Abstract
This article seeks to outline viable backup solutions provided for Salesforce.com. It also considers a ‘Practicable Backup Plan’ and employs it to evaluate the backup strategies with intent to confirm if they are credible. Over and above that, the paper lists strategic steps on how to assimilate Salesforce Backup frameworks into micro-organisations for data safety in the event of system failures and adverse data loss.
Introduction
Clarke theorizes that millions of individuals and micro-organisations have embraced the advent of “cloud service” backup models as the ultimate choice for computing administration (Clarke 2015, para. 1). Saving information on cloud repositories benefits users as it helps them elude on-site software installation as well as the corresponding administration overheads.
In the process, they disregard the advice given to reserve their records on local premises (Chalkidou & Bradley 2013, p. 42). This paper seeks to appraise the backup arrangements devised by Salesforce SaaS service provider in conjunction to outlining varied methods of how one can implement these arrangements.
Body
Background Facts on Salesforce
Myron (2009, p. 4) writes that Salesforce is a worldwide SaaS service vendor catalogued on the New York Stock Exchange. The proprietors have their company headquarters in San Fransisco, California with a multitude of other territorial offices dispersed in bordering states.
The corporation’s core service provision lies in the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) brand with diversified interests in various social networking packages such as the AppExchange. The Salesforce operatives designate their products with rapid scalability, data consolidation, data recovery, and backup models (Security: world-class security infrastructure 2005, para. 1).
Salesforce Backup Infrastructure
Salesforce has incorporated some backup solutions that embody thorough security infrastructure (Security: world-class security infrastructure 2005, para. 3). The data recovery design administered entails a state-of-the-art configuration that labours to assure unsurpassed safety and backing of customer data (Myron 2009, p. 5).
The backup solutions proffer complete redundancy, ongoing scrutiny of security breaches, automatic scheduling, imaging, and incremental backups. Salesforce system administrators have aligned all the SSL accelerators, web servers, network components, and load balancers in a redundant configuration (Security: world-class security infrastructure 2005, para. 5).
The database custodians reserve all customer files and carrier-class disk caches in data paths and RAID disks thus implementing frequent backups on a nightly basis. Illustrated below are the backup strategies available within the board.
Spanning Backup
‘Spanning Backup’ is a recovery in-app that facilitates automated and secure instant on-page restores, backups, and granular fields (Spanning Backup for Salesforce 2015, para. 2). Metadata, custom views, dashboards, user-prompted reports, email templates, and file extensions are among some of the data repair amenities empowered by the Spanning Backup application.
The on-demand app solution operates continually in the background and is always readily accessible for everyday use (Spanning Backup for Salesforce 2015, para. 3). Discussed below are the key capabilities of the in-app in conjunction with their corresponding screenshots (Spanning Backup for Salesforce 2015, para. 3-8).
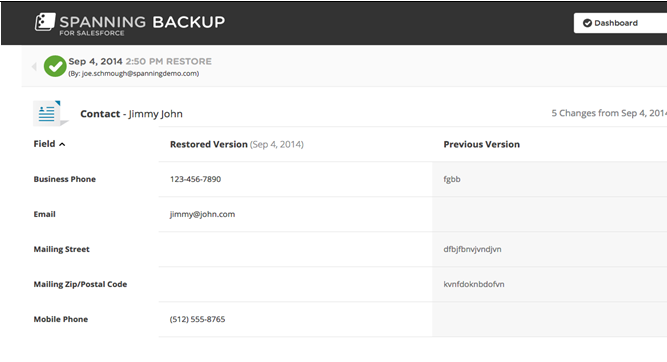
The “Easy Restore”
The ‘Restore Icon’ enables prompt reclamation of metadata, custom objects, and granular fields of data such as opportunity amounts, phone numbers, and attachments (see fig. 1).
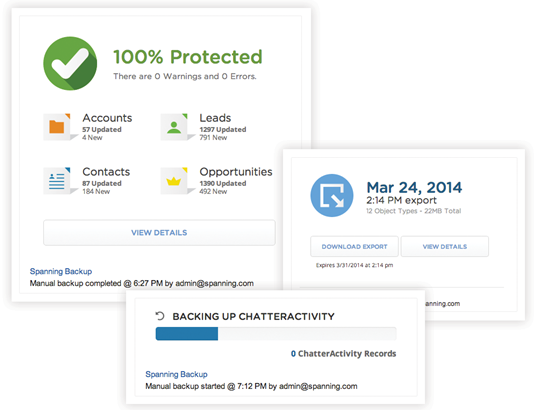
The “Integration Capability”
The ‘Integration option’ empowers end users to converse promptly with Salesforce administrators by way of interactive chatter posts, notifying them of the current configuration activities (see fig. 2).
