Introduction
Current information and communication technology is playing a major role in communications in the country. Because of the fast-growing information technology in the country, many parts of it still lag in embracing information technology as a way of communication and socialization. There is therefore a demand for equipping those areas with ICT Centers for communication and socialization in various destinations across the globe. These ICT centers can be set up in public places and be utilized by people who need them (Davies 2003, p. 23). Computers have changed the complete scenario of work and business. Apart from training and educational purposes, computers are widely used in many fields, starting from commercial and ending with home-usage. ICT Centers have been triumphant in capturing important market segments in the country because of their ease of access as well as the low-priced and customer friendly services they offer. Rock ICT Center can therefore utilize the advantage of the demand for ICT Center in the region, open a user-friendly ICT Center, and become a lead ICT Center provider in the region (Lokyer & Godorn 2005, p. 12).
Project Description
The setting up of an ICT Center in the hometown will cost 2000 dollars and will provide services to all the people in the town and its neighborhood. While studying the potential market, it was noticed that around 70% of the people of the town face communication and academic problems by lacking ICT centers. Furthermore, the project will be finished in two phases of two months under the guidance of the project manager. This procedure will be commercial and supervision will be conducted throughout the project head. The procurement will be conducted under competitive bidding and the Project manager along with representatives of the company and the stakeholders will be in charge of the vetting process. The project will be done in a government building allocated for the project and will serve as the center for the project.
Financial management plan
The project director will be in charge of the reporting and the running of the project’s expenses throughout the specified timeframe. For presentation and evaluation of the project’s expenses, the executive will be expected to be in charge of finances and he will carry out analysis during the weekly meetings to establish whether the budget is followed. Through consideration of the earned rate estimates, the project coordinator will be expected to account for the cost differences and present the results to the project group, something is done to establish the viability of the project. The costing of the project and the management-scheduling index will be forwarded to the assigned project supervisor every week. Variances of 10% or +/- 0.1 in expenses and the schedule management indexes will amend the situation of the cost to yellow or warning. This will be accounted for and if it is established that there is no minimum effect on the project’s expenses or program baseline, then there might be no action needed.
Change Management Plan
For intricate or great projects, administration of change may be included as an addendum to the project administration plan or separate as unrelated text. Any project team member or stakeholder may submit a change request for the project. The project administrator will be in charge of any changes to the venture, expenses, and timetable must meet the agreement.
Procurement Management plan
The project administrator will offer oversight and supervision of all procurement actions under the project. The administrator is expected to endorse all the procurement proceedings and events. The project overseer must endorse any procurement actions beyond the predetermined sum. Supervision of any chosen vendor or external source will be the responsibility of the project director and he will also be responsible for guaranteeing measurement of performance about the merchant offering goods/or services and this will be communicated to the contracted groups and purchasing department.
Risk management Plan
The approaches employed in the management of risks of the Rock ICT Center include a logical procedure by which the project group classifies scores and ranks a variety of risks. The attempt will be made beforehand to execute an improvement policy before the start of the project. The top of the list cautions are usually added to the risk management schedule and are assigned to risk managers for necessary actions and precautions to condone the risk in case it happens. The project manager will analyze every risk after the completion of the project and the necessary measures it took to neutralize the risks. This will be based on assessment and the project executive will identify the advances that can be made in the risk administration process for further projects. In case the project will need some improvements, the coordinator will capture them as part of lessons learned to establish the knowledge base for future utilization(Van-Oel 2004, p. 46).
Quality Management Plan
The quality and the completion of the work are upon the project team assigned particular roles in the project. The project supervisor(s) will be responsible for approving all quality standards for the project Rock ICT Center. As the project steps are executed, the manager will always ensure implementation issues and quality management are some of his roles. It is the responsibility of the quality service specialists to work closely with the project manager to ensure that the quality is adhered to throughout the project. The rest of the team members will be assigned specific duties as the project progresses and the various stakeholders will work with the project manager, as well as the specialists to guarantee standard quality management. In case of dissatisfaction regarding the quality measures, the team will report directly to the project manager.
