Abstract
McDonald’s uses employees to create a good picture in the minds of employees, stakeholders, and external customers. This is because they determine the profitability and financial stability of the organization. The organization cannot operate without their support and commitment. The employers have to sustain and monitor the image created in the minds of employees, shareholders, and customers to ensure profitability that arises from building of true commitment, self-actualization, pride, and belongingness in true spirit and words.
This paper utilized the use of quantitative research methods that involved the use of quantitative data to justify the objectives of the study. The quantitative data about the company was obtained from secondary sources of the company and included the company’s financial data that were obtained from newspapers, reports, magazines, books and journal articles among others. The targeted population was the entire of McDonalds.
The collected data was chosen through convenient sampling technique that proved vital in this report as compared to other sampling methods like stratified sampling. The collected data was analyzed both quantitatively and qualitatively. Qualitative analysis involved descriptive statistics and explanations on the company’s performance regarding its products.
Quantitative analysis involved use of statistics to justify the performance of the firm. The overall outcome pointed out that the introduction of McJobs affected the image of McDonald’s as the term associated with low paying jobs, low prestige, job with no future, and low benefits in the retail or service sector. McDonald’s had to take action immediately to prevent bad image.
Introducing
Kroc McDonald’s founded McDonald’s in 1955. McDonald’s is one the largest chains of fast food in the world offering the world’s favorite foods that include Big Mac, French Fries, Chicken McNuggets, Quarter Pounder, and Egg McMuffin. Its headquarters are at Oak Brook in Illinois.
The restaurant chain has approximately 31,967 restaurants in 118 countries. The business serves more than 58 million customers globally recording about the United States $ 23.5 billion (Gould, 2010). McDonald’s offers flexible schedules to help employees balance work and personal life. The business offers training and development programs to create opportunities for employees to acquire promotions and develop their careers (Qumer, 2009).
According to Punjaisri, Wilson and Evanschitzky (2008), the fast food retail stores and restaurants is associated with low paying jobs from the 1980s. Due to this, the term ‘McJobs’ was introduced meaning low benefit, low prestige, and no future job in the service sector. The term ‘McJobs’ targeted McDonalds because regulations on employees were strict and required semi-skilled workers.
The popularity of the term led to its introduction in the Oxford English Dictionary (OED) in 2001 and Merriam Webster Collegiate Dictionary in 2003. McDonald’s needed to acquire talented employees to improve performance but could not attract them because of bad perception on employee branding. McDonald’s had to redefine the term to remain relevant in the image and reputation of employee brand in 2000. This was important because employees are the greatest assets of the company (Qumer, 2009).
Redefining McJobs
McJobs had become a term referring to no growth of opportunities and low paying jobs. The publishing of the term McJobs in the dictionaries stimulated the need for McDonald’s to redefine its image through concentration on branding of employees. Employee branding is the retention and engagement of employees in the activities of an organization.
The management of McDonald’s chose employer branding because it is a powerful tool of creating good image and reputation to both the employees and the public (Qumer, 2009). Employee branding represent core values of the organization in systems, attitudes, culture, and customer relationship.
A strong brand of employees can paint a good picture in the minds of employees thereby influencing them to change the perception they had on the organization and association with McJobs. McDonalds has held organized campaigns in the strategy of employee branding over time to display the benefits and experience working at the restaurant. There have a series of advertising campaigns to change the perception on McJobs (Gould, 2010).
“My First Job” Campaign
McDonald’s launched a campaign on the television in 2005 to promote the importance of McJobs and to create a strong image on the employer brand. This campaign was geared at convincing the public that working at McDonald’s was the best choice for employees with the need to develop their careers and experience.
Leo Burnett Worldwide, Inc. organized and planned the commercial advertisement communicating the message of McDonald’s as a global employer. The advertisement engaged celebrities such as Carl Lewis the Olympic gold medalist and the singer, Macy Gray (Qumer, 2009). In total, 15 people featured in the advertisement as crewmembers of McDonald’s. The advertisement described them to have gained experience and background of their career at McDonald’s.
