Introduction
Lufthansa Airlines or Deutsche Luft Hansa AG is the leading carrier in Germany and one of the three prominent aviation companies in the world. Annually, the company operates flights for millions of passengers worldwide. The airline runs a fleet of about 370 aircraft, the bulk of which, 288, are owned rather than leased (Cui and Li, 2022). The firm’s workforce in 2017 consisted of over 130,000 individuals (Kuno, 2021). With flights to 18 local destinations and 193 major airports in 81 countries worldwide, the company is one of Star Alliance’s founders (Kuno, 2021). The airline offers business, economy, first, and class travel packages of premium economy. From these, most of the classes provided by the airline have lounges specifically for VIP (Very Important Person) travelers. The paper aims to develop a passenger traffic forecast for Lufthansa Group by recommending the appropriate forecast for the group to adopt. For Lufthansa to achieve this, the paper plans to provide evidence to support an understanding of how the market is and what is expected. The scope of the paper is to address both the short- and long-term needs for the group’s annual passenger volume projections.
Lufthansa Airlines
Fleet Composition
Presently, Lufthansa controls a principal fleet of aircraft comprising Boeing wide-body airplanes and Airbus wide and narrow body. The focal airliners included distinct classifications, such as the Airbus A330, Airbus A320ceo and A320neo, Airbus 350, and Airbus 340. At the close of 2021, the Lufthansa Airlines fleet included 713 air crafts (Relations, 2021). From these, the fleet’s average age of airplanes was approximately 12.7 years (Relations, 2021). At the close of the financial year 2021, the firm’s management decided to reduce the operational fleets according to their needs (Relations, 2021).
The approach by Lufthansa to reduce its fleet saw significant changes in the number of aircraft operated by the company. For instance, the Group estimated the retirement of the number of operational airliners at 44 (Carreira, 2018). That was purposed to regulate the impacts of operating costs on the company. However, Lufthansa introduced eleven novel planes to the fleet to replace the 44 retirements. Ten new aircraft (one A220-300, one Boeing 777F, three A320neos, and five A321neos), and a pre-owned, leased 777F, were added to the fleet (Carreira, 2018). In contrast, the company sold 36 older, less effective aircraft (eight Bombardier Q Series, three A321s, five Boeing MD-11Fs, four Bombardier CRJ900s, six A320s, two 747s, three 767s, and five A319s) in 2021, and 19 aircraft had their leases terminated (Magdalina and Bouzaima, 2021). Eighty-three airplanes have been retired since the coronavirus outbreak began. As of December 31, 2021, the following airlines are part of Lufthansa German Airlines: regional airlines, Lufthansa Cargo (LCAG), Germanwings and Eurowings Discover (LH), Eurowings (EW), Austrian Airlines (OS), and Brussels Airlines (SN) (Magdalina and Bouzaima, 2021). Table 1 below indicates a group fleet of commercial aircraft operated by Lufthansa Group.
Table 1: Shows Lufthansa Group’s commercial fleets at the close of 2021
Network Structure
Domestic and European Network 2019/20
Lufthansa Group is an international aviation company with operations across Europe. The Airline’s European network comprises aviation services, airlines, and Eurowings. The group established the categories at the beginning of 2019 to boost local and European service delivery (Kuran and Novak, 2018). These segments included SWISS, Brussels Airlines, Lufthansa German Airlines, and Austrian Carriers, the Group’s networks servicing the European market. Through Eurowings, the Lufthansa Corporation offers a novel for service-centered and price-conscious consumers in the structural development section of European direct traffic (Kuran and Novak, 2018).
On the contrary, regarding the domestic networks, Lufthansa operates aircraft from leading carriers, such as Austrian Airlines and SWISS Group. The airline companies present domestic consumers with exceptional services and quality products and services (Buff, 2021). The multi-hub approach has enabled the company to offer its clients a widespread local route linkage and probable flexibility throughout their journeys. From the assessment, Lufthansa Airline’s domestic and European networks are designed to give improved accessibility while offering quality and value to travelers (Iacarelli, 2021).
