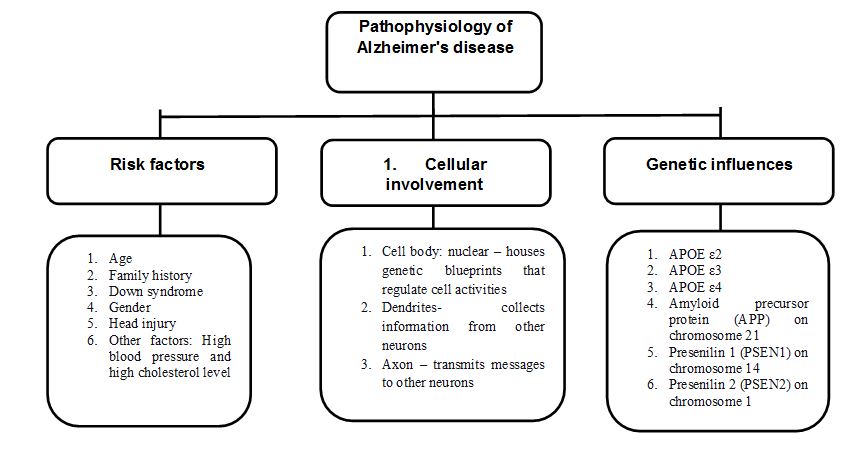
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an irreversible illness of the brain that kills and weakens brain neurons involved in thinking, memory, and other abilities. It is a progressive illness which symptoms and functionality get worse over time. It has no cure, but symptoms can be managed to combat the progression making it easy for the patient (Khan et al., 2018). The study will discuss the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease, such as risk factors, cellular involvement, genetic influences, and the interventions of the available therapy’s pharmacological Interventions.
Table 1: Concept map
Janet Riley can use the Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEI) as pharmacological intervention. There are Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors available: glutamine, Rivastigmine, and donepezil (Akıncıoğlu & Gülçin, 2020). These agents are based on research that shows people with Alzheimer’s disease have a deficit in cholinesterase production that leads to dysfunctions of the cortical cholinergic. The cholinesterase inhibitors inhibit the action and optimize the Ach levels available for postsynaptic simulants. The cholinesterase inhibitors improve the symptoms of Alzheimer’s but are not involved with any alterations of its natural clinical course. Due to this, the intervention is considered a symptomatic treatment for the Alzheimer disease.
Table 2: Pharmacological Interventions
A good communication plan is required to ensure that the information delivery to Janet Riley’s family is well perceived. It is important for the family to be involved as it ensures optimal functioning and patients’ quality of life. Firstly, the family needs to be explained the disease and its effects. They need to understand how Alzheimer’s functions: the risk factors, the symptoms, available treatments, mechanism actions of these drugs, and the benefits and risks of the treatment. Secondly, as a health practitioner, I will share resources concerning the issue. The resources include educational material from organizations of the Alzheimer’s associations and support groups. Lastly, I will educate them on assisting the patient in their regular activities. The communication plan will result in them enquiring about the future directions on the medication treatment. To respond to this, I will explain how therapeutical treatments that aim to alter the neuropathological changes in Alzheimer’s disease are showing significant results.
References
Akıncıoğlu, H., & Gülçin, İ. (2020). Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: potential drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry, 20(8), 703-715.
Khan, H., Amin, S., Kamal, M. A., & Patel, S. (2018). Flavonoids as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Current therapeutic standing and future prospects. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 101, 860-870.
Matsunaga, S., Kishi, T., Nomura, I., Sakuma, K., Okuya, M., Ikuta, T., & Iwata, N. (2018). The efficacy and safety of memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Expert opinion on drug safety, 17(10), 1053-1061.
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Yang, W., Gao, S., Lin, J., Wang, T.,… & Hu, H. (2018). Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibit apoptosis in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease induced by Aβ1-40. American journal of translational research, 10(3), 796.