Theories and Techniques
The Theory of Constraints
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a framework utilized to detect the most debilitating factors in the supply and production chain, in order to apply a 5-step process to help eliminate or mitigate the constraint to the point when it is not considered a relevant issue. The five steps of the theory are as follows (Franzetti, 2016):
- Identify the constraint. In order to solve a problem, the company must first recognize that there is one.
- Exploit the constraint. Provide a series of makeshift solutions to make short-term improvements to the issues.
- Subordinate the constraint. Review all other processes to discover ways to support the constraint.
- Elevate the constraint. If all previous measures are ineffective, develop specific interventions to eliminate the constraint.
- Repeat. Utilize the framework for a different constraint.
Nissan could apply this framework to resolve its supplier issue, as it presented itself to be a major factor even with the existent crisis measures present. By utilizing TOC, Nissan would be able to maintain stable production and supply the customers in all regions in the event of a catastrophic failure in any of their major production facilities.
Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a framework of continuous quality improvement aimed at exceeding the expectations of the customers. Implemented by major giants of the automotive industries, such as Ford, General Motors, and Toyota, it seeks to severely reduce the potential for production errors and defects. In addition, TQM helps simplify and streamline the system, thus leading to saving money on expenditures, refunds, and reconstruction (Franzetti, 2016).
The integration of TQM would be beneficial for the lines of products promoted in the company’s localized production facilities in Europe, Asia, and South America. It would allow implementing the same standards of production quality across the entirety of the supply network and speed up operations. If all suppliers were subjected to the same production standards, there would be no need for additional inspection of the materials and resources provided by them.
Data Analysis
Cause and Effect
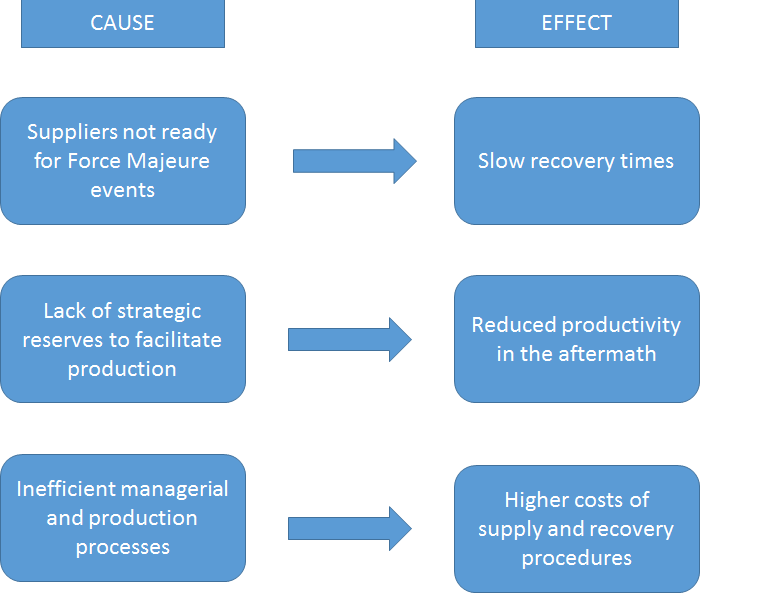
Although Nissan did have emergency measures prepared for the event of a tsunami followed by a nuclear meltdown, these precautions did not spread on their suppliers (Schmidt & Simchi-Levi, 2013). There were inconsistencies between how individual suppliers managed the crisis. As illustrated in Figure 1, several negative trends have emerged, including a lack of contingency plans for Force Majeure events, a lack of strategic reserves to supply Nissan while the lines are restored, and poor quality management, which resulted in higher costs and slower recovery times. As a result, Nissan suffered marginal production drops, as it struggled to find new suppliers to make up for these inadequacies (Schmidt & Simchi-Levi, 2013).