American Network 2019/20
The establishment entered the U.S. market after acquiring Brussels Airline in 2019 to boost its international operations (Huffman, 2020). This move allowed Lufthansa Group to expand its operations within the country by presenting unique services in states like Chicago and Georgia. For instance, Lufthansa offers first-class flights from Chicago to Frankfurt to its consumers who have achieved the 85,000 miles threshold consuming the firm and its partner’s air travel services (Huffman, 2020). The award for the first class travel is first released to new members who have achieved the Miles requirement before it is discharged to the loyalty program members. On the other hand, in Atlanta, Georgia, the Airlines Corporation allows its consumers a bargaining deal once they have realized the 55,000 miles limit (Huffman, 2020). In this case, the passengers are permitted free Business Class travel from Atlanta to any city within Germany.
Passengers can achieve mile expectations through acquisitions with Lufthansa’s hospitality partners. For instance, an individual can gain a 5,500 bonus Lufthansa mile for a two-night visit to Le Meridien, New York (Aubakirova and Konovalova, 2019). Equally, a three-day car rental in Los Angeles allows passengers to get 950 Lufthansa miles (Aubakirova and Konovalova, 2019). Therefore, passengers’ miles are increased whenever they make premium reservations. Expanding operations within the American marketplace will help the airline business boost its consumer base by 30 percent compared to its previous 15 percent market control in the region (Ginter and Linntam, 2019). From the evaluation of the Lufthansa Group’s American network, the organization has established a solid market presence owing to its exceptional deals and services.
African Network 2019/20
Brussels Airlines, Eurowings, and Austrian Airlines aim to introduce their sales activities in Africa comprehensively. With these carrier companies being associates of the Lufthansa Group, they intend to align their sales networks for corporate consumers and travel agencies within Africa. Brussels Airlines has prominent expertise and presence in Africa with a network of 23 destinations, particularly in Central and West Africa (Merkel, 2018). Consequently, to share this achievement and support the incorporation, the Lufthansa Corporation intends to establish all sales operations in Africa in Brussels. The company adopted this approach to monitor, improve and ensure the successful integration of its services in South Africa and East African markets following the 2019/2020 schedule (Schmidt, 2020). Consequently, Lufthansa Airline’s African customers will benefit from improved travel flexibility that covers the overall Lufthansa Group Africa network.
Asian Network 2019/20
With several operations currently established in other global regions, Lufthansa intends to boost its consumer base within the Asian market through various approaches. For instance, in October 2020, the company authorized flight schedules for its premium carriers, notably SWISS, Lufthansa, and Austrian Airlines (Lufthansa, 2020). The three operators would conduct 14 weekly flights between Thailand and Europe. This approach was aimed at helping Thailand to open its business market to the world. Similarly, the airline firm uses its Airbus A380 to expand the passenger capacity for Thailand on Lufthansa’s Bangkok to Frankfurt itinerary (Cui and Li, 2021). Lufthansa Group has dominated the market as the only European airline operating the A380 to Thailand, demonstrating its inclination to premium service and unique travel experiences.
Moreover, an introductory flight from Munich that successfully landed in Shanghai Pudong International Terminus allowed the Lufthansa Group to operate an A380 from Frankfurt and Munich to Shanghai twice daily. The company also introduced the A340-600 from Frankfurt to Shanghai, further expanding its overall capacity by 10 percent to and from China (Group, 2020). Additionally, through its associate, SWISS, Lufthansa Corporation introduced an Airbus A340-300 that will service a novel long-distance destination Osaka from March 2020. the group further reinforced this strategy by launching a Boeing 777-300ER to operate flights to the Japanese capital, Tokyo (Group, 2020). Therefore, the Asian Network plays a significant role in expanding Lufthansa Airlines’ consumer base owing to the region’s demand for premium and unique carriers.
The Mix of Traffic and Product
Leisure Travelers
Lufthansa Airlines has five service operation segments: Catering and IT service, Maintenance Repair Overhaul, Logistics, and Passenger Airline Group. The target market for the passenger airline group division is leisure travelers. This collection of travelers do not have a specific target age cluster; thus, it is centered on individuals’ lifestyle. Leisure travelers constitute 20 percent of the carrier’s annual passenger traffic (Chepkonga, 2021). However, this population is expected to decline owing to the existing COVID-19 restrictions on travel. The airline company offers these passengers various services depending on the type of class they intend to consume (Akbar and Kisilowski, 2020). Generally, leisure travelers are consumers with relatively high disposable income and thus tend to fly first class. Consequently, the firm’s cost-based approach has influenced the pricing strategy for leisure travelers.
