Introduction
Research Background
Safety and security over the cyberspace has become such an important issue in determining consumer behavior. Thus the introduction of a Secure Online Shopping System (SOSS) is vital towards survival of an online business.
Secure online shopping system is a platform where consumers of the product are able to make orders on particular product and make payments using their credit cards. The SOSS platform will ensure the safety and security of those cards.
Research carried out by different organizations shows that the level of trust of internet shopping of many Chinese has increased making them willing to shop online as long as their security is ensured (Ira 2002).
Since the development of electronic commerce, practitioners of E-commerce have strived to gain insight into consumer behavior in cyberspace. SOSS target to woe global consumers of beauty products to make their purchases online.
Economical and social responsible purchasing behaviors of consumers have become significant determinants of consumer behavior therefore SOSS will ensure that consumers’ social and economic welfare is well thought-out.
According to Ira (2002), online consumers continued to use the internet amidst the economic recession experienced in Europe. According Kotler (1997), the highest number of internet users in China are those aged between 25 to 44 years.
It further states that online purchases amongst these internet users are done by those in their late teens and early twenties. As a result, the SOSS platform will be used as that mainly target the individuals in the age bracket that use internet shopping frequently. It is thus important to establish how SOSS will influence behavior of customers in the Chinese Market.
Statement of the Problem
Each year, vast numbers of new products in different groups are launched globally. Factors such as growing advertising costs and increasing competition have made the successful implementation of a new product more difficult in recent years.
The concept of E-commerce in relation to the topic of online consumer behavior has been examined by different researchers in a variety of contexts. Despite the immense progress that researchers from different business disciplines that have made on this vast and new concept, none of these studies have focused on the security dimension of online shopping.
Thus, introduction security aspect of online shopping services will be analyzed to establish its influence on behavior of consumers. To achieve this broad objective of increasing online customer base for the products offered in Chinese market, we analyze online consumer behavior in a systematic manner using various consumer behavior theories and models.
Consumer behavior theories have been applied to study online consumer behavior; however, gaps still exist between the online and offline consumer behavior that warrants further studies. Consumers are generally influenced by two factors: internal influences and external influences.
Internal influences are personal feelings and thought that includes; self-concept, motivation, attitudes, emotions and perceptions. These factors generally influence perception, purchasing patterns, and attitude customers develop towards a product or a service offered by the business.
Besides, these factors are directly linked to internal and external interacting social aspects that control the pattern of thought and expressed feelings.
Resonating on the facets of internal and external influences, this paper develops a comprehensive matrix for purchasing patterns exhibited by customers within the Chinese market in order to understand how SOSS influences the behavior of consumers in e-commerce.
Purpose of Study
To succeed in the e-business era therefore, companies need create adept initiatives and maintain long term sustainable relationship with loyal. SOSS is proficient platform that will help e-businesses remain relevant in this digital period (Ira 2002).
Then purpose of this study is to explicitly review emotions and motivations as the emerging forces within consumers that activate certain behaviors. Emotions are described as temporary state that show present changes in motivations whereas motivation are persistence need that stimulate long term goals in consumers.
These emotions control direct and indirect behavior inclination that arouse the instinct to purchase or refuse to purchase. Though a temporary state of mind, emotions challenge the market preference and direct judgment to buy. Therefore, the research is specific on how SOSS will impact on consumer behavior by arousing their motivation to buy products online.
The aim is to find respondents who are the potential, if not actual customers of our online products who fall within the category of youths and young adults described in the introduction. One reason that informed the decision was the fact that such respondents are categorized as the most internet shoppers in China.
Limitations of Study
The study aims to make sure that the respondents chosen are aware of the brands investigated. Thus, a certain degree of familiarity with internet shopping and the security risks will be a prerequisite among the interviewees, in order to carry out meaningful discussions.
As a result, consumers who do not show any familiarity of the brand will not include as respondents despite having knowledge of online shopping.
Besides, being an empirical study, the researcher will depend on responses by these respondents that might not give accurate data.
Therefore, biased or selfish responses will have negative effects on the final outcome and this may render some of the findings inaccurate. In addition, the researcher may experience the constraint of time delays in sending the responses.
Review of the Literature
Koufaris (2002) asserts that the previous studies have been relatively fragmented with contradictory results. A large body of knowledge has been developed in consumer behavior analysis by influential authors such as Engel and Nicosia among others.
