Background
Over the decades, different institutions fostered the development of distinct models of care focusing on the alleviation of major problems. One of the significant challenges within the Dubai government emergency department encompasses overcrowding. The initiative causes profound adverse effects among the patients and medical practitioners cause of the drawback in the processing timeline amid patients that risks poor service delivery system.
Research by Kader (2019) indicates that insufficient supply of equipment and facilities poses a dynamic hindrance towards the performance outlier among the nurses and the effective patient treatment. Salim and Rahman (2020) stipulate that the problem of congestion of patients in Dubai healthcare facilities violates the UAE Vision 2020 pillar on boosting the quality of medical care.
In a different spectrum, lack of adequate studies involving the assessment of the setback of congestion within the healthcare institutions contributes to the prevailing factor within the Dubai territories. A quantitative and qualitative survey regarding the inherent perplexity renders proficient outcomes and insights upon the effective solution outline.
The emergency departments in Dubai face various issues due to the overcrowding of patients within the facilities. Al-Alawy et al. (2021a) articulate that it is essential for the government to implement strategies that enhance the performance between the nurses in the service delivery system. The efficiency in the processing of the clients fosters a trickle-down effect towards the actionable handling of various illnesses without the risk of death among the personnel (Nichols, 2012).
Delays within the entity bring about distractions among the parties due to the prominent consideration of compromising quality over quantity to reduce the workload. In different research by Al-Alawy et al. (2021b), installing technology and an effective policy plan for the managerial team and the employees steers the intensification to the coordination and assortment of the activities elevating the profitability margin.
Aburayya et al. (2020) depict that the attested dissatisfaction among sick individuals in Dubai is a consequence of the long waiting queues before accessing assistance from a doctor. Different illnesses demand dynamic attention among people (Strselecka et al., 2021). Primarily, the analysis demonstrates that Dubai is the only city highly affected by the issue of overcrowding of casualties. Below is the tree diagram for the problem statement:
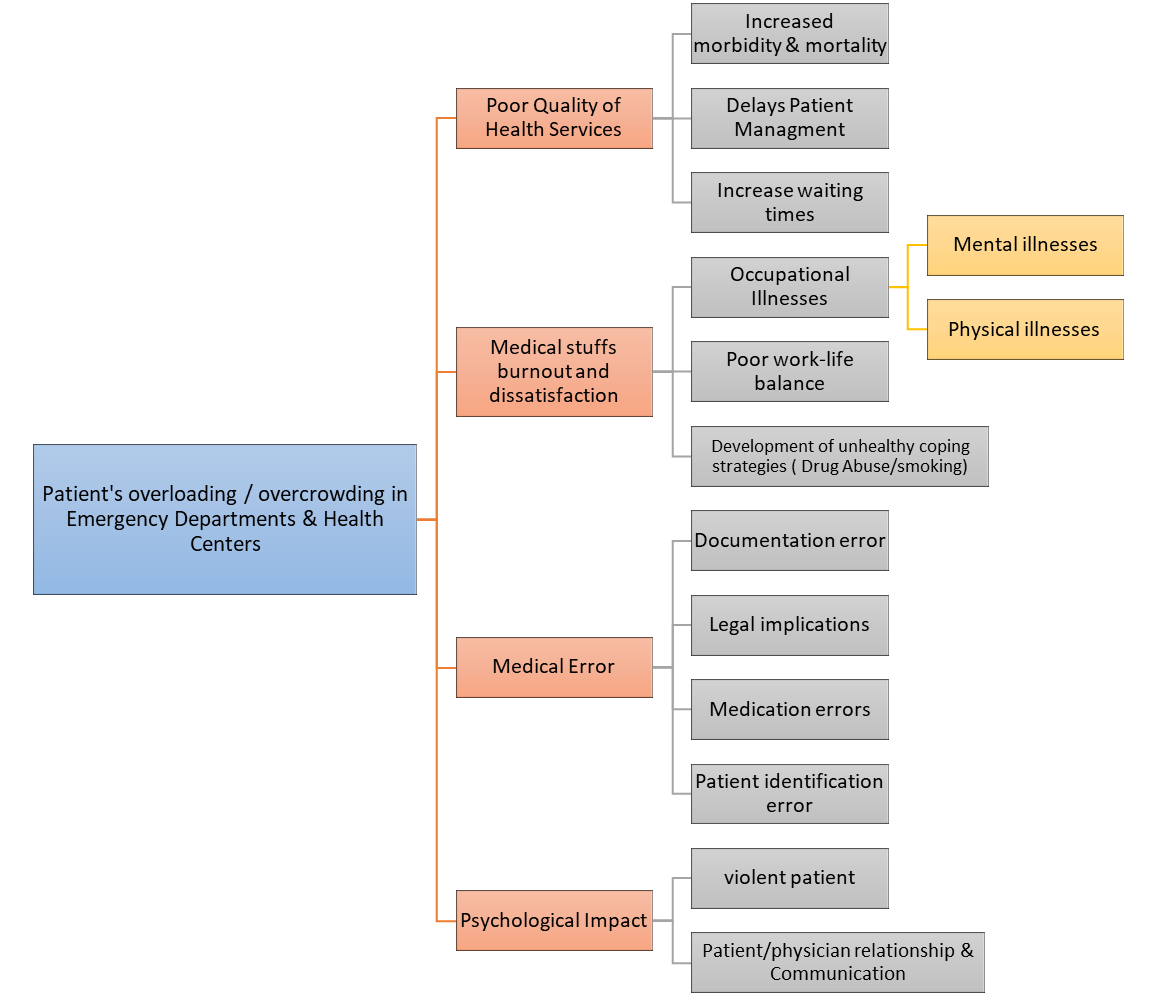
The rationale for Government intervention
The rationality for the government intervention is an important factor cause of the emergent issues on healthcare operations. The overcrowding of patients in the emergency departments compromises the standards of engagement between clients and workers. Improving quality of services within the medical care sector involves enhancing the accessibility of functional tools and expertise among nurses (Kader, 2019). The approaches foster the alleviation of the overload and the emergent inherent issues regarding burnout amid the healthcare practitioners and customers’ dissatisfaction.
Intensifying stress among the laborer risks the occurrence of a higher marginal error among the personnel. Therefore, rendering administrative support surges the system performance with the UAE. The persistence of the issue endangers the reputation of the city’s ability to provide competent care plans among consumers (Muslim, 2019). The significance of addressing the hindrance engulfs triggering savings on incurred costs while coordinating the distinct activities.
