Problem Statement
- The national debt is growing at an alarming rate.
- Deficit predicted to be over $17 trillion in a decade (Elmendorf, 2011).
- Research is necessary to determine cause of national debt and provide recommendations to alleviate the problem.
Research will determine whether National Debt is growing due to:
- High levels of deficit spending.
- Federal government continues to borrow money from foreign countries.
- Many baby boomers retiring which increases government spending on social security.


Argument: the Con’s
- Previous levels sales of notes, treasury bills, and bonds for every foreign country not examined.
- Federal government decision to borrow from foreign countries and sale of the bills and bonds not determined.
- Study is limited to levels of deficit spending, continuous borrowing, and expenditure on social security.

Argument: the Pro’s
- The study sheds light on the consequences of high deficit levels, continuous borrowing, and high expenditure on social security.
- The Study gives insight into why the national debt has risen over the decade.

Hypothesis/Introduction
H1: High levels of deficit spending have no direct influence on increased growth of the national debt.
H2: Increased federal government borrowing from foreign countries has negative effect on the national debt.
H3: High rate of retirement of baby boomers increases social security expenditure and hence the national debt.

Literature Review
Theoretical Studies
Dynamic economy theory: government utilizes budget deficits and surpluses to cushion taxpayers from a rapid increase in tax rates.
The theory protects citizens from incurring extra tax burden that the government may impose due to budget deficits (Battaglini & Coate, 2007).
Federal Reserve
- Policies and laws allow the Congress to recommend borrowing of money, to alleviate budget deficits.
- When a government is operating under deficit, it borrows money from treasury.
- These allows it to operate under deficit budget.
- The US is engaged in massive borrowing to stimulate economic growth and finance social programs.
Social Security
- Baby boomers consume significant part of Social Security funds: of the 50 million Social Security beneficiaries, 64% are retired workers.
- This beneficiaries are projected to increase over the decade.
- Social Security benefits are going to increase from current 4.8% to 6% of GDP by 2035.
- Projections indicate that current fiscal policy of the United States is unsustainable.
- The United States national debt has doubled within 8.
- By 2020, the rising health care costs, and population aging will place an extra burden on the budget.
- The government needs to use a new measure of inflation to decrease mandatory spending by approximately $6 billion by 2016 (Elmendorf, 2011).
- Baby boomers are causing economic changes via Social Security.
- From 1950s to 2008, budgetary allocation of funds to Social Security, Medicaid and Medicare increased significantly by 55.9%.
- Exponential increase in interest payments means that national debt because of Social Security benefits will increase (Clemmitt, 2008).
- Borrowing by the US is not lucrative since it is economically unsustainable.
- In 2009 treasury borrowed 3 trillion, which formed about 10% of GDP, and increase the national debt to form 50% of GDP.
- Government needs to increase taxes and reduce expenditures to cope with increasing national debt.






Methodology
Survey was conducted by collecting secondary data from Treasury, Social Security, and Congress Budget Office (CBO).
Quantitative research used to ascertain the extent to which deficit spending, borrowing of money and retirement of baby boomers influence national budget.
Primary sources such as Treasury, Social Security, and CBO provided firsthand data.