A large part of this literature concerns differentiable products, thus, may not be explicitly applicable in a service such as online shopping. It is therefore necessary to understand the intrinsic differences between offline and online consumer behaviors.
Attitude and Perception on Online Trade
Attitude is the general evaluation that consumers engage in before deciding to purchase a particular product or service. Attitudes are direct personal experiences that are influenced by consumers’ personality, advertisement, family and friends.
Perceptions are unique ways through which consumers internalize and interpret information about a product. Consumer engagement is essential towards winning and maintaining a client especially in a competitive market setting where the best offer carries the day.
The offer could be in the form of price, quality, and quantity. When information on attitude is verifiable, it is easy for a company to execute a well researched plan within allocated resources.
The processed information is used by consumers in making “the buying decision,” as such, SOSS provides consumers with the platform to share information on the internet.
There has been substantial research on consumer behavior, examining the decision process, and influences upon it, in terms of storage and brand characteristics and consumer behaviors (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008).
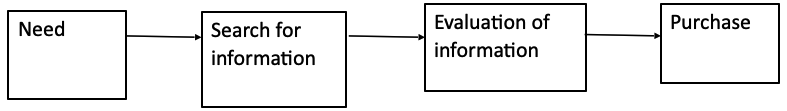
Central to the theories of consumer behavior is the conviction that different consumers go through markedly complex decision making process that is influenced at different stages by a number of possible variables. The buying process normally begins with the need for a particular product or good.
The need that is created prompts the consumers search for available information concerning the good or service that can satisfy that need. Having considered the available information, consumers then evaluate alternatives before making a purchase (Kotler, 1997, p.17).
SSOS will not only avail the information on the product, but also ensure that customers security of their information making shopping accurate and safe.
External Influences of Online Buying Behavior
Several external influences affect online consumer behavior. These influences include individual culture and sub-culture, group associations, social cultural and household structure. Under SOSS we classify external influences as negative externalities that determine consumer behavior.
Consumer behavior studies have shown that consumers’ attitude, opinions, belief, and values shape consumer buying decisions. Products that consumers view to be violating their cultural belief often attract fewer customers (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008).
In fact, cultural beliefs influence and dictate how consumers meet their needs. Often, customer tend to associate satisfaction and value of a good on cultural believe or inclination in line with the preset societal mindset.
Culture controls dressings, morals, and even association. As long as a service or a good is associated with positive result, the sales for such a good are likely to skyrocket. On the other hand, the reverse often leads to damning or uncomfortable response from potential customers who may appear reluctant to play along (Ira 2002).
Therefore, acceptance of a good or service is a reflection of its responsiveness to culture and a target group’s social affiliation.
The household structure basically represents the household composition in terms of age, occupants and their incomes (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008). On the other hand, groups in the context of consumer behavior represent individuals who share a set of common values, norms and beliefs.
The group and the household to which a consumer belongs to has a significant influences on consumer behavior that is influencing the decision making process. Mass media services are mainly concerned with generation of modern cultures.
Cultural values normally influence whatever values that are generated by mass media. Cultural values normally dictate what consumers would purchase; in fact, people buy certain signs when they are driven by the implication conveyed.
Moreover, semiotics plays a significant role in the ads because it inspects signs and implications that are conveyed and thus alerts the users about the relevance of a product.
E-Commerce Models
The Models of Intention, Adoption, and Continuance are essential in investigating the concepts of intention, adoption, and continuance on the process of online consumer purchasers.

(Source: Kotler 1997)
This model is an integration of two models of consumer behaviors: Kotler’s expectation-confirmation model and Ira’s attitudinal theoretical model (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008). The attitudinal theoretical model is used in examining the variables informing consumer purchasing intention and adoption.
According to this model, “behavior is principally determined by intent. Other factors like, perceived behavioral control, subjective norms, and attitudes are also shown to be related to an appropriate set of significant normative, behavioral, and control values about that behavior” (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008, p. 89).
However, this model does not explain consumer behavior in relation to repurchase. Ira’s expectation-confirmation model, on the other hand, focuses on past purchase behavior of consumers. This model is used in explaining consumer satisfaction with a service or good through their repeat purchases.
Thus, “consumer satisfaction is the key focus of this model and expressed via the gap that exist between the perceived performances” (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008, p. 78).
