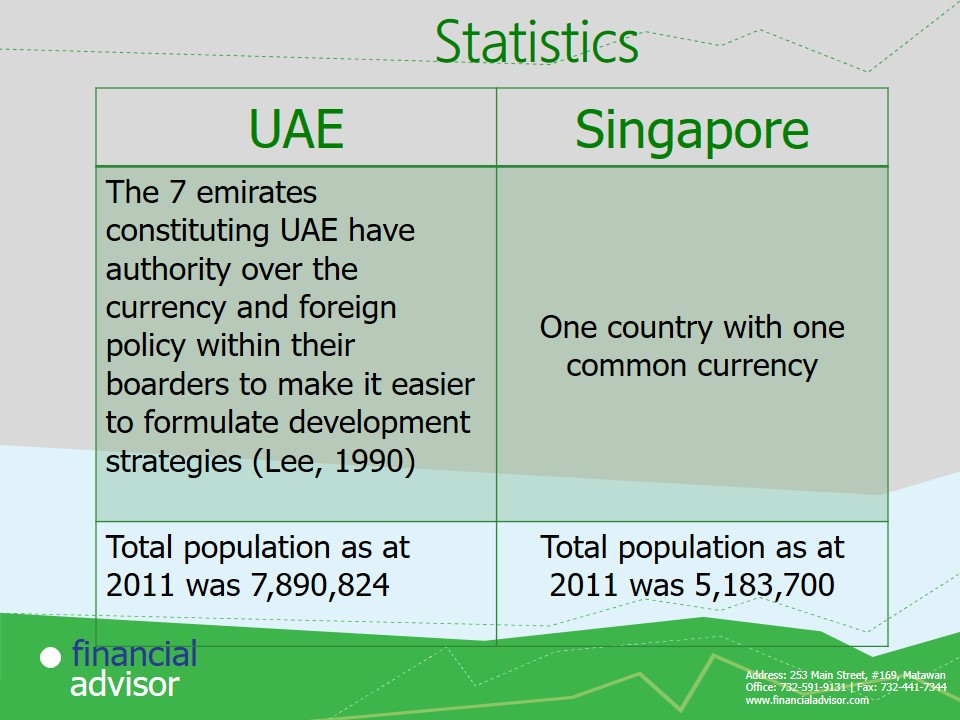
Statistics
The population statistics are essential since they influence the level of deposits retained with the bank and the loans issued.
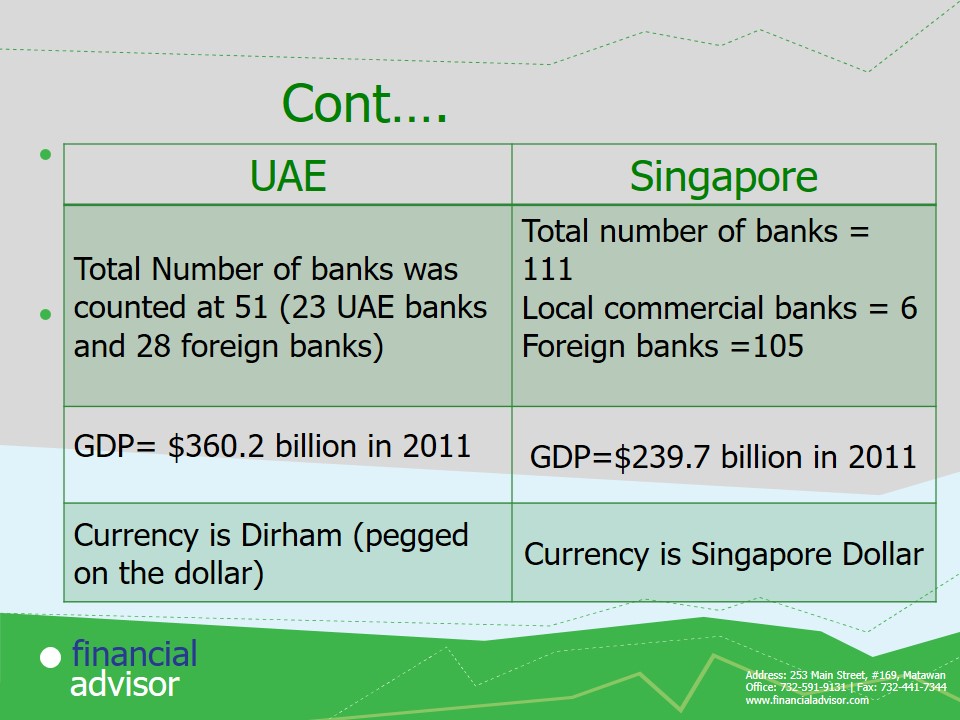
Pegging a the Dirham against the dollar boost stability of the currency. This is meant to improve investor confidence. However, it transfers the economic waves of the dollar to the dirham in case of a crisis and limits the freedom of the central bank in regulating the currency.
