The problem in the first article was the area of IT security as it relates to social networks within an organization. Recently, there have been many trends the security of information and communication technologies, in particular, due to the expansion of the reach of social media which increase the size of social network, which has taken the rates sharing personal and working information to very high levels and also posed increased risks to data networks.
One note is that this article does not specifically analyze social media networks, but more so social networks. Within this, every growing data-intensive environment, there is the unique need to secure enterprise data within this environment. This gap poses new increased risks. Social media networks which could pose some increased risks, however, could prove some advantages in increasing the stretch or mixing the diversity of the social networks, due to the intense popularity of social networking service and it mediums. The use of this services by employees within the organization, and the need or desire to share information across social media mediums could expand the present stretch of social networks within an organization. Thus, access to readily available information and the need to connect to others yields both benefits and undesirable consequences within an organization. (Dang-Pham, Pittayachawan, & Bruno, 2016)
Employees remain the biggest risk within the organization to IT security. However, employees can also be a significant asset to reduce the risks that are related to information security. Understanding compliance behavior remains crucial for organizations to secure its data by leveraging their human capital resources. The general problem is that technology-based solutions do not sufficiently address gaps in information security compliance. The study posits that employees’ outcome beliefs shape the employees’ views about conformity with compliance. Intrinsic benefit shapes benefits of conformity, any rewards that are received, the benefits of any conformity while intrinsic value forms the costs of compliance to the employee, the vulnerability of resources, and any sanctions that could be levied. Ths problem area looks at the risk of noncompliance with IT security policy to the business and evaluates the implementation of training and IT programs. (Bulgurcu, Cavusoglu, & Benbasat, 2010)
Comprisals within IT security and vulnerabilities have resulted in the increase in ransomware attacks and other types of cybercrime including, financial fraud, stalking, and blackmai(Gradon, 2013). There is a lot of literature that covers these areas and many of the theories which evolve around this subject matter of security as it relates to the business enterprise. As this area in an area of increasing vulnerability, I would like to extent the research into this area. For this reason, and much more, my contribution within this area has significant worth. One item that was unique, within the research model, what that the article used network analysis.
So many emerging behavioral security studies focus on ways to improve compliance within the security arena by fear, and newly by looking at the intrinsic beliefs and social relationships between individuals. How do we relate the structural patterns and integrate them into the organization to the benefit of security? One of the most critical issues in the research field remains that many end-users in organizations do not possess the sufficient knowledge to mitigate information security risks (Rocha Flores, Antonsen, & Ekstedt, 2014).
Many areas look at fear to spur compliance and also look at security training as a check-the-block mechanism to spur compliance. A gap that remains how do you spur interest in the subject area, or within information technology fields in general. Does fear longterm create legitimate compliance or only short-term benefit? How do employees interpret conflicting information from varying sources, some who agree with their interpretations and some and disagree with their interpretations of security beliefs? How do we resolve internal conflict between a close colleague and an expert within the field? Can we use the structural patterns between individuals, experts, and non-specialists, to garner interest? What happens if that garnered interest conflicts with intrinsic belief? How do we prevent the dissemination of incorrect information across these mediums?
The research questions involved in this article posed are why employees willing to share information security advice and secondly what are the structural patterns of the information security advice sharing networks are. The research within these two articles revolves around these two questions. The literary review looks at what motivates employees to share security advice and looks at particular behaviors could have some influence. The reason this is studied is that active security knowledge sharing helps to develop self-efficacy and complaince and helps to prevent the redevelopment of new security practices that may already be commonplace. The article poses that many of the prior works looked at intributes of individuals, however, did not look at how these attritubutes interact together in a social media forum with connects people how may be very different, from different organizations and separate geographically.
These are several areas that are studied in many prior works. These draw upon many theories including the Theory of Planned Behavior and Motivational Theory which is prevalant in many security works. The first three hypotheses were developed from this theory. The Theory of Planned Behavior has been looked as an antecedent ot compliance. This article looks at the sharing activity itself. These are based on the premise subjective norms motivate an individual’s intention to share security knowledge, percieved behavioural control, and attitude. This is included and extended in many works and the literature review surrounded these these works. This article also looked at personality relationships and how they relate to their perceptions of security. Prior studies looking at traits which affect the perception on security studies.