Business Travelers
Business travelers form 40 percent of the company’s service consumers, with the number projected to increase over the subsequent years (Bhasin, 2019). This group of travelers is usually inclined to minimize transport expenses, saving them more money for their private operations. Therefore, Lufthansa Airlines offers relatively low costs to business travelers. Since this cluster of consumers purposes to save more money, the carrier offers unique services, such as a 31-inch seat with free meals, drinks, and AVOD screens for entertainment.
Visiting Friends and Relatives (VFR) Passengers
Visiting friends and relatives (VFR) travelers are another category of passengers consuming Lufthansa Airlines’ services. The Group of customers constitutes 10 percent of the company’s overall market base (Cui, Li, and Lin, 2018). The traffic is expected to grow over the years owing to the services offered by the company. For instance, Lufthansa Airlines offers comfort and services, such as food, drinks, and bed, to accommodate the needs of both children and parents. The carrier allows VFR passengers to contribute to travel preferences through its passenger airline group division (Cui, Li, and Lin, 2018).
Employees
The company currently has 105,290 workers and will generate a revenue of EUR 16,811m by the close of the financial year 2021 (Cui, 2019). Lufthansa Airlines does not outsource its employees since it does not operate any oversea offices. The firm’s employees are positioned within Germany and are tasked to offer services in Lufthansa’s segments, such as Eurowings, Aviation Services, and Network Airlines. The aviation services comprise MRO, Additional Businesses and Group Functions, Logistics, and Catering (Cui, 2019). Lufthansa introduced these subdivisions to facilitate the distribution of its staff according to their expertise and the functionality of departments.
Capacity
The carrier experienced a loss of capacity during the coronavirus period. According to research conducted by Reuters, the firm currently projects its functions to reach 70 percent capacity and a further 85 percent by 2023 compared to the pre-pandemic levels (Staff, 2022). This increase is attributed to the current ease of global travel restrictions. Lufthansa Group also aims to satisfy post-pandemic demands by acquiring 10 Boeing and Airbus passenger Aircraft and ten cargo planes (Albers and Rundshagen, 2020).
Competitive Environment
Lufthansa Group always follows its mission statement: to connect economies, cultures, and people sustainably. The group uses digitization and innovation potential to increase efficiency and develop consumer-focused products (Lufthansa Group, 2022). Identity and corporate responsibility are put into practice locally and are supported by an overarching functional process, which enables economies of scale and synergies. Further, the airline strictly focuses on operational stability, costs, and reliability in every area, established in Lufthansa Group DNA (Lufthansa Group, 2022). The group values the safety of its employees and flight operations and always makes it a top priority.
Financial Status
The firm recorded a loss of $6 billion during the first pandemic year (Report, 2021). However, the airline substantially recovered and reduced its losses to $2.5 billion (Report, 2021). Considering revenue, Lufthansa Corporation generated an income of $17 billion in 2021, a 24 percent increase compared to the financial year 2020, when it made $13.8 billion in proceeds (Report, 2021). The organization’s restructuring, operations transformation, and expense reductions influenced the annual earnings increase. That was further facilitated by the steep rise in travel services during the summer holidays.
Market Analysis
Political Factors
Travel restrictions & Vaccination Passports
The travel limitations and vaccination passport requirements in the many nations where Lufthansa serves can significantly and immediately influence Lufthansa Airways’ business operations (Bogatov, 2022). Even a slight change to specific medical certification requirements or travel laws in one of Lufthansa Airlines’ principal operating nations could significantly affect the airline. The company must also consider the clients’ immunization records when scheduling flights to various locations.