Oil is the greatest contributor to UAE’s GDP.
Singapore main contributor is international trade. Its is the most open country to foreign business.
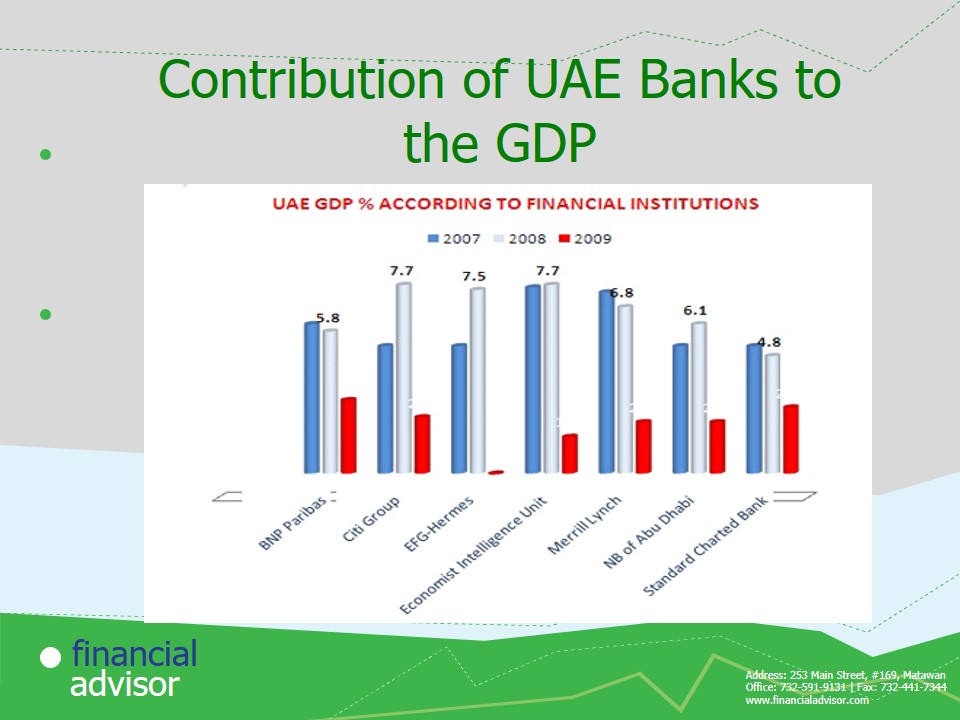
Contribution of UAE Banks to the GDP
The largest financial contributor to the GDP was:
- 2007: Economist Intelligence Unit with 7.7%.
- 2008: Citi Group and Economist Intelligence unit , each with 7.7%.
- 2009: BNP paribas and Standard Chartered Bank.
