Executive Summary
Human resource is a solitary basis of competitive benefit and is mostly significant in the competitive milieu, which is advancing quickly. By way of facilitating the growth of particular firm capabilities, human resource might contribute to the continued firm’s competitive benefit.
Indeed, the formation of the links amid practicing human resource strategy, and the general business deliberate goals is the main concern of Rotana strategic human resource administration.
The Rotana HR executives are capable of planning programmes because of the relationship between them and the organization employees. This will give rise to the accomplishment of the improved operational outcomes accruing from greater presentation in the corporation.
In this context, it is possible to delineate the tactical human resource administration after accentuating the significance of human resources as a basis of competitive benefit.
Introduction
The businesses environs are swiftly changing to bring some variations characterized by specific economic phenomena. Among these phenomena, there are product marketplace rivalries that are continually cumulative, changing financier and consumer demands, as well as globalization. Thus, most organizations including Rotana necessitate for frequent development in performance to compete effectively in this competitive market setting.
Actually, market presentation can be upgraded through improving the swiftness and efficiency in flea market, innovative procedures and products, increasing quality, and decreasing the costs of manufactured goods. The present day firms recognize human resource personnel as the utmost essential sources in the corporations’ structural composition.
Several other sources of competitive advantage are becoming less powerful as they were initially. This accrues from the increasing significance attached to the employees, and the manner in which competitive advantage is executed by organizations.
To think through policy and human resource administrative issues for the growth of diverse HR reference framework, it is essential to be aware that there is a change in the source of competitive gain (Becker and Huselid 899). In fact, the provision of competitive gain can still be realized via economies of scale, protected bazaars, technological procedures, and products, which exist as the traditional basis for success.
However, for the sustainability of organizations like Rotana, the HR administration remains a vital aspect. The function of human resource administration materializes to be moving up the chain of command.
This is in line with the understanding that organizations find human resources very important. This paper highlights and discuses the significances of HR management and the manner in which these practices add value in an organization (Björkman and Lervik 325).
Strategic Human Resource Management
The acquisition as well as retention of well-motivated, dedicated, and experienced labor force is the main intention of the human resource administration in an organization. In fact, this brings about strides in developing and enhancing individuals’ intrinsic aptitudes besides assessing and satisfying their future wants.
Moreover, the delivery of endless growth and learning opportunities support their employability, potential, and involvement (Boxall 267). The business requirements related to training and management development actions, selection, and staffing structural processes are also involved. Conversely, a fresh relative change in the meadow of human resource administration is represented with SHRM.
Concerning the firm’s presentation, the schemes of human resource administration play a significant role as far as strategic human resource management is concerned. These systems emphasizes mainly on the orientation of human resource as a way of attaining competitive benefit.
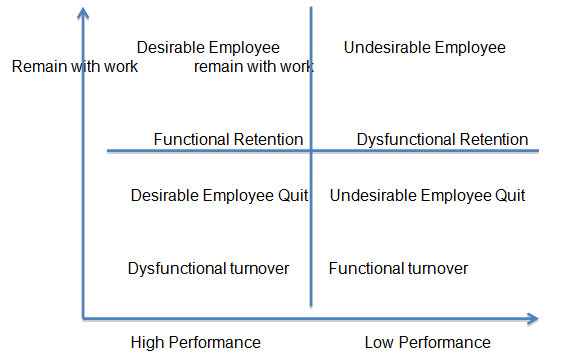
Therefore, a number of organizations are familiarizing themselves with practices and strategies of human resource. This awareness generally augments the monetary, quality, and output presentations in dissimilar organizational departments (Ahmad and Schroeder 21). The strategic retention and separation of employees as well as the type of turnover and retention usually depend on various factors (see the diagrams in the appendix).
HR as a competitive benefit source
Porter Michael placed the notion of competitive benefit into the difference of opinion. Competitive advantage ascends on or after the formation of consumers’ worth as Michael emphasizes. Such products and services are observed as being inimitable according to the industry thus emphasizes on viewing a specific product souk or purchaser group.
Organizations like Rotana can then employ several outlines of nonspecific policies including focus, differentiation, and cost leadership to achieve competitive benefit. Essentially, the organizational presentation is affected by the ecological determining factors as stipulated in the extensively accepted Porter’s opinion (Batt 541).
Conversely, the firms’ source of competitive benefit mainly lies in the application of respected package resources during the disposal of the firm as specified in the organizational resource-based outlook.
The relations amid firm’s presentation, policies, and internal resources make the advantage derived from competition to differ. It differs from the strategic administration paradigm that focuses on environs according to this viewpoint.