The advertisement also covered the promotional activities of the organization in rewarding talented employees, such as from a regular restaurant employee to a Chief Executive Officer (CEO). McDonald’s conducted a survey on the employee satisfaction with the treatment at their workplaces to show the organization’s concern on the welfare of its employees (Gould, 2010).
McDonald’s People Project
Cawley Nea/TBWA became responsible for changing the negative perception of the public and employees on McDonald’s in Ireland. The project addressed issues on employee morale through providing flexible schedules, training, and career development for its employees. The project was to change the negative perception about employers at McDonald’s. The project was to redefine the position of McDonald’s employers at their real brand image.
The project involved strategic analysis on the employees and the public perceptions on the McDonald’s employers and the key decision makers. The public targeted mostly on the teenagers with part time jobs and their parents and the employees comprised of the crewmembers and the store managers (Gould, 2010).
The team carrying out the project worked closely with the departments of human resource and marketing to gather the required information on the project. The insights gained from the project would help develop and implement the employer brand. McDonald’s used the theory of ‘hierarchy of needs’ to understand the employee expectations from the employer. Abraham Maslow developed this theory to describe the pattern in which humans’ motivations passes.
The theory focuses on motivation and personality. McDonald’s wanted to identify the needs that are unsatisfied in the organization to satisfy them. McDonald’s collected opinions from crewmembers, store managers, teenagers on part time jobs in the organization and their parents, and other important influencers in the organization (Qumer, 2009).
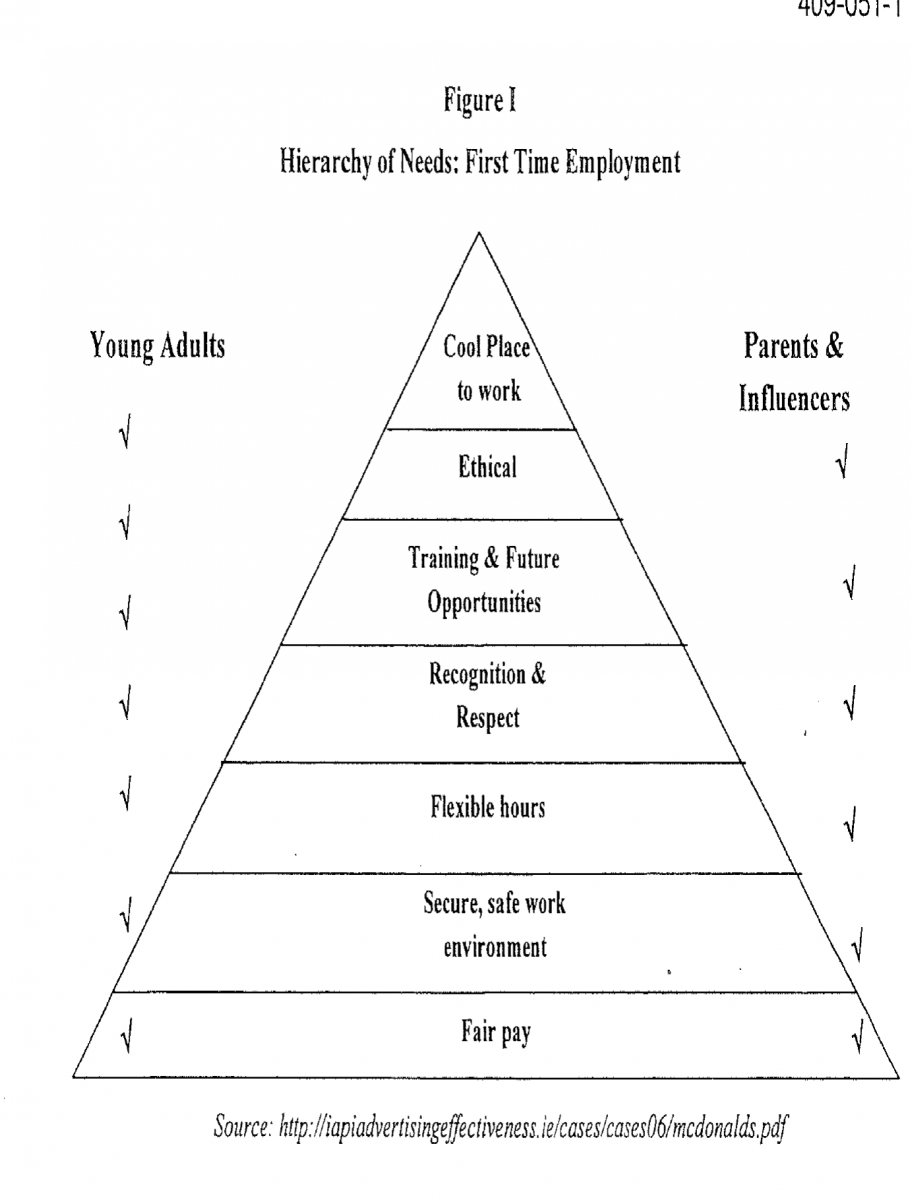
(Source: Hierarchy of Needs: First Time Employment, Qumer, 2009)
The project made some changes with the launch of the ‘McPassport’ campaign. This campaign communicated on the need for employees to realize that the training, skills, and experience derived from McDonald has the potential of developing their careers to qualify them to work beyond their country borders (Rosethorn, 2009).
The employees had the opportunity of working anywhere in the world. Other activities of the McDonald’s People Project were to introduce a new identity and logo that represented the diversity of culture and experience created at McDonald’s and change of employee uniforms to casual T-shirts to improve their experience at their workplaces. The project extended to Australia, the United Kingdom, and France. The project won the HR Excellence Awards 2007 for successfully changing the brand image of employers at McDonald’s (Lindsay, 2005).
“Not Bad for a McJob” Campaign