Project Evaluation
The pivotal role of ICT in the development of the knowledge economy is widely recognized. There has been substantial investment in the use of ICT over the recent years, of course not unique in this respect: the integration of the use of computers and the internet for academic and economic improvements have been for many years now. Given this investment and the importance of computers and the internet in modern-day society, the impact of that investment must be evaluated to establish the extent to which people should access the use of computers and the internet. Almost a decade ago, Barton (1998) remarked, about Britain, that “despite the massive investment of time and money in information technology, it is difficult to get a clear evidence of value-added about It to use in developing countries”(p. 67). Despite the continued levels of investment in recent times, Tarle (2004) noted that the recent usage of the internet and computers by the majority of people in developing countries is not commonplace. Country’s Department of Information and communication, while noting the importance of ICT as a tool for communication and academic assistance is now widely recognized but less embraced in some regions, Ofsted(2004), stated that “government’s aim for integration of communication to some areas is a reality in only small of minority regions” (p. 21).
One kind of ICT evaluation has been widely undertaken in the evaluation of its infrastructural development in major cities. Despite this being an essential evaluation, statistics, such as ICT distribution in some parts of the country is an indicator of the distribution of ICT in the country. It is, however, a mistake to equate the availability of the hardware with its essential use.
A different dimension was the one adopted by Harrison (2003) in which the study was set out to determine whether those people who used and are familiar with the use of computers have better business investments and communication channels than their counterparts who do not. The most familiar qualitative approach to assess the impact of usage of computers and the internet is by observation of the location of social site users. The communication commission of a given country mainly adopts this approach. Van Oel (2004) reported that in addition to the monitoring by the communication commission, government agents discussed the findings on the ICT usage with a wider country population and encouraged the use of ICT. Haydn (2001) stated that types of ICT that may be the addition of value to the society vary depending on the mode of its use. Some techniques of evaluation also have particular applicability. Barton, (2000) conducted a study whereby he compared the time businesspersons spend on sending business reports manually with the time taken to send them online. This comparison was informative as it depicted a potentiality of value addition in the use of ICT. The rural community therefore like any other people deserves the right to be equipped with ICT.
Research indicates that the South African business community has rapidly benefited from the use of the internet with most press advertisements employing the use of a universal resource locator (URL). The billboards along the roads, radio, and television shows have their websites, social sites while newspapers, and journals have adopted the online versions. Electronic banking has also been embraced by most banks making it easier for people to make transactions any time and in any place. There have also been increased teacher-student interactions in the institutions of higher learning through the web-based student-teacher interactions systems which are provided for submission, tracking, and marking of assignments and projects.
However, results have shown limited and inconclusive evidence of the downstream impact of public access with communication and information technology. Research studies suggest that access to ICT by the public is doing less to the public than expected. This is not primarily, because public access has no impact but it is because the use of ICT in different regions varies and their utilization is unevenly distributed (Klaas 2006, p. 10). Research indicates that some internet providers such as cybercafés are economically sustainable because of their economic orientation (Bell 2006, p. 199). A study by Kumar (2006, p. 21) suggests that the subsidies of financial access have been able many nongovernmental organization newsstands to stay in operation, while the kiosks owned by private entities had closed down. This could be attributed to the use of ICT in marketing and searching for the sources of products from the market while privately owned kiosks could not afford the luxury of the integration of ICT.
Public access ICT avenues have continued to face challenges associated with the demand for their services. Amariles (2006) states that commercial internet centers in small towns and villages face a task of limited user base and the necessity to convince the user base on the importance of ICT services but if embraced, there was a higher likelihood of attraction to a variety of user bases. The current livelihood is, however, more incentive in the usage of ICT services. This could trigger their participation (Nickson 2001, p. 3). One of the considered key determinants of ICT usage for many years has been education combined with a view that this kind of service has been targeted by elite and financially able people of the society (Etta & Parvyn 2003, p. 89).