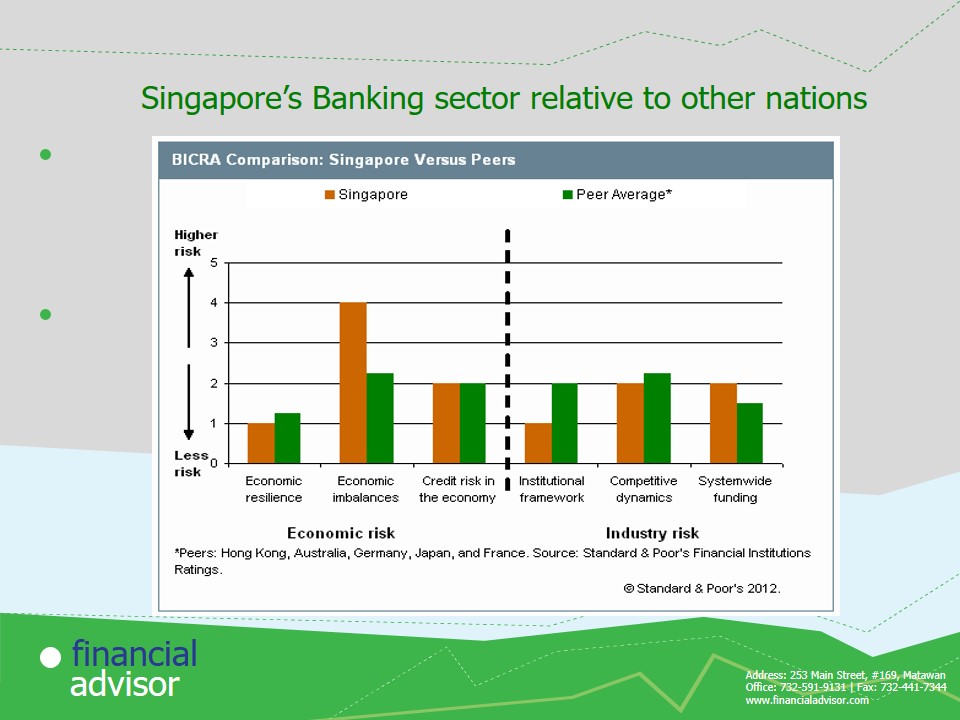
Singapore’s Banking sector relative to other nations
In the year 2011, Singapore’s banking economic resilience was similar to that of other nations.. However the economic imbalances were higher.
Economic resilience refers to one’s ability to utilize the available resources for their economic development.
Economic imbalances refers to instability in the economy in general.
Roles of UAE central bank
- Ensure stability and convertibility of currency into other currencies.
- Balance economic development through cerdit balancing.
- Monitor the banking industry.
- Play the role of the government’s bank as prescribed within the law.
- Offer advisory services to the government on monetary matters.
- Secure government reserves of gold and foreign currencies.
- Play the role of bank of banks in the country.
Stability refers to the ability to maintain a steady figure in the international markets. It is regulated through inflation adjustment measures.
Monitoring banking industry entails dictating interest base rate, issuing policies on deposit held with it by the banks.
Role of bank of banks: other banks bank with it just as individuals bank with it.
It is vital to note that all financials institutions are under the watchful eye of the central bank.

Government policies
- The Central bank issues and manages currency in the counties.
- Licensing is facilitated by the Local Licensing Authority in consultation with the Central Bank of UAE.
- Strict measures are instituted to those found guilty of money laundering in accordance to the Money Laundering Act.
- Federal law allows financial institutions to share information to minimize fraud.
- The Act restricts any transaction from the following illegal activities; drug trafficking, kidnapping, breach of contract, firearm dealers, bribery, embezzlement, environmental violation, fraud etc.
- The maximum amount that can be allowed into the country without declaration is AED 40,000.
- All transactions above AED 2,000 have to be verified with proper identification and be well documented (Ibp Usa, 2009).
Money laundering refers to the illegal operation of individuals as banks.
Sharing of information on fraud minimizes incidences of fraud.
These regulations are meant to boost the level of security as relates to financial matters.


Banking regulations in UAE (Goldsworth et al.,2007)
- Rules governing the banking sector are set by the Central Bank of UAE.
- Categories of institutions and their roles:
- Commercial Banks- receives money from the clients, grants loans, market and sale different investment products and services.
- Investment Banks- provide long term financing, issue financial instruments, manage investment portfolios.
- Financial establishments- give loans and lease of equipment and machinery.
- Financial intermediaries- act as brokers, sell both local and foreign shares or other financial instruments.
- Monetary intermediaries- exchange money.
- Investment consultants- advice clients on the investment strategies.
- Sets the base rate for interest on loans. Was 1.0% in 2011.