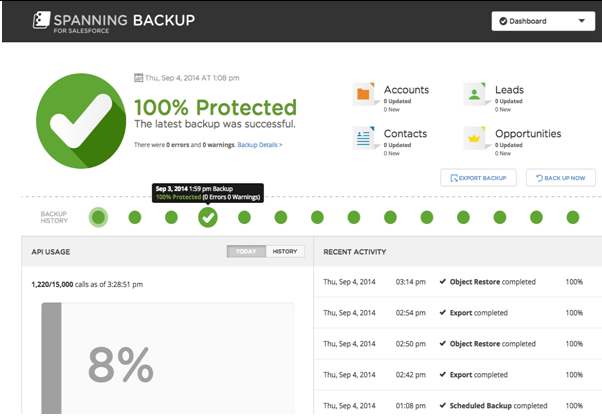
“Administrator Tools”
The ‘Administrator tools’ provide the client with a responsive interface to track the intricate descriptions of daily backup results, status, and warnings. The tools also manipulate the exhausted API calls, dissolve backup errors, and issue error-correction directives (see fig. 3).
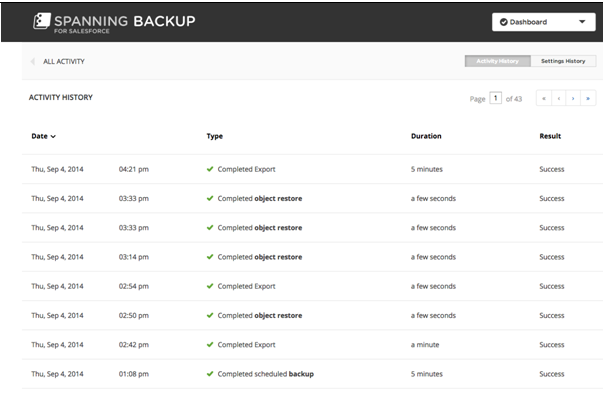
“Proactive Notifications”
The ‘Proactive notifications’ tool serves as an advisory element to guide the consumer along the activity monitoring of exports, restores, backups, and dynamic updates (see fig. 4).
The “Export Capability”
The ‘export capability’ capacitates brisk data recovery using granular exports and searches (see fig. 5).
CloudAlly
Salesforce has also employed a supplementary backup mechanism, namely the ‘CloudAlly backup service’ to further their efforts in data hold up and reclamation (Salesforce Backup 2014, para. 1).
CloudAlly expedites substitutive storages of customer data comprising of metadata and chatter feeds in its unlimited receptacles. The app also disburses reports of daily incremental backup tasks and archived folders through data loaders and import wizards (see Table 1).
Table 1: CloudAlly Utilities
Practicable Backup Plan
Mader assures that the implementation of commendable data recovery and backing structures is crucial to the success of micro-organisations (2005, p. 24). A backup framework strives to safeguard against data loss by way of making sure that you can restore your records in the event of system malfunctions or damage of chief business information (see Table 2).
Table 2: Backup Layout Plan for Remote Storage and Processing Strategies
Evaluation of Salesforce Backup Solutions
This segment gauges the credibility of the Salesforce backup configurations by way of comparing their arrangements against the stipulated backup plan projected above for accreditation purposes. Service evaluation is integral to helping business officers develop strategic positions on whether to integrate the backup resolutions and packages by way of examining the suitability of the provider’s backup system.
Service valuations and nomination of enterprise backup solutions accentuate recovery processes by analyzing data locations, scalability, accessibility, and security protocols (Chalkidou & Bradley 2013, p. 43).
Preimesberger (p. 24) narrates that the data recovery complex needs to cover speedy, testable, and selective reclamation solutions that capacitate restoration of single and entire domain file sets. Explained below are the pivotal areas for authenticating the services of Salesforce.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure involves preventative activities that focus on the reproduction and replication of data sets from the provider’s servers onto the client’s on-site storage media, outlines Clarke (2015, para. 17). Salesforce highly recommends users to back up their data in local repositories to abate costly recovery fees during data regeneration and restoration (Security: world-class security infrastructure 2005, para. 2).
The Salesforce team has presented several viable approaches such as the ‘backupify’ medium to those who wish to enforce local replication to ensure faster accessibility and increased data security.
It nominates engagement of data export tools such as data loaders, granular fields, and import wizards to use in duplication of congruent folders as well as CSV formatting (Salesforce Backup 2015, para. 2). The company has gone a further step in integrating export tools and data loaders in its commercially available backup solutions mainly the CloudAlly and Spanning Backup apps.
File Precautions
Clarke (2015, para. 19) registers that care activities entail preemptive courses of actions aimed at safeguarding the vendee’s files and folders at all available levels. The precautions call for administration of malware detection software, the creation of new file accounts and repeated document saving to reduce file damages, deletions, and errors.
Preimesberger (2011, p. 22) forwards that Salesforce holds file precaution pursuits in high esteem as it has instigated numerous backup utilities such as administrator tools, and the integration interface in its Spanning Backup app. The administrator tools trail day-to-day backup results, status, saves, inaccuracies, and warnings, which constitute malware detection pursuits.