Kotler (1997) found that personal innovativeness of individual consumers is key personality characteristic that give an explanation of consumer online behavior. Baskerville (2004) contends that consumers’ trust on the internet is a significant determinant of online shopping.
E-commerce is non discriminative on the size of business since even retail chains are in a position to trade online. Moreover, this model of business operation functions exclusively online (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008).
In addition, “web tracking technology permits sites that practicing E-commerce to monitor customer satisfaction and preference” (Ira 2002, p. 56). These aspects allow such companies re-model to customize service delivery and maintain quality. At technological advancement improves, E-commerce is likely to widen further.
Consequently, it is cheap and easy to operate and open online stores “without a brick –and-mortar presence” (Thomson, Peteraf, Gamble, & Strickland 2008). In addition, E-commerce offers entrepreneurial opportunities to persons in all business fields. The recorded sales data estimate progress at 4% annually across the globe (Ira 2002).
Ira (2002) states that “It wasn’t until 1994 that e-commerce (as we know it today) really began to accelerate with the introduction of security protocols and high speed internet connections such as DSL, allowing for much faster connection speed and faster online transaction capability”(Ira 2002, p. 46).
However, full adaptation of E-commerce begun in 2000 in America and Europe by pioneer companies such as Amazon and eBay which became prominent in E-commerce for many brands of products (Baskerville 2004).
Model and Hypotheses
Conceptual Framework
- The aims and objectives of this research paper are:
- To gauge and quantify the reasons for the behavioral influence of SOSS in online trade within China.
- To identify the underlying factors that influence online purchasing behavior within China.
- To identify the most profitable online business model in the stratified market of China.
- To establish the most appropriate technique for introducing and maintaining sustainability of e-business within the borders of China.
Research Questions
- What are the profitable e-business models today? How do they compare to those that failed?
- How to transfer consignment business model to e-commerce especially in a specialized niche market?
- Will people accept consignment business model in China? What difficulties are facing?
Hypotheses
Below are the null and alternative hypothesis based on the research problem.
- H1o. There is no link in e-business efficiency and purchasing behavior in China.
- H1a. There is a link in e-business efficiency and purchasing behavior in China,
- H2o. There is no link between e-business model and success of an online business.
- H2a. There is a link between e-business model and success of an online business.
- H3o. There is no link between online brand awareness and the ease of online sales.
- H3a. There is a link between online brand awareness and the ease of online.
Research Methodology
Research Design
Both descriptive and qualitative research methods will be used in this inquiry. Qualitative research method is a design which typically investigates behavior when it naturally occurs in a non contrived situation.
On the other hand, descriptive survey designs will be used in preliminary and exploratory studies to allow researcher to gather information, summarize, present and interpret for the purpose of clarification.
Descriptive investigative research is anticipated to produce statistical information about facets of SOSS that concern business that operate online Investigation of the problem will be conducted by means of both literature synopsis and empirical investigation.
Subjects of Study and Sample Size
The population targeted by this study includes 3 randomly picked participants within the Chinese market. To generate the sample size for this study population, the research will adopt the formulae created in 1972.
Sampling Formula
n=N/ (1+N (e2))
Where:
n = sample size
N= Target population
e= Degree of freedom
n=3/ (1+3*0.052)
n=3/1.025
n= 1.025
From this population, random sampling will be applied and questionnaires with close ended questions given to each participant.
Data Collection method
In the collection of data procedure, the research will adopt a drop and pick module for the sample population. Each respondent will be given a time frame of a week to respond to questions in the questionnaire. Where necessary, further clarification will be accorded to participants.
Statistical Techniques Used
Data analysis will begin from the onset of the interviews until the process of interviews is completed. After all the data are collected, the analysis of the transcripts will be reduced through a procedure known as coding. At this stage the researcher will conduct data reduction, presentation and interpretation.
The researcher will carefully but accurately transcribe the responses from participants recorded telephone calls as well as audio recordings. Transcripts from the interview questionnaire will be read and key points noted. Similarities and differences will be identified and key challenges presented by the managers, teachers and educators noted too.
After the analysis of data details, symbolic qualitative and high technological ways were employed to arrive at conclusions. The content analysis was used due to its ability to review a wide range of non-construction data.
