middle East and North Africa region have been considered as the most attractive markets over the past decades (Sele, 2006). The attractiveness of these countries increases due to economic performance and high population. These countries have experienced a significant increase in the number of MNCs entrants into different economic sectors (Sele, 2006).
To generate sales revenue from the international market, the MNCs are increasingly integrating diverse marketing strategies. One of the strategies involves advertising. The marketing strategies should not only adhere to the best marketing practices but should also be ethical. There are different cases of ethics involved in marketing. One of the notable cases arises when marketers overemphasize a vulnerable market segment in the pursuit of sales revenue (Jeurissen & Ven, 2006). Over the years, advertising has been characterized by cases of controversy and scandals. Jeurissen and Ven (2006) identify “Benetton’s controversial series of ads which featured delicate subjects such as discrimination and HIV/Aids, to sell colorful clothing at the higher end market” (p.430). Klein, Laczniak, and Murphy (2006) accentuate that most ethical cases in marketing involve product safety, misleading advertising campaigns, and illegal product pricing schemes amongst others. The violation of the stipulated laws and obligations further constitutes unethical marketing (Klein et al., 2006).
Problem Statement
Over the past years, Nestle has been involved in an aggressive market expansion. One of the markets that the firm has entered entails the United Arab Emirates. Its decision to enter the UAE market was informed by the identification of the huge market potential concerning baby food products. The UAE is one of the most attractive baby food markets. Thus, the intensity of competition in the market is substantially high, which increases the probability of the industry players violating the stipulated code of operation. The UAE government recognizes breastfeeding as an essential element in promoting society’s welfare. Efforts to restrict the promotion of alternative products to breast milk have failed due to political interference. The UAE has adopted the International Code of Marketing operation that the industry players are required to observe in their marketing practices. One of the Code’s stipulations entails restricting the promotion of products in healthcare facilities.
Documented literature identifies an increase in the public outcry on multinational corporations’ involvement in immoral economic colonialism (Sele, 2006). A notable example relates to Nestle’s involvement in the aggressive commercialization of its pure life in Pakistan. The company’s marketing activity was misleading and hence against the welfare of the Pakistan community. Despite Nestle’s success in positioning itself in the global food industry, the firm has been involved in cases of unethical marketing practices in the international market.
To achieve a competitive edge in the United Arab Emirates baby food market, Nestle broke the code of conduct by colluding with stakeholders in the medical profession. The firm influenced medical professionals to prescribe new mothers in the UAE to use its baby formula brand NAN. Langen et al. (2013) contend that despite the intensity of competition in the food market in the emerging and industrialized economies, consumers have a choice of the product to purchase. Thus, firms should not engage in unethical marketing practices. On the contrary, Langen et al. (2013) affirm that effective product differentiation should be used as a strategy for influencing the consumers’ purchase decisions. Nestle’s violation of the International Code in marketing its NAN infant formula product in the UAE and the internationally might limit the firm’s capacity to develop sustainable competitive advantage. Therefore, it is imperative for the company’s management to appreciate and adopt ethical marketing practices.
Aim and Objective
The purpose of this paper is to examine the ethical issue associated with Nestle’s violation of the International Code in marketing its NAN formula products in the UAE. To achieve the research goal, the research will focus on the following research objectives.
- To examine the impact of Nestle’s violation of the International Code on the company’s image.
- To explore the impact of the ethical issue at Nestle on the customers’ intention to purchase the NAN infant formula
The above research objectives will be achieved by answering the following research questions.
- What impact did Nestle’s violation of the International Code in marketing the NAN brand have on the company’s company image?
- What effect did the violation of the International Code have on the customers’ intention to purchase the NAN infant formula?
Significance of the Study
The study’s findings will provide Nestle’s management team with comprehensive understanding on the impact of its unethical practice on the company’s competitiveness in the international market. By relying on the market intelligence generated and the study’s recommendations, the Nestle’s management team will be in a position to undertake the requisite adjustments in its marketing practices. Subsequently, the likelihood of Nestle restoring its image and competitiveness will be improved substantially.
Limitations of the Study
The study specifically focuses on the issues associated with the Nestle’s violation of the International Code in its marketing practices. Moreover, the study is limited to the company’s operations in the United Arab Emirates.