This was a poster campaign on the ‘McJob’ label highlighting the positive practices of the business and the advantages of working at McDonald’s in 2006. Approximately 1225 restaurants of McDonald’s in Britain adopted the slogan ‘not bad for a McJob’ in the poster campaign.
There were 18 different poster adverts created to conduct the campaign (Gould, 2010). The posters illustrated the good working conditions at McDonald’s, promotion, pay, and health benefits available at McDonald’s. These posters were to contradict the bad perception created on the McJobs to make them appear beneficial to the people that seek for them.
The issues addressed involved the discounts, respect, flexibility, packages, benefits, value and opportunities that McDonald’s offered to its employees. The poster adverts created awareness and communicated about the company’s efforts to create the best working environment for its employees (Mandhanya & Shah, 2010).
Outcomes in Achieving McDonald’s Talent Management Strategy
The strategy of employee branding provided McDonald’s with a competitive advantage. The company attracted the interest and attention of influential people, such as the members of parliament in Britain and company directors leading to its consideration by the OED in 2007. Employee branding created better human capital practices, attracted, and maintained talented employees in the organization. McDonald’s attracted potential applicants, such as bankers, accountants, and architects in 2009 (Bhattacharyya, 2010).
The strategy was successful in portraying the image real to the organization and that the organization wants to portray to the target audience through organizing a variety of campaign and advertising programs. These strategies were effective because the company managed to gain support of influential people and the public (Punjaisri & Wilson, 2011).
Although OED insist that the meaning of McJobs is still right, McDonald’s continue to make success in attracting and maintaining talented employees. Fairhurst, a manager at McDonald’s confirmed that employees have reduced the turn over level. The low absenteeism and improved retention of employees is a good sign of increase in the satisfaction of employees on the employers of McDonald’s (Wilden, Gudergan & Lings, 2010).
Sustainability of the Employee Branding Strategy Steps
McDonalds faces a huge challenge changing people’s perception and the real employee experiences at the company (Bhattacharyya, 2009). McDonald’s has the task of holding workshops to communicate on the employment experience, threats and culture of its employees and offer objectives that challenge the people’s perception about McJobs.
McDonald’s has to ensure that the positions of entry level offer realistic salaries, personal development opportunities, and good working conditions to prove that the organization is consistent and ready to satisfy the needs of its employees. McDonald’s sustainability of the steps depends on the period the organization will take to provide skills and self-confidence to its employees that lasts a lifetime (Moizer & Towler, 2007).
