The acquisition of needed competencies for a nursing practitioner occurs in a progressive manner. Nurses need to harmonize theories and practical knowledge to develop the required wisdom in the health sector. In modern times, nurses need to acquire new knowledge in order to provide services that are commensurate with the changing needs of clients.
The medical practitioners need to access critical information from reliable sources regularly. The search for knowledge for nurses should be appropriately structured. The nurses should identify their needs. The medical professionals should deduce data from identified sources and synthesize it to create necessary practices to guide their work. Information should be adequately processed so that it becomes useful to a nursing professional (Hartley, 2008).
This study demonstrates the application of nursing informatics to healthcare practice. The research evaluates the component by the creation of a clinical research thesis. The document provides knowledge by formulating a research question and identifying the gaps that should be filled. Nursing informatics helps to demonstrate the development of various constituents like data, information, knowledge and wisdom. McGonigle and Mastrian (2012) advance the notion that one can recognize the essentiality of a continuum in nursing practice. The authorities underscore the need for a clinical study thesis. The task can help one progress from information to wisdom.
The clinical question I have developed relates to Mr. Olivier Turner. The Essex Hospital, New York, admits him due to a heart condition. He also contracts hospital-acquired pneumonia after having stayed at the health facility for 3 months. Mr. Turner obliges to all medical subscriptions assigned to him by the doctor but does not keep high levels of hygiene while at the hospital. For example, he does not regularly wash his hands after visiting the toilet. Mr. Turner needs to know why he has got hospital-acquired pneumonia. However, I am not sure of the cause of his disease and decide to conduct a research on the matter. I use a PICO to help focus on my clinical question. I identify the patient’s challenge, examine the hospital’s management practices, and assess the alternative cure for the patient and probable counterproductive results.
Do sanitary practices like washing of hands reduce the probability of contraction of hospital-acquired ailments for patients? A number of common hospital-contracted infections include staphylococcus, pseudomonas, and enterococcus (Hummel, 2010).
I already know diverse issues relating to this topic. One of the methods of hygiene maintenance may entail regular hand washing for victims. Patients who sustain required levels of sanitation may avert the eventuality of acquiring diseases while at the hospital. A patient who cleans his hands makes the initial step towards avoidance of infections. Health facilities should encourage their patients to utilize hand sanitizers. Hospital-acquired ailments comprise of 50% of all patient complications in hospitals. Health experts advance that 83% of diseases can be stopped by cleaning one’s hands (Lakes, 2008). This paper asserts that hand washing can help in the avoidance of hospital-acquired pneumonia (US Department of Health and Human Services, 2013). Infectious germs found on hands may be common means to spread infections. The vast majority of hospital-contracted infections occur through the contact from one patient to another (Knowledge Base, 2008).
However, I need extra information to respond to the question. I am planning to engage in the exercise of statistical analysis of the prevalence rates of hospital-contracted ailments in several hospitals. The analysis of relevant data will help me know whether patients clean their hands regularly while at hospitals or not (Lakes, 2008). A detailed report on the circumstances under which hospital-contracted ailments occur may be critical in meeting the goals of my study. A survey of clinics with superior hand washing frequencies and those with low hand washing percentages will be essential. This aspect may determine the role hand washing plays in the prevention of hospital-contracted infections. It may also include hand hygiene adherence rates and qualitative studies on hand sanitation.
First, I intend to identify relevant data for interrogation, get the information from a number of nursing web platforms and use numerous databases to acquire the information. For example, sites like “CINAHL Plus” incorporate a pool of nursing journals with background information on hospital-acquired disorders. I would also use the resources available from the Walden Library to access relevant and remarkable articles for my research (Nursing Times.net, 2009).
This paper identifies different utilities available in the Walden Library. The library contains journals that provide statistics on sanitation and its significance as a preventive procedure to infections. The databases on nursing provide crucial information on family nursing indices and the prevalence rates of different ailments in the US. They can also be useful in the development of a framework for answering my question. The library contains resources with relevant data on the culture of hand washing for patients in the selected healthcare facilities. The resources provide essential information on diseases contracted in hospitals. PubMed Data Site is important because it provides insights into how one can track the association between hand washing and the spread of hospital-acquired diseases. HighBeam Resource and Journal of Hospital Infection database gives access to the predominance of hospital-acquired diseases and how they manifest themselves in patients.
I would like to focus my attention on reliable articles by checking some related articles from the Walden Library. I would type relevant words in the “search bar” to enable me to locate my area of interest. I would also try to use such phrases as “hospital-acquired ailments” and “importance of hand washing for patients” to make an in-depth research (Rogers, 2013).