Situational Analysis
The UAE baby food market has undergone notable evolution over the past few years. The market’s growth has been spurred by different factors such as an increase in the rate of urbanization and emergence of a middle-class population. Moreover, the high rate at which women are directly being involved in the labor market has increased the adoption of convenience-oriented lifestyles concerning taking care of their babies (Nielsen, 2015). Thus, baby formulas and processed baby foods have increasingly become desirable. The involvement of a large number of women in employment has made most mothers consider replacing breast milk with baby formula. The preference of the baby formulas arises from the need to balance between the infants’ nutritional needs and the mothers’ demand for convenience.
The Asia-Pacific market accounts for 49% of the total global sales of baby food products while North America and Europe account for 19% and 27% of the total sales. The Middle East and North Africa markets are characterized with the highest rate of growth (Nielsen, 2015). The UAE recorded the highest rate of growth concerning baby formula sales at 20.6% between 2012 and 2014 (Nielsen, 2015). The graph below illustrates the growth of the baby food market between 2012 and 2015 across the emerging economies. According to Graph 1, the UAE is has a considerably high potential for growth compared to other economies.
Table 1
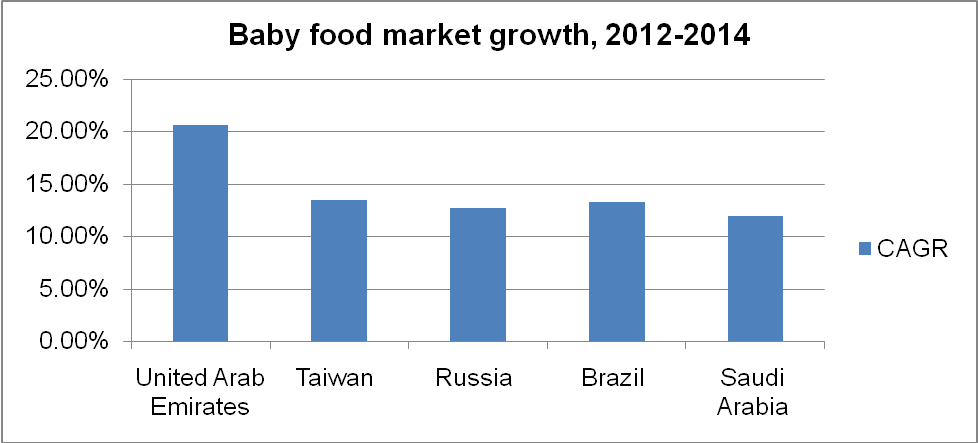
The baby food companies are investing in aggressive marketing strategies to generate sales revenue (Ken Research, 2014). The high growth potential of the baby food market has remarkably shaped the baby formula market in the UAE. Between 2012 and 2017, the baby food market in the UAE is expected to grow with a CAGR of 16.8% concerning revenue (Chibber, 2014). To exploit the market opportunity available in the UAE, Nestle announced its decision to invest $120 million for the construction of a processing plant in Dubai World Central. The processing plant was expected to be operational by the end of 2015 (Valdini, 2015). The prevailing situation in the UAE’s baby food market can well be illustrated using the Porter’s five forces.
Threat of New Entrants; Low
The UAE government is committed to stimulating the country’s economic growth through promotion of international trade. Subsequently, the government has increasingly relaxed international trade barriers hence establishing international cooperation. The country’s economy is projected to experience robust growth arising from the oil and non-oil sectors (United Arab Emirates, 2014). The UAE is further the largest export markets, which increases its attractiveness to international companies. This aspect makes the threat of entry to be substantially high. Nevertheless, Nestle has established a substantial competitive advantage hence limiting the impact of the threat of new entry. The new entrants are required to establish a high competitive advantage to survive in the market.
Threat of Substitute; High
The attractiveness of the UAE baby food market has increased the presence of diverse baby food and formula brands. Thus, the market is characterized by numerous baby formula substitutes. The large number of substitutes pressurizes the industry players to ensure that their products remain competitive.
Supplier Bargaining Power; High
The operational efficiency of the baby food processing companies is directly influenced by the relationship established between the firm and the suppliers. The suppliers of the raw materials used in the production of baby food and formula products can influence the competitive advantage of the food processing companies. For example, setting the price of the raw materials at a high point can limit the processing companies’ capacity to set competitive prices. Additionally, the suppliers can influence the acceptance of the final product in the market because of the quality of the raw material. Nestle has developed a strong relationship with its suppliers located around the world. The firm ensures that the suppliers adhere to the stipulated quality requirements.