Rules set include:
- the ceiling for the deposits by the bank.
- the interest rates on loans issued by the banks.
- the minimum capital requirements for incorporation as a company.
Commercial banks are expected to determine their interest for loans above this margin. For instance a commercial bank could issue loans at 5% p.a.
Regulation of the interest rates sways the influx of money in the economy.
When the rate is high, few people take loans and money supply in the economy goes down. People have less to spend and therefore demand for goods goes down resulting in a drop in the pricing. This way the central bank regulate inflation.

Regulatory capital in UAE
- Commercial and Investment banks must have a minimum paid capital.
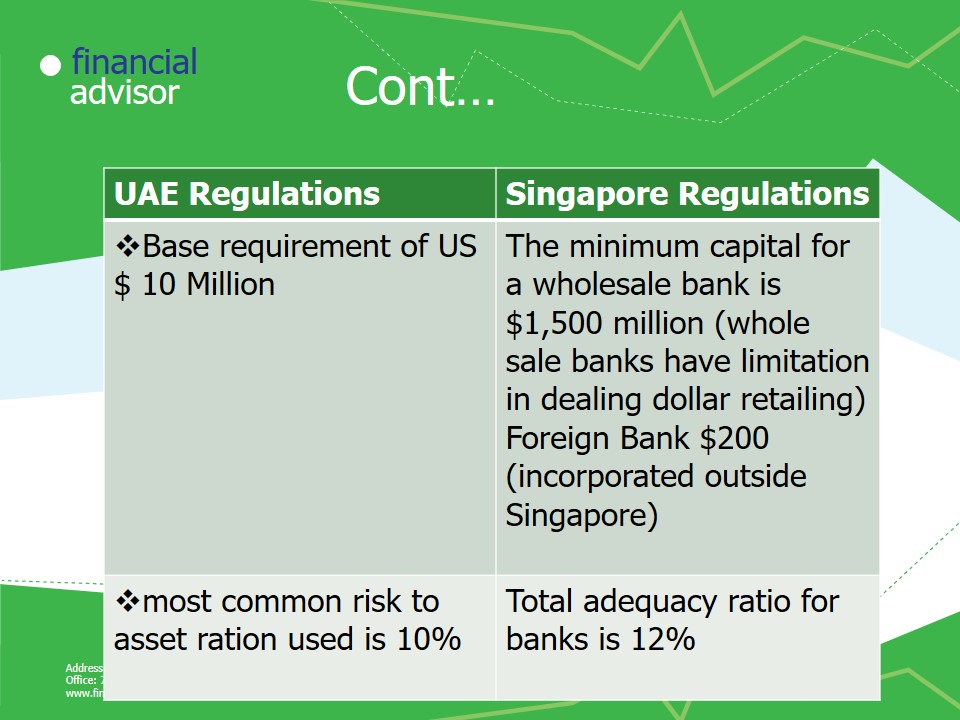
- Base requirement of US $ 10 Million.
- Capital adequacy of the banks are established using the risk asset ratio as shown below most common used is 10%.
Risk ratio refer to the assets of the bank expressed as a ratio to its debt or credit.

Risk to asset proportion
- Assets of the bank.
- Expected risks.