I would locate the sites that link hospital-acquired infections to poor hygiene conditions. The relevant topics would feature the two variables under investigation. I would conduct a preliminary examination of the topics to establish their reliability and relevance to the goal of my research. For example, I would need an outline of statistics relating to hospital-acquired diseases. I would adopt the information and consolidate it into a conceptual structure to create the association between hand washing and the spread of hospital-acquired diseases. I would create graphical and tabular representations of the analyzed data to demonstrate the relationship between the two subjects of my evaluation.
I would collect the raw data, examine and convert it into useable knowledge. I would draw several recommendations for implementation in order to help in the mitigation of hospital-acquired diseases. I would start a program to persuade patients and nurses in various health institutions to avoid the spread of hospital-acquired diseases. I would launch awareness efforts program aimed at informing and educating the staff and the patients in hospitals on the need to wash hands regularly. This aspect would minimize the spread of hospital-acquired diseases. Specialists in family-based care facilities need to conduct awareness initiatives aimed at sustaining sanitation interventions. The intervention measures should guide patients on how to keep high standards of hygiene.
In conclusion, the data collected would let me verify and validate the information after I confirm its relevance to the study. Consequently, the information would transform into applicable knowledge upon its scrutiny. The knowledge gained would form wisdom which would, in its turn, evolve into a data-information-knowledge-wisdom continuum that highlights my work and decisions in nursing practice. The sensitization campaigns may be, therefore, based on the wisdom gained from research and practice.
Adoption of a New Technology System
I am a nursing director in a medical center located in upstate New York. The center is small, and hence, its facilities and resource scope may be limited to a given extent. I need to conduct a needs assessment of the institution in order to address the requirements of the hospital in terms of its integration of EHRs (Refers to electronic health records).
I would consult the finance department and the overall administrator to realize the limit of expenditure for my intended program. I would develop a questionnaire and distribute it to all health practitioners in the center. The research method would help me comprehend the best practice designs in the market for EHRs. I would also determine the nurses’ perceptions of the program and their experiences in the same. The feedback from my colleagues would enable me to engage external facilitators from the medical field to help me make informed interventions. The specialists would give insights into the nature of internal and external environments while aligning the EHR systems to the organizational objectives.
A number of strategic components that would help me integrate the EHR systems include SWOT, PESTLE and scenario-building analyses. The scientific methods would enable me to put all the required factors in perspective before the final implementation process begins. I would need to formulate a program-specific monitoring and evaluation tool that would provide feedback at all stages of the administration of the EHRs. I would also establish an efficient communication instrument to guide and coordinate the implementation process.
A nurse can have significant influence on the success or failure of the adoption of EHRs. This research identifies a number of essential stages in implementing a new EHR project. I would present the new EHR program guide to the nurses in a systematic manner. I would start by organizing the implementation team and identifying a system champion. I would also determine the scope of the project and analyze the expectations of the health institution. I would proceed to establish and launch the project plan. The typical components of an implementation guide would include workflow and process analyses.
An expert should conduct an adequate analysis or evaluation of the existing process and procedures. The organization should identify opportunities for improvement and, as appropriate, implement those changes. In addition, it should identify the sources of data including the interfaces to other systems. System installation should follow the aspects like fitting of hardware and software and upgrading of IT infrastructure. Staff training, communication, and launching the system should be present among other activities.
The Everett Rogers‘ five qualities would improve the probability to succeed in the implementation of the new EHR project. The first quality would comprise of a relative advantage. It would be essential to compare the new system with the previous ways of operations management. This aspect would be significant in determining merits that would accrue from the new approach. The second strategy would entail ensuring compatibility with existing values and practices. This fact would be consequential in affirming that the new project operates harmoniously with the existing culture of the organization. The third quality would denote simplicity of the program.
The administrator of the system would need to possess the capacity to master the new technology. A difficult program would result in resistance from the workers. Fourthly, trialability would be essential. It would provide the medical center with the opportunity to explore the capacity of the new system. The final quality would entail observable results. The facilitator would employ tangible evidence to demonstrate that the new project can make positive contributions to the medical institution. The realization of these qualities would be remarkable in promoting the likelihood of success in implementing the EHR systems.
Nurses facilitate and promote the enforcement of new technology systems in healthcare settings. This point is effective because they have a unique appreciation of healthcare issues that may influence the process of transformation. Nurses can provide essential feedback on new systems in an organization. They possess the theoretical knowledge that can be relevant to the success of new systems.
The nurse can design an evaluation instrument for the implementation of a new program in terms of its impact on quality, costs and patient satisfaction. The professional can help in conducting an assessment of the system in order to boost patients’ access to healthcare before its final adoption by a given institution. The expert can also provide an effective strategy for interrogation to determine such elements as staff skills, availability of health information, and the capacity of the health facilities. Healthcare organizations may be able to address their challenges upon the enactment of a new EHR program. The nurse can assess the level of dependence on the system, new types of administration errors, the level of work the system can do and the attitudes of practitioners to ensure the system’s successful adoption. The nurse can act as an intermediary in the change of technology. The facilitator also needs to incorporate other people taking part in the implementation of a new EHR program like IT experts, doctors, and accountants.