Buyer Bargaining Power
The availability of numerous substitutes of baby formula products in the market has led to significant increase in the consumers’ bargaining power. This aspect has arisen from the remarkable decline in the cost of switching to a competitive product. This issue presents a challenge for baby food producers to ensure that their products are of high quality to minimize the likelihood of switching to a competing product.
Competitive Rivalry; High
Many baby food-processing companies characterize the industry. Some of the dominant players include Kraft Foods, Mars Incorporated, Danone, and Mondelez International Incorporation. These companies are a major source of rivalry to Nestle. Apart from the international companies, local companies further characterize the baby food market in the UAE. One of the notable companies entails the Hassani Group of companies, which is one of the largest local firms. These companies are increasingly adjusting their operational strategies to develop their global market share. Nevertheless, Nestle has developed a strong market position. To gain an edge in the Islamic countries, baby food processing companies are progressively introducing a wide range of halal baby food and formulas. Subsequently, the UAE market is currently experiencing an increase in the brand of baby food products (Simpson, 2012).
In summary, the UAE baby food market is very attractive, which creates an opportunity for the baby food processing companies operating in the industry to generate revenue and profit. However, the capacity to tap the market opportunity depends on the strategic management practices adopted by a firm.
Literature Review
Development of a strong brand comprises one of the most effective approaches that an organization can adopt to attain a high competitive advantage. Companies experience challenges in developing competitive advantage through the introduction of new products. On the contrary, companies are increasingly acquiring other brands to enter new markets. Nestle has over the past few years acquired different companies such as Breyer’s Grand Ice Cream, and Ben and Jerry’s Homemade Ice Cream (Bolling & Gehlhar, 2005).
Despite the adoption of such strategies, the importance of developing a strong brand in the existing and new markets should not be underestimated. M’Zungu, Merrilees, and Miller (2010) emphasize that brand constitutes a vital intangible resource in the improvement of an organization’s capacity to survive the increasing complexity of the contemporary business environment. Scholars and business practitioners are progressively being concerned on how to exploit the benefits associated with a strong brand.
M’Zungu et al. (2010) conceptualize brand equity to be comprised of different aspects that include brand association or image, brand awareness, brand loyalty, and perceived quality. The level of brand awareness has a significant impact on the consumers’ purchase decisions. Additionally, brand awareness influences the customers’ perceived value of a product and hence its brand image (Sinha, Ahuja, & Medury, 2010). To generate a sustainable competitive advantage, it is fundamental for organizations to establish strong mental associations. Companies are increasing the volume of their investment in marketing activities such as advertising. Nevertheless, most companies have not developed sufficient understanding of the value of establishing strong mental representation. The mental representation developed influences the customers’ behavior (Friedman & Leclercq, 2015).
However, the success with which an organization leverages on brand equity is influenced by the effectiveness of its brand management approaches. Eisingerich and Rubera (2010) argue that brand management “is a complex set of activities that involve managing relationships with customers and other stakeholders, while accounting for a firm’s past actions and reputations and competitors’ actions, to build a strong image that wins consumers” (p.66).
There are different considerations that organizations should consider in the brand management process. One of the considerations entails brand orientation. This approach focuses on establishing and sustaining a relationship with the target customers to protect the brand’s identity. Past studies conducted shows that brand orientation improves the effectiveness with which the marketing strategy adopted improves a firm’s performance (M’Zungu et al., 2010). This assertion arises from the view that the memory created in the customers’ minds on the brand increases the likelihood of the customers’ continued usage of the product (Sinha et al., 2010).
In the process of implementing the different brand management practices as an approach to improve performance, it is essential for organization’s management team to avoid being involved in negative business events. Negative events include any activity conducted by an enterprise that might culminate in the development of negative thoughts regarding a company and its products amongst the target customers (Li, 2015). Therefore, a positive correlation exists between a company’s involvement in negative events and brand attitude. A negative event instills a sense of fear in the consumers’ purchase decision process.
