Introduction
X-rays are “electromagnetic radiation of exactly the same nature as light, but much shorter than light wavelength” (Künzel, Okuno, Levenhagen and Umisedo, 2013). X-ray images are generally found in most health facilities such as orthopaedic, dentist, and chiropractor departments. X-ray radiology techniques have been effective forms of managing cancer through imaging processes. The method is cost effective and easy to use in emergencies. However, the efficacy of an X-ray technique depends on the image quality, which relies on the X-ray absorption through the exposed tissues. There are different X-ray procedures, such as computed tomography. Computed tomography uses a contrast agent that is “injected directly into the blood stream followed by immediate imaging” (Künzel et al., 2013). The role of a contrast agent is to enhance attenuation of the X-ray procedure in the area of the targeted body part.
In X-ray imaging, a number of things take place. When light strikes an object, the object, tissue in this case will absorb, reflect, transmit, or refract light (fig. 1). X-ray transmission depends on photons of light. The absorbed photons usually never pass through the tissue. Reflected photons also do not gain access to the inside of the object. Instead, they turn back towards the source of light. Still, transmitted photons pass through the object. Refracted photons also pass through the object, but the object usually changes the rays as they leave.
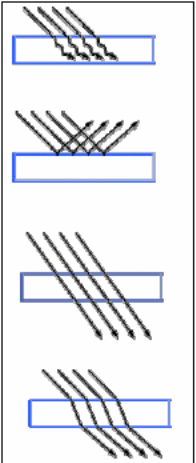
X-ray absorption in medicine
X-ray found its application in medicine because of its abilities to pass through the body. Any object that is between the X-ray tube and a thin plain film normally produces a shadow that creates a negative image. The procedure has been effective because tissues of the body have abilities to absorb X-ray, but at different rates. However, the challenge has been that most tissues of the body normally consist of water. This makes the resulting image to look similar during X-ray processes. Radiographers have generally identified few tissues, which have distinct differences from one another in terms of X-ray absorption.
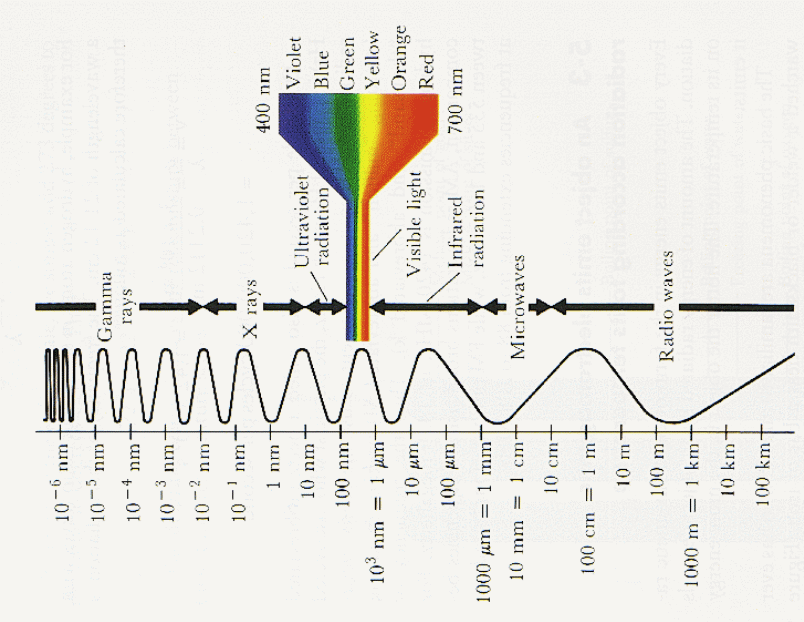
Knowledge of electromagnetic spectrum and X-ray spectrum are imperative for many diagnostic X-ray imaging usages. This also includes dose calculation and energy decomposition (Duan, Wang, Yu, Leng and McCollougha, 2011). Radiographers have noted the rise in estimates that involve patient doses during CT procedures. In addition, knowledge in clinical dual-energy has also become critical for radiographers. This results from the high photon flux, which makes it difficult to estimate or measure spectra from the X-ray tube of the scanner. Radiographers have relied on indirect approaches in order to estimate the level of spectrum during transmission. Duan and colleagues noted that there were a number of methods applied in estimating CT spectra, but they concluded that the “expectation maximisation (EM) method was an accurate and a robust method of solving the spectrum measurement problem” (Duan et al., 2011).