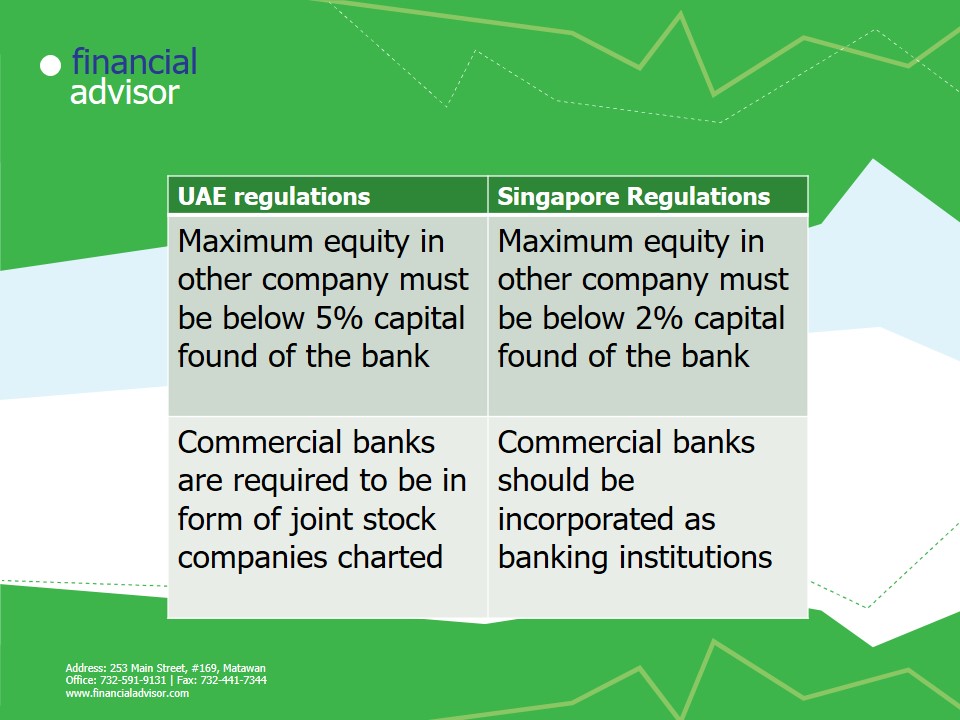
All commercial banks are required to be in form of joint stock companies charted by decrees law (Tan, 2002).
Commercial bank capital is minimum of $40 million and the same for its branches.
Financial institutions are expected to increase their assets in order to minimize their risks.
Roles of Monetary Authority of Singapore(MAS)
- Acts as the Central Bank of Singapore:
- formulates monetary policies;
- issues currency;
- oversees payment systems;
- Acts as the bank and financial agent of the government.
- Supervises financial systems and ensure financial stability.
- Responsible for the official foreign reserves.
- Development of Singapore into an international financial centre.
Note:
Most of the banks in Singapore are offshore banks.
Payments systems include:
- MAS Electronic Payment System (MEPS+).
- MAS’ real-time gross settlement system.
- Continuous Linked Settlement (CLS) System.
- This is a global system.
- Singapore Automated Clearing House.
The SACH is an association to establish, manage and administer clearing services and facilities for cheques as well as debit and credit items of its members.

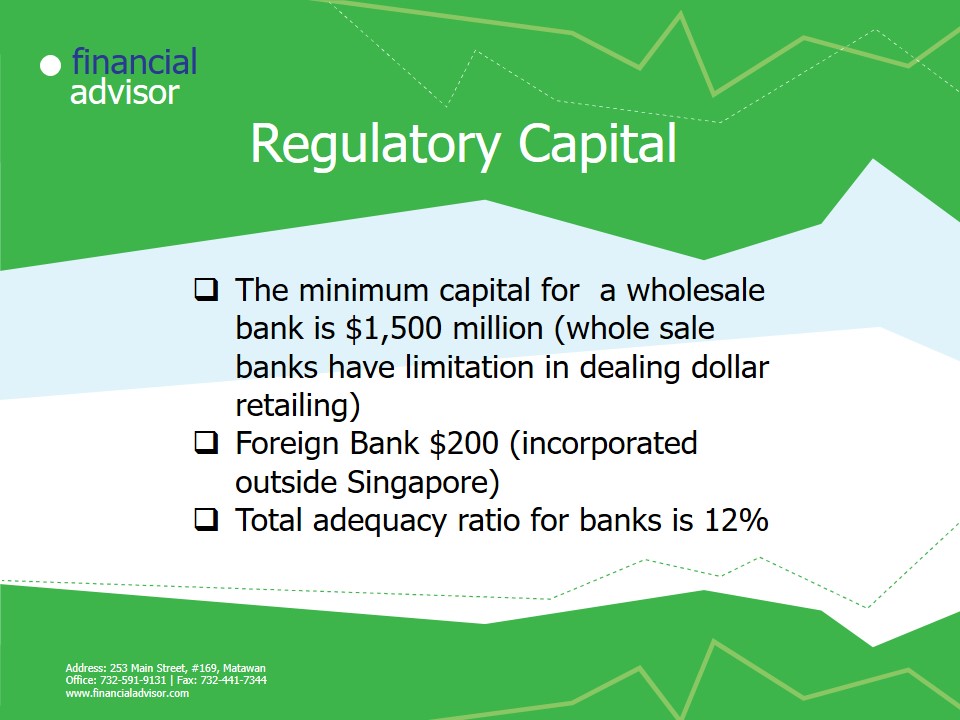
Regulatory Capital in Singapore
- The minimum capital for a wholesale bank is $1,500 million (whole sale banks have limitation in dealing dollar retailing).