Creation of a Flow Chart
The role of a workflow analysis is to control process configurations that exploit the real use of assets. The examination also helps in reducing actions that do not enhance the value of an intervention. The analysis of the workflow processes employs different tools. The instruments help in the identification of ways of decreasing waste and enhancing the value of work. A flowchart may be one of the regularly used workflow analysis techniques. It helps identify the areas that may need a restructuring (Capuono et al, 2010).
One of the general and frequent events that occur in my organization includes the admission of patients. I would like to evaluate this event of patient reception in my organization. The occurrence is usually regular, and it can be restructured to improve on its efficiency. I would design a flowchart to represent the current workflow of patient reception in a systematic order.
I would use a patient satisfaction inventory analysis as a metric to determine the effectiveness of the current workflow and identify areas of poor performance. I would administer a questionnaire to those patients who may have experienced the reception services of the facility previously (Cain & Haque, 2013). I would use the questionnaire to inquire their opinions regarding the effectiveness of services and possible areas of improvement. I would identify the areas of poor performance from the complaints submitted in the opinion questionnaire by the patients.
I would consider their proposals on how the reception process can be efficient. I would also adopt new recommendations on the workflow and compare the efficiency of the mechanism. I would highlight areas that may be ineffective or redundant and also I would detect those points that can add value.
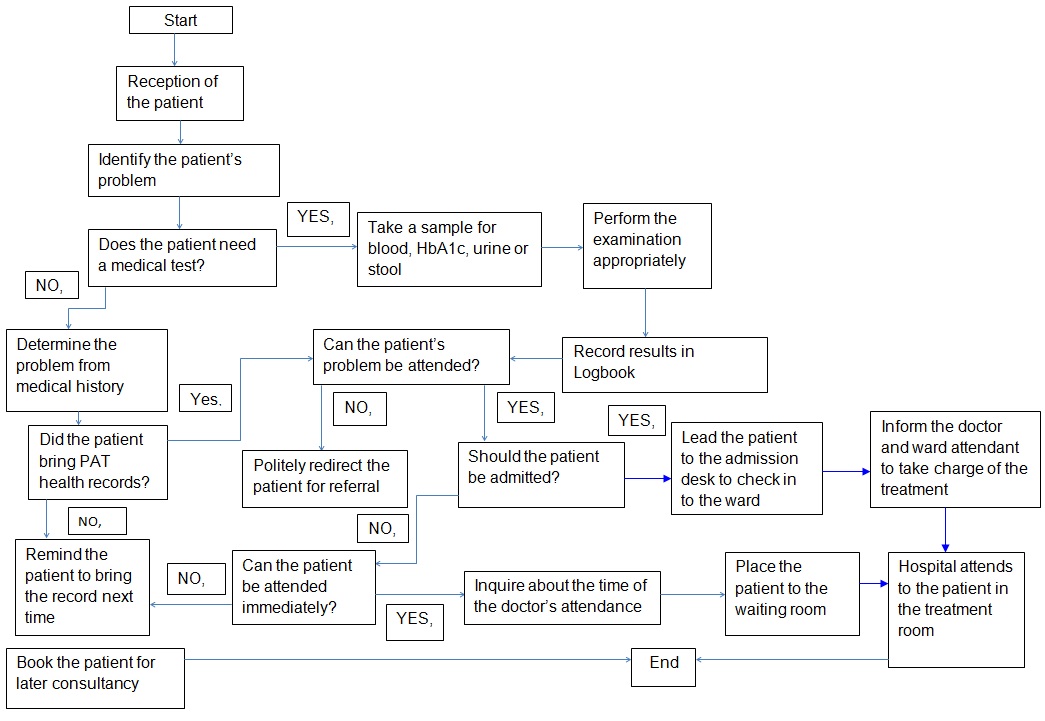
The process of patients’ admissions starts with welcoming them. This aspect happens at the reception desk. The patients may record their belongings in the reception books. The receptionists are normally in charge of this procedure. They also record the details of the patients in a spreadsheet. The technology used is the Microsoft Excel software. The policies involved in this stage entail the use of proper etiquette for the receptionists when interacting with patients. The patients must first identify themselves by providing their personal details. The hospital needs to preserve the details of all the patients it admits. This aspect helps the institution track the progress of patients for the future use and preserves relevant data for statistical analysis.
