Introduction
The integration of IT in the business processes of a company became a commonly used method to overcome particular problems in the company’s functioning. In that regard, it can be stated that the answer to whether such integration can live up to the expectations of the management can depend on different factors, among which is the nature of the problems that the company is facing.
This paper analyzes the aforementioned statement based on the case study of Palm Island Restaurant, in which a decision should be made regarding a proposal to use an information system to solve an initial problem of profit decrease and the customers’ dissatisfaction. The paper creates a working system for the aforementioned case, summarizes the restaurant’s value chain, and the impact of IT on this chain stating that “the proposed information system accomplishes little in solving Palm Island Restaurant’s problems.”
Analysis
Work System
Creating the Work System (WS) for the restaurant, a definition of the WS in general should outline the main approach in analyzing the proposed change. In that regard, “[a] work system is a system in which human participants and/or machines perform business processes using information, technologies, and other resources to produce products and/or services for internal or external customers” (Alter, 2002b). Accordingly, the work system that will be created will demonstrate the system without the IS in work. Thus, in order to clearly define the WS in this case, a snapshot of the system will identify the main stages, participants and processes in the work system. Based on WS framework the work system will include the following:
- Participants – the participants in the case are the staff members of the restaurant, including waiters, kitchen staff, sales and accounting personnel, and reception personnel (if any). Basically, the participants are those who participate in any of the business processes indicated below.
- Information – this term implies the type of information created and exchanged by/between the participants of WS. The information in the case of the restaurant include the following:
- Reservations information
- Order information
- Cooking information (cooking time and meal readiness time)
- Products inventory management
- Meals’ bills
- Technologies – the technologies shall include the tools used in the current context of the restaurant. Without the proposed IS being implemented, it can be assumed that the main technologies currently used include the usage of computers to maintain the accounting information of the restaurant, i.e. bills, expenses, salaries, rent, etc, and typical communication methods, i.e. telephones, mobile phones, faxes, and assumingly the internet to manage the communication with the suppliers.
- Customers – The customers are “people who use and receive direct benefits from the products and services produced by the work system” (Alter, 2002a). The external customers of the system include the typical restaurant’s visitors who order food, either in the restaurant or at home. The internal customers include the participants of WS as intermediary links in the system, as well as the business partners of the restaurant, e.g. suppliers.
- Products & Services – the products and services include the physical items such as the meals, services such as food delivery, taking orders, cooking, etc, and intangibles such as enjoyment of the food, relaxing atmosphere, satisfaction with the service, etc.
- Business Processes – the typical business processes, considering the established workflow for twelve years, include the following:
- Managing reservations, i.e. all the tasks related to providing the information regarding reservations
- Taking the orders and informing the customers on the approximate time of their delivery
- Delivering the orders to the kitchen
- Cooking the order
- Delivering the order to the customers
- Calculating the bill
- Managing supplies and inventory, i.e. buying products, storing them, and checking their availability.
- Environment – strong competition, assumingly one of the factors in the present problems of the restaurant. Additionally, organizational environment possibly includes problems of the personnel serving their friends, and lack of control of the processes in the restaurant.
Based on the snapshot, the opportunities and the problems that can be extracted from the aforementioned factors can be summarized in the following figure.
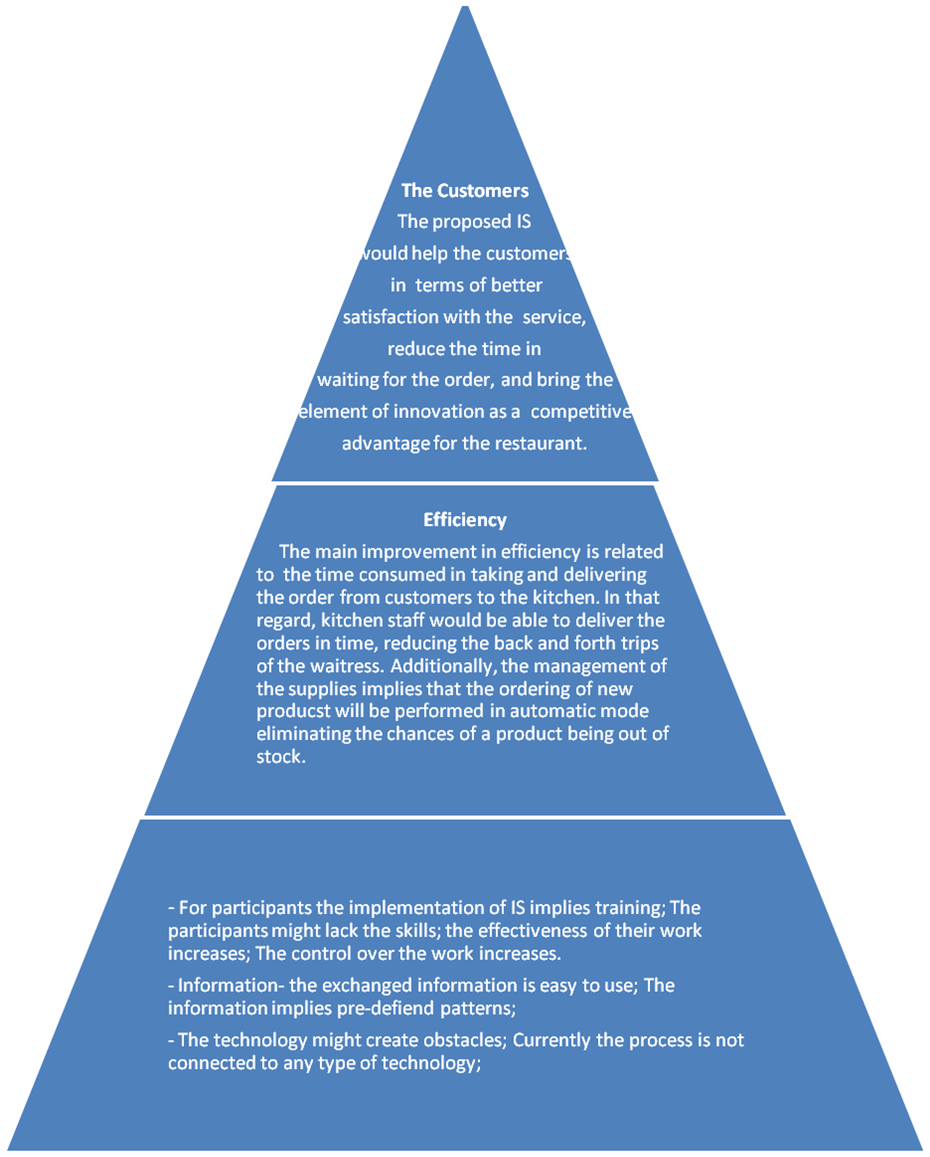
Value Chain
The value chain can be defined as the activities through which the company develops a competitive advantage and creates a shareholder value (“The Value Chain,” 2007). The primary chain activities and their relation to the context of the present case can be summarized as follows:
