The business plan of an outpatient surgical center known as Red Rocks Ambulatory Surgery Center, L.L.C., which is a for-profit business, is presented in this report. The aim of this business is to provide patients with a broad spectrum of diagnostic and therapeutic surgical services. The mission of the surgical center will help in achieving its short-term and long-term goals.
From the vision of Red Rocks Surgery Center L.L.C., it is observed that it will provide surgical services with a goal of exceeding patient expectations in a setting designed to create a positive healing experience for its patients and their families. It is a cooperative joint venture with Your Best Health Surgical Services and Healthy Living Hospital.
The center will provide surgical services including Surgical Accommodations, Staff Accommodations (Clinical), Staff Accommodations (Administrative), and Patient/Family Accommodations. The plan discusses market conditions and trends. Also, it provides details of licensing, training, and certification requirements. The SWOT Analysis helps in reviewing both internal and external environments.
The business plan provides the financial analysis of the proposed business and its financial statements that indicate the financial feasibility of the proposed business. The financial analysis underlines necessary assumptions to support financial projections presented in the document. Also, it provides a brief description of the source of funds. The report ends with Ambulatory Surgery Preliminary Plan and Ambulatory Surgery Schematic Plan that will be implemented by the proposed business.
General Company Description
Red Rocks Ambulatory Surgery Center, L.L.C. (Red Rocks ASC) is a for-profit outpatient surgical center providing patients with a broad spectrum of diagnostic and therapeutic surgical services. Our state-of-the-art facility has been designed and equipped with the most up-to-date medical and surgical technology. The soothing surroundings and dedicated staff are focused on creating a calm and relaxing environment for patients and their families during their surgical procedure and recovery.
Mission Statement
Red Rocks ASC will be the surgical facility of choice for physicians and patients who prefer to undergo elective outpatient surgery in a caring atmosphere with the highest quality of surgical expertise, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Red Rocks ASC is committed to its values:
- Quality: Our dedication to quality includes continuous performance improvement that ensures positive outcomes and utilizes innovative methods to assure that we exceed our patients’ expectations.
- Professionalism: Our entire organization understands that respect and courtesy are vital components of our everyday culture along with integrity and ethics in all that we do.
- Patient satisfaction: Our teams will strive to exceed our patients’ expectations and needs and our success will be measured by their satisfaction.
Vision
Our vision is to provide the greatest surgical expertise in a caring and comfortable atmosphere. Red Rocks ASC will encompass state-of-the-art surgical technology in a cost effective manner. We will provide surgical services with a goal of exceeding patient satisfaction in a setting designed to create a positive healing experience for our patients and their families.
Red Rocks ASC is a limited liability corporation formed in cooperation between Healthy Living Hospital and Your Best Health Surgical Services. By joining together in a unique partnership to create Red Rocks ASC, our physician and administrative leaders are able to draw on years of expertise in providing healthcare services to patients in our community. Our experienced and knowledgeable staff members and physicians are not just employees but are active and engaged members of the community.
Products and Services
Red Rocks ASC is a cooperative joint venture formed in collaboration between Healthy Living Hospital and Your Best Health Surgical Services. Together, this well-established community hospital and the well-respected healthcare professionals have joined forces to create an ambulatory surgical center (ASC) dedicated to providing patients with the latest advances in surgical care in a state-of-the-art facility. Rec Rocks ASC is committed to providing care focused on comfort and convenience of both the patient and their family.
Surgical Services
As an ambulatory facility, Red Rocks ASC provides general surgical services performed on site in a dedicated surgical facility. This is an outpatient based center with no capacity for overnight stays. All patient care services will be completed and the patient discharged within 10 hours of total care and recovery time at the facility. Primary revenue sources will be generated from surgical services and other medical procedures performed on site. The bulk of payments will be received from reimbursement from insurance companies and patient generated revenue from co-pays, deductibles, and self-pay patients.
Red Rocks ASC is capable of performing a broad array of diagnostic and therapeutic interventions including minimally invasive, percutaneous or laparoscopic, and open surgical procedures. Orthopedic, podiatric, pain management, and ophthalmology procedures are anticipated to be the greatest percentage of procedures performed. Plastic surgery, otolaryngology and general surgery procedures will round out the main types of procedures performed. The facility will not provide gastroenterology endoscopy services, as a dedicated endoscopy facility is located in the general vicinity of the hospital campus.
Overview of Facilities
Surgical Accommodations:
- Three Primary Operating Suites, including a dedicated orthopedic procedures room equipped with state-of-the-art clean room filtration technology
- Minor Procedure/Treatment Rooms
- Eight-bed pre-procedure holding bay
- Eight-bed post-anesthesia recovery bay
- Two physician consultation rooms for multiple functions
Staff Accommodations (Clinical):
- Male/Female changing area with dedicated locker space in each for 25 staff members including shower and toilet facilities
- Employee break room with full kitchen facilities
- Operating Room Director dedicated office space
Staff Accommodations (Administrative):
- Four patient registration cubicles
- Employee break room with full kitchen facilities, restrooms
- Dedicated office space for scheduling, prior authorization, coding and billing, health information management, administrative management staff
Patient/Family Accommodations:
- General waiting area with a maximum capacity of 25 people
- Surgical waiting area is capable of holding up to 15 people
Market Analysis
The main marketing mix for this center includes people who are in need of elective surgery. The primary surgical patient needs will include orthopedic, ophthalmologic cataract procedures, gynecological, urological, plastic surgery, and other general surgery procedures that do not require an overnight patient stay (Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the US…, 2016). This may also include patients recovering from minor accidental injury, such as broken bones, whose condition may require non-emergent elective outpatient surgical procedures as part of their treatment and recovery plan (IBIS World, 2016).