Economic Aspects
GDP Growth per Geographical Area
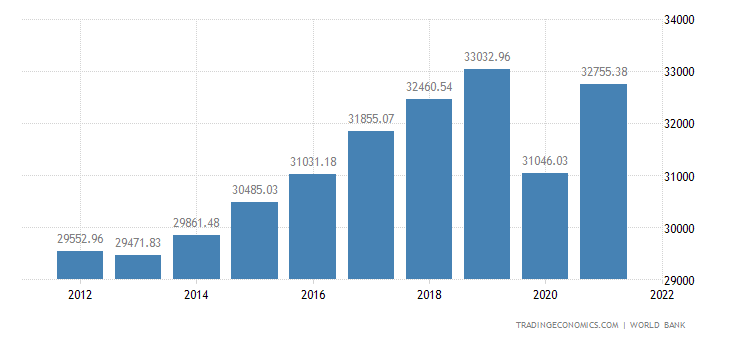
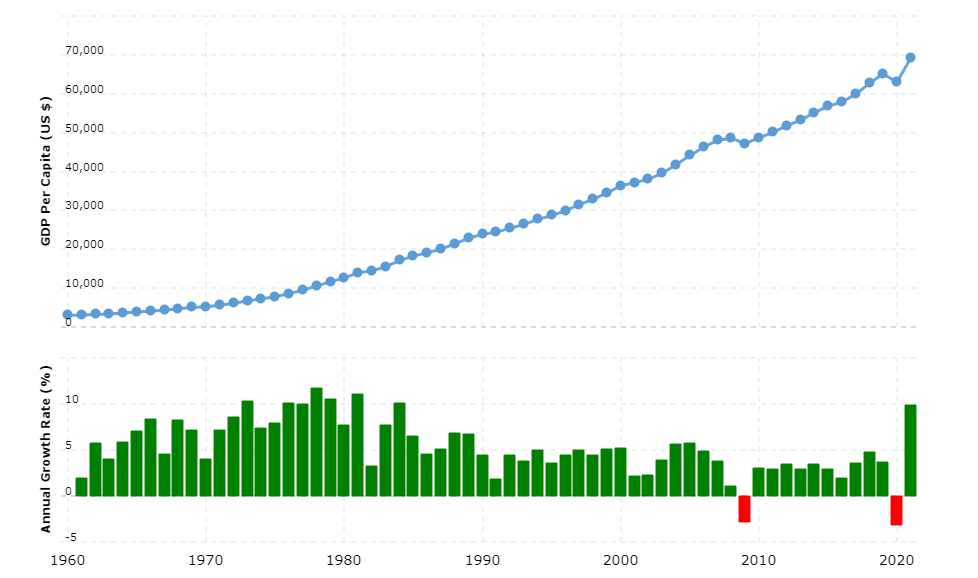
The GDP growth in different regions is expected to surge following trade and travel restrictions uplifting. For instance, the American market’s GDP growth has grown by 9 percent, from $69,288 in 2021 to $63,028 in 2020 (Baxter and Srisaeng, 2018). Similarly, the GDP of the Asia and Pacific region has experienced a 13.53 percent rise from the previous year (Baxter and Srisaeng, 2018). In the European marketplace, the GDP growth has experienced a stable increase over since 2012. The data shows a continuous upsurge in the GDP of various geographical zones in which Lufthansa Airlines. Figures 1 and 2 indicate the rise in the GDP of the European and American economic zones over the years.
Social Factors
Disposable Income and Unemployment Rate
Compared to the European and American regions, Asian consumers have increased disposable income due to the region’s low unemployment rates. That presents a lucrative business for the airline due to an expected surge in demand for its premium and unique services. However, the African market challenges Lufthansa Group’s global expansion efforts as the region has low disposable incomes and high unemployment rates (Chevtaeva and Guillet, 2021). Therefore, the carrier should comprehensively evaluate its needs and channel its resource into establishing dominance within the Asian markets.
Interest Rates
The interest rates impact the demand for Lufthansa Airline’s products and services. Increased interest rates necessitate the carrier to focus on internally generating capital to fund its expansion operations than borrowing from banks (Johansson, 2021). As a result, the company’s pricing structure will be affected as it will be compelled to raise travel prices to accommodate the expensive budgets. Consequently, the company will experience declined brand loyalty and constant efforts to manage operational costs.