Policy Objectives
- To intensify the public awareness level regarding overcrowding in healthcare facilities as a social issue.
- To provide the necessary materials and equipment for fighting the core issue.
- To enhance the reduction of the work burden among the medical practitioners to improve the quality of operations.
- To facilitate the appropriate developmental plan for the system in Dubai.
- To render the improvement of medical care’s public image across UAE.
Policy Context
The policy focuses on the integral value of boosting the standard of operations within the healthcare sector in Dubai. UAE Healthcare Department (n.d) considers the research an essential platform to address the issue of the overcrowding of patients within the facilities that compromises the quality and profitability scale. Adequate insights on the interdependent relationship and the alternative solution render the influential outlier on workers’ performance and customer satisfaction.
Policy Scope
The distinct measures used in addressing patient overload in Dubai include:
- Community-based awareness
- The development of a list of illnesses referred to paramedics, and when the patients are in the red zone, they contact the doctors.
- The encouragement of the community on visiting PHC for easier access.
- Ensuring the increase in the PHC clinics within the Dubai community.
- Triaging training among the doctors for effective performance.
- Enhancing provision of protected emergency care services.
- Fostering timely response to emergency incidences.
The key stakeholders involved in implementing the policy plan enshrine the medical staff, DHA, community patients, emergency department personnel, and the primary healthcare centers. However, other entities that encounter the significant impact of the situational platform include government, the World Federation of Public Health Associations (WFPHA), Joint Commission International Accreditation (JICA), and healthcare departments of government hospitals in Dubai.
Analyzing the Policy Evidence Base
PESTLE Analysis
Political
- The amount of financial resource from the government budget.
- The government regulatory framework.
- The stability of the political situation.
Economic
- The waste of the medical recourse practice.
- The employment rate of nurses in Dubai.
Socio-cultural
- The demographic emergent trend.
- The birthing rates.
Technological
- Effective social media marketing initiative.
Legal
- The employees’ protection legal clause.
- The patients’ protection law.
Environmental
- The recycling and the management of waste.
- The eco-friendly products’ attitude.
SWOT Analysis
Internal variations
Strengths
- The decreased time during the interaction between patient and physician.
- The administration of earlier treatment.
- The increase in the satisfaction index among patients.
- The higher probability of necessary and accurate tests.
- The elimination of the process on sick peoples’ treatment.
Weaknesses
- The increase in the lower acuity patients.
- The mental and physical demand for the physicians.
- The increase in the workload with reduced nurses’ population.
- Extra costs for the hiring of other medical practitioners.
External variations
Opportunities
- The positive public relations.
Threats
- The increasing population density.
- The stressing condition of the public domain risks a decrease in the budget and efficiency.