The center will be able to handle the surgical needs of many patients with its twenty surgeons and other employees that have been put into place for nursing, sterilization and rehabilitation. In addition, low-acuity patients may be referred to the ambulatory surgical center by the hospital, allowing for the facility patient load to remain focused on high-acuity patients whose care requires overnight or multiple day inpatient stays. This increases the volume of surgical procedures for the ambulatory surgical center and helps to accommodate the needs of the hospital, surgeon, and patient for both inpatient and ambulatory surgical services.
Trends
The outpatient surgery center is a perspective-driven example of modern medicine. Plenty of operations that have previously required extensive hospital treatment are now completed in outpatient conditions during one or within several days. The popularity of ambulatory surgery centers is enormous (Boodman, 2014). They have been rising in popularity since the 1970s (IBIS World, 2016), although there are many concerns about the legitimacy and safety of such centers following the death of Joan Rivers, who was undergoing treatment at a similar type of center in Manhattan (Boodman, 2014). These safety concerns may be assuaged by proper certification for the center, as well as highly qualified staff overseen by the hospital’s large surgery staff of twenty surgeons. The supervising staff can assist in preventing the violations of accreditation that led to Joan Rivers’ death (Boodman, 2014).
The paramount mission of the Center for the outpatient surgery is the extension of healthcare opportunities for patients providing surgical treatment in a quick, efficient, and comfortable environment. The reduction of the time and cost of the treatment occurs due to the use of high-tech equipment and minimally invasive techniques (Al-Amin & Housman, 2012). Therefore, the Center for the outpatient surgery is an effective clinical and organizational direction of development for modern medicine and public health. The patient flow should be optimized by minimizing the patient wait time and delays.
Licensing
It goes without saying that any medical activity is a subject to compulsory licensing. To obtain a license, the potential outpatient surgery center should have an appropriate space, a list of necessary medical equipment, and staff members who have obtained valid certificates and licensures (Mercier & Philip, 2009). The consideration of the licensing application takes place within a two-month period. The license applies only to a specific address. The difficulty lies in the fact that each health care service requires a separate license. A specially created registry can: 1) maintain the necessary documentation, 2) registration, 3) temporary disability materials, 4) regulate the flow of patients, 5) receive calls, 6) manage the implementation of hospitalization, and 7) solve transportation issues.
Employees
Employees that are needed per operating room will include one registered nurse (RN), one scrub technician, four pre-operative RNs, four post-operative RNs, two registration clerks, one custodian, two sterilization clerks, and a receptionist with knowledge of medical billing and coding. All employees must have proper training and licenses in their fields (Accreditation Organizations, 2016). The center itself must maintain standards set by the American Association of Accreditation for Ambulatory Surgery Facilities (AAAASF), Healthcare Facilities Accreditation Program (HFAP), and Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC) (Accreditation Organizations, 2016). The AAAASF measures and monitors medical competence. The AAAHC uses peer-based measurements to accredited facilities. HFAP surveys hospitals for quality of care and medical competence (Accreditation Organizations, 2016).
The outpatient center must provide care and have certified and licensed employees able to provide the quality of care needed for these organizations to approve the center for accreditation so that it can be trusted as a safe source of healthcare. Aspects of meeting physician needs on both the surgery center’s performance, and that of the main operational room in the hospital should also be thoroughly considered. In order to avoid any misunderstanding, it is essential to provide investigations and elaborate a uniform standard of health care provision.
Training and Certification
Advances in technology, globalization, and constant organizational transformation are forcing medical centers and their employees to learn and acquire new skills, and developing new business models to work with new technologies. In order not to lose their competitive edge, medical centers have to constantly increase the pace of acquisition of necessary knowledge and skills. Such a need presents the center’s management with a dilemma: On the one hand, employees need more training hours, but in the framework of constant change, the number of hours devoted to training is strictly limited. In this connection, the surgical learning is the best solution to the problem. Using this approach, the maximum efficiency will be achieved through the training of specialists empowering the development and implementation of short and narrowed-focused lessons that are required for surgeons and employees.
The basic idea of surgical training in this business plan is based on the fact that employees do not need comprehensive training, concerning the new technology or program (Maruthappu, Duclos, Lipsitz, Orgill, and Carty, 2015). They will however, need to learn more specific aspects related to the current operation.