- Foreign Bank $200 (incorporated outside Singapore).
- Total adequacy ratio for banks is 12%.
Regulations in Singapore (Tan, 2005)
- Secrecy of information (no information about the account holders is disclosed).
- No advertising or offer to make a deposit.
- Must maintain adequate amount of bad and doubtful debts before announcement of profit.
- Cash balances not more than 30% of their deposits.
- Bank must have a well detailed risk control measure in its business activities it undertakes.
- For an institution a license is mandatory and should operate on activities indicated on the license.
- Maximum equity in other company must be below 2% capital found of the bank.
- Maximum rights in property less than 20% capital found (International Business Publications, 2007).
- Any change of location by a bank must be approved by MAS.
Maintenance of records is meant to ensure the bank does not overstate its assets and compromise its finacial position in future.
This ensures that there are sufficient funds for the customer to withdraw. If the public realized a given bank does not have sufficient cash or is on the verge of collapse, they might all the demand their money and throw the economy into a turmoil.
Ensures the bank has much of the cash their funds in liquid form in case of economic down turn in future.
The change in location notification, helps the bank keep track of the financial institution. All for economic safety.



Risk Control
- The banks are required to establish an account in Singapore to cover risk that may accrue in banking industry (Venardos, 2010).
- Banking investment restricted to certain amount of company capital.
- Capital adequacy must not be below 12%.
- Clear placement of banks balance sheet on each branch.

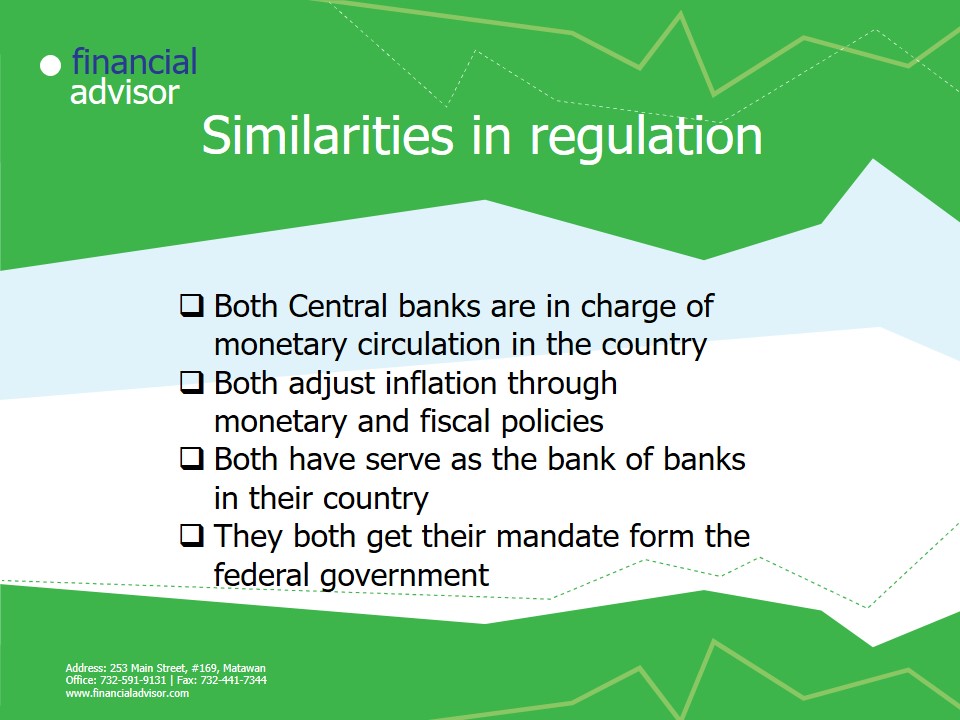
Similarities in regulation
- Both Central banks are in charge of monetary circulation in the country.