Roman (2002) indeed suggested that locating telecommunication center services in libraries hinders adoption by those who consider libraries as places for intellectuals. The study in China however has produced different results as it was shown that there was no relation between the education level and internet access of the community (Ulrich 2004, p. 45). There is a sense in most cases that the small towns or villages do not take full advantages of the public access avenues; this is particularly by those who are considered disadvantaged or those who could be of benefit to them coupled with the fact that there are little ICT infrastructures developed in such regions (Kaiser 2005, p. 112). In developed countries, this is attributed to low levels of awareness, lack of interest, or even the higher profile of private forms of access (Brophy 2001, p. 17). It has also been attributed to low patronage and affordability barriers (Perkinson 2005, p. 46). The general explanation has linked this with fewer public access levels and hence does not make the society relevant (Eve, 2003).
Usage of ICT has shown specific usage patterns and perceptions (Best 2007, p. 53). Wheeler (2006) in her study on female internet kiosks discovered no scientific forbiddance in female’s capacity to use public access facilities and there was no evidence that internet access had contributed to women empowerment. However, the study showed that women in Egypt benefited from improved access to information and professional development, maintenance of social networks, and social and political awareness. Many researchers have evaluated the comparison of ICT with the general public. The main users of public ICT access venues are young and educated youths of high social-economic statuses and without disability, and have the experience to access the internet from other locations (Adomi, 20007). Uses of these venues are noticeable and are mostly confined to social sites. Many commentators as disappointing results view overall trends, however, there still have one author who noted that the materiality of public access venues to the bourgeoisie generation could not be discounted (Haseloff 2005, p. 17).
The research study investigated the influence of information communication and technology on the rural areas and established that the reasons for underdevelopment may be attributed to the low priority assigned by the government to the rural areas in developing the ICT infrastructure. Moreover, the budget for the development of ICT in rural areas is controlled by a marginal percent. Some of these issues are becoming a major hurdle to the people of the rural areas and have given the priority preference to the government to address the aforementioned issues before they can think of the importance of ICT. ICT has been shown to play a vital role in the increment of competitiveness of a country as research shows. This can be done through speedy efficiency in the production process, improved information access, increased markets. Global social networks facilitation. Coverage and efficiency of service provision have also by health provider companies have also been improved through the use of ICT. Education in general and trade services through e-commerce has also been improved by the use of ICT (Samwel 2006, p. 223). The importance of ICT in rural areas cannot, therefore, be undermined as it can be used to reduce the digital divide and as well bridge the gap between those with access to ICT and those with limited access in regards to their social, economic, or geographical reasons.
Aims and the overview of the Evaluation
Very few published researches are available as evidence on the efficacy of ICT initiatives in a country regarding communication, business, and academic use. The report aims at bringing to the context the importance of ICT in society. The aim of the evaluation was also to establish the importance of ICT usage in society and the impact on businesses and academic studies. The objectives of the evaluation can be summarized as done below:
- To assess the extent of the usage of Information technology in the country
- To investigate the contribution of ICT to businesses and education
- to make recommendations on the importance of increasing ICT in some regions in the country
- To assess the extent to which people in some region use ICT to support research for students
The evaluation examined the availability of information and communication technology in some regions and compared it with the usage of ICT in other regions. It also looked at the extent to which people use ICT to extend and speed up business processes. Empirical evidence had been collected from some sources.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Major issues identified in regards to ICT acquisition, diffusion, and infusion in rural areas indicate that there is:
- Limited income to acquire access to ICT tools.
- Lack of vital minimum skills to use ICT.
- Limited awareness in regards to using ICT in the enhancement of livelihoods.
An absence of the perceived need for ICT, in essence, the service considered useful or expected by the community. Furthermore, most of the service providers are not attracted to invest in ICT facilities due to they think there is not enough benefit.
Moreover, the need to have long term, able, and self-managed projects to be appropriated by the rural communities cannot be done away with. To achieve this, there is a need to carry out community-generated enthusiasms with the assistance of the trained technical support plus collaboration with local national, and international stakeholders. Major limiting factors in rural areas are the monopolistic nature of telecommunication service providers who perceive that the development of ICT in rural areas is costly. The research analysis is needed to determine the role of the government and the stakeholders in finding solutions to ICT problems in rural areas and find alternative solutions to equipping the rural community with information and communication technology.
