Background and Introduction
With increased technology, individuals and businesses are increasingly using laptops for various personal and business functions. Laptops are electronic gadgets with a microprocessor that depends on power supply to function. Solar energy is freely available and can be tapped for charging laptops; the technology can be adopted for use in laptops. Secondly with globalization and the growth of tourism industry, there is need for a reliable devise that can be relied upon to undertake computer services and offer video recording services. When with the product, a customer only need to buy one product that covers computer and video needs. Numerous advantages can be derived from using solar charged laptop with video recording components; its invention is likely to form a niche market for the innovator. Nokia is an international electronics company that has the potential of meeting the demands of the above mentioned niche market. This report discusses the implication of developing the new products in the market to the market from a managerial accounting point of view.
Manufacturing Company Information
This report will discuss the cost and revenue implication of adding solar charged laptops with video recording devices in the line of Nokia products. In the analysis, it will focus on the following areas:
- Expected sales price and sales budget: this is the price that the laptops will be retailing
- variable costs and fixed costs: it will use cost accounting methods like activity based costing, breakeven points, job costing and process costing approaches
- Profit planning or profit maximization approaches; was thorough which profits will be maximized will be discussed
Historical information about Nokia
The international Phone industry is advancing fast with both multinational and domestic companies in the market; among the main players include Apple Inc. Samsung, Dell, HP, Acer, Nokia, and Lenovo. Nokia is an international electronics company listed in New York Stock Exchange and Frankfurt Stock exchange, with its headquarters in Finland; according to the company’s website, the company in 2010 enjoyed a market share of about 37%,. It aims at increasing the market share to over 40% by the end of 2011; other than in the phones segment, the company has diverted to fast growing Smartphone’s, musical gadgets and some electronics accessories.
In the efforts of using its brand name (brand extension strategy), the company has the potential of diversifying to laptops with a better touch; solar charged laptops. It has a strong brand all over the world, the companies positioning statement is “technology connecting people”. The company’s headquarters are located in Keilaniemi, Espoo. One of the strongest points that the company has is a strong and effective human resources capital distributed in the various countries that the company operated: currently it has a total number of employees over 123,000 distributed in various countries. It has it presence as a selling point of full branch in over 120 countries. In the year 2009, the company was able to make a profit of €1.2 billion this was over 10% than what it had recorded the previous year. In 2010, the company’s operations increased to record a revenue of €42 billion and operating profit of €2 billion; the main driver of this profits are sales of phones, which in 2010, the segment enjoyed an average of 32% of worlds phone market. Other than the phone assembling, the company offers financial services with the target customer as people on transit. The idea of the company was started in 1865 however; it became a telecommunication company in 1960’s.
Nokia is one international company that has a simple and straightforward mission statement as “Connecting People”. Its vision statement is “Our strategic intent is to build great mobile products” (Nokia Official website, 2011), this vision statement has more focus on the phone section of the company as the main business segment that the company has. The main purpose of the company is “Our job is to enable billions of people everywhere to get more of life’s opportunities through mobile” (Nokia Official website, 2011). To ensure that the company fulfils its vision, mission and purpose, it operates under marketing values and principles; they include innovation, products development, respect for the people and respect for research and development projects (Nokia Official website, 2011).
New product Identification
Justification of the proposed project
Technology is on the rise, there is a shift from the old office business where employees were required to report in offices to do their jobs, today home based working has taken preference. People are using desktops, teleconferencing technology and laptops for this noble task of serving their employer when at home; alternatively with the growth of the tourism industry, there are a number of people who are moving to paces of leisure where they need computers and video recorders;
Solar power is relatively cheap than electricity; this will reduce power bill budget and ensure. If they are adopted by a company, they will reduce a proportion of electricity bill in trading profit and loss account. This will lead to an increased profits and money for expansion will be availed. Large amounts of revenue from business results in increased government revenue through taxes; this will lead to developmental projects being implemented for the betterment of the users (Lucey & Lucey, 2002).
Some places do not have reliable supply of electricity but they enjoy sunlight’s that can be used with the laptops; other than the un-reliability, the company will tap a niche market of people who travel a lot for long distances; when they are using solar charged laptops, then they will go on with their business uninterrupted. Take the case of tourists who go deep in the juggle, they need laptops to record some findings as well as connect with the outside world, when such laptops have been developed, they will be a blessing to such people.