On the other hand, proactive notifications in combination with the integration interface provide concurrent communication channels and chatter posts (Spanning Backup for Salesforce 2015, para. 7). They strive to keep track of the ongoing configuration processes, backups, proactive updates, and restores thus acting to preserve records and real-time support from the administrators.
Backups
The ‘backups’ subdivision covers all constitutive areas relating to system failure, hacking attacks, theft, data corruption, and overwrites (Clarke 2015, para. 21). ‘Backup’ activities highlight essential items such as data encryption, and backup receptacles to prevent fallouts and use of obsolete storage media (Clarke 2015, para. 20).
Mader (2005, p. 25) says that Salesforce Backup formulas guarantee vigorous and satisfactory backup reserves in store. To start with, Spanning Backup extends tools useful for dire granular exports, backups, page restores, and updates.
Secondly, the CloudAlly standby service offers indispensable practicalities such as backup metadata scopes and supportive features including the backup production and sandbox. It also implements optional backup confirmation of daily email summaries (SalesForce backup 2014, para. 4).
Generic Risk Assessment
As regards data preservation, Myron (2009, p. 46) postulates that agencies should examine information security risks before assimilating backup structures.
Risk assessment assists senior business executives single out the most appropriate alternatives with zero-risk tolerance and powerful data recovery schemes (Mader 2005, p. 26). High-risk areas relating to inadequate backup structures compose of unauthorised access, severe environmental storms, power failures, erroneous service interruption, and new data formats.
Implementation Strategy
An implementation tactic embodies the mechanism of transforming generic risk assessment findings into practical measures (Clarke 2015, para. 25). This section sets out well-coordinated methodologies of how end users can exert the feasible backup plan above in their routines to insure themselves against data loss.
Design a Work Plan
Clarke attributes that you should first formulate criteria manuals for recruiting a gratifying backup provider; one who is financially stable, well founded, dependable, and trustworthy (2015, para. 4).
Preimesberger advises that you should solicit for references, storage facilities, as well as pricing (2011, p. 25). You should also perform some preliminary reviews concerning the vendor’s system redundancy, data encryption, physical security, user authentication, and database security.
System Installation
Once contented, you may proceed to install the backup structure with the help of a consultant. You may need to alter varied aspects of the backup system to appeal to your personal needs, suggests Mader (2005, p. 26). The Salesforce APIs come in handy when reconciling items such as automation frequency, metadata, full backups, and environmental change detection (Security: world-class security infrastructure 2005, para. 10).
Policy Controls and Procedures
You may also need to draft principal procedures and policy controls about Salesforce data privacy bills provided for under the federal HIPAA Acts (“Security” 2005, p. 2). It is also obligatory to set forth a list of contract agreements and covenants to govern the business relationship between you and your backup software supplier.
Of vital significance is developing concessions on quality assurance processes, archival of records, data locations, file precautions, accessibility, processing options, data encryption, backup timeframes, and storage media spooling intervals.
Training
At this stage, you can start enlisting the help of a competent instructor to coach your workforce on how to operate and manipulate the SaaS backup entity.
You can reserve a large enough conference hall for the training sessions, where the instructor shall first issue passwords and usernames to the relevant staff (Chalkidou & Bradley 2013, p. 45). After that, the trainer will outline a condensed overview of the system in conjunction to illuminating the benefits of the backup complex.
System Review
The system review is a follow-up exercise that entails periodic monitoring, evaluation, and consideration of the add-on complex to determine if it has sufficed the organisation’s needs (Clarke 2015, para. 28). Preimesberger also advocates for reevaluation of the procedures and outcomes of the recovery processes after one and six months respectively (2011, p. 26).
Conclusion
As regards service evaluation, Salesforce Backup strategies are commendable to any Enterprise Software Entity as they dispense instant restores, granular exports, proactive updates, and real-time chatter feeds. Senior business executives looking to implement the Salesforce Spanning Backup and CloudAlly service apps are sure to achieve maximum protection against destruction of sensitive customer files.
References
Chalkidou, T & Bradley, M 2013, ‘Saving to the cloud’, Parks & Recreation, vol. 48, no. 10, pp. 41-48.
Clarke, R 2015, Managing the Risk of Cloudburst: Backup Strategies for Users Dependent on Service Providers. Web.
Mader, C 2005, ‘Recover and repair lost data’, Windows IT Pro, vol. 11, no. 10, pp. 23-28.
Myron, D 2009, ‘Salesforce.com: one leader. one decade. $1 billion’, CRM Magazine, vol. 13, no. 11, pp. 4-6.
Preimesberger, C 2011, ‘Private vs. public clouds: the fight has just begun’, eWeek, vol. 28, no. 10, pp. 19-26.
Salesforce Backup 2014. Web.
Security: World-Class Security Infrastructure 2005. Web.
Spanning Backup for Salesforce 2015. Web.