ICT centers in rural areas demonstrate a tremendous future for the improvement of the business, as well as social interactions and education in rural areas. Internet application however is still being hindered by problems related to few or lack of facilities, limited support from the rural community, poor information and communication technology infrastructure, and lack of or limited bandwidth among other problems. Bangeman (2004, p. 56) observed that the first countries to embrace ICT technology, especially the developed countries, have reaped the greatest rewards starting from increased economy to improved warfare and health. It is therefore the responsibility of the government and the relevant stakeholders to equip the rural parts of the countries with ICT to improve their living standards starting from education ranging to commerce. This will be beneficial not only to the rural community but to the government economy as well.
Future research studies should be carried out to establish the impact of ICT in the rural community or better still focus on challenges facing the supply of ICT in rural areas. There is a big gap to be filled between the benefits ICT has to the urban people and how it has done the same to the rural community. The rural society, if they involve ICT in production, marketing, and distribution as well as researching, the countries will reap heavily from the outcome and the economy will be boosted (Soderland, Pinto & Morris 2011, p. 23).
Need for the project
In recent times, people in the town are lagging behind technology, despite the country being the one that evolved in the use of technology. There is little interaction in town due to the lack of computers and the internet yet, but social media has made it easier for people to interact globally. Students in the surrounding environs also find it difficult to research their academic works because of the lack of ICT centers and are forced to travel long distances for such services. The idea of building Rock ICT Center is to ensure students of the town and its environs have access to the internet to assist them in academic work and at the same time assist people to interact socially and embrace technology.
Project scope statement
To purchase and conduct installations of company computers and software within one and a half months at a cost no more than 2000 dollars
Project Manager
As the project manager,, I am hereby authorized to controlling,monitoring and participating in each part of the project. I have to ensure that the assigned project has the best meet to the different departments, which involved project team, all contractors, all suppliers, project supervisor, project quality supervisor, etc., and make sure have effective communication with each department. The contractors and suppliers also need to be inspected that weather they achieve the project requirements, a Health, Safety, Environment management system (HSE) is expected to be implemented. I have to monitor different stages of the project is done and completed in time and within the given budget. During the project proceeding, the present situation of staff, assets, and equipment also needs to be under consideration. What is more, during implementation, control over the project and corrective actions also need to be taken as well.
Deliverables
- Fully conditioned and working computers
- Updated and fully functional software
- Working and functional hardware
Milestones
Technical requirements
- The installation must meet the local technology codes
- All computers must be able to run all the Microsoft components
- Internet and Ethernet cables must be able to transmit the internet
- The computer room must accommodate more than 25 computers
- All the computers must be fitted with security antivirus
Limitations and exclusions
The purchase and installations will be done to the specifications and designs of the original blueprints provided by the customer
The customer is responsible for choosing a monthly broadband access subscription
The generator is not included in products purchased
The contractor is responsible for sub-contracted work
Installation work should be limited to weekdays, 8: 00 AM to 6: 00 PM
Main requirements for the project
Accessibility
A high-quality project should have the desired information so that one can find it pleasant. It is expected to be in a suitable format and should not be disorderly with extraneous material. Large plans are awkward, although it is vital to have inclusive plans for the project. There should be clarity and convenience of the data and should be in a prescribed order in a known consistent and non-redundant format.
Clarity
A project is difficult to use with confidence if its data is not clear hence if they cannot be used with confidence, there is no reason for gathering them at all. There is a reason to leave room for interpretation and if the project is detailed enough, there is a need to be broken down further for the sake of clarity.
Specificity
A project should be specific in addressing what to be done when to be done, who to do it, and the cost of doing it. If not all of these are understandable, then the project is not explicit.
Precise
The issue of the relation of the unit to quantify to the total magnitude of the measurement is accurate. For example, if a project analysis takes 14 programmer years, the supervisor would not be concerned with the units of time. The programmer weeks would be almost certainly the premium level of particulars they will consider.
Accuracy
Of all the requirements, accuracy is probably the most crucial. The main concern of a project is generating plans with unsurprising accurateness. As long as one works on superior projects and takes part in development teams, small-scale mistakes will balance with each other and the mutual results will be more precise.