Another opportunity that the company will benefit from is the notion and the perception that current market of laptop has on the prevailing ones, they feel they are not doing them much justice since one has to charge the battery that hardly lasts for three hours. When a reliable solar charged laptop is developed, then the company can win a potion of the existing market as well as upcoming market (Zi-Lin, Kwanghui & Pho-Kam, 2006).
The solar Charged Laptops project
To start the project, the company will have to make an additional plant that will be used as the assembly point for the laptops; this will call for incurring of some expenses that will be accounted for, as fixed assets for the company and others will be amortized (Horngren, Srikant & George 2006). The initial costs that cannot be expensed either as fixed or variable expenses, but will be in the balance sheet are:
- Cost of buildings: there will be the assembly point to be constructed
- Research and development costs
- Cost of land (this will be subject to whether an additional land will be acquired for the project)
- Plants and machinery (Sadler, 2003)
Segment Budget
Expected sales (sales forecast and sales budged)
Assuming that the project will start on 1 January 2012, the expected quarterly sales from the company will be as follows:
When the project has started running, the company will have to incur some costs in respect to the project, costs can be classified as fixed or variable costs:
Fixed costs
Fixed costs are costs that do not relate to any production but exists as long as a business is there. They include license fees, rent, management salaries and security costs among others. When calculating the cost of an item, they are spread all over the products produced to determine the particular cost. The following are the fixed costs that will be incurred in the project:
- administrative expenses
- Factory rent (if any)
- Legal fees and licenses
- Utilities
- Insurance
- Payroll salaries (Horngren, Srikant & George, 006).
The budget for fixed costs will be as follows:
(Please note the fixed costs are expected to remain constant throughout the period)
Quarterly Budgeted fixed costs
The costs will be incurred whether a production has taken place or they it has not taken place.
Variable cost
Variable cost takes a broader perspective than fixed cost; a cost that pertain a specific process or batch or one that can directly be associated with a certain unit produced. It also includes marginal production costs analysis, process costing and batch costing.
The following are the variable costs that will be incurred:
- Costs of direct labor and casuals costs
- Cost of materials
- Packaging costs
- Transporting costs (Lucey & Lucey, 2002).
The costs will only be incurred when a certain production has been made from the plant:
The following diagram shows the relationship between fixed and variable costs:
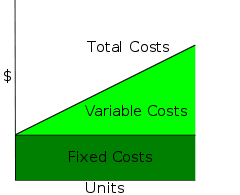
From the above diagram, it can be seen that variable costs are increasing when the units produced increase but fixed costs remain constant.
To determine costs, the company will be using Activity based costing method; activity based costing is a cost estimation and allocation method that allocates specific costs to a certain product not only in batch numbers but also in units form. Nokia should consider using the method for budgeting and pricing strategies as it offers a chance to the management to establish linkages and areas that are not efficient; it ensures that certain cost can be attributed to certain commodities especially when a company is dealing with more than one product. When dealing with more than one product: some fixed costs, though incurred by the entire company as a whole, relate more to some products: when accounted for using activity-costing method actual cost to be attributed to a commodity can be precisely known. This makes costs incurred by a certain product to be approximated more precisely. The price set for a commodity by management is an element of costs incurred when producing the commodity; activity cost methods offers a more precise cost of a product thus manages the price given on the product (Lucey & Lucey, 2002).
The following budget represents the variable costs per unit:
At least for the first year, the costs are expected to remain constant and not change.
Pricing for the commodity
Since the company has the idea new in the market, the company should use premium pricing method to set the prices of the commodities; the approach adopted by premium pricing models is selling of products at relatively high prices than that offered by the competitor (in this case the competitors will be other electricity charged laptops in the market). The strategy is particularly effective with unique or new products in the market (Carlon, 2009).
The cost of one unit of the solar charged laptop will be $800.