Stakeholder Engagement Plan
Patient
Dubai is one of the cities in the UAE that harbor a significant population of individuals from different regions. Therefore, emergency department overcrowding contributes to problems for patients by increasing their waiting time, length of stay, morbidity and mortality (Salway et al., 2017). The policy proposal will address patient needs and aim to improve the quality of health care services in Emergency Departments and Health Centers. Hence, it is expected that this group of stakeholders will support the change.
Medical Staff
The patient overload poses an imminent effect on the medical practitioner’s due to the persistence in maintaining high standards under stressful conditions. The current policy problem implies medical staff burnout and dissatisfaction, which, in turn, contribute to occupational illnesses, poor work-life balance, the possibility of developing unhealthy coping strategies, and medical errors (Bahadori et al., 2017). The policy proposal will reduce overburden on the medical staff, which justifies the assumption that this group will support it.
Emergency Department
The central role of the healthcare management team enshrines advocating for timely care for customers to avoid the risk of complications. Emergency Departments in Dubai are affected by the overcrowding problem. The proposed policy recommends adequate strategies after analyzing the current situation. It addresses issues associated with overcrowding in emergency departments, such as difficulties in bed management and poor patient flow. Therefore, it is expected that emergency care providers will support the suggestion.
Government Hospital
Patient protection is a prominent factor across the Dubai environment, hence involving the administrative organs in the outlying conditions. The primary purpose of the Dubai Health Authority (DHA) is to protect public health and ensure an accessible and efficient health care system. DHA will be involved in the policy implementation process as the health care regulator. Furthermore, it is crucial to raise public awareness and encourage the population’s trust in the healthcare system.
Primary healthcare centers
There is an interdependent relationship between sustainability and the medical care index across the public domain. Overcrowding in primary health care centers results in increased waiting times, prolonged patients’ length of stay, poor access to services, financial losses, and dissatisfaction in patients and staff (Salway et al., 2017). The support of this group is expected since the policy proposal aims to provide all necessary equipment and materials necessary to eliminate the problem.
Government institutions
A nation’s administrative mandate enshrines incorporating measures that enhance equity in the distribution of services. The UAE has a government-funded health care system that includes public facilities, clinics, hospitals, and medical services. The overcrowding problem decreases the quality of care, thus interfering with the government’s objective to maintain a high standard of medical services (Bahadori et al., 2017). The policy proposed addresses the health care system issue, which allows for expecting support from the governmental institutions’ side.
World Federation of Public Health Associations (WFPHA)
The plan on alleviating the issue of overcrowding in the facilities in Dubai renders the importance of the entity’s participation in the practice to assert international standards. This non-governmental organization aims at encouraging partnerships among public health professionals that promote health care safety and quality through action and collaboration. Hence, WFPHA can contribute to the development of the proposed policy. It is crucial to include the institution cause of the prominent effect of the adversities to the global population.
Joint Commission International Accreditation (JICA)
Different stakeholders focus on the implementation of strategies that elevate the welfare of the personnel. Joint Commission International (JCI) provides the service of international health care accreditation to medical facilities worldwide. JCI can assist in developing and implementing high standards-driven policy to improve the quality and safety of care in the UAE. Healthcare Department of the government hospitals in Dubai. In this case, JICA’s involvement fosters significant attribution of dynamism in the perspective of the proposal.
Policy Theory of Change
The study’s primary purpose enshrines the assessment of the impact of overcrowding of patients within Dubai government emergency departments. The efficiency in processing of clients fosters a trickle-down effect towards the actionable handling of various illnesses without the risk of death among the personnel. Delays within the entity cause distractions amid the parties cause of the prominent consideration of compromising quality over quantity to reduce the workload (Chang et al., 2018).
Although the overload is a significant issue, a different factor attributing the necessity of addressing the matter is the concentration of ill people without emergency attendance baseline. Research by Idil et al. (2018) focuses on effects of non-urgent patients and demonstrates proficiency in the percentage distribution causing the hindrance. At least 36.4% of the patients required urgent care, while 30.9% had opportunities for alternative solutions. The factor that contributes to the leading cause is the lack of medical insurance, which results in patients rushing to the governmental ED hospital.