Process Map for Nissan Versa
Nissan Versa is one of the low-cost models currently produced by Nissan. Sold for about 12,500 dollars. Although considered the cheapest model currently available in the list of Nissan products, it shows good performance in safety, speed, comfort, and fuel consumption. The model is produced primarily in Mexico. The process map for Nissan Versa is demonstrated in Figure 2:
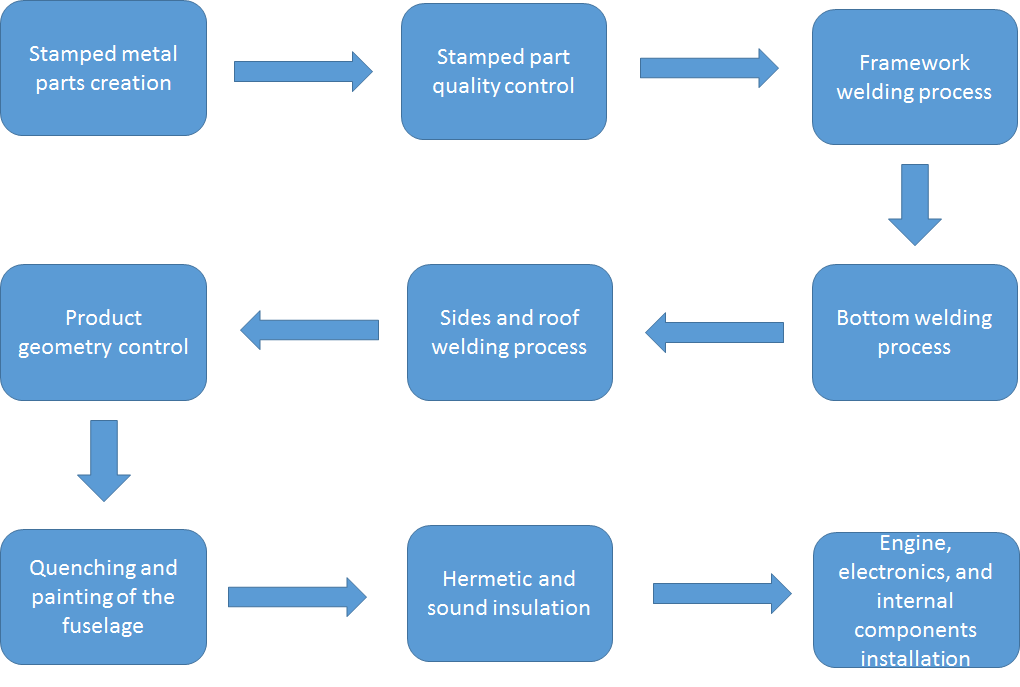
The process/value map is a very important tool for an operations manager. It shows the type of work done at every step of the production process, the value put in each of these steps, and whether or not it requires relying on additional outside suppliers to complete the operation. Using the initial process map provided above, it is possible to optimize and streamline the production. One of the examples of such optimization is the construction of a whole-cycle plant, where every operation, starting from stamping metal and ending with the assembly of the engine and the chassis is completed locally (Franzetti, 2016).
Choosing the Location for a New Manufacturing Plant
Fig. 3. Location Analysis.
Figure 3 illustrates two potential choices for Nissan for the construction of a new factory. The weight section indicates the importance of each individual factor for the company. As it is possible to see, political risks, transportation costs, and labor productivity are the three major factors for Nissan to consider, with rental costs, labor costs and taxes were less influential (Schmidt & Simchi-Levi, 2013). In order to determine the best possible solution, it is required to multiply the assigned points and weight and compare the combined results. The calculations are as follows:
- Mexico City = 0.25 x 70 + 0.20 x 40 – 0.20 x 85 + 0.15 x 90 + 0.10 x 80 + 0.10 x 90 = 39 points.
- Columbia, SC = 0.25 x 80 + 0.20 x 90 – 0.20 x 75 + 0.15 x 55 + 0.10 x 50 + 0.10 x 50 = 41.25 points.
The reason why labor productivity was deducted instead of added to the sum is that it represents a positive feature, whereas the rest (taxes, costs, instabilities) are negative features. As a result, the choice with the least negative points is to be considered superior. As Mexico has the least negative points, it should be chosen as the new location for the factory.
References
Franzetti, C. (2016). Operational risk modelling and management. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis.
Schmidt, W., & Simchi-Levi, D. (2013). Nissan motor company Ltd.: Building operational resiliency. Web.