Work Breakdown Structure for purchase and installation of computer systems
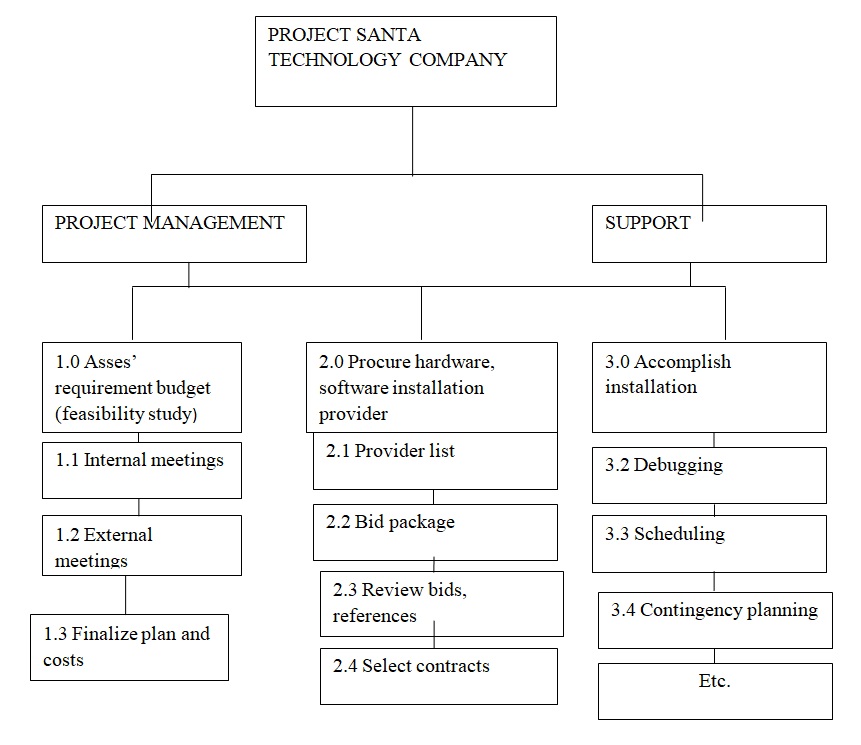
Risk identification and management
There is a higher probability of time constraints from the process of a feasibility study to the accomplishment and installation process. The project will ensure external and internal meetings are conducted in the shortest time possible and the process of procurement is done in haste. Tender bids will be advertised and the closure of tender will be given in short notice to allow quick application. Review of bids will also be quickened to ensure the project is given in a stipulated timeframe.
To avoid capital and budgetary issues, the project will request for an increase in the budget during the feasibility study to accommodate emerging budgetary issues such as increased cost. Market research will be conducted to establish the variation of the prices of the software, hardware, and computers, the tender will be awarded to the cheapest bidder to cut the cost and prevent budgetary outflow.
The contracted bidders will be vetted to ensure they are right for the job and the signing of the contract will involve legal intervention to prevent a breach of contract. The period will be included in the contract to stipulate the time needed for delivery to prevent time loss
The project will ensure there are no software and hardware malfunction risks by ensuring purchase is done to a distributor with a proven track of quality products to prevent malfunction. A substitute distributor will also be contacted in case of a malfunction of the products while pre-tests will be conducted before the purchase of the products.
Delayed delivery of the equipment may also hinder the timeframe of the project due to late delivery by the contractor. The project may switch to a subcontractor with a proven record of accomplishment to ensure that delivery is on time. Capability assessment may also be done to the contractor and previous customers are asked to check the reliability of delivering of products.
The probability of having inadequately trained personnel may arise since they may not be accustomed to new software and hardware hence they may be unable to use the system properly. The project will ensure the personnel is involved from the start of the project and the training procedures would be reviewed and enhanced to ensure they are familiar with the system.
