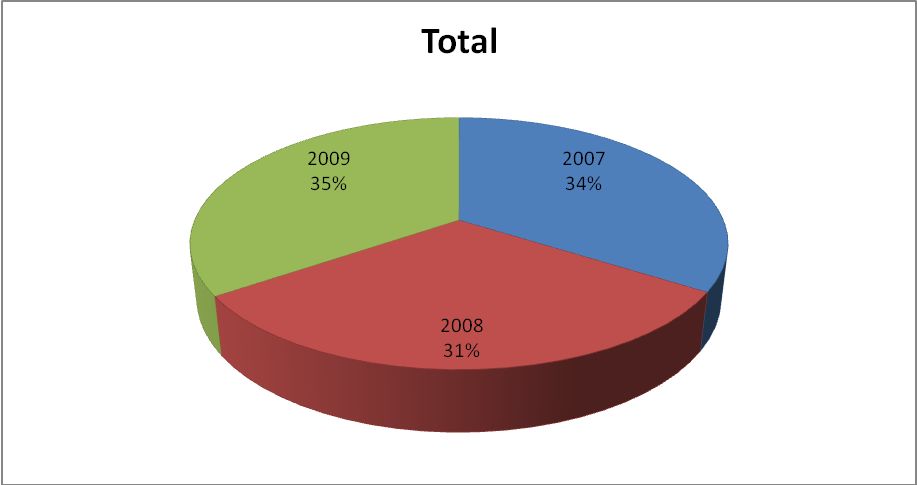
The graph above shows that energy consumption was highest in the year 2009. The most efficient use of energy was in 2008. For January 2009 had the highest consumption as compared to all the other years. In February, the consumption for 2007 was nearly as much as that of 2009. The same applies to march, April, May, and June. In these three months, there is a significant difference in the quantity consumed over the three years.
The months of July and August both in 2007 and 2009 had the highest consumption rates, although the used quantities were close to each other. September and October also had high quantities used up, and a large discrepancy between the two years. From November to December, the routine resumed, with 2009 still recording high-consumption rates as compared to 2007 and 2008. It should be noted that 2008 was the most energy-efficient year after recording the least usage per hour throughout the year.
The main anomalies present in the statistics occur in the second year, where figures are extremely lower than those of the adjacent years. In the year 2007, the month of August recorded the highest consumption, while December recorded the highest return for 2008 and 2009 had August and September with the highest consumption quantities.
It should be noted that in this year, several months had extremely high-consumption amounts, as compared to figures recorded throughout the three years. The figures for 2007 fluctuate heavily hence establishing a trend is difficult. For 2008, there is a sturdy amplification in the utilization rate, even though the intervals are closely spaced.
Importance of Energy Control
It is vital to ensure efficiency in the workplace by establishing benchmarks to assess performance and determine competence periodically to gauge the actual production against the planned volume. It is because energy is a crucial but expensive resource for any business model. It underscores the need for a functional energy management surveillance scheme to facilitate attaining efficiency (UNDP, 2010).
The dangerous effects of global warming further illustrate the need for these regulations. It is brought about as a consequence of the increased discharge of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels. This makes it imperative for management teams to know trending and analysis of trending graphs and other data. Compiling the data collected from multiple scenarios will aid in the prediction of future trends, hence make planning easier. Since carbon trade has been earmarked for the future, it is crucial to establish mechanisms that will prevent misuse and subsequent wastage (Verisae Inc, 2010).
All in all, companies will be compelled to operate their assets at optimal levels to maintain energy efficiency. This cause will be complemented by enforcing smart grids and active response functionalities while citing the best performance as the target. Scrutinizing energy management will be instrumental in guaranteeing the use of substitute energy sources (Michigan municipal league, 2009).
Standards that will be enforced:
- Companies should set up a safe and methodical course of action before discharging equipment and appliances.
- Before any repairs are carried out, circuits and all other equipment using electricity sources should be disconnected.
- All nonelectrical energy in devices should be relieved if the appliance may re-energize sections of the electric circuit.
- All capacitors and capacitance rudiments on the ground should be discharged at all times they are not in use (Verisae Inc, 2010).
References
Michigan municipal league. (2009). Implementing Energy Control Procedures. mml.org. Web.
UNDP. (2010). An Overview of Energy Efficiency and Its Benefits. Undp.org. Web.
Verisae, Inc. (2010). Compliance and Beyond: Managing your CRC Performance. Verisae.com. Web.