The bremsstrahlung process (radiation generation) results in the production of polyenergetic X-ray output. However, it is important to determine attenuation qualities of the X-ray beam through measurable methods. Seiber and Boone note that measurement of “the x-ray beam intensity is performed using ionisation chamber dosimeters, which are comprised of electronics, a voltage source, and separate air-filled chambers of known volume” (Seiber and Boone, 2005). During the ionisation process, “electrodes gather and evaluate electronic charges that emanate from the x-ray–induced ionisation of air molecules within the chamber” (Seiber and Boone, 2005). About 33 eV is the mean amount of energy that an atom air needs to ionise a pair of ion, which consists of a positive atom and a negative electron. On the other hand, X-ray exposure shows the quantity of electron charges released in a given volume of air. Radiation dose shows the amount of absorbed energy during X-ray procedures in every unit mass. In X-ray exposure, the dose that the patient receives is normally ten percent less relative to air karma that is evaluated in the chamber of ionisation, mainly in mGy. Seiber and Boone observe that an “accurate measurement of x-ray beam attenuation needs to exclude scattered radiation, and this requires the use of so-called “good geometry” (Seiber and Boone, 2005). The approach applicable in a good geometry is a clear collimation of the X-ray beam. This restricts the beam to the outer side of the system. The system must be at a considerable distance from the attenuator, which could be about 20 cm in order to eliminate any possibilities of scattered X-rays entering the ion system.
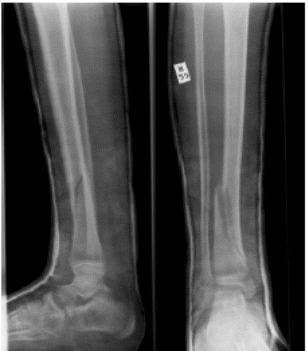
Radiologists have used X-rays to analyse tissues, which exceptionally have different components in terms of density and characteristics. It is simple to recognise the differences in soft tissues of the bone after the X-ray procedure. However, it has been extremely hard to notice differences that exist in several soft tissues. Usually, the ability of X-rays may be spatial resolution, but X-ray spatial resolutions are normally of high quality than those of ultrasound or MRIs. Orthopaedic procedures relied on X-rays to examine bone fractures as the best method (fig. 3). X-ray films normally have whitish colour, but when X-rays reach the film, they turn dark and reflect the generated image. Excess X-rays on the targeted body part can lead to an extremely dark image. Usually, the bone absorbs or deflects rays, which may not be in the film. Thus, the bone may appear white on the film. Thick bones may result in light images on the film. In osteoporosis, X-rays are not common. The density of the bone has effects on the X-rays. This implies that radiologists should also examine bone density in advanced conditions.
The radiographic image contrast relies on the quality of radiation absorption by the body tissue on focus. In this context, radiographers have introduced various means such as nanoparticles in order evaluate the X-ray image through X-ray spectroscopy (Künzel et al., 2013). Künzel and colleague examined “the spectral changes on X-ray beams transmitted through a gold nanoparticle aqueous solution registered with the X-ray spectrometer because this detector had a good performance in the diagnostic energy range” (Künzel et al., 2013). This study demonstrated that a gold nanoparticle aqueous solution enhanced the rate of X-ray absorption from 20 percent to 60 percent on X-ray beams produced between 20 kV and 120 kV, correspondingly. In addition, they also noted that electron-dense nanoparticles resulted in increased X-ray absorption at low concentration of X-ray beams. Hence, the target body tissue could produce best image contrast.
However, the diagnostic X-ray imaging depends on the attenuation of the X-rays in the body tissues (Seiber and Boone, 2005). In this case, the transmitted and absorbed rays results in the creation of a two-dimensional image. This shows the anatomy of the body tissues.
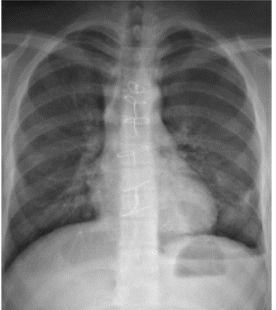
X-rays may not provide the desired results when examining small fractures in complex body parts and joints. In addition, the procedure may also be challenging in growth plates among young people. In some instances, an MRI could be effective in determining ligament problems or joint defects.
Modern technologies have allowed new imaging machines to store digitised forms of X-ray images. This has been important in emergency situations in which reproduction of such images are necessary for rapid care provisions. Moreover, modern X-ray machines have resulted in fast and easy processes for capturing X-ray images for quick diagnosis. Still, some users have noted that X-ray machines are not expensive relative to other imaging technologies.