Stakeholder Map
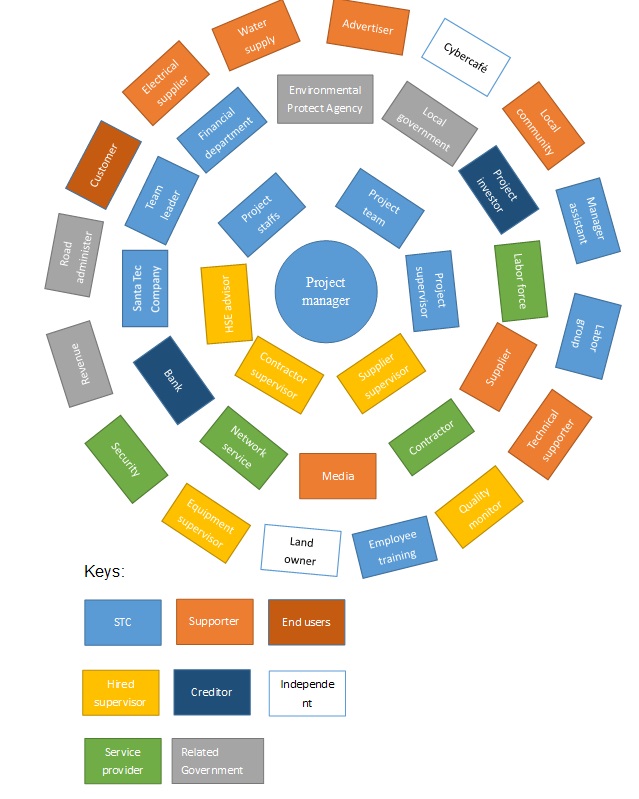
Evaluation of Stakeholders
The project manager is the driver of the project and in charge of monitoring and overseeing the project. The project staffs are the planning department to provide developing plans for the project. The project team and the project supervisor are responsible for working through a stipulated timeline to ensure the project is accomplished. The HSE advisor, the contractor supervisor, and the supplier supervisor are hired to provide advice about health, safety, environment (HSE), and monitoring the contractors and the suppliers with more professional standards. These people are the Direct Interest Groups, and make up the core team.
The second level of stakeholders involved the financial department, the project’s creditor, banks, and investors, they manage the fund and provide enough money to ensure the project is accomplished. The service providers include network service, the contractors, and the labor force, also related to the project; they offer service during the processing of the project. The Santa Technology Company is the contracted company to oversee the establishment of the project. Another two key factors of this level are the supporters, which include the suppliers and media, and the related government department.
The last level of stakeholders, which have an indirect influence on the project. Except for supporters, hired supervisors, service providers, and related government departments, the end-users of the project and the competitors are also the stakeholders.
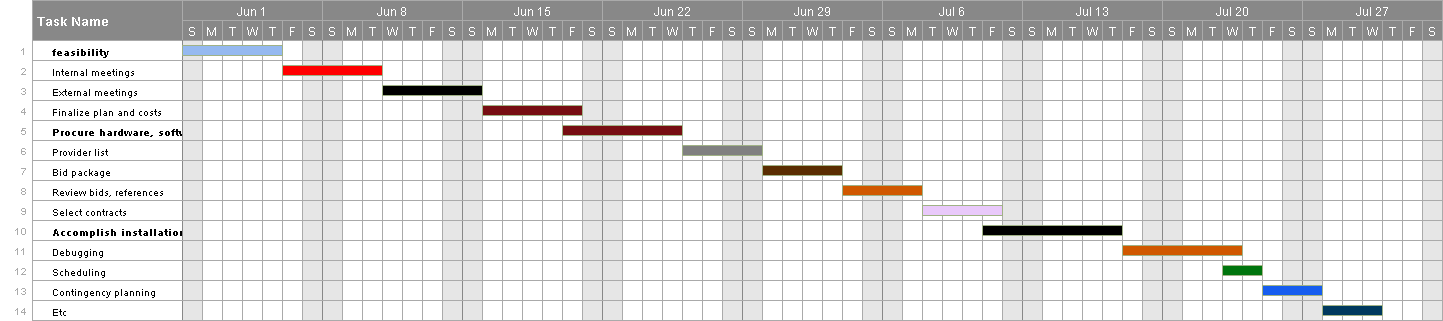
Gantt Chart
Project Team Structure
Organization Evaluation
Santa Technological Company submitted the proposal to acquire the tender and bid on the respected tender notice issued by Nation Media Group. Santa Technological Company has a well-organized project team as well as necessary equipment for the purchase and installation of computer accessories and has a record of completed tasks before and therefore is the best for the job
Memorandum to the manager
To: Philip Sang
From: Yanju Hu
Date: 4/12/2014
Re: Project Guidelines
The following steps have been to ensure the success of the project.