The Nestle’s violation of the Ethical Codes stipulated by the UAE government concerning the marketing of baby formula products in the country’s healthcare facilities constitutes a significant negative event. Li (2015) emphasizes that negative events can lead to destructive effects on a company’ image and hence its competitive advantage. For example, Nanjing Guanshengyan, a Chinese company was declared bankrupt due to its involvement in using expired materials. Similarly, the Toyota Motors was forced to recall a significant proportion of its cars because of default braking system. However, Toyota Motors has experienced significant recovery in its performance over the recent past because of effective brand management (Li, 2015). Thus, avoidance of negative events is fundamental.
Methodology
The purpose of this study is to knowledge the impact of the ethical issue involving the violation of the International Code in the Nestle’s efforts to gain an edge in marketing its NAN baby formula brand in the UAE on the company’s performance. The study intends to gain an extensive understanding of the impact of the ethical issue on the company’s competitive advantage. To achieve the study’s purpose, some research procedures have been taken into consideration. First, the study is based on the exploratory research design. Hair (2006) identifies the capacity to discover new relationships, ideas, patterns, and themes as one of the fundamental strengths associated with the adoption of the exploratory research design. The adoption of the exploratory research design has also created an opportunity for inclusion of qualitative and quantitative research techniques. The application of the exploratory research design has been enhanced through the integration of the case study approach. The rationale for integrating the exploratory case study is to establish the causal relationship between the negative event associated with the promotion of the NAN baby formula product and the firm’s competitive advantage.
To derive sufficient data, a survey on the consumption of baby formula products in the UAE was conducted. The survey involved 100 participants who were selected using the simple random sampling technique. The use of the simple random sampling technique enabled the research sample to be representative by eliminating bias in the construction of the sample study. The research data was collected using questionnaires as the data collection instrument.
The questionnaire was electronically distributed to the respondents. The questionnaire involved both open and close-ended questions. The respondents were informed of how confidentiality of the data collected would be ensured. The data collected is analyzed by employing the descriptive statistics techniques. The choice of this technique is to improve the efficiency of evaluating the data collected using qualitative and quantitative techniques.
Findings
Respondents Demographic Characteristics
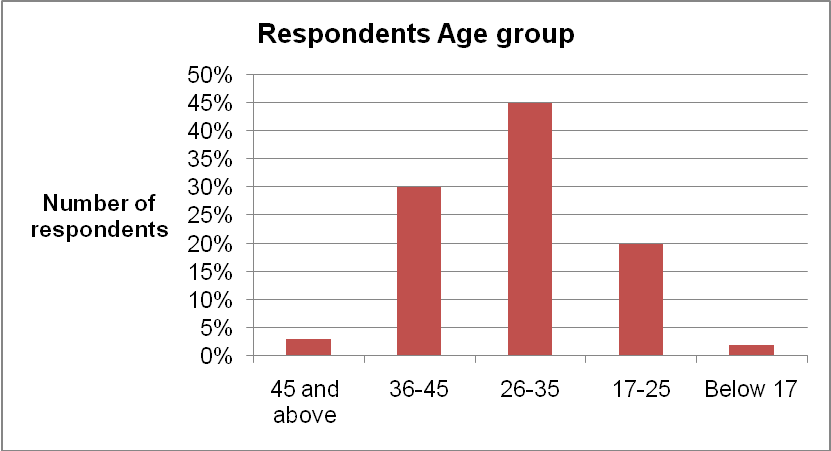
The research participants involved in the study belonged to different age group as illustrated by the graph below. Most of the respondents were aged between 26 and 35 years.
Table 1
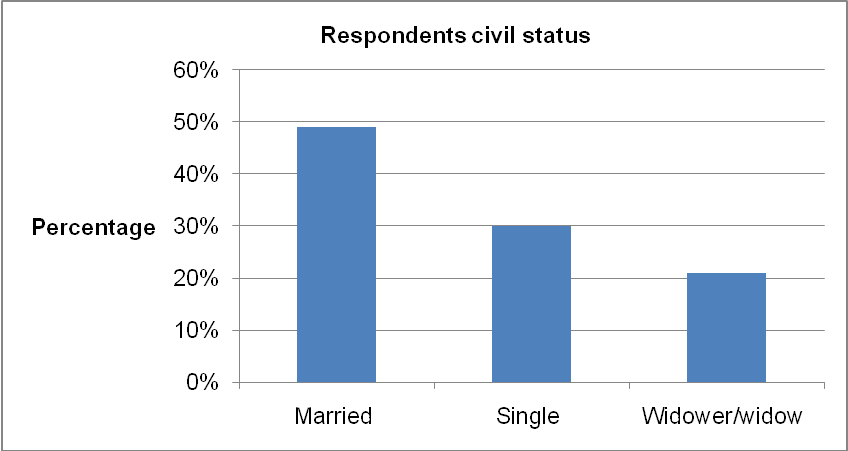
In addition to age, the respondents’ civil status differed as illustrated below.