The reduced content should be transformed into short courses that are fast to develop and easy to use. Short training programs are more easily integrated into the working schedule of the staff. The attendance of training courses will be increased by the fact that the programs are short and more engaging As a result, the progressive ambulatory surgical center will benefit from optimally trained and certified staff.
Construction
In the planning of a new ambulatory surgical center, construction factors are another important consideration. Constructing a new space will include the cost of construction. In addition, it will also include the need for zoning and bringing the building up-to-code, according to city requirements. The design of the building must include handicap accessibility, since many patients may require the need for wheelchairs before or after surgery. Parking should be ample and easy to access for patients (Boodman, 2014). The design of the outpatient surgery center should follow the overall design of the hospital to provide continuity. All the rooms should be equipped with special chairs and other utilities necessary for the pre-and post-operation periods. The number of operating rooms should be approximately seven, to provide timely surgeries. At the same time, the center should include physician space; such as changing rooms and workspace for paperwork. Staff space, such as changing rooms, should also be included. It is also important to point out that the creation of a break room for relaxation and rest will reduce the stress level of employees. Its design should be performed in a shade of green, as such color contributes to pacification and comfort.
The billing system should be organized appropriately to guarantee the calculating costs of medical service queries to the insurance companies and their processing. Revenue cycle management activities including prior authorizations, calculation of copayment, cost-share and deductibles, and third party payer claim processing will be performed on a dedicated practice management system.
Equipment
The equipment of the center for outpatient surgery will allow for providing virtually the entire spectrum of surgical operations from the day surgery category. In particular, the following equipment is necessary to provide the appropriate treatment:
- Endoscopic equipment for endo-surgery;
- Holmium laser that was previously inaccessible under the conditions of ambulatory operations to treat diseases of the bladder wall using it as a laser scalpel;
- Ultrasound devices in both the operating and observation rooms;
- Medical facilities including apparatus for RFA and EVLT, heart monitor and/or a pulse oximeter, blood pressure monitors, ventilation apparatus, defibrillator, operating table, medical couch;
- Consumables: disposable kits for the operating field, intravenous catheters, gloves, etc.;
- Sterilization equipment;
- Medicines according to the profile of the medical center;
- Anesthesia equipment, equipment tracking, monitors, and others will ensure the high-quality of operations using all the possible kinds of general and local anesthesia. For example, equipment installed for the anesthesiologist and expert classes will include anesthesia-breathing apparatus of Draeger.
Daycare chambers will be equipped with functional beds, Ventilator Puritan Bennett 560, and oxygen concentrators. The installed equipment will allow monitoring the condition of the patient transmitted from the operating room, and to react promptly to any deviation from the norm.
Expenses
The main costs for the implementation of the business plan will relate to equipment and facilities as well as the medicine purchase. When planning costs, the fact that the center will be inactive during the licensing period should also be taken into account. Staff costs related to wages includes the monthly labor costs of personnel and tax rates. Capital expenditures include the following expenses:
- Building of premises for the outpatient surgery center, design, and repair facilities;
- Licensing;
- Equipment, furniture, air-conditioning, and ventilation system.
Fixed costs related to the work of the center will comprise:
- Production costs include cost of materials for the surgery complex, repair costs, clothing for staff;
- Administrative and office expenses such utilities, current expenses for office supplies and materials for office equipment, security alarm);
- The total labor costs;
- Constant marketing costs.
In addition, electricity, thermal energy, and other resources should be considered while planning costs.
Operational Plan
Red Rocks ASC was founded by Healthy Living Hospital, in conjunction with Your Best Health Surgical Services. It is operated and managed by Red Rocks L.L.C. Board of Directors, with the help of many others, as seen in the organization chart.