Breakeven analysis
Break even analysis is a cost management strategy that determines level at which fixed are covered by the sales made from a certain products. When calculating the amount of products that needs to be produced by a firm to cover its costs as well as the ones needed to make a certain profit, project managers use breakeven methods; it can be calculated using mathematical interpolations as well as through the use of a diagram (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011). The diagram below shows how breakeven point can b calculated by a graph:
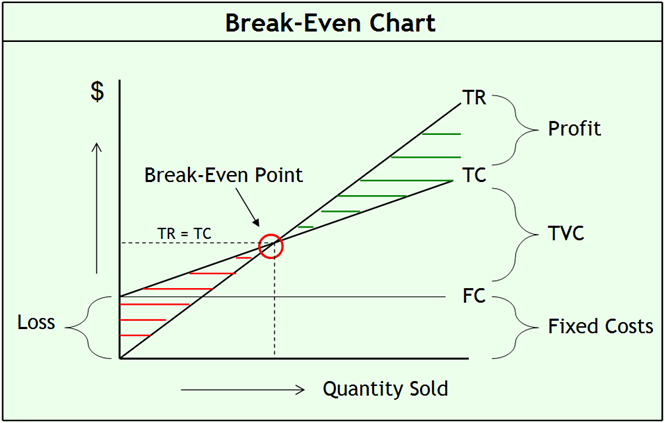
The following are the uses of a break-even graph:
- To advise the company on the amount of products that need to be produced to have the total costs and total revenue be the same; at this point, the profit of the firm is nil
- The approach can be used to calculate the amount of profit or loss that can be attained if a certain business was to operate at a certain level or a certain output is made from the process.
- It is used to interpolate sales revenue and production costs for an effective management.
The management should understand that for an effectively managed business, there should be cost management strategies as well as improving the sales of the company; the two management principles will be the main areas of concern in the company. Occasionally, the company will be undertaking internal and external analysis to assist in establishing areas that can be improved to increase the company efficiency and competitiveness (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011).
In the case of Solar charged laptops at Nokia, the breakeven point will be subject to the budgeted sales and the fixed costs as well as variable costs; it is calculated as follows:
- Breakeven point then total fixed costs = total revenues from sales
Alternatively:
- Formulae: break even = fixed costs/contribution per unit
The break-even points in the above:
- The fixed costs for the three periods will be 64,000,000
- At breakeven at every quarter, then quarterly fixed cost = the quarter’s total collection
- 64,000,000 + 400x = 800x (where X represents the number of laptops to be incurred to break even)
- Then 400x= 64,000,000
- When the above equation has been solved then X = 160,000 units every quarter.
From the above projected sales, it can be seen that the company will only start making a profit after the third quarter.
Alternatively, the breakeven points for the whole year will be as follows:
- = (64,000,000*4) + 400X = 800X ((where X represents the number of laptops to be incurred to break even)
- = 64,000,000= 100X
- X= 640,000 units
This shows the net effect after the end of the year will be a net loss since the budgeted units are 570,000 but breakeven units are 640,000. This creates a deficit of 70,000 units.
Contribution
The contribution margin of a product is calculated as the difference between the sales price and the fixed costs: when calculating the breakeven point, it can be used as follows:
break even = fixed costs/contribution per unit (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011)
In this case, the contribution margin is: $800- $400 = $400
Breakeven using contribution margin:
Per quarter: 64,000,000/400 = 160,000
Per year: (64,000,000*4)/400 = 640,000
External and internal analysis
The strength of this segment will undoubtedly be engineered by Nokia’s internal managerial mechanisms. In order to have a competitive edge in selling its product, and services it will be advisable for the company to take advantage of its ability to compete favorably with equal players in the market; it should take advantage of brand extension strategy for an effective market entry. A strategic marketing plan is the only way out. Through this arrangement, the company will be able to adopt different modalities and outreach programs of reaching out to its consumers. In a market mostly controlled by the efficiency and the affordability of the products as well as quality, it will be an open strength for the company to explore more on innovations. In retrospect, strategic marketing plan should be in a position to document explicitly the various channels that can be used by the company to allocate more resources towards improving quality (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011).