Table 2
Analysis of Findings
Implementation of the stipulated methodological procedures led to the revelation of diverse aspects related to the study topic. First, the study sought to understand the proportion of respondents who consider the consumption of infant formula as an alternative to breast milk. All the respondents (100%) affirmed their recognition of the infant formula as a convenient alternative to breast milk. This aspect explains why the UAE is experiencing growth in the size of the market for infant formula products. However, the respondents’ opinion on the effectiveness of the infant formula as a replacement for breast milk differed considerably as illustrated by the graph below.
Table 3
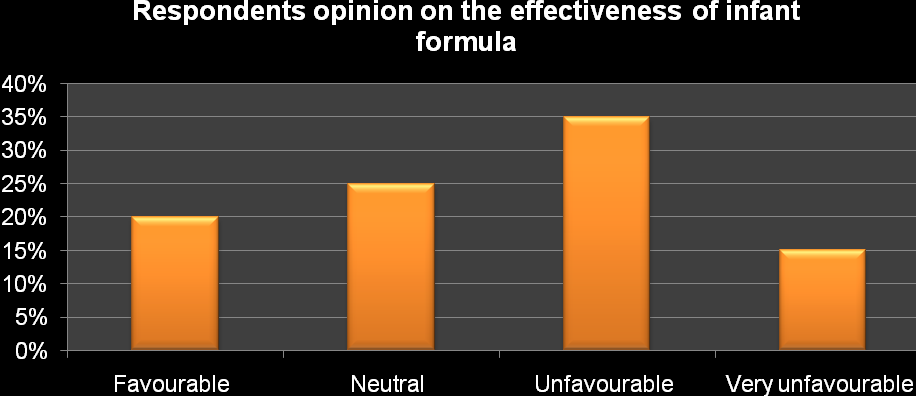
In spite of the general acceptance of infant formulas, only 20% of the respondents consider the infant formulas to be effective compared to breast milk. This aspect is underscored by the high rate (35%) of respondents who consider infant formulas as unfavorable. This aspect explains why infant formulas are being adopted due to the need for convenience.
The study further sought to understand the most important factors that the respondents consider in making a decision to purchase baby formula products. The response obtained varied. Forty-three percent (43%) of the respondents identified the brand of the product as the most important factor while 30% of the respondents identified quality as the major driving factor. On the other hand, 15% of the respondent identified price as the critical factor that informs their purchase decision. Only 7% and 5% of the respondents identified packaging and availability as the fundamental attributes in making the decision to purchase infant formula.
Table 4
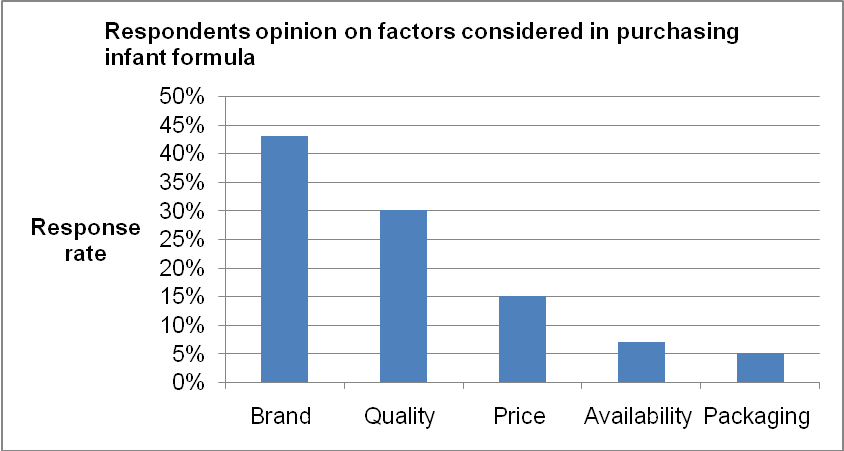
The graph shows that most respondents anchor their decision to purchase infant formula on the brand. This finding highlights the importance of firms that specialize in the production of infant formula developing a strong brand. Moreover, quality constitutes a major driving factor in the marketing of infant formula. The study further sought to understand the customers’ brand preference. Subsequently, the survey involved exploring the preference of the major infant formula brands. The table below illustrates the responses obtained.