Technological Aspects
Lufthansa constantly strives to advance its operations technologically in various ways. For instance, the company has adopted technology to acquire eco-friendliness aircraft to improve capacity and convenience if there is an accident in the aviation industry (Johansson, 2021). The success of Lufthansa depends on technological development as well. It plays a significant role in the corporation’s success, from making reservations to managing activities. In addition, more people around the world are using cell phones. Modern technology has been adopted by carrier businesses, such as Lufthansa, to grow the businesses and promote their offerings. The company has also improved its website to enhance customer engagement and ensure effective bookings and service payments.
Environmental Factors
The carriers’ corporations have concentrated on mitigating global warming and lowering CO2 emissions by approximately half since 1990 (Vaughan, 2021). Lufthansa Airlines has changed its on-the-ground and in-the-air activities to fulfill its environmental obligations better. In addition to regularity or reasonable operational control, scalability actions are crucial for coping with enhanced notoriety. Comparatively speaking, the carrier has effectively handled its natural influence, thus increasing customers’ needs and building a more extensive clientele.
Legal Factors
Several legal considerations impact Lufthansa’s operational processes globally. Despite several nations having deregulated, there is still a vast maze of rules, such as health limitations, that affect airline firms nationally and internationally. Employment rules have also influenced the aviation industry, limiting the outsourcing of workers (Kim and Son, 2021). Finally, its financial performance has been equally affected by traveler safety and natural effects related to currency and commerce. Therefore, to strengthen its operations and international customer base, Lufthansa’s management needs further assess these legal considerations.
Forecast Methodology
Quantitative Methodologies
Straight Line Approach
The straight line approach is one of several businesses’ leading and favorable forecasting methods. In this case, a financial expert can utilize historical statistics and trends to predict future income progression. For instance, when determining the passenger traffic forecast for Lufthansa Airlines, the company can use its previous passenger travel information to calculate the prospective rise (Cui, Hu, and Yu, 2022). That will enable the carrier to plan and determine service demand before expanding its operations and purchasing aircraft.
Moving Average Approach
The moving average method allows companies to assess their underlying sequence of sets of data to determine an approximation of the imminent values. The typical moving intermediate techniques are the 3-month and 5-month moving averages (Briscoe et al., 2019). Therefore, the profit information is positioned in the vertical column to execute the moving average projection. That follows the creation of two columns constituting the 3-month and 5-month moving averages.
Growth Compound Projection
The compound annual projection method determines the rate of return (RoR) needed for an investment to progress from its inception to the actualization stage. The technique effectively determines the level a business venture has grown annually and the profits re-invested at the close of each year (Mallikarjuna and Rao, 2019). Growth compound projection can determine Lufthansa’s market expansion operations by calculating the RoR.
Econometric Methodology
The econometric method is applied in the economic discipline to predict changes in demand, supply and price. The model integrates complex data and insight throughout the procedure of creation. Furthermore, the model is effective when forecasting prospective progressions in the economy (Ellibeş and Candan, 2021). Lufthansa can use econometric methodology when determining the fiscal growth of a region, thus selecting the lucrative markets.
Qualitative Methodology
Bottom-up Approach
Bottom-up forecasting is employed in estimating a corporation’s future performance. This technique entails a thorough evaluation with low-level company data and continuously progressing to the revenue. The bottom-up strategy in the case of Lufthansa Airlines will commence with the comprehensive product or consumer information, slowly broadening the airline’s profits (Rutkowski, 2020). Therefore, the bottom-up procedure can enable Lufthansa Group to calculate the sales of tickets, online reservations, and service demand.
Lufthansa Airline Forecast
Total Passenger Numbers per Geographical Area
With operations throughout the globe, Lufthansa Airlines has a vast consumer base, especially in America, European, Africa, and Asian regions. In America, the company enjoys a consumer base of 7 million (Böhm et al., 2021). That is owed to the company’s operations and premium and unique services, attracting consumers from different states. Similarly, the company controls a 15 percent market share in the region, representing 10 million consumers (Böhm et al., 2021). However, the carrier contains a relatively low market share in Africa, with a total customer number of 2 million. Finally, Lufthansa Airlines owns 50 percent of the European aviation industry, with 15 million passengers traveling from the region annually (Böhm et al., 2021). From the assessment, the reason for selecting this methodology is that Lufthansa Airlines dominates the American, Asian and European markets despite facing challenges in successfully establishing its operations within Africa.
