History of the firm
Procter & Gamble is a multinational company that is based in America. The company trades in consumer goods. William Procter and James Gamble founded the company in 1837. Both founders originated from the United Kingdom. William dealt with the production of candles while James dealt with the production of soaps. In 1837, they merged their operations to form Procter & Gamble. In 1859, the company had eighty employees, and the sales had reached a value of $1 million. Over the years, the company diversified its products and increased the number of production plants through construction and acquisitions.
This increased the profit earned. An example of a major business combination that was made by the company was the acquisition of Gillette in 2005. Also, in 2009, the company sold the prescription-drug business to Warner Chilcott for $3.1 billion. Also, the company sold its food business to Pringles in 2012 for $2.75 billion. The operations of the company have changed significantly since its formation. Currently, Procter & Gamble is a public limited company that traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Besides, it is a component of two major industry indices, these are, Dow Jones and S&P 500 (Dyer, Dalzell, & Olegario, 2004).
Key defining moments
One of the key defining moments for the company was the introduction of Tide in 1946. Tide was one of the major iconic and successful products introduced by the company since its formation. The revenue generated from the sale of Tide facilitated the innovation of new products and expansion into new markets. The revenue of the company after the introduction of Tide went up to $11 billion in 1946. This was about three times the revenue earned in 1945. The second defining moment was the innovation and the endorsement of Crest toothpaste by the American Dental Association. This also boosted the revenue earned by the company.
The third defining moment was the introduction of Pampers. Even though, it was unsuccessful when it was introduced in 1961, the company improved the quality and price of the products, and it turned out to be a key invention in the market. Introduction of Pampers also improved the sales of the company. The final key defining moment for the company was the acquisition of Gillette in 2005. The acquisition was approved by various government authorities, and it was worth $57 billion paid through share acquisition. The acquisition enabled the company to emerge the top in the industry.
Further, the acquisition of Gillette increased control over shelf space for the company. This increased market share and market power. This can be attributed to the fact that both companies had strong brands in the market. Further, it was estimated that the acquisition would increase the rate of annual growth of the company from 4-5% to 6-7%. Finally, the acquisition resulted in cost savings by about $14 billion. Thus, it can be noted that the acquisition had a lot of economic significance for the company (Dyer et al., 2004).
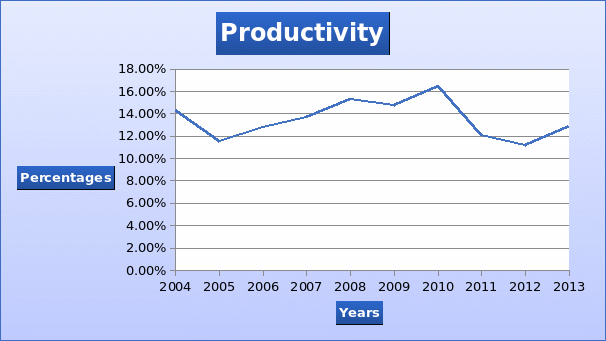
Productivity and economies of scale
In recent years the success of the company is attributed by economies of scale that results from a portfolio of its prominent brands. The economies of scale, which the company has built over the years, have enabled the company to produce goods at a lower cost per unit as compared to its competitors. Lower cost per unit has increased the competitive advantage of the company. The productivity, which is the ratio of input and output, will be measured by the ratio of free cash flow to revenues (Dyer et al., 2004).
The productivity level has been quite volatile over the years. The highest level of productivity was attained in 2010 (Stowell, 2010). In recent years, it can be noted that the company is experiencing a drop in productivity, as shown in the graph below. This hurt the profitability and efficiency of the company.
Technological changes
In recent years, there has been continuous advancement in technology. Besides, it has been observed that technology plays a major role in shaping competition and the success of a business. Thus, the rate of technological advancement is a major risk factor that affects the operations of the company. One of the major technological changes that affected the operations of Procter and Gamble is the introduction of electronic markets and advertising. The new technology required the company to create online platforms where buyers and sellers could interact to exchange commodities and also allow the company to advertise its products.
Also, the company faced a challenge of introducing advanced information technology in its internal operations. The company incurred a massive capital investment to introduce new technology. Currently, the entire operations of the company rely on information technology. Despite the success achieved by the company in coping up with the speed of technological advancement in these areas, it still faces a major risk of failure in any of the major information technology systems, networks, and other sites. The possibility of failure arises from security threats and computer crimes (Dyer et al., 2004).
Government regulation and economic indicators
The business of Procter and Gamble Company is heavily affected by the volatile global economic conditions. Currently, the company sells its products in more than 180 countries. Revenues from consumer products have a direct correlation with global economic conditions. Thus, if the economic conditions are volatile, then the operations of the business are highly interrupted. The major areas that are normally affected are consumer spending, supply chain, and credit markets. Also, instability of the government sectors and financial sectors in some of its major markets affects the operations of the business.
An example is instability experienced by countries in the European Union. This affects the revenue earned in these regions. Another example of government interruption that had a significant impact on the operations of the business was the government decision to devalue the currency of Venezuela against the dollar. The company had net monetary assets of about $1.1 billion held in local currency. Thus, the devaluation decision exposed the company to losses.
Further, the company incurs expenditure that is related to compliance with the various laws and regulations outlined by the federal government and its agencies. Even though the company considers this expenditure to be immaterial, it anticipates that the expenditure will increase, thus increasing the cost of operation as a result of new and tighter regulations. Further, the company faces several antitrust litigations, especially in Europe that arises from regulations on competition (Dyer et al., 2004).
References
Dyer, D., Dalzell, F., & Olegario, R. (2004). Rising tide: Lessons from 165 years of brand building at Procter and Gamble. US: Harvard Business Press. Web.
Stowell, D. (2010). An introduction to investment banks, hedge funds, and private equity. US: Academic Press. Web.