Table 5
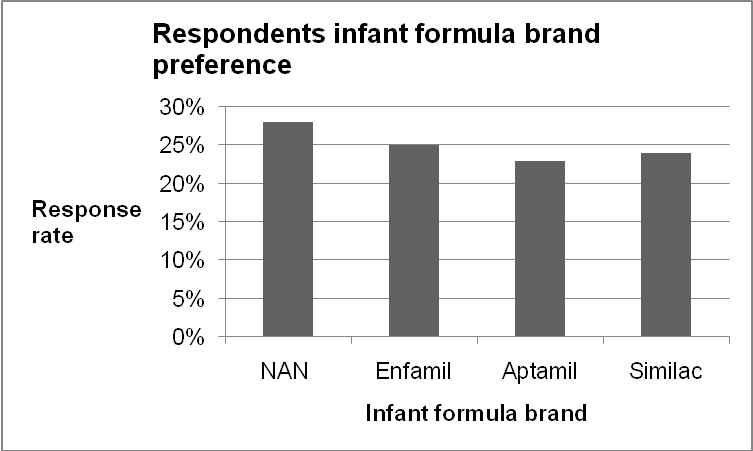
Graph 6 indicates that Nestle’s NAN infant formula brand has developed remarkable brand preference amongst the customers in the UAE. However, the intensity of competition amongst the three brands is substantially high as illustrated by the slim difference between the level of brand preference across the three four brands identified.
Despite the identification of price as one of the factors considered in making the purchase decision, the study sought to understand the degree to which the respondents are satisfied with the Nestle’s pricing policy. The table below illustrates the responses obtained.
Table 7
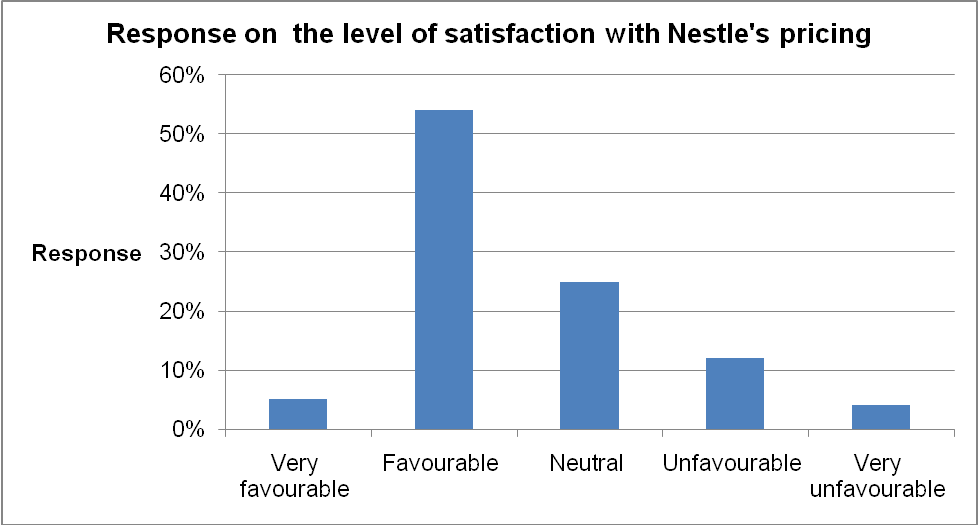
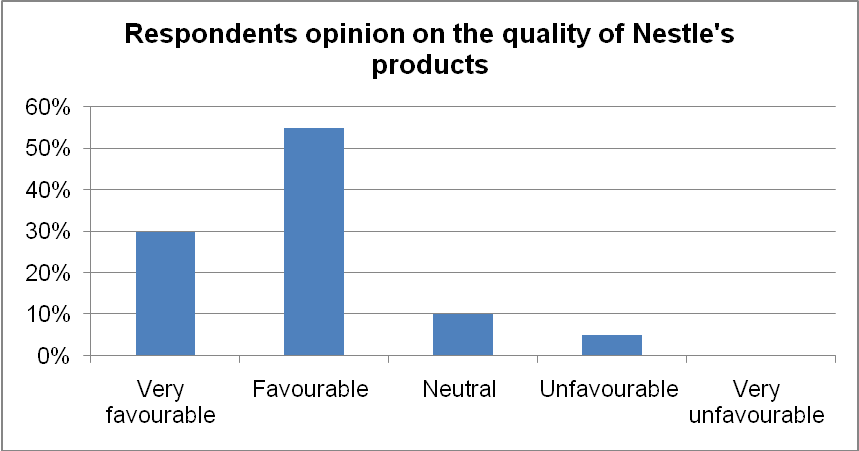
The graph shows that most customers are satisfied with the companies’ pricing as indicated by the high rating on the customers’ perception of the pricing policy to be favorable. Moreover, the study affirmed quality as one of the major factors that are contributing to the increased acceptance of NAN infant formula amongst customers. Thirty percent (30%) of the respondents affirmed that they are very satisfied with the quality of the firm’s product. The table below illustrates the responses obtained concerning quality.