Short-term Forecast Scenario 1: Vaccine Effective
The effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine will play a significant role in establishing a short-term passenger traffic forecast. According to research, the vaccine’s success will influence the number of passengers flying with Lufthansa Airlines from December 2021 to April 2022 (Helmold, 2020). Assumption one, the usefulness of vaccinations will facilitate the alleviation of travel bans, thus opening the global market for trade and tourism sectors. Assumption two will further lead to an increased demand for air services following a long year of lockdown and travel bans.
Short-term Forecast Scenario 2: Vaccine Ineffective
Despite the effective and secure vaccine that is globally available, Lufthansa will expressively impact the airline industry suppose the inoculation is unsuccessful. For instance, Lufthansa will compel the carriers to ground more aircraft and reschedule flights from the pandemic hot zones. Furthermore, airline companies, such as Lufthansa Group, have introduced the work-from-home program that allows its workers to operate remotely (Januschowski et al., 2020). Assumption one will help facilitate services, such as reservations, cargo clearance, and flight schedules. Assumption two, the approach is, however, expected to cover four months as preparations are made to identify alternative markets with low coronavirus prevalence.
Long-Term Forecast
Long-Term Domestic Forecast
The consensus regarding the long-term forecasts for Lufthansa Airlines is expected to vary in different regions. To establish a robust and reliable passenger traffic projection, the company should implement the straight line approach to determine the expected demand within each region (Assimakopoulos, Makridakis, and Spiliotis, 2018). Assumption one, the company is expected to grow its revenue within the next five years in its domestic market. Assumption two, Lufthansa will realize this long-term prediction by introducing local flights to open various towns to the global platform.
Long-Term Europe Forecast
Lufthansa Airlines’ long-term passenger traffic forecast within the European market is fundamental to realizing continuous performance. The company will understand the demand projections within the European markets by utilizing the historical travel routines of passengers. Assumption one, Lufthansa’s Europe traffic will expand by 4 percent within the next three years (Semenoglou et al., 2021). Assumption two uplift of travel bans, the desire to travel, and the effectiveness of the vaccines.
Long-Term Forecast North America
Considering the importance of the North American market to Lufthansa Airlines, long-term forecasting on the regions is fundaments to determine productivity. Before an irrepressible 2021, the passenger traffic within, to, and from North America will continuously rise in 2023 as the local American marketplace gradually returns to the pre-pandemic tendencies and the current enhancements in global travel (Semenoglou et al., 2021). Assumption one, in 2022, the passenger traffic is expected to hit 95 percent of the 2019 volumes, and with a complete revival in 2023, the growth will reach 103 percent (Semenoglou et al., 2021). Assumption two, the North American market will present increased demand, thus progressive returns for Lufthansa Group
Long-Term South and Latin America Forecast
Comparable to other regions, Latin American passenger traffic has been resilient throughout the COVID-19 period. The market’s 2019 traveler numbers will reach 103 percent in 2024 and 101 percent within the Caribbean region (Pressroom, 2022). Assumption one, the region is projected to experience a high surge in 2022, considering the limited travel bans and active passenger movements in the region and to/from the United States. Assumption two, the South and Latin American zone presents a vibrant market for Lufthansa to utilize.
Long Term Africa Forecast
The African passenger traffic opportunities are declining within the near future owing to the slow inoculation efforts. Furthermore, the market has experienced a significant economic impact from the pandemic, thus a reduced consumer disposable income. The consumer numbers from and within the continent will rise gradually compared to other markets to realize a 76 percent change from the 2019 levels (Pressroom, 2022). Assumption one, Lufthansa, is expected to change as the passenger forecast will reach a 101 percent rise exceeding the pre-pandemic levels (Pressroom, 2022). Assumption two, Lufthansa Group should ensure that it gradually introduces its regional operations to evade increased operations costs and low profits.