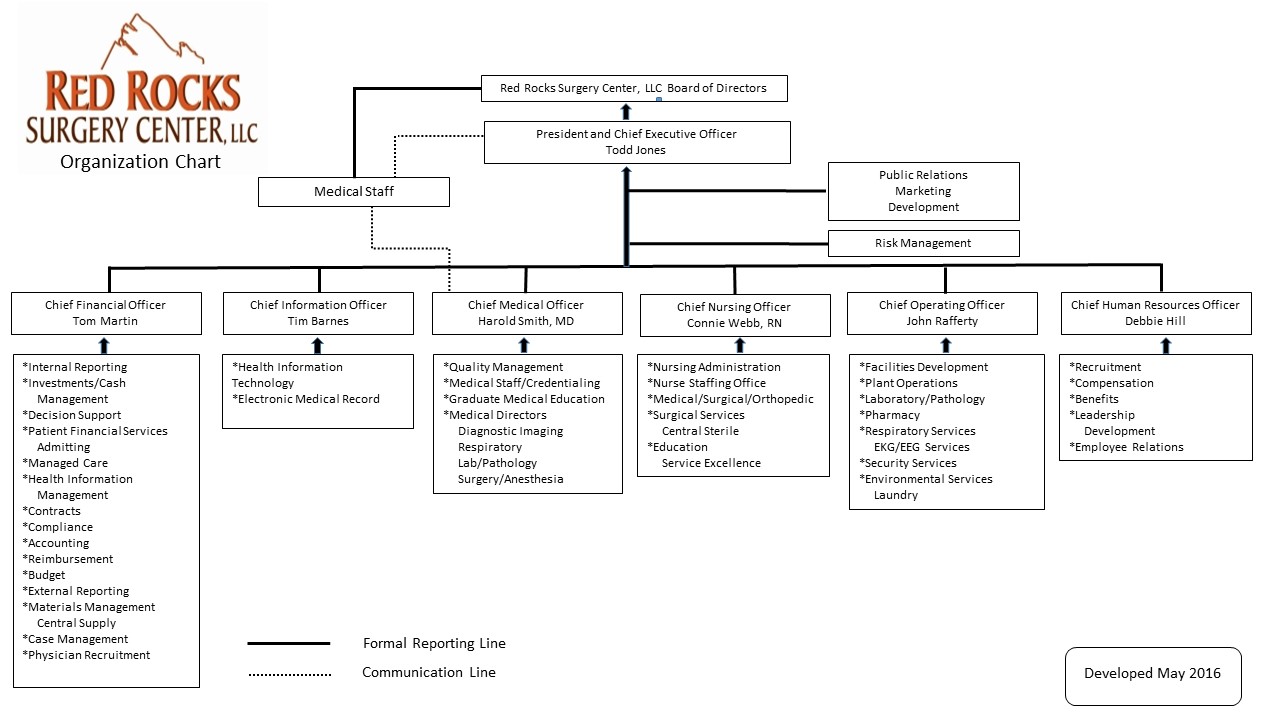
Surgeons hold leases with Red Rocks Ambulatory Surgery Center, L.L.C., which require a renewal process every three years. Red Rocks ASC operates with the guidance of facility policies, which are to be followed strictly by all employees. Facility policies are reviewed by the policy committee every five years or sooner if needed.
All potential employees of Red Rocks ASC must undergo a face-to-face interview process, pass a pre-employment drug screen, be current on all necessary immunizations as outlined in the employee packet, including influenza, and hold an active license (if necessary) in the state of Arizona. Once hired, employees are required to complete a mentorship program through Red Rocks ASC. The mentorship program begins with a minimum of three days of training, with additional days required per specialty field. Training will include an overview of the company, expectations, policy overview, disciplinary action steps, a tour of the facility, and two to six weeks of specialty training with a mentor, depending on the area of interest. Employees must be able to pass a skills interview by the end of the mentorship period or continue with additional training until competency is met. Employees must be able to pass a random drug screen and stay current on necessary immunizations.
In the event of unforeseen circumstances, such as a reduction in patients or employees, Red Rocks ASC will consult with the Board of Directors to make the best decision in order to continue providing patient care. In the event of a decrease in patient load, Red Rocks ASC will make every effort to continue to employ every employee, with the possibility of an employee transfer to Healthy Living Hospital, with every intention to return to Red Rocks ASC when the patient load increases. Red Rocks ASC will make every effort to prevent employee loss due to a decrease in patient load, by actively advertising services and striving to maintain and improve patient satisfaction. In the event that Red Rocks ASC experiences a decrease in employees, advertising efforts will increase in order to maintain employee and patient satisfaction and quality of care. Employee transfers from Healthy Living Hospital will be honored as temporary or permanent employees of Red Rocks ASC.
Red Rocks ASC will strive to maintain high patient satisfaction, with the goal of always improving. Patient satisfaction surveys will be offered during discharge and mailed home to those who wish to complete the surveys at a later date. Results of the survey will be kept in a database to track patient satisfaction and to help develop plans of improvement.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis Template
Situation being analysed: Red Rock’s Ambulatory Surgery Center
Strengths
A significant strength would be the close association and location near to the hospital. Many patients will express misgivings about going to ambulatory surgery centers because they are not ‘real hospitals’, such as the fears expressed by Wendy Salo (Boodman, 2014). Being attached to a hospital with such a reputable staff of surgeons can help ease the concern of some patients. It can also provide more outpatient services with a hospital affiliation (IBIS World, 2016). One of the most important advantages is the unloading of hospital beds by transferring part of routine surgical interventions in terms of health centers, which operates in the hospital structure. At the same time, the organization of early discharge of patients from the hospital with subsequent follow-up care in the clinic would benefit both the center and patients (Merrill & Laur, 2010). All patients will be placed in the superior chambers equipped with modern facilities and are under round-the-clock supervision of qualified medical staff so that they will feel comfortable and calm. Moreover, the postoperative complications in the surgical day hospitals are on average less than 1% (Carey, Burgess, & Young, 2011). The quality of operations in the outpatient surgery center is defined by experienced surgeons and nurses. Comparing volumes within the main operating rooms with those of outpatient environment, one might note the increased capacity of the latter. What is more, one might note such advantages as follows:
- Reduced wait times for patients. Outpatient surgery centers have shorter wait times and fewer budgetary constraints (IBIS World, 2016);
- The release of specialized surgical hospital beds for the treatment of clinically complex patients;
- The same surgeon holds the complete continuity of the examination and treatment of patients; preoperative preparation, surgery, postoperative treatment until the patient’s hospital discharge;
- Patients stay at home in habitual environment (Grisel & Arjmand, 2009);
- Active lifestyle contributes to the rapid recovery;
- Reducing the probability of in-hospital infections and thromboembolic complications in patients;
- Significant financial savings (Ambulatory Surgery Center Association, n.d.).