- Both adjust inflation through monetary and fiscal policies.
- Both have serve as the bank of banks in their country.
- They both get their mandate form the federal government.
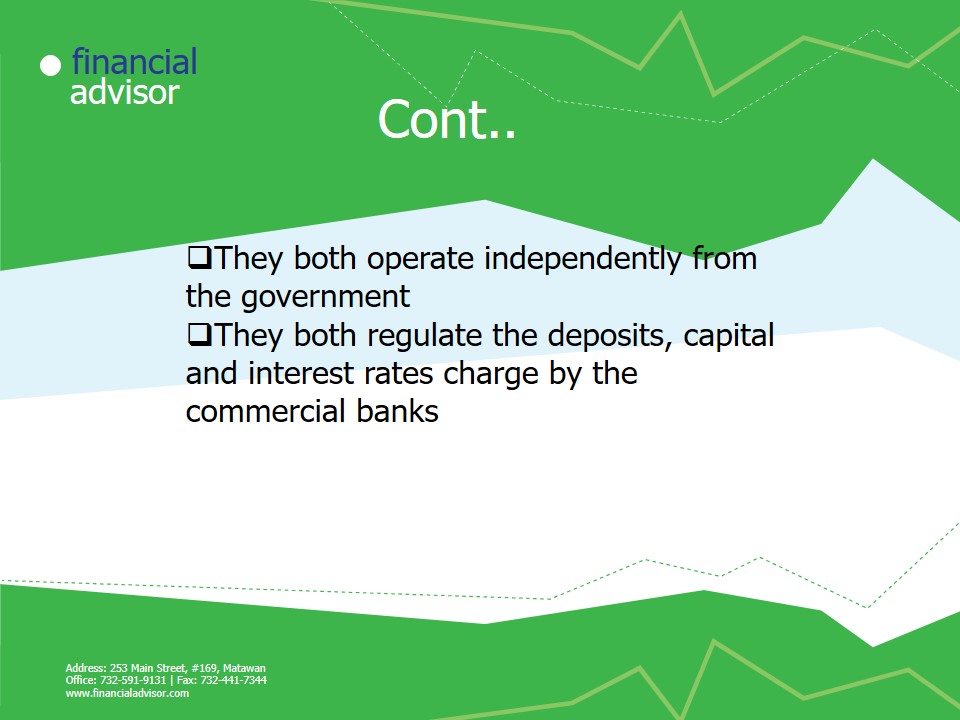
- They both operate independently from the government.
- They both regulate the deposits, capital and interest rates charge by the commercial banks.
Central banks are also referred to as lenders of last resort since they can bail out financial institutions in case of a crisis. This fall under the bank of banks.
Differences
- Roles are similar but mostly differ in figures.
- Differences are summarized in the table below.
References
Goldsworth, J., Kalin, C., & Muller, W. (2007). Anti-Money Laundering: International law and Practice. New York: John Wiley &Sons.
Ibp USa. (2009). Singapore Customs, Trade Regulations and Procedures. Singapore: Int’l Business Publications.
International Business Publications. (2007). Singapore Business Law and Handbook. New York: Int’l Business Publications.
International Publications Staff. (2001). Dubai Offshore Investment and Business Guide. Dhubai: Int’l Business Publications.
Lee, S. (1990). The monetary and Banking Development of Singapore and Malaysia. Arts Link: NUS Press.
Singh, S. (2009). Bank Regulations. New York: Discovery Publishing House.
Tan, C. (2002). Singapore Financial and Business Sourcebook. Arts Link: NUS Press.
Tan, C. (2005). Financial markets and institutions in Singapore. Arts Link: NUS Press.
Venardos, A. (2010). Current Issues in Islamic Banking and Finance: Resilience and Stability in the Present System. Boston: World Scientific.