According to ASPE (2021), the proportion of emergency department visits generally reflected changes in health insurance coverage rates. It implies that unaffordable insurance costs lead to an increase in the number of non-urgent patients visiting the establishments. The understaffing in hospitals which prevents effective management of an increased number of patients is a significant outlier contributing to the poor service delivery and the trickle-down effect of the benefits and adversities. Below is a diagram of the policy theory of change:
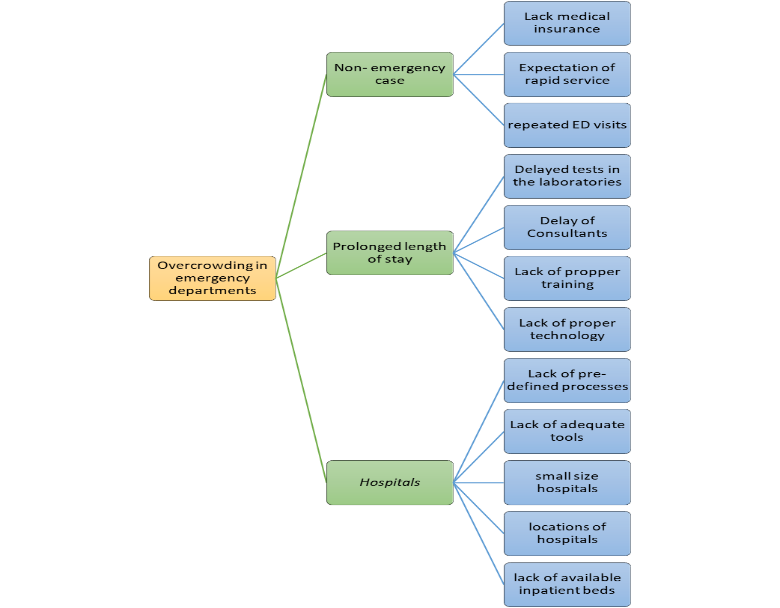
Policy Impact and Outcomes
Identifying and Appraising Policy Option
References
Aburayya, A., Alshurideh, M., Albqaeen, A., Alawadhi, D., & A’yadeh, I. A. (2020). An investigation of factors affecting patients waiting time in primary health care centers: An assessment study in Dubai.Management Science Letters, 1265–1276.
Al-Alawy, K., Moonesar, I. A., Mubarak Obaid, H. A., Al-Abed Bawadi, E. I., & Gaafar, R. (2021a). Hospital accreditation: A review of evidence, regulatory compliance, and healthcare outcome measures. Dubai Medical Journal, 4(3), 248–255. Web.
Al-Alawy, K., Azaad Moonesar, I., Ali Mubarak Obaid, H., Gaafar, R., & Ismail Al-Abed Bawadi, E. (2021b). A mixed-methods study to explore the impact of hospital accreditation.INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, 58, 004695802098146.
Bahadori, M., Teymourzadeh, E., Ravangard, R., & Raadabadi, M. (2017). Factors affecting the overcrowding in outpatient healthcare.Journal of education and health promotion, 6, 21.
DHA. (2018). Dubai clinical services capacity plan 2018-2030. Web.
Howlett, M. (2019). The policy design primer: Choosing the right tools for the job.Routledge.
Kader, B. A. (2019). New steps to reduce crowding at Emergency units in Abu Dhabi. Health – Gulf News.
Mirhaghi, A., Kooshiar, H., Esmaeili, H., Ebrahimi, M., (2015). Outcomes for emergency severity index triage implementation in the emergency department. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 9(4), OC04–OC07. doi:10.7860/jcdr/2015/11791.5737
Muslim, N. (2019). Public hospitals to charge only after patient stabilises. Health – Gulf News.
Nichols, L. M. (2012). Government intervention in health care markets is practical, necessary, and morally sound. The Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics, 40(3), 547-557.
Salehi, L., Phalpher, P., Valani, R., Meaney, C., Amin, Q., Ferrari, K., & Mercuri, M. (2018). Emergency department boarding: A descriptive analysis and measurement of impact on outcomes.Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine, 20(6), 929-937.
Salim, F. M., & Rahman, M. H. (2017). The impact of joint commission international healthcare accreditation on infection control performance: A study in Dubai hospital.GATR Global Journal of Business Social Sciences Review, 5(1), 37–45.
Salway, R. J., Valenzuela, R., Shoenberger, J. M., Mallon, W. K., & Viccellio, A. (2017). Emergency department (ED) overcrowding: Evidence-based answers to frequently asked questions.Revista Médica Clínica Las Condes, 28(2), 213-219.
Strzelecka, A., Stachura, M., Wójcik, T., Kordyzon, M., Chmielewski, J. P., Florek-Łuszczki, M., & Nowak-Starz, G. (2021). Determinants of primary healthcare patients’ dissatisfaction with the quality of provided medical services. Annals of agricultural and environmental medicine.
UAE Healthcare Department. (n.d.). Health strategies, policies and laws – the official portal of the UAE government.