Weaknesses
A significant weakness is the ambulatory surgery center’s affiliation with a hospital. While this can be viewed as strength, it doubles as a weakness. Both the ambulatory surgical center and the surgical services department of the hospital have goals based on volume and revenue. In addition, competition from other local ambulatory surgical centers could potentially reduce the volume of procedures, thereby reducing revenue (Courtemanche & Plotzke, 2010). Another weakness is the need for the center to be constructed. Construction costs, zoning, and time are all involved in the construction process, which can be a weakness for the center. Lastly, this new ASC will take time to develop a presence and reputation within the community in order to gain both respect and acknowledgment as its own entity rather than being known as the hospital’s surgical center.
Opportunities
The content of operations of the ambulatory surgery center is determined by the variety of forms of its activity:
- The outpatient center is part of the overall hospital, but it will be its own separate entity (Pickles, 2015). This means that the center will have its own financial statements. It also requires a deep understanding of the regional health care delivery system in order to provide legally and ethically sound care (Pickles, 2015).
- Selection of patients with surgical diseases among the population including the workers and employees of industrial enterprises, institutions, and other organizations;
- Implementation of permanent relationships with the clinics and dispensaries;
- Clinical diagnostic study of supervised patients using modern methods and equipment;
- Consultative reception of patients of surgical clinics and dispensaries for the selection of patients requiring surgical treatment; definition of the indications for surgery, preoperative examination, the scope of the operation, and capabilities;
- Diagnostic use of invasive techniques, performance of operations according to the approved list, the observation of patients operated on in the next few hours after surgery in the recovery room of the hospital, day surgery follow-up treatment at home;
- Comprehensive treatment of patients with surgical diseases including drug and infusion treatment, the use of extended wear bandages, physiotherapy, plasmapheresis, medication blockade, and the necessary range of rehabilitation measures (Starr, 2012);
- Organization of follow-up care for operated patients for a timely implementation of the necessary therapeutic and preventive measures to prevent disability and reduce its period. Research and comprehensive assessment of the short- and long-term results of the surgical treatment and the development of evidence-based recommendations.
- Further training of surgeons and nursing, training of graduates of medical institutions.
Threats
The main threats include competition with other hospitals and other centers. This can especially be an issue with the large amount of distrust people feel for outpatient surgery centers (Boodman, 2014). Competing with other organizations can entail providing the best care possible. It can also involve providing a more comfortable and compassionate environment that will be memorable to patients in their difficult and often scary times of receiving surgery.
Initial capital requirements are one of the biggest threats facing ASCs (IBIS World, 2016). Being part of a hospital can help this center establish the capital needed to get started. Still, it will be a major financial endeavor. One of the other project risks is associated with possible changes in the financial situation in the country, due to the influence of internal or external factors. One more threat category may include a possible increase in costs and timing on the establishment of the center’s services or a possible reduction or increase in prices for services.
The probable management risks are related primarily to the inability of managers or a team to implement the project objectives and to achieve goals set in the business plan. The reduction of this type of risk is largely determined by the effective selection of personnel. To reduce this type of risk, it is possible to use the potential of employment agency as well as the use of the resource business consultants, who have extensive experience in implementing projects.
Other risks include all kinds of risks of natural disasters, other force majeure related to property damage and clients’ lawsuits in connection with human error. The above risks are easily minimized through insurance mechanisms. Based on the foregoing, all of the project risks can be regarded as moderate that is quite acceptable for the successful implementation of this business plan. Finally, taking into account all the above issues, it seems possible to implement the business plan within half a year.
Financial Analysis
Underlying Assumptions
The Collaborative Learning Community (CLC) Red Team has based this financial analysis on the following:
- Red Rocks Ambulatory Surgery Center, L.L.C. is expected to yield an annual revenue growth rate between 7%-8% per year. With the recent changes to Medicare reimbursement, this rate may be slightly lower than expected, although, the center does expect yearly revenue growth (Koenig, Doherty, Dreyfus, & Xanthopoulos, 2009, p. 22).
- Due to the collaboration of Healthy Living Hospital and Your Best Health Surgical Services, this entity will have the financial backing to proceed with the addition of the outpatient surgical center that will be constructed in a new space attached to the hospital.
Sensitivity Analysis
The CLC Red Team understands that due to Medicare reimbursement rates that there may exist a slowing of the expected yearly revenue growth, but it is not deterred by this because it recognizes that the need for surgical procedures will not decline due to changes in the economy. In addition, there are those individuals who are covered by private insurance who will need Red Rocks ASC’s services: therefore, the CLC cannot find a reason as to why this organization will not enjoy financial growth.