Long-Term Asia Forecast
The slowed uplift of global travel bans and the prospects of novel local limitations during the pandemic indicates that Lufthansa will impact passenger traffic. According to research, the traffic from within and in Asia will stretch to 68 percent of 2019 levels in 2023 (Pressroom, 2022). Assumption one, the 2019 levels will be realized in 2025 owing to a slowed regional global passenger number recovery (Pressroom, 2022). Assumption two, this region presents the weakest results compared to other leading markets.
Conclusion
Lufthansa Group remains one of the globe’s most successful aviation companies. The carrier has established dominance in European and American markets through its premium and unique services. The organization also efforts to lift global market share and competitive edge within its operational bases by introducing new and innovative aircraft to the regions. However, the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, such as travel restrictions and border closures, have limited its global operations. The business should adopt the straight-line forecasting approach to the dominant external influences to determine its pre- and post-pandemic viability. Therefore, Lufthansa Airlines should focus on long-term forecasting strategies to boost its passenger traffic and strategic growth across the global market.
References List
Akbar, Y.H. and Kisilowski, M. (2020) ‘To bargain or not to bargain: Airlines, legitimacy and nonmarket strategy in a COVID-19 world’, Journal of air transport management, 88, p. 101867. Web.
Albers, S. and Rundshagen, V. (2020) ‘European airlines′ strategic responses to the COVID-19 pandemic (2020)’, Journal of air transport management, 87, p. 101863. Web.
Assimakopoulos, V., Makridakis, S. and Spiliotis, E. (2018) Statistical and Machine Learning forecasting methods: Concerns and ways forward | PLOS ONE. Web.
Aubakirova, D. and Konovalova, N. (2019) ‘Management of Financial Stability in Airlines: Problems and Solutions’, in International Conference on Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication, pp. 573–582. Web.
Baxter, G. and Srisaeng, P. (2018) ‘Cooperating to compete in the global air cargo industry: The case of the DHL express and lufthansa cargo ag joint venture airline “AeroLogic”’, Infrastructures, 3(1), p. 7. Web.
Bhasin, H. (2019) Marketing Mix Of Lufthansa Airlines – Lufthansa Airlines Marketing Mix, Marketing91. Web.
Bogatov, N. (2022) ‘Customer segmentation in airlines strategic network planning’.
Böhm, M. et al. (2021) ‘Process mining at Lufthansa CityLine: The path to process excellence’, Journal of Information Technology Teaching Cases, p. 20438869211022370. Web.
Briscoe, N. et al. (2019) Forecasting species range dynamics with process‐explicit models: matching methods to applications – Briscoe – 2019 – Ecology Letters – Wiley Online Library. Web.
Buff, N. (2021) ‘Impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic on the European airline market with a focus on the business model of the Lufthansa Group’.
Carreira, J.F.S.F. (2018) Airline Fleet Composition: Analysis and Planning. PhD Thesis. Universidade de Coimbra (Portugal). Web.
Chepkonga, F. (2021) ‘Analysis of Lufthansa Airlines Marketing Strategy’, Finance~Notes Bulletin. Web.
Chevtaeva, E. and Guillet, B.D. (2021) ‘A review of communication trends due to the pandemic: perspective from airlines’, Anatolia, 32(1), pp. 168–171. Web.
Cui, Q. (2019) ‘Investigating the airlines emission reduction through carbon trading under CNG2020 strategy via a Network Weak Disposability DEA’, Energy, 180, pp. 763–771. Web.
Cui, Q., Hu, Y. and Yu, L. (2022) ‘Can the aviation industry achieve carbon emission reduction and revenue growth simultaneously under the CNG2020 strategy? An empirical study with 25 benchmarking airlines’, Energy, 245, p. 123272. Web.
Cui, Q. and Li, X. (2021) ‘Which airline should undertake a large emission reduction allocation proportion under the” carbon neutral growth from 2020″ strategy? An empirical study with 27 global airlines’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 279, p. 123745. Web.
Cui, Q., Li, Y. and Lin, J. (2018) ‘Pollution abatement costs change decomposition for airlines: An analysis from a dynamic perspective’, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 111, pp. 96–107. Web.