The actual scenario was then analyzed through mathematical, statistical, and computational modus operandi to derive quantifiable results. Basically, the process relied heavily on respondent information from the twenty four participating organizations (Ira 2002).
Open ended online questionnaires were the main data collection tools since the process relied on voluntary response. This type of purposive sampling is done through the outlines of criteria which the participants have successfully fulfilled.
Open-ended questions were designed to allow the participants to fully express their experience without being too confined within the boundaries of a question. The semi-structured interview was used as it allowed the greatest possible advantages in creating an understanding of the experiences of the participants.
The structured set of questions acts as an outline allowing for the participant to inject personal perspective and diverse lines of inquiry that may not have occurred to the interviewer.
To make the responses inclusive despite the few numbers of respondents interviewed, the participants were selected from four different regions within China. The respondents differed in age but fell within the age bracket described as internet shoppers (aged between 25 to 44 years).
However, it is worthy to note that due to the limited number of respondents, the interviewees could have been more representative. Nonetheless, the aspects of sex, age, and occupation were taken into account considering the target customers described in the introduction (See Transcripts in Appendix I).
The entire interview questions and answers given by respondents are attached in the transcripts as an appendix I.I.
Findings and Analysis
Before engaging in a business activity, it is vital to access its merits and demerits, risks involved security of the transaction, and regulative organs that directly provide protection from unpredictable and unethical practices by competitors.
The participants opine that the main disadvantage of E-commerce is the fears and doubts by potential customers who don’t how it works.
In this case, the potential customers are afraid of purchasing products online because of doubt on reliability, practicality, and risks involved especially when delivery is done to a wrong party.
Some of these customers may be curious on appearance and reality and may develop a negative attitude after an assumption of possible fraud. Besides, online stores do not give an option for wear, touch, trial of the product before purchasing.
Therefore, the sale of products such as furniture might be challenging. Moreover, invasion of malware and malicious codes in online stores might turn a simple business transaction into ‘Hellgate’ transmitting virus to PC of potential clients (Baskerville 2004).
In addition online trading limits the social aspect of shopping in which parties involve interacting physically with one another. Due to surge in the use of E-commerce, several security reasons have been identified by the participants, especially in safety of information exchanged.
The occurrence of some security threats has compromised the principles of authentication, privacy, and non-repudiation which is fundamental in protecting security breaches such as Denial of Service.
The most common threats in E-commerce include ICM Flood, Teardrop Attack, Plashing, Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks, and Brute Force Attacks. These practices aim at compromising integrity of E-commerce.
Recommendations
In the face of globalization and the development of e-commerce competing companies apply strategic techniques to in their products and services to avoid being obsolete.
The companies compete through product differentiation through focusing on the service-dormant paradigm with investments in new technology, people, and policies. These investments are imperative for organizations as because customer’s attitudes and motivation significantly influences the consumer behaviors.
The earliest marketing principle of marketing was the model introduced by McCarthy in 1960 was the 4Ps marketing mix, defined by Product, Place, Price, and Promotion.
This marketing model was further modified by Bettman in 1979 to include the service industry introducing three additional variables: People, Physical evidence and Process (Baskerville 2004).
Due the unique characteristics of the service industry: intangibility, inseparability, and heterogeneity, these products can be offered to the market for an acquisition, consumption, attention, and use.
The product can include the services, places, persons, organizations, physical objects and ideas. From this definition the new service: SOSS that we want to introduce in the operations of online shop in China will fall under a service.
The reality of e-commerce in the market guarantees that the service will be very important in ensuring that new and existing customers are given the opportunity to shop cheaply and conveniently for the beauty product with an assurance of privacy and confidentiality.
The Price is the amount charged for a product or service offered by a particular business organization (Kotler 1997). The service that SOSS creates is relatively inexpensive since customers will not be charged for using online shopping services, rather they are charging for the product and deliver costs.
Apart from these direct costs the customers will have to incur internet service charges by their providers. SOSS therefore reduces the product cost and time incurred by offline shoppers for our products by maximizing on economies of scale since these products are likely to sell in large scale.
Process refers to the mechanisms, procedures and flow of activities through which a service is delivered to customers. Koufaris (2002) notes that the process of delivery is an important variable that creates a difference to the benefits the consumers in the service industry reap.