When X-rays go through the body tissues, they usually lose some of their energies to the body tissues through the following ways. First, scattering leads to energy loss because the X-ray photon may not have the required amount of energy for electron emission from the atom (1 to 30 keV). Second, in some cases, the X-ray photon may radiate all its energies to electron, which may then leave the atom (1 to 100 keV) due to photoelectric effect. Third, there is also Compton scattering. This process of energy loss involves a collision an X-ray photon with other loose electrons. During the collision, electrons normally acquire energies while the scattered X-ray photon travels in various directions from the area of the collision with a low-level of energy (0.5 to 5 MeV). Finally, pair production also leads to loss of energy in an X-ray photon. For instance, when an X-ray photon with high concentration of energy, which could be greater than 1.02 MeV, enters nucleus with high concentration of electricity, changes may occur in the process of converting such energy into a positron and an electron. The particles destroy each other and result in two photons with high concentration of energy.
Risks associated with X-rays in medicine imaging
There are several risks, which relate to usages of X-ray imaging in the body. Radiographers believe that X-rays that go through the body and strike the film do not have harmful effects on the body tissues because they are transmitted photons. However, it is imperative to note that not all X-rays that go through the body normally pass through to the film. This is important in the production of images. Rays that strike bones and other thick body parts do not pass through to the film. Hence, it is critical for radiographers to understand what happens to X-ray beams that do not leave the body. These X-ray beams retain their high-energy properties within the body because it is difficult for energy to disappear. Rather, this energy finds its way into the body tissues. X-ray beams have abilities to transfer their energies to the body electron, which may result in significant damages to the body cells and organs. Electrons could spread such damages to other cells throughout the body in the process of ionisation. While cell damages could take place in several ways, it could be extremely dangerous when such damages have affected cellular DNA.
Damages to the DNA system change the DNA signal, which may affect new body cells. This may cause tumour in the body. While ionisation takes place during X-ray procedures, the body has the ability to repair some damages. However, conventional X-ray procedures still have greater risks than modern approaches, but the level of risks have declined significantly.
A reduction of X-ray doses results in little radiation, which could reduce cases of cancer in the body. People get radiation from the sun and the environment, but every X-ray procedure result in an exposure of 1/5th of radiation relative to radiation people get from other sources every year. While this may be safe for users, it is necessary to avoid high rates of exposures and avoid cases of repeated X-ray procedures, particularly during medical procedures. Radiographers must be careful with pregnant women because they must not use X-ray beams near foetus. In such cases, ultrasound has been effective for pregnant women, particularly near the foetus.
Issues regarding damages to biomedical specimens have led to low applications of new discoveries in X-ray tomographic procedures (Fahimian, Mao, Cloetens and Miao, n.d; Langer, Cloetens, Guigay and Peyrin, 2008).
Conclusion
X-ray medical imaging relies on several factors. These include variations in the attenuation of the X-ray beams by the target body tissues, transmitted X-ray absorption, the changing of the absorbed X-ray energy into light for visibility, and the processing and presentation of the X-ray image on the film either on ‘hard’ or ‘soft’ copy on a light emissive display.
The loss of X-ray beam energy may cause damages to the body tissues. While modern technologies have reduced such risks, X-ray procedures still present risks to patients. Hence, radiographers should avoid multiple X-ray procedures whenever possible.
Reference List
Duan, X, Wang, J, Yu, L, Leng, S and McCollougha, C 2011, ‘CT scanner x-ray spectrum estimation from transmission measurements’, Medical Physics, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 993–997.
Fahimian, P, Mao, Y, Cloetens, P and Miao, J, n.d, Low dose x-ray phase-contrast and absorption CT using Equally-Sloped Tomography. Web.
Künzel, R, Okuno, E, Levenhagen, and Umisedo, N 2013, ‘Evaluation of the X-Ray Absorption by Gold Nanoparticles Solutions’, ISRN Nanotechnology, vol. 2013, no. 865283, pp. 1-5.
Langer M, Cloetens P, Guigay J P and Peyrin F 2008, ‘Quantitative comparison of direct phase retrieval algorithms in in-line phase tomography’, Medicine Physics, vol. 35, pp. 4556-66.
Seiber, A and Boone, J 2005, ‘X-Ray Imaging Physics for Nuclear Medicine Technologists. Part 2: X-Ray Interactions and Image Formation’, Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 1-16.