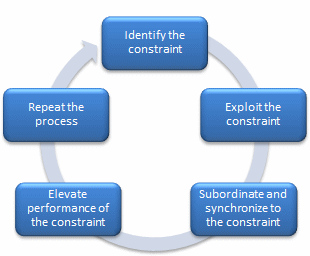
Constraint
Management personnel and supervisors use constraint management to assist workers focus on their respective roles while delivering various roles. In other words, management teams and supervisors are in a position to pursue only crucial aspects of making sure that a business entity succeeds. Better still, vital conditions that assist a business organization to attain the set objectives are known as constraints (Hamid, Ghafoor and Shah 551).
Some of the important roles played by constraints include generating goods and services within the required time, improved satisfaction of customers and increased productivity. For example, the operating expenses in a firm can be the main constraint that impedes the profitability of a firm. Unless managers focus on reducing expenses, an organization might eventually operate at a loss and stall down. This can be a series of steps as shown below:
Bottlenecks
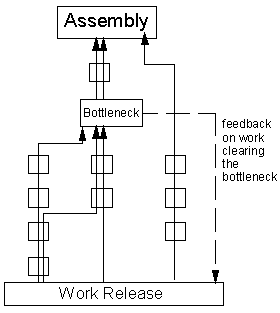
A bottleneck is a single process in an entire chain or process of production that impedes the progress of others processes within the chain. Within any given supply chain, the throughputs of a process are determined by bottlenecks. In order to improve cash flow, it is crucial for the management to recognize the reality on the ground and make necessary adjustments. Bottlenecks generally slowdown production processes (Zhao, Langendoen and Fransoo 110). For instance, upstream bottlenecks can be caused by the absence of refinery supply and a smelter in the case of a firm that deals with oil production. From the point of work release to assembly, a bottleneck reduces capacity of other processes (Tamilselvan, ,Krishnan and Cheraghi 5).
Product Mix
Product mix refers to various product items or lines that a firm offers to the targeted market (Wilson and Ali 380). For example, multiple product lines are sold out by a young firm. In some instances, there might be a lot of similarity in the items being sold. A case example is a firm selling bar soap and washing liquid. Razors and diapers may also comprise of product mix of an organization. The importances of product mix include customer satisfaction, high volume of sales and increased profitability. The figure below shows how to determine product mix.
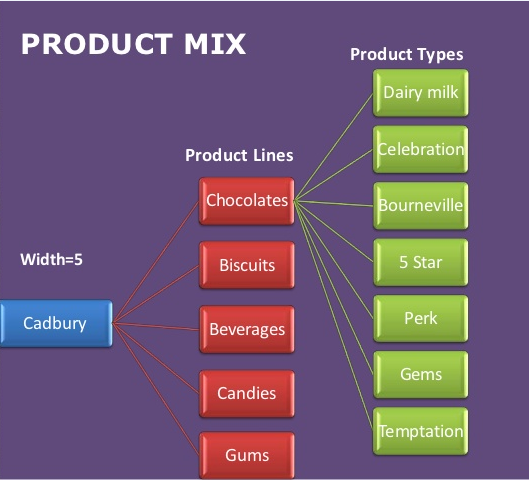
In order to determine product mix, it is vital to start by analyzing the production process. Thereafter, the various costs of the products should be calculated. The next step involves examining the vital constraints encountered by the product mix. Gross revenue is then computed followed by studying costs and benefits. This process is important because it assists management teams to assess the viability of products being offered in regards to customer satisfaction and revenue generation.
Drum-Buffer-Rope Systems
This refers to a solution for planning and scheduling activities in an organization. For a fact, the overall output of production of a firm is determined by both adequate and limited resources (Beebe and Ali 1702). However, this theory focuses on the input of scarce resources that affect the final output. Hence, the pace for other inputs demanded by an organization are set by the drum or limited resources. This theory is important because managers and supervisors can fully understand how to utilize scarce resources to optimize production. For example, a firm that deals with oil refinery should consider sourcing for cheap energy supplies in regions with poor supply of power and other energy resources.
Line Process
A line process refers to a manufacturing process that is repeated on a continuous basis. The same flow is used to pass all products. In other words, the same operations, machines or equipment are used in any given line process. The importance of line production is that the needs of a smaller group can be catered for very well (Mayer, Melitz and Ottaviano 520). Besides, the production can be continued for a long time without stoppages. The above is illustrated below:
Works Cited
Beebe, Ryan, and Ahad Ali. “Simulation and Modeling of Fuel Tank Assembly and Process Analysis for Line Performance Improvement.” IIE Annual Conference.Proceedings (2009): 1700-1705. Print.
Hamid, Syed Ali Raza, Hateem Adnan Ghafoor, and Tamkeen Zehra Shah. “Work Environment and its Impact on Triple Constraint of Project Management.” Information Management and Business Review 4.10 (2012): 545-552. Print.
Mayer, Thierry, Marc Melitz, and Gianmarco Ottaviano. “Market Size, Competition, and the Product Mix of Exporters.” The American Economic Review 104.2 (2014): 495-536. Print.
Tamilselvan, Prasannavenkatesh, Krishna Krishnan, and Hossein Cheraghi. “Measurement of Shifting Bottlenecks in a Non-Buffer Production System.” IIE Annual Conference.Proceedings (2010): 1-6.Print.
Wilson, Shellyanne, and Nazma Ali. “Product Wheels to Achieve Mix Flexibility in Process Industries.” Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 25.3 (2014): 371-392. Print.
Zhao, Lei, Floris Langendoen, and Jan Fransoo. “Supply Management of High-Value Components with a Credit Constraint.” Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal 24.2 (2012): 100-118. Print.