McDonald’s needs to access the gap created between the internal reality and external perception of work and work towards redefining the term ‘McJob’. The company can decide to offer quality jobs, career progression opportunities, and new learning and development programs to boost its employee brand. The company is aware that it will take time before it changes the external perception, but it is willing to take the risk in the long term (Andrikopoulos & Koronis, 2007).
Potential Risks of Employee Branding
The strategy was successful in convincing some of the members of the public and employees that McDonald’s is a suitable working area for talented employees. The problems arises because the OED dictionary failed to consider this attempts and successes of the business in creating strong image of its employees making the strategy less sustainable. This would mean that McDonald’s would have to put more efforts into the strategy leading to additional costs on the operations of the business (Price, 2011).
Some observers felt that the strategy was a tactic by McDonald’s to promote the brand and not the employee brand. They argue that McDonald’s wanted to gain free publicity. The people also said that the dictionary meaning was less relevant in the image of the company and what was important was the price and quality of products that the organization offers to customers. McDonald’s should have confidence in the product and services they provide that depict its offer of good jobs in the organization (Raj & Jyothi, 2011).
Conclusion and Recommendations
Good image was important to attract and maintain talented employees in the workplace to create competitive advantage in McDonalds. The steps taken by the organization to redefine McJobs was very important in sustaining the long-term operations of the business. The employer branding initiatives were effective in communicating to the external audience because it changed the perception of some of the great influencers in the society like parents, teenagers, and members of the parliament.
They included creation of career sites, advertising campaigns, projecting opinion of employees, and promotions. The initiatives targeted on changing the perception of people on McJobs by convincing them that working at McDonalds had benefits. The company had to focus on employee satisfaction and present a good image of its employers. McDonald’s should make employee branding a lifetime strategy to ensure good image of the company in future, avoid additional costs on campaigns and promotions, and ensure attraction and maintenance of talented employees.
References
Andrikopoulos, A. & Koronis, E. (2007). Reputation performance: a portfolio selection approach. International Journal of Business Performance Management, 9(4), 406-418.
Bhattacharyya, D. (2009). Compensation management. New Delhi: Oxford University Press.
Bhattacharyya, D. (2010). Human resource development. Mumbai: Himalaya Publishing.
Gould, A. M. (2010). Working at McDonald’s: some redeeming features of McJobs. Work, Employment & Society, 24(4), 780-802.
Lindsay, C. (2005). ‘McJobs’, ‘good jobs’ and skills: job-seekers’ attitudes to low-skilled service work. Human Resource Management Journal, 15(2), 50-65.
Mandhanya, Y. & Shah, M. (2010). Employer branding – a tool for talent management. Global Management Review, 4(2), 43-48.
Moizer, J. D. & Towler, M. (2007). Research and development resourcing when faced with fundamental market dynamics. International Journal of Business Performance Management, 9(4), 434-452.
Price, A. (2011). Human resource management. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.
Punjaisri, K. & Wilson, A. (2011). Internal branding process: key mechanisms, outcomes and moderating factors. European Journal of Marketing, 45(9/10), 1521-1537.
Punjaisri, K., Wilson, A. & Evanschitzky, H. (2008). Exploring the influences of internal branding on employees’ brand promise delivery: implications for strengthening customer-brand relationships. Journal of Relationship Marketing, 7(4), 407-424.
Qumer, S. (2009). Employee branding at McDonald’s: redefining McJobs. Mexico City: ICMR Center for Management Research.
Raj, A. & Jyothi, P. P. (2011). Internal branding: exploring the employee perspective. Journal of Economic Development, Management, IT, Finance & Marketing, 3(2), 1-27.
Rosethorn, H. (2009). The employer brand: keeping faith with the deal. New York, NY: Gower Publishing Limited.
Wilden, R., Gudergan, S. & Lings, I. (2010). Employer branding: strategic implications for staff recruitment. Journal of Marketing Management, 26(1/2), 56-73.