Source of Funds

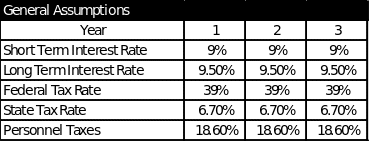
General Assumptions
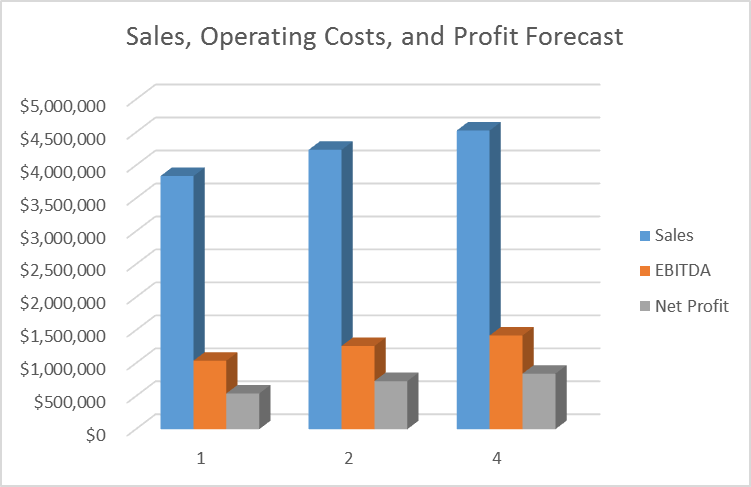
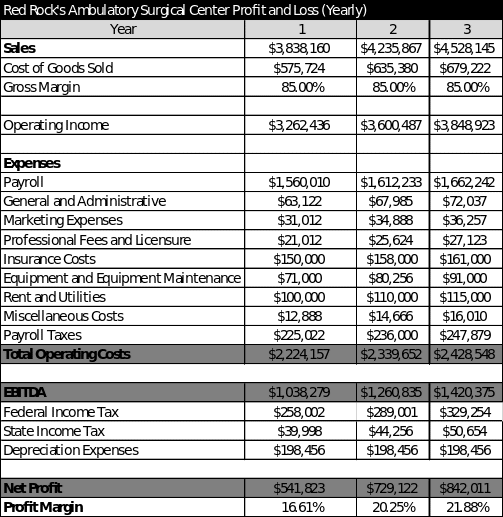
Profit and Loss Statements
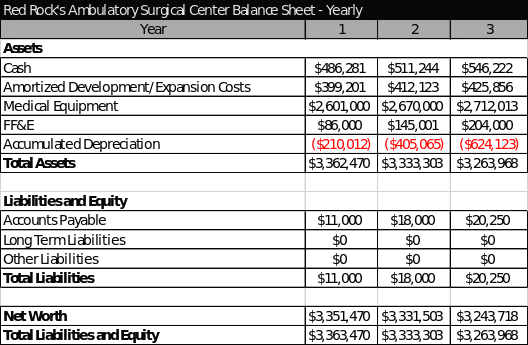
Balance Sheet
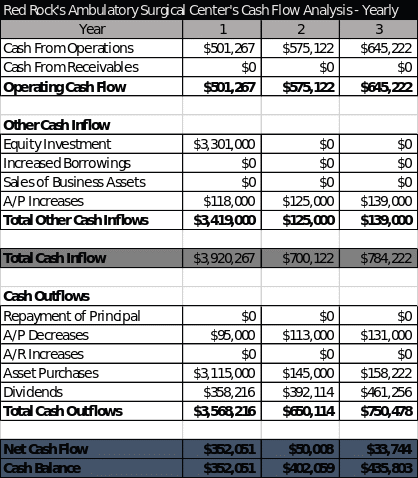
Cash Flow Analysis
Breakeven Analysis
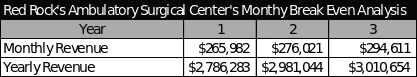