The article reviewed the Accountablity Theory and developed the second hypotheses from this theory. Within this theory, accountability is attached to the self image, and this motivates inviduals to comply. This theory remains a fairly new theory introduced in 2015 and has been introduced by many different security domains. This theory looks at the not only at how the individual looks at the compliance of the individual but how that accountability relates to organizaitonal accounatability amd there desire to share security advice.
The IVs, independent variables, in the study were the attitude towards performing information security behaviors, subjective norm, perceived behavioural control, perceived accountability, the occurrence of giving work related advice ties, the occurrence of interpersonal trust ties, and the occurrence of giving security troubleshooting ties. These were divided into different categories of the node effects, or source of security advice, and network effects. The study looked at how security knowledge was transfered though the network effects between different nodes.
The dependent variable within the article is the occurrence of giving security advice ties between two randon employees. The article further analyzes the connections that allow the dissimination of security related information.
This study looked at network analysis to determine how individuals in the organization, based on how these social networks developed, would dissiminate this information. One interesting finding in work is that employees are perceiving subjective norms about performing security behaviours are less likely to give security advise to others. One reason that the article meantioned this is that individuals could add social pressure on these individuals. I pose that this could be negative pressue as well, even though this was not mentioned within the article. So, an employee’s behavioural norm could remain in conflict with the organization culture. This area of study is one area that was not revieweded and is an area that we could review further.
Literature Review
The problems of the modern day cyber security are as urgent as never before. With enterprises relying on computer and internet networks more and more often, IT security faces a significant number of issues. Researchers determine the nature of such problems in different ways. For example, Grau and Kennedy (2014) define such problems as “common threats faced today, such as malware, physical attacks, social engineering, social media, misuse, errors, and environmental effects” (p. 53). Moreover, the problems are approached from the perspective of their relation to different strata of society (e. g. citizens, governments, banks, and key infrastructures). The authors then note that the problems are caused by various “actors.” These are “the criminal,” “the hactivist,” and “the nation-state” (Grau and Kennedy 2014, p. 54).
Based on these findings, authors present the current trends and trends that are in development as of now. There are six current trends of interest. Firstly, the man-in-the-browser attacks, which are characterized by the criminal’s attempting to emulate a believable browser experience to gather information on security details (logins, passwords, etc.). Secondly, the ransomware is emerging; it is a malware that is embedded in the operational system as an anti-virus or any other type of malware protecting software. The goal of this malware is also to gather sensitive or compromising data. The third trend is the development of polymorphisms. This is a sophisticated malware that is generated for each user while remaining equal functionality-wise. Remaining trends drawn out by the authors include other types of malware (package exploit kits, new-generation botnets) and methods of causing network malfunctions (DDoS)
Other researchers focus on different topics; some may argue that these subjects are based on more general problems. Chin, Kaplan and Weinberg (2014) concentrate on the general problems that the current cybersecurity units face. These include insufficient cyberattacks protection, minimal efforts of improving cyber security in various institutions, and low engagement of senior leaders of public and private institutions in the problems of cyber security. Another article by Tisdale (2015) suggests that, despite the widespread problems which seem to take over the cybersecurity efforts, it is wrong to approach the solution search in technical, and information technology connected way. Instead, Tisdale argues, recent researches in cyber security call for a “comprehensive approach that considers business objectives, governance, and risk management along with organizational psychology and other factors such as those described in the Clinger-Cohen Act” (p. 191).
Thus, the trends may be perceived in different ways and via different approaches. Some argue that the cyber security efforts must be focused on fighting off the new-generation malware developed en masse by various criminals and criminal collectives across the world. Others call for developing a new perspective that would alter the approach to cyber security with taking different nuances into account. As of right now, there is no way to tell which approach will be the most beneficial one. However, while some tend to focus on developing the methods to fight off malware and cyber attacks, other researchers create new-generation tools that allow ensuring a higher quality of cyber security. For example, Fielder, Panaousis, Malacaria, Hankin and Smeraldi (2016) in their article provide “an analysis of a hybrid game-theoretic and optimisation approach to the allocation of an SME’s cyber security budget” (p. 22).