- Inbound logistics – the purchase and the storage of the supplies used in preparing the meals.
- Operations – the transformation of the supplies into the finished products, i.e. meals. Mainly, the processes imply cooking and serving the meals.
- Outbound logistics – In the present case this activity primarily implies the delivery of the meals to the customers, and the corresponding factors such as timing, and the quality of the meal presentation.
- Marketing & sales – conformity of the product to the needs and the expectations of the customers, through promoting the quality and the pleasant atmosphere in the restaurant.
- Service – in this context, such activity implies the additional factor in the restaurant beside the meal itself, such as the quality of the service, the treatment of the personnel, their responsiveness, etc.
It can be seen that technology in general is used in all of the activities in the present WS. Nevertheless, IT in particular if implemented as recommended it will affect such activities as inbound logistics, outbound logistics, and the service. In that regard, the changes imply changing the activities themselves, either through changing the activities or changing the configuration of the chain. In the case of the inbound logistics, the effect of IT can be seen through the reduction of the costs of storage and delivery, through raising the effectiveness of the supply chain communication. In other activities, the influence of the IT can be seen through the reduction of the operations time. In terms of service, the value-adding impact can be seen through the factor of innovation for the customers, through which a competitive advantage can be gained. Based on interviews in which the impact of using the PDAs in restaurant was assessed, the customers “were impressed with the technology and [the way] it was positively contributing to the reputation/image of the organization (Prasad, Scornavacca, & Lehmann, 2005). It can be seen that an important activity, i.e. operations, has the main value-adding process in cooking and preparing the meal. In that regard, it can be stated that the usage of IT is not affecting that part of the value chain. Generally, the impact can be summarized, in cost reduction, time effectiveness, control, and the innovation factor, all of which are contributing to the restaurant’s competitive advantage.
IS and the Palm Islands Restaurant’s Problem
In the restaurant business the quality of food and the atmosphere of the restaurant are the main factors, which can be seen ahead of other variables such the effectiveness, control, and time. In that regard, it can be seen that the implemented IT does not address these main factors, and accordingly, assuming that effectiveness, time and innovation were not the main factors for the decline in profit, it can be stated that IT will bring little to solve such issue. From a similar case, mainly revolving around the introduction of PDA in the work of restaurant’s personnel, it was stated that the main benefits were related to information management, administrative tasks and decision support (Prasad, et al., 2005). Nevertheless, it can be stated that the innovation might bring a boost in the sales of the restaurants, assuming that the quality of the food and the atmosphere are constant, if the cost effectiveness was transferred into cost reduction, and the innovation was properly promoted.
Conclusion
The emphasis on computerized tasks might take away the attention from other areas in the business, such as the setting of the restaurant, the type of food served, and the quality of service. The proposed solution can be effective in terms of gaining control over the restaurant’s processes, increasing the effectiveness, and bringing a temporary effect of innovation.
References
Alter, S. (2002a). Three Critical Checkpoints The Collaboration Triangle: A Tool for Improving IT-Business Communication. CIO Insight, 1(9), 1.
Alter, S. (2002b). The Work System Method for Understanding Information Systems and Information System Research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 9, 90-104. Web.
Alter, S. (2004). Making Work System Principles Visible and Usable in Systems Analysis and Design StevenAlter.com. Web.
Alter, S. (2004). Work System Basics. StevenAlter.com. Web.
Alter, S. (2007). Could the Work System Method Embrace Systems Concepts More Fully? Information Resources Management Journal, 20(2), 33-43.
Prasad, M., Scornavacca, E., & Lehmann, H. (2005). Using Wireless Personal Digital Assistants in a Restaurant: impact and perceived benefits. Web.
The Value Chain (2007). NetMBA.com. Web.
Sousa, K. J., & Valvo, R. (2001). The Impact of Information Technology on Value Chain Management. Small Business Advancement National Center. Web.