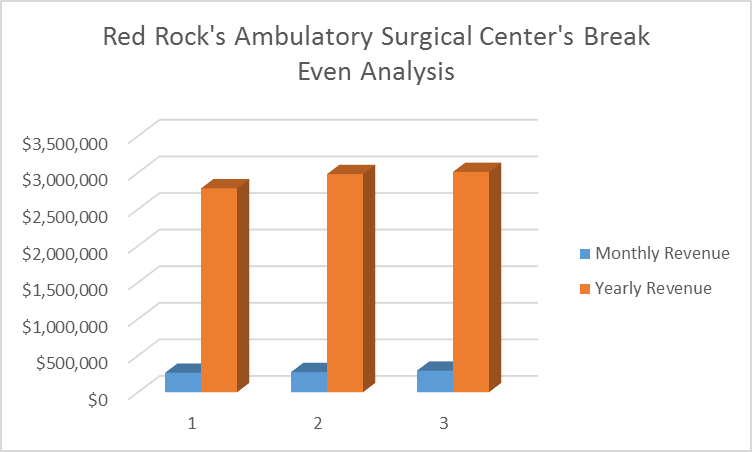
Appendices
Ambulatory Surgery Preliminary Plan
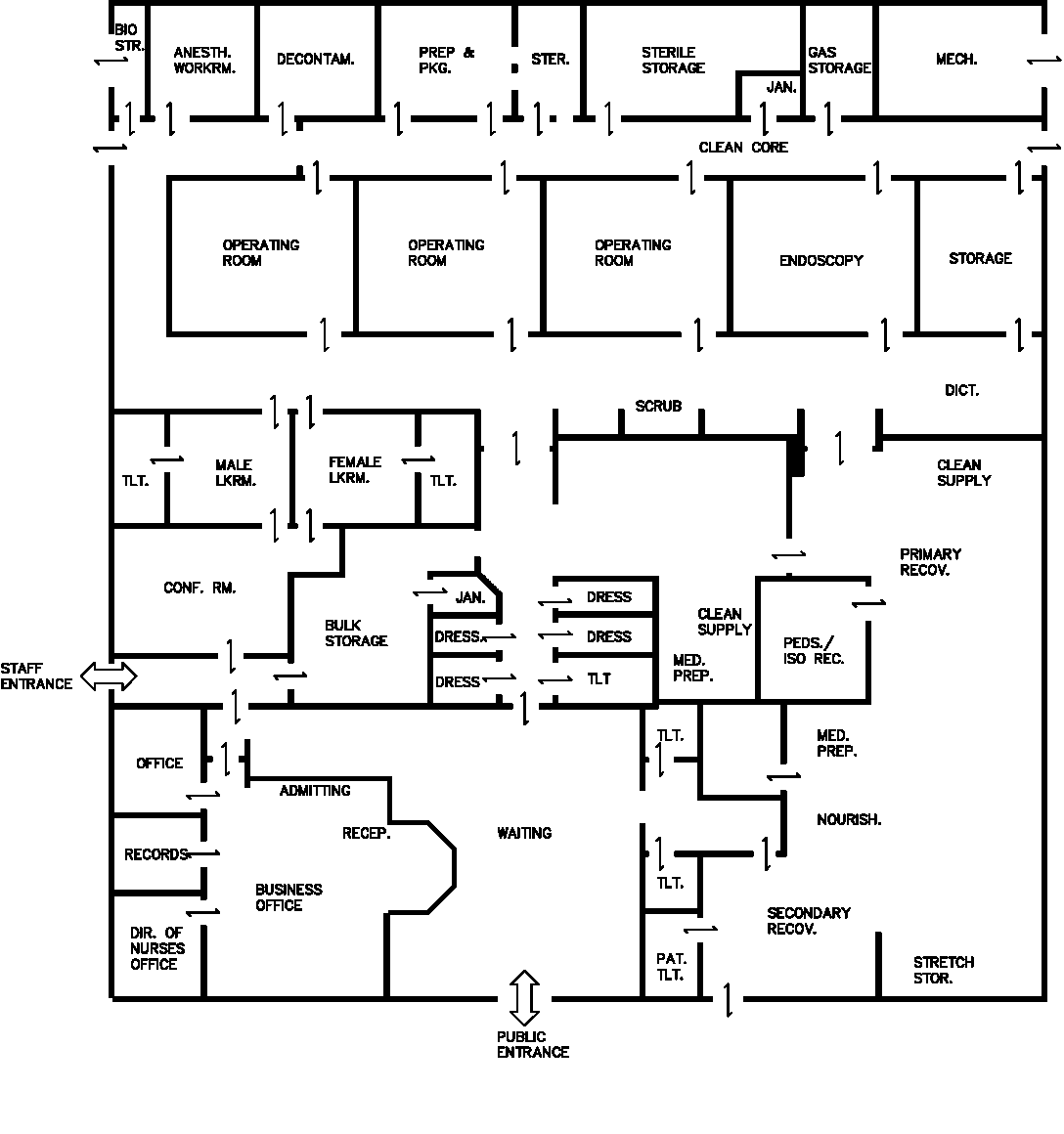
Peripheral Core
Pre-op Holding
Storage
The preliminary plan clarifies the ambulatory surgery unit space requirements by showing the location of all the fixed walls and open areas and identifies entrances, exits, and exact traffic patterns.