Another example of approaching cyber security is, for instance, an article by Craigen, Diakun-Thibault and Purse (2014) that has a goal of providing a more precise definition of what the cybersecurity must be. The authors conclude that “the more inclusive, unifying definition presented in this article aims to facilitate interdisciplinary approaches to cybersecurity” (Craigen, Diakun-Thibault & Purse 2014, p. 18). Thus, a more sophisticated theoretical approach is taken to represent the goals of cyber security. This allows for clearer understanding of the primary focuses that the cyber security units must preserve.
On the other hand, some researchers tend to concentrate on identifying practical approaches either undertaken by some organizations, or the approaches that are still being developed. For example, Nelson and Madnick (2017) provide a “list of approaches around cyber-security measurement and reporting” (p. 12). These approaches include measures of cyber-security compliance, tracking of risk based on business models, and cyber-risk activities tracking. Thus, it is evident that there is a focus on both theoretical and practical aspects of the problem.
The proposed study is going to consider both the theoretical and practical aspects of cyber security and apply the resulting information to social networks in an attempt to determine the factors that tend to affect the level of security in social networks. Social networks are becoming exceedingly popular with some of them being made for recreation and others for business (Saridakis, Benson, Ezingeard, & Tennakoon, 2016). As for network security, it is a complex and costly activity, which, however, is necessary to protect the shared data and users’ privacy (Jang-Jaccard & Nepal, 2014).
A preliminary research implies that cyber security in social networks is a relatively understudied topic, but it is apparently significant because of the above-mentioned issues and the legal and ethical requirements to protect the information and privacy of the users (Jabee & Alam, 2016; Jang-Jaccard & Nepal, 2014). Moreover, it has been established that improved security is also a factor that the users take into account when choosing to employ a social network (Jabee & Alam, 2016; Kwon, Park, & Kim, 2014). In other words, legal, ethical, and survival reasons make cyber security a modern challenge for networks, which calls for extensive research. The proposed study will attempt to find and possibly explain the patterns in the development of network security. The specific research question that the proposed study intends to consider can be phrased as follows: do the size (number of users) and purpose of a social network affect its security level?
Research Model
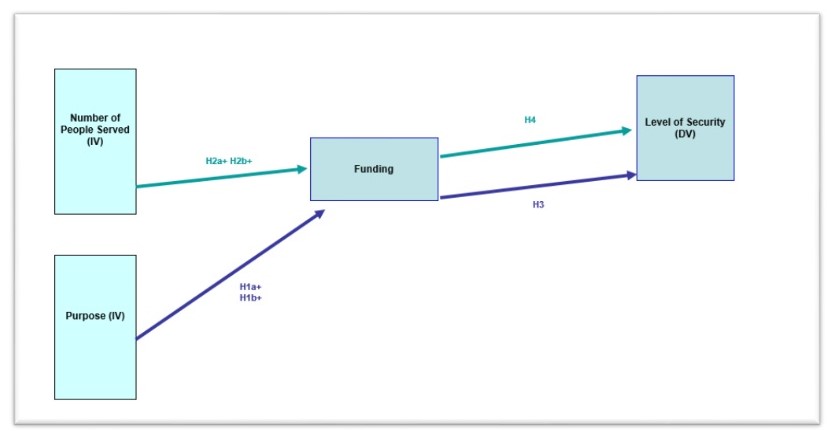
The research model discusses the following variables. The independent variables include the size and purpose of the social networks that are going to be studied. The size is going to be operationalized as the number of users; the upcoming research will indicate which networks can be viewed as relatively big or small. The purpose is going to include business and recreation purposes. The dependent variable is the security level of the social networks. It is going to be operationalized through the number of safeguards employed by the networks and their relative effectiveness (Jabee & Alam, 2016).
The specific criteria will be developed with the help of the literature on the topic. The mediating variable that is expected to limit or expand the effect of the independent variable on the dependent one is the funding (resource availability) of the networks. The future research will demonstrate if it is possible to find the information one the networks’ funding, which will help to operationalize the variable. When the specifics of the variables’ operationalization are apparent, an appropriate statistical analysis tool will be chosen.
Hypotheses
Four hypotheses that consider the relationships between variables can be proposed.
- H1: the level of security of social networks depends on the purpose of these networks.
The first hypothesis implies that the purpose of the networks can define the sensitivity of the data used, which may call for additional safeguards. As a result, the following sub-hypotheses are offered.
- H1a: the level of security increases for business-related networks.