Table 8
Considering the ethical issue associated with the Nestle’s approach to marketing, the study sought to gauge the respondent’s opinion on the company’s brand image. Table 3 below illustrates the responses obtained.
Table 9
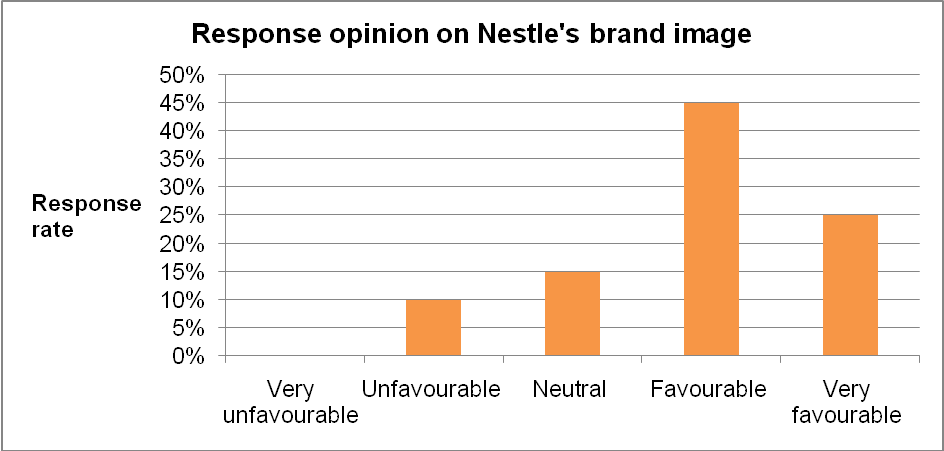
Graph 5 indicates that Nestle has developed a remarkable brand image. Moreover, 75% of the respondents argued that Nestle has succeeded in developing a strong brand reputation. The respondents identified the quality of the firm’s infant formula as the core factor that has contributed to the development of the company’s brand reputation. One of the strategies that the firm has adopted in its quest to enter the UAE market entails investment in aggressive marketing communication. The firm has adopted integrated marketing communication approach in creating brand awareness. The graph below illustrates the respondents’ opinions on the effectiveness of the firm’s advertising strategy.
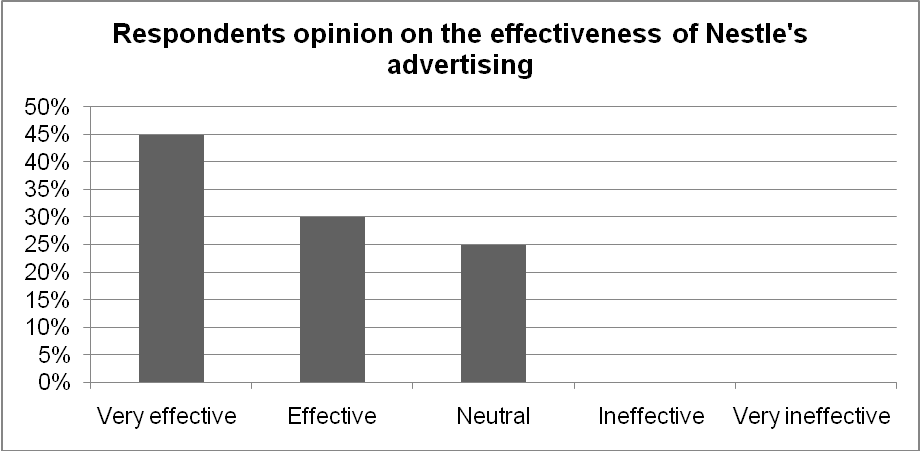
In spite of the company’s success in developing a strong brand image and reputation, a significant proportion (75%) of the respondents are of the view that the Nestle’s advertising approach is inclined to pressurizing mothers to replace breastfeeding with its infant formula, NAN. The respondents’ argued that the company’s violation of the International Code might affect its market acceptability in the UAE hence damaging its brand image.