The company is likely to face some obstacles that may deter the company from progressing towards a particular direction. One of the weaknesses is attitude that customers have upon new things introduced in the market. Laptops are expensive commodities, which no one would be willing to have a try and test method. When discussing the concept of strategic market planning, we discover that resources are vital for an organization to effect significant changes. Another area of inevitable weakness is an expansion plan that entails diversifying the level of the company activities. This may take different forms. A critical look at geographical expansion depicts a glaring possibility of other stringent market uncertainties. Right at the onset, strategic planning will demand strategic resources, both human and financial, to make any significant move. Besides, implementation of the proposed market research will require mutual consent from all the affected divisions in the company. This will not only consume time as decisions are being made, but many uncertainties abound especially on the verdict of the company (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011).
To have a sustainable competitive advantage, there is need to improve the products with time. The company will have a research and development team that will be mandated to survey the market and advice the management on measures to take to ensure that it remains competitive. Another way is the use of appropriate advertising and marketing strategies. Promotions are done in the effort to either introduce a new product or increase the market segment. To engage in a promotion, the first thing to understand is the availability of the target customers. Where are they likely to be found? Are they free in the mornings is it in the afternoon? After realizing their availability and the fact that they can give you time to sell your products, and then know the age of the market. If the promotion is for the introduction of a new product, then a lot should be invested in assuring the client of better quality than that offered by the competitor. The existence of opinion leaders should be evaluated. The customers are likely to follow the opinion leaders in making their decisions. The existence of groups in the society and their matching lifestyles can also be of great use. The way the consumers react is that they will follow the others. Investment should be made in this. If the promotion is for an already existing product in the market, the approach should be from the angle that we are thanking our customers. If the customer feels appreciated and recognized he will develop loyalty and influence other to follow his way (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011).
The following is Nokia’s financial ration analysis
To show the Nokia’s financial strength that can be used to finance the new project, the following are the relevant financial ratios for 2010:
Current Ratio
Current ratio calculates the rate at which a company can meet its short-term financial obligations: it thus evaluates the strength and management of working capital: it is calculated as follows:
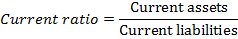
Nokia current ration 2010 is 1.6 (see the companies attached financial statements)
Debt to Equity Ratio
The ratio measures a company’s financial advantage, it compares the ration between owner’s equity and the amount of borrowed capital, and it is calculated as follows:

Nokia Debt to Equity Ratio 2010 is 0.29 (see the companies attached financial statements)
It is important to calculate the financial advantage of the company, high financial advantage are an alarm call.
Dividends payout ratio
The ratio calculated the portion of earnings that were given to the shareholders: it calculates the rate of return that investors should expect from the company:

Nokia Debt to Dividends payout ratio 2010 $0.487504 (see the companies attached financial statements)
Earnings per share
EPS is the amount of earning in an organization that can be attributed to a single share; it is calculated as follows
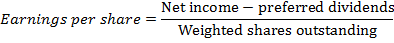
Nokia Earnings per share (DILUTED) ratio 2010 is 0.29 (see the companies attached financial statements)
0.62
Price Earnings Ratio
The ratio evaluates the strength of a certain share in the company and compares it with the earning per share: it is calculated as follows:
- Market Value per Share
- Earnings per Share (EPS)
Nokia Debt to Price Earnings Ratio 2010 is 22.7% (see the companies attached financial statements) (Carlon, 2009).
Conclusion
Laptops are gadgets whose use is on the rise in the recent changing world of technology; Nokia can use brand extension marketing method to venture in the segment in the business. They use electric power to operate; solar energy is freely available energy source that can be tapped to charge laptops; this new invention has not been implemented in the world. The company has the financial capability to make the expansion in the market; in the first year, the company first year the company may not breakeven however, with an increased sale and marketing, the company is likely to enjoy an increased sales and profits at a result.
References
Carlon, S. et al. (2009). Accounting: Building business skills. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Horngren, T., Srikant M., & George F.(2006). Cost accounting: A managerial emphasis. Boston, MA: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Lucey, T. , & Lucey, T. (2002). Costing. London: Cengage Learning
Noreen, E., Brewer, B., & Garrison, H. (2011). Managerial accounting for managers. New York: McGraw Hill.
Nokia Corporation. (2011). Web.
Sadler, P., (2003). Strategic Management. Binghamton: New Down Press.
Zi-Lin, L. , Kwanghui and Pho-Kam, W. (2006). Entry and Competitive Dynamics in the Mobile Telecommunications Market. Research Policy. 35(8), pp. 1147-1165