- H1b: the level of security decreases for recreation-related networks.
- H2: the level of security of social networks depends on the size (number of users) of these networks.
The second hypothesis implies that a bigger number of the users can either result from greater security or call for better protection of the users (as follows from the literature review). As a result, the following sub-hypotheses can be offered.
- H2a: the level of security increases for larger networks.
- H2b: the level of security decreases for smaller networks.
It is also noteworthy that, as shown in the literature review, the security of networks is a complicated and costly phenomenon. It can be suggested that the availability of resources can limit or improve the ability of a network to ensure security. Thus, two additional hypotheses discuss the mediating variable.
- H3: the relationship between the purpose of the network and its level of security is mediated by the funding of the network.
- H4: the relationship between the size of the network and its level of security is mediated by the funding of the network.
The hypotheses and the variables are shown in Figure 1.
Sample
The sampling strategy is going to use quota sampling to cover all the required “types” of networks, including big, small, business-related, and recreational ones. The coverage will improve the sampling validity (Terrell, 2015, p. 87). Apart from that, the size of the sample needs to be considered to ensure reliable results; this aspect can be calculated after more or less comprehensive information on the currently existing social networks that fit the search criteria is gathered.
Limitations
Some of the limitations of the proposed study can be determined at this stage. In particular, some problems with attaining the information on the funding of social networks can be anticipated. Also, the choice of business-related networks is expected to be more limited than that of the recreational ones. Finally, the current operationalization efforts suggest that the criteria for the dependent variable need to be very carefully considered to provide an objective relative assessment of the level of security in networks. The first two issues imply the possibility of inefficient sampling, which will be limited by the availability of the information; the last issue suggests that the quality of research will depend on the quality of the criteria for the dependent variable. In other words, the latter issue may but does not have to result in limitations. Other limitations will become more apparent as more information on the research is gathered.
References
Chinn, D., Kaplan, J., & Weinberg, A. (2014). Risk and responsibility in a hyperconnected world: Implications for enterprises. Web.
Craigen, D., Diakun-Thibault, N., & Purse, R. (2014). Defining Cybersecurity. Technology Innovation Management Review, 4(10), 13-21.
Fielder, A., Panaousis, E., Malacaria, P., Hankin, C., & Smeraldi, F. (2016). Decision support approaches for cyber security investment. Decision Support Systems, 86, 13-23.
Grau, D., & Kennedy, C. (2014). TIM lecture series – the business of cybersecurity. Technology Innovation Management Review, 4(4), 53-57.
Jabee, R., & Alam, M. A. (2016). Issues and challenges of cyber security for social networking sites (Facebook). International Journal of Computer Applications, 144(3), 36-40.
Jang-Jaccard, J., & Nepal, S. (2014). A survey of emerging threats in cybersecurity. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 80(5), 973-993.
Kwon, S., Park, E., & Kim, K. (2014). What drives successful social networking services? A comparative analysis of user acceptance of Facebook and Twitter. The Social Science Journal, 51(4), 534-544.
Nelson, N., Madnick, S. (2017). Trade-offs between digital innovation and cyber-security. Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Saridakis, G., Benson, V., Ezingeard, J., & Tennakoon, H. (2016). Individual information security, user behaviour and cyber victimisation: An empirical study of social networking users.Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 102, 320-330.
Terrell, S. (2015). Writing a proposal for your dissertation. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
Tisdale, S. M. (2015). Cybersecurity: Challenges from a systems, complexity, knowledge management and business intelligence perspective. Issues in Information Systems, 16(3), 191-198.
Bulgurcu, B., Cavusoglu, H., & Benbasat, I. (2010, September). Information security policy compliance: an empirical study of rationality-based beliefs and information security awareness. MIS Quarterly, 34(3), 523-548.
Dang-Pham, D., Pittayachawan, S., & Bruno, V. (2016). Why employees share information security advice? Exploring the contributing factors and structural patterns of security advice sharing in the workplace. Computers in Human Behaviors, 196-206.
Gradon, K. (2013). Crime science and the Internet battlefield: securing the analog world from digitial crime. Secur Priv, 93-95.
Rocha Flores, W., Antonsen, E., & Ekstedt, M. (2014). Information security knowledge sharing organizations: Investigating the efect of behavioral information security governance and national culture. Computers & Security, 43, 90-100.