Conclusion
The UAE baby food market is characterized by a high potential for growth as illustrated by the situational analysis conducted. However, it is imperative for baby food processing companies to formulate effective marketing strategies. One of the aspects that firms should consider relates to brand management. The study’s findings indicate that the Nestle brand has developed a significant brand awareness, brand image, and reputation. Nevertheless, the company’s violation of the advertising code stipulated by the UAE government might diminish the progress that the firm is making in its quest to tap the UAE market. The violation of the code of advertising might adversely affect the company’s reputation. The customers might perceive the collusion with health care facilities through the prescription of its infant formula brand, NAN to newborns and infants as a form of coercion.
Recommendations
To improve the probability of developing a high competitive edge in the UAE infant formula market, the Nestle’s management team should consider the following issues.
- Adherence to the stipulated legal and regulatory requirements; the company should ensure that its advertising policy is aligned with the country’s legal stipulations such as the International Code that the UAE has already adopted.
- Marketing research and employee training; the company should consider undertaking an extensive market research to understand the prevailing cross-border differences in the UAE. This move will ensure that its marketing activities such as advertising do not violate the country’s norms and values. The firm should further train employees on the importance of ensuring that the identified norms and values are observed.
- Brand management; the company should continuously utilize the findings of the market research in improving its effectiveness in undertaking brand management. This aspect will culminate in a remarkable improvement in the company’s brand equity.
Future Research
Due to the time and financial constraints encountered in conducting the research, this study does not outline the approach that the company should adopt in improving its effectiveness in creating brand awareness in the UAE market. The study only emphasizes the ethical dimension of advertising. Therefore, future research on how to address the challenge that the firm faces is necessary.
References
Bolling, C., & Gehlhar, M. (2005). Global food manufacturing reorients to meet new demand. Web.
Chibber, A. (2014). Middle East a ripe market for baby food makers. Web.
Eisingerich, A., & Rubera, G. (2010). Drivers of brand management commitment; a cross-national investigation. Journal of International Marketing, 18(2), 64-79.
Hair, J. (2006). Essential of business research methods. New York, NY: M.E Sharpe.
Friedman, M., & Leclercq, T. (2015). Brand discrimination: An implicit measure of the strength of mental brand representations. PLoS One,10(3), 1-24.
Jeurissen, R., & Ven, V. (2006). Development in marketing ethics. Business Ethics Quarterly, 16(3), 427-439.
Ken Research: UAE baby food industry outlook to 2017. (2014). Web.
Klein, T., Laczniak, G., & Murphy, P. (2006). Ethical marketing; a look on the bright Side. Marketing Management Journal, 16(1), 228-243.
Langen, N., Grebitus, C., & Hartmann, M. (2013). Success factors of cause-related marketing in Germany. Agribusiness, 29(2), 204-227.
Li, Y. (2015). The severity of negative events in enterprises affected consumers’ brand attitudes. Social Behaviour and Personality, 43(9), 1533-1546.
M’Zungu, S., Merrilees, B., & Miller, D. (2010). Brand management to protect brand equity; a conceptual model. Brand Management, 17(8), 605-617.
Nielsen: Oh, baby; trends in the baby food and diaper market around the world. (2015).
Sele, K. (2006). Marketing ethics in emerging markets, coping with ethical Dilemmas. Indian Institute Management Review, 18(1), 95-104.
Simpson, C. (2012). World’s first halal baby food means convenience for Muslim mums.
Sinha, N., Ahuja, V., & Medury, Y. (2010). Effective brand management through consumer profiling using clustering. IUP Journal of Brand Management, 3(2), 24-33.
United Arab Emirates: Challenges and Opportunities – The UAE food industry. (2014). Web.
Valdini, C. (2015). Nestle to build $136 million Dubai factory.