Cui, S. and Li, Z. (2022) ‘Airlines Benchmarking Analysis based on Financial Performance Emirates, Southwest Airlines, Singapore Airlines and Lufthansa’, Academic Journal of Business & Management, 4(2).
Ellibeş, E. and Candan, G. (2021) ‘Financial Performance Evaluation of Airline Companies with Fuzzy AHP and Grey Relational Analysis Methods’, Ekoist: Journal of Econometrics and Statistics, (34), pp. 37–56.
Ginter, C. and Linntam, A. (2019) ‘Passengers Are Not Automatically Responsible for Fines Imposed on Airlines Estonian Court Declares a Lufthansa Standard Term Unfair’, European Review of Private Law, 27(5).
Group, L. (2020) Lufthansa German Airlines boosts its service between Shanghai and Europe by deploying A380, Lufthansa Group. Web.
Helmold, M. (2020) ‘Pricing in the Aviation Industry’, in Total Revenue Management (TRM). Springer, pp. 129–137.
Huffman, L. (2020) How to Book Lufthansa and Lufthansa Partners with Points (and Get a Rubber Ducky), FinanceBuzz. Web.
Iacarelli, G. (2021) ‘L’impatto della pandemia di Covid-19 sull’equilibrio economico finanziario aziendale: il settore del trasporto aereo: Lufthansa Group, International Airlines Group, Air France-KLM Group’.
Januschowski, T. et al. (2020) ‘Criteria for classifying forecasting methods’, International Journal of Forecasting, 36(1), pp. 167–177. Web.
Johansson, M. (2021) ‘A Study on Airlines’ Marketing Messages in the Middle of Covid-19’.
Kim, H. and Son, J. (2021) ‘Analyzing the environmental efficiency of global airlines by continent for sustainability’, Sustainability, 13(3), p. 1571. Web.
Kuno, N. (2021) Analysis of airlines state during pandemic. PhD Thesis. National Aviation University.
Kuran, M.F. and Novak, A. (2018) ‘Brief Economic Analysis and Comparison of Turkish Airlines, Lufthansa Group, Air France? KLM’, AUTOBUSY–Technika, Eksploatacja, Systemy Transportowe, 19(6), pp. 888–893.
Lufthansa, G. (2022). Group Strategy. [online] lufthansagroup.com. Web.
Lufthansa, G. (2020) Lufthansa Group Airlines will Start Carrying Passengers on Inbound Flights to Bangkok, Lufthansa Group. Web.
Magdalina, A. and Bouzaima, M. (2021) ‘An empirical investigation of European airline business models: Classification and hybridisation’, Journal of Air Transport Management, 93, p. 102059. Web.
Mallikarjuna, M. and Rao, R.P. (2019) ‘Evaluation of forecasting methods from selected stock market returns’, Financial Innovation, 5(1), p. 40. Web.
Merkel, M. (2018). Short-and long-term effects of labour disputes in airlines: an investigation into the Lufthansa labour dispute 2014-2017. Master’s Thesis. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Web.
Pressroom, I. (2022) Air Passenger Numbers to Recover in 2024. Web.
Relations, L.G.I. (2021) Fleet, Lufthansa Group Investor Relations. Web.
Report, F. (2021) Annual Report 2021, Lufthansa Group. Web.
Rutkowski, M. (2020) ‘Financing Models of the Airlines Fleet as a Factor Affecting the Income Statement’, in 13th International Scientific Conference “Analysis of International Relations.
Schmidt, K.C. (2020) ‘Strategic Alliances as a form of Coopetition and its impact on the Performance of Airlines: A Case Study analysis of Lufthansa, Finnair, and Alitalia’.
Semenoglou, A.-A. et al. (2021) ‘Investigating the accuracy of cross-learning time series forecasting methods’, International Journal of Forecasting, 37(3), pp. 1072–1084. Web.
Staff, S.F. (2022) Lufthansa To Operate 85% Of Pre-Pandemic Capacity This Summer, Simple Flying. Web.
Vaughan, A. (2021) ‘Airlines lobby against green plans’. Elsevier.