Through facilitating particular firm growth of capabilities, schemes of human resource according to resource-based viewpoint contributes to continued competitive benefit. To gain a competitive benefit, the inimitable competencies for administering human resource have attribute from the continued superior presentation in several corporations.
However, this might contribute to disadvantaged competition and susceptibility supposed the schemes of human resource destroys the present and/or inhibit the growth of fresh capabilities (Becker and Huselid 900).
The output of labor force is the fundamental in aspect of a healthy economy and lucrative corporation. It is essential for human resource to identify why triumph can readily not be imitated, but continued by rivals.
However, success developing from effective administration of people in an organization is frequently not transparent or detectable as the basis. Certainly, the soft flank of business is laid off occasionally that it might be elaborated through culture and the way people are oriented as well as the effects of this on their skills and manners (Boxall 267).
The way individuals are coped frequently fits in a system hence it is hard to understand the dynamic forces of a corporation and how it functions even when there is no dismissal (see diagrams in appendix). Hence, it is problematic copying much stuff but then it is again easy to copy one thing.
For the corporation to sustain and achieve competitive benefit, the human resource management needs to accomplish several objectives. The company must gain the peoples’ commitment to the standards and missions of the organization.
Secondly, the corporation must strive to encourage enthusiastic commitment to organizational functions (Cabrera and Bonache 54). For the business triumph, remuneration, appraisal, and inspiration of workers’ manners, the firm needs to describe the desired behaviors.
Moreover, the organization necessitates taking strides to improve and obtain intellectual capital through recognizing the knowledge desirable for consumer satisfaction and meet the set objectives.
Lastly, the organization by augmenting skills and aligning the aptitude to administrative objectives, it must invest in people through the reinforcement and introduction of education procedures to gain and sustain competitive advantage (Boxall 268).
Therefore, it is significant to comprehend the relationship amid business policy and human resource administration to realize all these objectives.
How strategic management add value to the Rotana chain of hotels
Researches indicate that the current labor market is more competitive and getting the right employee with the right skills is not easy. The greatest challenge organization faces not only Rotana but also equally corporations or firms in the industry, is how to make potential employees acknowledge that the organization is the best place to work.
In addition, the organization human resources management faces difficulties in bringing the best interviewee through appointment and employment process. However, the organization ensures that its best employees are retained by ensuring that they understand the firm’s goals and are committed to attain those goals (Ahmad and Schroeder 21).
Besides, the company retains its best employees through motivation and providing a friendly work environment as well as structures that enable employees to give their full potential.
The organization acknowledges the importance of effective management of human resources in the current swiftly and exceedingly competitive environment. The human resources department fully understands that effective discovery and management of the employees are critical to the success of the organization.
The organization top management understands that infusing the right mind-set and conduct in employees is the only way through which the organization can lead in the market place.
Management can add value when they help junior employees attain the organization as well as personal goals (Arthur and Boyles 78). It is about what the employees and the organization gains from the human resources policies that have been put in place.
In essence, the company human resources department will not pursue and encourage activities that do not add value to the success of the company. In other words, the human resources pursues its value propositions, which are practices that produce positive results for the company key stakeholders including employees, customers, line managers and shareholders.
In Rotana, managing human resources is understood as an activity that contributes positive value to the key stakeholders (Boswell 1490). The organization human resources management has moved from supervisory tasks and operation administration to strategic function in order to contribute positively to the organization results.
Managing diversity in employees
The company HR has succeeded because it has taken into consideration work place diversity. In this context, work place diversity refers to the ways through which individual employees differ. Indeed work place diversity includes both organizational-related and personal attributes.
The human resources management has ensured that each individual cultural values and attributes are harnessed with the organizational goals. This has enabled the company to produce superior problem solving strategies, ensured creativity among employees and increased quality decision-making (Aryee 237).
This has translated into improved services to the company clients as well as increased market share. Appropriate management of workplace diversity has resulted into increased competitive advantage to the firm.
The company human resources have also undertaken proactive diversity management strategies in its employee management to add value to the outcomes of the individuals. In fact, strategies that the company has undertaken to improve individual outcome and job satisfaction have contributed hugely to the organization.
The strong foundation in values such as equity, respect, and fairness has helped the company to tap into the values of diversity (Carmeli and Schaubroeck 392). Improvements in individual successes have trickled down to the group processes and outcomes that in effect have benefitted the company.
Recommendations
The HR department should add more value to the company by encouraging innovativeness in employees as well as implementing innovations. In addition, the HR department should prioritize the improvement of the overall company productivity.
Moreover, there should be a genuine partnership between the department and line managers. This partnership should be aimed at dealing with low morale of employees, which in effect have negative impact on the competitive success of the company.
Besides, the HR department of the company should focus on the cost reduction strategies as well as tapping into the expertise and technology to improve human resources services.