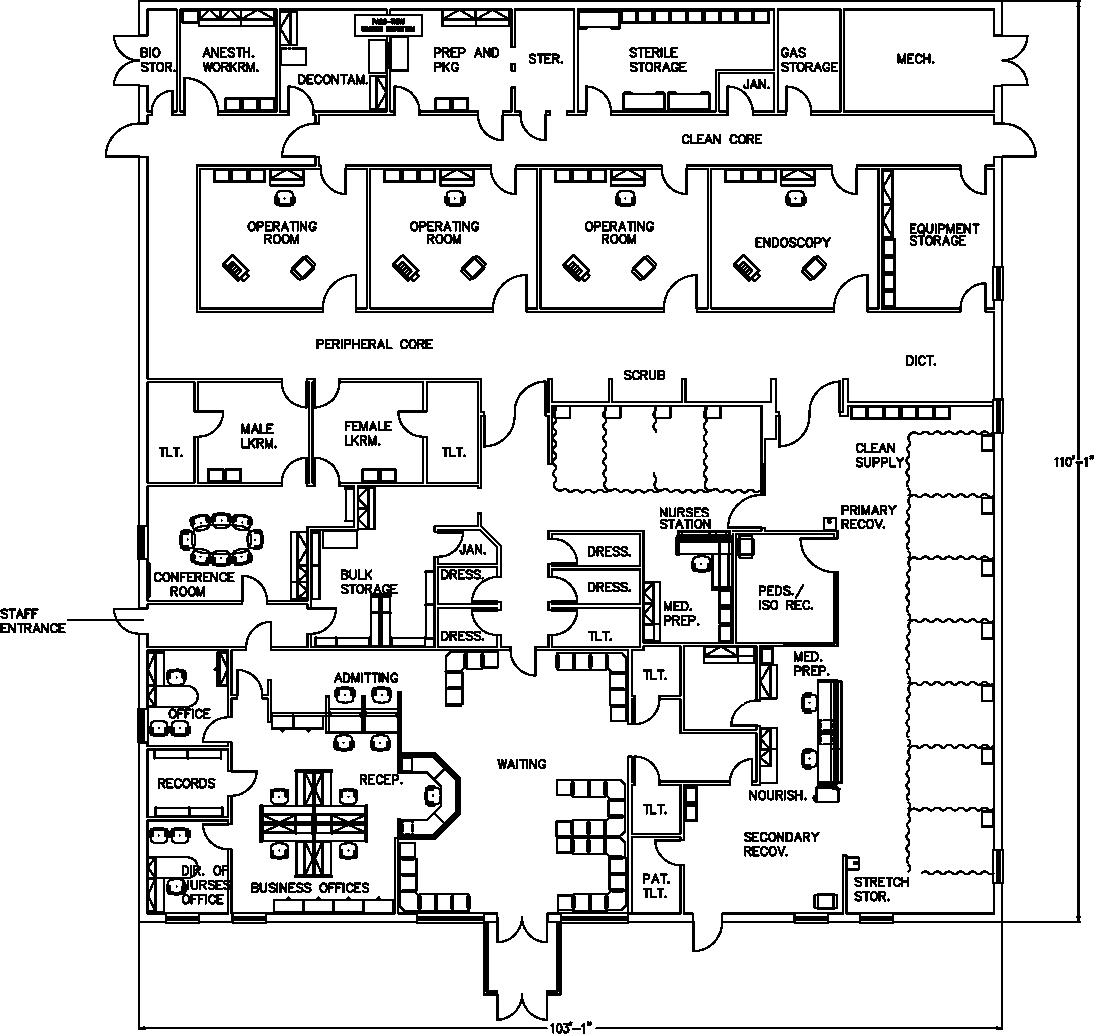
Ambulatory Surgery Schematic Plan
The schematic plan shows all of the specific movable modular casework, modularfurniture systems, and materials handling components appropriate for a typical ambulatory surgery unit.
References
Accreditation Organizations. (2016). Ambulatory Surgery Center Association. Web.
Al-Amin, M., & Housman, M. (2012). Ambulatory surgery center and general hospital competition. Health Care Management Review, 37(3), 223-234.
Ambulatory Surgery Center Association. (n.d.). ASCs: A positive trend in health care. Web.
Boodman, S.A (2014). Popularity of ambulatory surgery centers leads to questions about safety. Kaiser Health News. Web.
Carey, K., Burgess, J. F., & Young, G. J. (2011). Hospital competition and financial performance: The effects of ambulatory surgery centers. Health Economics, 20(5), 571-581.
Courtemanche, C., & Plotzke, M. (2010). Does competition from ambulatory surgical centers affect hospital surgical output? Journal of Health Economics, 29(5), 765-773.
Grisel, J., & Arjmand, E. (2009). Comparing quality at an ambulatory surgery center and a hospital-based facility: Preliminary findings. Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, 141(6), 701-709.
IBIS World. (2016). Ambulatory surgery centers in the US: Market research report. Web.
Koenig, L., Doherty, J., Dreyfus, J., & Xanthopoulos, J. (2009). An analysis of recent growth of ambulatory surgical centers. ASC Coalition. Web.
Maruthappu, M., Duclos, A., Lipsitz, S. R., Orgill, D., & Carty, M. J. (2015). Surgical learning curves and operative efficiency: A cross-specialty observational study. BMJ Open, 5(1), 1-7.
Mercier, D., & Philip, M. (2009). Is Your Ambulatory Surgery Center Licensed, Accredited or Certified? ASA Monitor, 72(8), 10-14.
Merrill, D. G., & Laur, J. J. (2010). Management by outcomes: Efficiency and operational success in the ambulatory surgery center. Anesthesiology Clinics, 28(2), 329-351.
Pickles, V. (2015). Strategic planning for your surgery center. Ophthalmology Management. Web.
Starr, C. (2012). Ambulatory surgical centers: Good for you and your patients. Medscape. Web.
SWOT analysis. Businessballs.com. Web.