The second stage of the workflow entails identification of the patients’ problems. The nurses on duty take charge of this process. The patients explain orally their problems to the nurses. The technology used may be a Microsoft Word application for recording the medical history of the patients. The procedures involved at this level denote in-depth examination skills by nurses to understand the nature of the victims’ problems. The nurses should understand the patients’ medical histories to diagnose the main causes of their problems. The processes can only occur if the nurses find it necessary to determine whether medical examinations may be needed or not. They may carry out blood, stool, HbA1c and urine samples. The results should be recorded in logbooks. These processes may happen in the nurses’ chambers. Information from the patients’ explanations or past medical records may be required to make decisions about the victims.
The third step of the workflow entails decision making on whether the patients’ conditions can be resolved in the hospital. Nurses or doctors are the ones to arrive at such decisions that are to be made upon the medical examination (Bravo, 2011). The nurses or doctors may examine the victims to determine the extent of their problems. Doctors can either attend patients in hospitals or make referrals. These procedures may occur in the patients’ examination rooms. Medical expertise may be essential in conducting these processes. The results of medical tests or past health records of the patient may be required when making decisions. The technology that might be needed at this stage is a desktop HbA1c analyzer. Screening technology is also applicable in such cases (Keohane, 2008).
The doctors may conduct tests on the patients to reveal the nature of their problems so it could help them decide on the likely medical interventions. The policies and rules of the stage may include provision of samples requested by the doctors. A double verification may be conducted and corresponding results can be shown to the patients. This aspect may happen when the doctor wants to determine the disorder the patient has been affected by. The step may help the doctor prescribe the suitable medication for the patient.
The fourth stage may depend on whether the patient should be admitted to the hospital or not. The doctor may carry out this process after examining the patient and determining the nature of his/her problem. Medical results from blood, urine, glucose or stool tests may be essential at this stage in order to help medical attendants reach an informed decision. Information retrieved from the medical examination results is to help them decide on further actions to be taken. This procedure may occur in the medication room. The doctor may need to communicate with the respective wards upon admitting a given client. This aspect may allow the ward to allocate space to the patient.
The hospital nurses are in charge of patient’s admission before they join the wards. Nurses should conduct surveillance in the respective wards. However, a patient should be given immediate medical attention if s/he doesn’t not require admission. The doctor is to make the decision at this stage. If the patients can be attended immediately, they may need to be led to the outpatient section for the doctor’s attention. If fulfillment of this requirement is impossible, they may be given deferrals at the reception desk for later attention or consultancy. This aspect may mark the end of the patients’ reception workflow.
The extent of the disease and its severity index as a measurement of technology determine the steps to be taken. In addition, the doctor can apply relevant treatment technology according to the diagnosed disease. The policies and rules in this stage may involve appropriate determination of the patient’s condition. This fact may happen after the victim is hospitalized to the appropriate wards based on his/her conditions. In addition, the patient should be given the facility’s dress code and informed about the treatment and nutrition schedules of the hospital.
This paper does not provide any metric to be used in measuring the soundness of the workflow. However, complaints regarding patient reception can be forwarded to the hospital management for appraisal. The workflow of the patient reception needs to be efficient. However, this paper observes the need to value the workflow (AMIA, 2011).
In conclusion, this research lays stress on the health practitioners stating that they are to be aware of the flow of activity to determine its efficiency and weak links. The ultimate purpose of the activity is to efficiently deliver the health facility’s mandate. However, in some cases the organization of activities may be ineffective. An ineffective workflow may result in waste of time and subsequent failure to respectively handle the reception process.
References
AMIA. (2011). Nursing Informatics. Web.
Bravo,D.F. (2011). The Relationship between Hand Hygiene Compliance and Nosocomial Infections. Durham, NC: The Duke University of Nursing.
Cain, C., & Haque, S. (2013).Organizational Workflow and Its Impact on Work Quality.Web.
Capuono et al. (2010). Work flow analysis: eliminating non-value-added work. Journal of Nursing Administration, 12(4), 34-41.
Hartley, C.L. (2008). Nursing in Today’s World: Trends, Issues, & Management. London, UK: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Hummel, J. (2010). The ultimate directions for meaningful use of EHRs. Journal of Health Care Compliance, 12(5), 49–50.
Keohane, C. A. (2008). Quantifying Nursing Workflow in Medication Administration. JONA: Journal of Nursing Administration, 23(2), 19-26.
Knowledge Base. (2008). Hospital Acquired Infections. Web.
Lakes, P. (2008). Flowchart Setup Report. Web.
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (2012). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge (2nd ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Nursing Times.net (2009). Defining Nursing Knowledge. Web.
Rogers, E. M. (2013). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). New York, NY: Free Press.
US Department of Health and Human Services. (2013). What are some of the workflow considerations when implementing quality metrics. Web.