Step 1- request for the project
Every project has a stakeholder and in Rock ICT Center, the stakeholders include the CEO of the rock company and the sponsors of the project. Chosen employees of Rock ICT Center are stakeholders and representatives are chosen from the sponsors to oversee the projects.
Step 2- Pre-project Deliberation
Projects have a great effect on the preservation and support of activities of the technical devices.
Step 3- Before Project agreement
The shareholders at this stage are supposed to have had sufficient data to facilitate decision-making on whether to continue with the project or not. The results of this pre-agreement are to:
- Clarification of data assumptions
- Understand project deliverables
- Know the risk costs
Step 4- project agreement
- The project manager of the Santa Technology Company has to formally write up the company.
- The allocated project manager and associates
- Timescale
- The extent of Santa technology Company participation in the project
Step 5- Project Implementation
The concerned manager will be in charge of all forms of communications whereby he will be expected to:
- focus on project meetings and attend them as arranged by stakeholders and the holder(s)
- offer direction as required by the accord
Step 6 After project activities and review
The Staff in charge of the project will meet to transition the project to the mode of purchasing and installation.
Analysis of motivation
At the start of the project, the project was positively motivated mainly because they were assigned to their respective positions, and the laid down guidelines were available. The team projected motivation and worked tirelessly to meet the timeline as stipulated by the project and despite the pros and cons of the project. Partway through the project, the project team continued to dedicate their spirit to the job and showed their commitment in their respective designation and there were more team-building meetings to assess their motivation.
Summary Closure Report
The goals of the project were:
- To develop an ultra-modern ICT Center through the purchase and installation of computers and software
- To work with the stakeholders to develop an internet center with a running internet to facilitate technology
Project highlights and best practices
A complete Modern ICT Center was designed and tested within the ICT Center.
Recommendation by the stakeholders directed the installation and the running of the system with enhanced software and new machines for faster and easy web surfing
Project closure synopsis
This project is being closed because the project-funding period has expired
Project Metrics Performance
Functional performance
- Be able to run and operate the web for the people in need of the internet
- Be able to perform other functional services such as typing
Cost-effectiveness for operations
- The magnitude of operations to current web usage
- Cost of hardware that is required to monitor and facilitate internet
Ease of Use
- Estimated Cost of the final product
- Ease of maintenance of the ace
Milestone and deliverables Performance
A new ICT Center for accessible cyber services and training that use Ethernet communications in their operations. The present state of technology in the area of the project is low because of a lack of internet access (Burke 2013, p. 29). The report describes a cyber system that will increase technology in the region.
The ICT Center consists of 26 computers fitted with needed software for typing and printing as well as internet cables channeled to one router, supported by a booster to enable faster surfing of the web services, and downloads.
Schedule Performance
Meeting with the management of the company and the stakeholders to discuss the feasibility study and the costs of the project and to prioritize the functionality of the design and finalize the costs
Procure hardware and software provider for computers through advertising tenders to eligible bid
Budget Performance
Metric Performance Recommendations
Recommendation 1
Design a modern internet center with a high-speed internet connection
Justification
The current usage of the internet in the region is based on mobile devices and therefore does not support heavy web browsing and moderate file sharing.
Recommendation 2
Design printing services in the station to allow for one-stop internet services
Justification
The current printing service centers in the region are not equipped with internet and hence cannot offer broad internet services
Advantages
The cost of cyber charges and printing charges will be the benefit of the center as opposed to taking printing services away.
Disadvantages
Higher costs of purchase of the equipment
Project Closure Tasks
Resource Management
Funding is needed to provide good purchasing of quality equipment. A training plan needed for the installers and the maintainers of the system
Communications management
Weekly meetings that include the management of the contracted company, the stakeholders, and the representatives of the project team took place to share notes on the development of the project.
Project Closure Report Approvals
Prepared by:
Project Manager Santa Technology Company