Cost reductions will in turn free more resources that can be used to sustain and realize the general business strategies. Generally, the human resources sector ought to introduce programs that will advance the productivity of the recruits, efficiency, and fulfillment.
In essence, the company value should be added through the pursuit of aggressive goals, developing and implementing innovation productivity, creation of more products and services that are new as well as applications and ideas. Moreover, the company should become customer oriented, helping customers attain their needs and goals, as well as linking the human resources plans with the needs of the customers.
In addition, Human resources management should add more value to the company by ensuring that the right qualification and caliber of existing employees are maintained. In additions, the employees’ skills and qualifications, job descriptions and profiles should much the job roles.
Additionally, the HR division ought to make certain that the recruits guidelines and measures are without fail adhered to all over the corporation. The HR must also ensure that the staff ratios are in line with the projected costs of the project.
This will make certain that the corporation utilizes simply the precise number of recruits it necessitates and in unison retains the corporations’ profitability limits, which give rise to continuous practicability of the corporation.
The HR unit ought to make certain that the in-house workforce shifts are accomplished well and in a reasonable style. For instance, the employee selection and promotion is done equitably and fairly using similar criteria.
This guarantees that the exact groups are appointed and are endorsed to hold higher positions, which consecutively boosts the efficacy in task accomplishments and amplified competence in delivering the assigned tasks. Mode of payment should also be based on the modes that enhance fairness and equitability.
The remunerations base should be reviewed on a yearly basis taking into considerations the state of the economy, skills, and positions among other factors.
Conclusion
Strategic human resources management provides tools that the organization can use to leverage the employees value as well as other stakeholders to improve their performance. One of the tools is effective diversity management. Productive diversity management of employees forms the foundations for managing employees, which underpins the competitive advantage in the international market place.
In many ways, managing diversity improves the firms’ decision-making process and increases the level of competitiveness in the global markets. In fact, through strategic management of Rotana human resources, the firm will be able to make workforces potentially aware that the organization is the best workplace.
For instance, strategic human resource management will enable Rotana to attract only the unsurpassed applicants via the hiring and recruitment processes besides having the capacity to retain a significant portion of the employees (see appendix).
When Rotana successfully manages the human resources, the employees might be able to understand the corporation’s goals and remain committed towards accomplishing them.
However, this can only be realized through the provision of structures and environment that motivates the employees to offer the best services. Thus, in the current vastly aggressive and swiftly varying marketplace setting, the premeditated tasks played by the corporation’s human resources aid in ensuring the malfunction or sensation of a business.
Works Cited
Ahmad, Sohel, and Schroeder, Roger. “The Impact of Human Resource Management Practices on Operational Performance: Recognizing Country and Industry Differences.” Journal of Operations Management, 21.1 (2003): 19−43. Print.
Arthur, Jeffrey, and Boyles Trish. “Validating the Human Resource System Structure: A Levels-Based Strategic HRM Approach.” Human Resource Management Review, 17.1 (2007): 77−92. Print.
Aryee, Samuel. “Developing and Leveraging Human Capital Resource to Promote Service Quality: Testing a Theory of Performance.” Journal of Management January, 23.1 (2013): 234-256. Print.
Batt, Rosemary. “Strategic Segmentation in Front-Line Services: Matching Customers, Employees, and Human Resource Systems.” International Journal of Human Resource Management, 11.3 (2000): 540−561. Print.
Becker, Brian, and Huselid, Mark. “Strategic Human Resources Management: Where do we go from here?” Journal of Management, 32.6 (2006): 898−925. Print.
Björkman, Ingmar and Lervik, Jon. “Transferring HR Practices within Multinational Corporations.” Human Resource Management Journal, 17.4 (2007): 320−335. Print.
Boswell, Wendy. “Aligning Employees with the Organization’s Strategic Objectives: Out of ‘Line of Sight’, out of Mind.” International Journal of Human Resource Management, 17.9 (2006): 1489−1511. Print.
Boxall, Peter. “Achieving Competitive Advantage Through Human Resource Strategy: Towards a Theory of Industry Dynamics.” Human Resource Management Review, 8.3 (1998): 265−288. Print.
Cabrera, Elizabeth, and Bonache, Jaime. “An Expert HR System for Aligning Organizational Culture and Strategy.” Human Resource Planning, 22.1 (1999): 51−60. Print.
Carmeli, Abraham, and Schaubroeck, John. How Leveraging Human Resource Capital with its Competitive Distinctiveness Enhances the Performance of Commercial and Public Organizations. Human Resource Management, 44.4 (2005): 391−412. Print.
Appendix
Strategic Retention and Separation of Employee
Type of Employee turnover + Retention