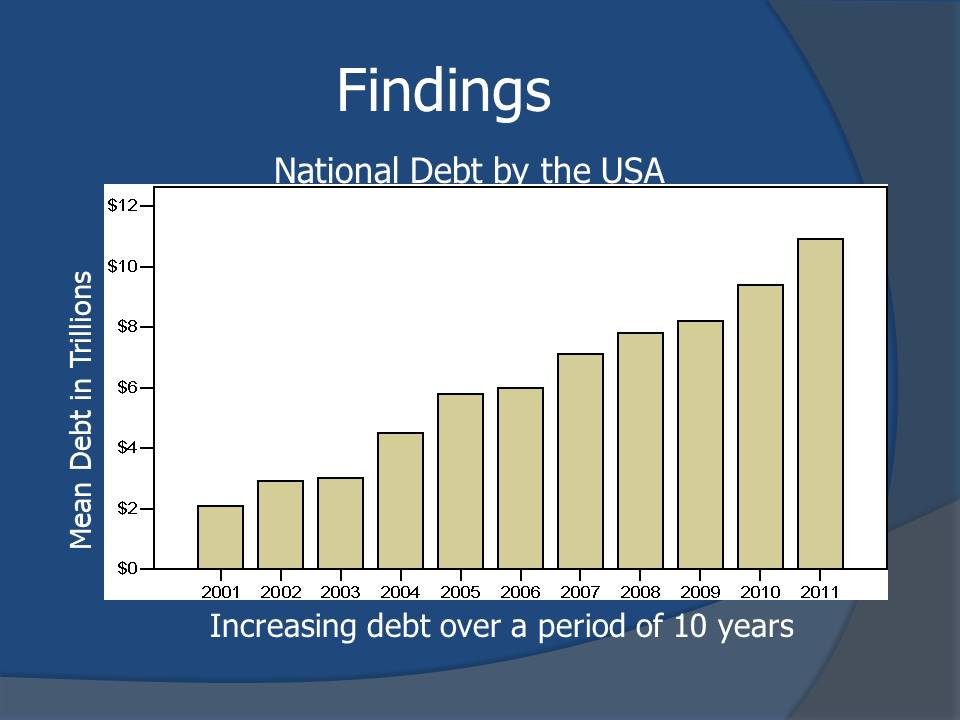
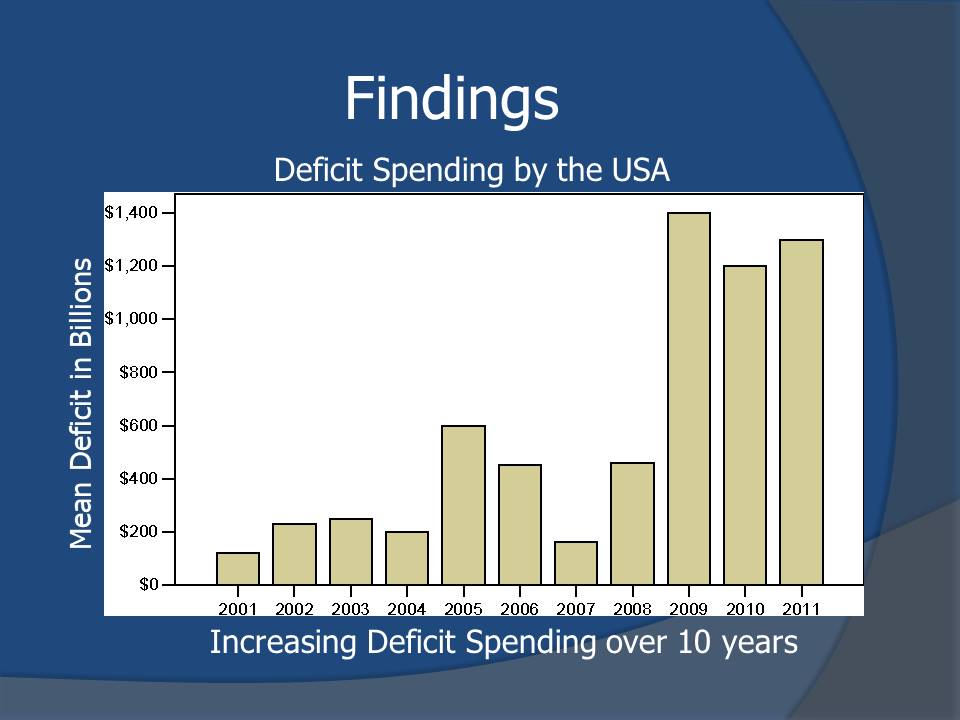
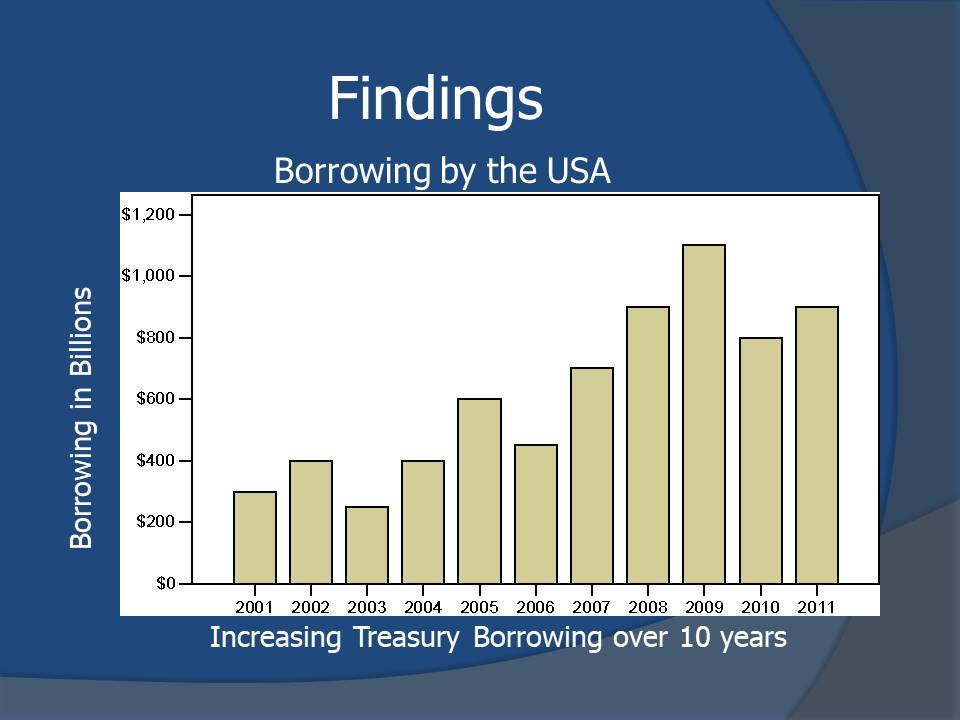
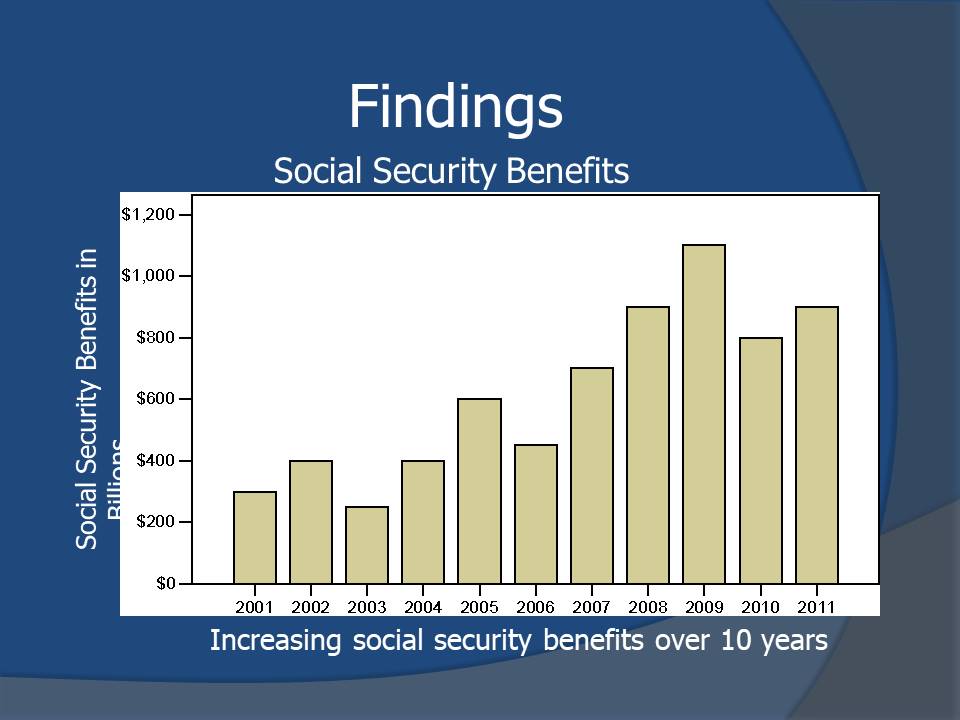
Findings
- There is a correlation between deficit spending and national debt.
- Deficit spending contributed significantly to the national debt in the last 10 years.
- Borrowing has been cumulatively contributing to increase in national debt in previous 10 years.
- The government has been concomitantly increasing its borrowing rates to enable it to perform its obligations.
- Social Security borrows funds from government to compensate for increasing beneficiaries.
- Baby boomers are therefore responsible for drastic increase in national debt.



Conclusion
Research has demonstrated that Hypothesis 2 and Hypothesis 3 are valid:
- Increased federal government borrowing from foreign countries has negative effect on the national debt.
- The retirement of baby boomers has and will continue to increase the national debt.
- The national debt has been increasing proportionately as Social Security benefits.
- Borrowing of funds to cater for deficits have been responsible for the alarming increase in the national debt.
- High numbers of retiring baby boomers are to blame for skyrocketing benefits and national debt.
- Government needs to formulate stringent policies and laws to alleviate increasing national debt.


References
Battaglini, M., & Coate, S. (2007). A Dynamic Theory of Public Spending, Taxation and Debt. Department of Economics; Princeton University, 1-58.
Clemmitt, M. (2008). The National Debt. Congressional Quarterly Researcher, 18(40), 937-960.
Elmendorf, D. (2011). Reducing the Deficit: Spending and Revenue Options. Congressional Budget Office, 1-240.