In a normal offline buying scenario, customers are likely to queue for the service or product. This is quite time consuming as the customers have to be present physically. SOSS will eliminate this process by timely delivery thus eliminating the requirement of the physical presence of customers at the shop.
SOSS customers will be able to receive the products they have ordered via the online portal. This will ensure that the products are delivered to specific customers at the right time.
Customers will be required to provide information about their physical address to facilitate the process of transportation and delivery. With the information in their database SOSS takes into consideration the Place aspect of 7Ps marketing principles.
The environment in which a service is assembled and where the customer and the service provider interact is what is referred as “Physical Evidence” in 7Ps marketing principles (Koufaris 2002).
Managerial Implications
As a matter of fact, visualization is dependent on internet networking and the ability of the targeted clients to access the same. Reflectively, the success of online trading and marketing depend on the type of business, the nature of products, and model of website in use.
In the contemporary society, it is in order to state that online trade made possible through the invention of websites is the only future way of doing sustainable and customer friendly business. Thus, it is important for small, medium, and large business to embrace technology in order to remain competitive in the hostile global business environment.
Every aspect of life is actively influenced by the revolutionary technological orientation and customers would gladly go for convenient purchasing tools. These services include all the tangible representation of the service being offered, such as, business cards, brochures, reports and Signage.
For example, the design, furnishing as well as the neat arrangement of products on the shelves that will be shown on the website will influence customer perception on the quality of our products.
Since our online customer are not physically present at the shop, the neat and attractive display and descriptions of products on the SOSS website will give our online shoppers cues that will help them understand the nature of the products they are ordering.
Introduction of the Wi-Fi, iTunes, Blackberry applications, and Amazon search engines have made an online trade simple and reliable. For instance, the Wi-Fi and blackberry application permits potential client and seller to video conference and strike a deal irrespective of the distance between these parties.
Besides, potential clients are now in a position to bargain, view, and make modifications to their product before making payment. In addition, these gadgets are portable and have widened access to products online without necessarily being connected to the traditional wire internet which was slow.
Attitudes are direct personal experiences that are influenced by consumers’ personality, advertisement, family and friends. Perceptions are unique ways through which consumers internalize and interpret information about a product. Consumer engagement is essential towards winning and maintaining a client especially in a competitive market setting where the best offer carries the day.
The offer could be in the form of price, quality, and quantity. When information on perception is verifiable, it is easy for a company to execute a well researched plan within allocated resources. The processed information is used by consumers in making ‘the buying decision’.
Thus, our business will endeavor to incorporate SOSS within these engines to ensure convenience on the side of consumers and constantly mobile trade. Reflectively, these aspects will influence the decision science and successful management of our business.
Conclusion
From the examination of our findings, we can wrap up that the extent, to which consumers associate to Secure Online Shopping System (SOSS), is dependent on the degree of the perceived safety of the system and ease of use. Consequently if a high-level of perceived safety and ease of use is achieved, consumers tend to refer more notably to the system.
On the other hand, the use of online shopping seems to be dreaded by online consumers when the degree of perceived safety is not achieved or relatively low. Furthermore, the safest and convenient the online consumers perceive an online shopping system in their mind, the more likely it is for them to use it when making online purchases.
From the above research, markets are provided with a rich knowledge of consumer behavior as dependent on the degree of perceived positive and negative beliefs on a brand. Therefore, through improved advertising, balanced prices, and quality, markets will be in a position to monitor emotions and motivations which serve as the emerging forces within consumers that activate certain behaviors.
These emotions control direct and indirect behavior inclination that arouse the instinct to purchase or refuse to purchase. Though a temporary state of mind and emotions challenges the market preference and direct judgment to buy or reject a brand.
These articles facilitate the process of examining the decision process, and influences upon it; in terms of storage and brand characteristics and consumer behaviors.
Finally, this research has been conducted in a very meticulous setting with predetermined respondents’ characteristics. Therefore, we are aware of the possibility that the results could have turned out differently if respondents were picked randomly from across the social divide.
References
Baskerville, R. (2004). International e-business marketing. Alabama: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Ira, K. (2002). E-Marketing: What Went Wrong and How to Do It Right. Los Angeles: K&A Press.
Kotler, P. (1997). Marketing management: Analysis, planning, implementation and control. Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs.
Koufaris, M. (2002). Applying the technology acceptance model and flow theory to Online consumer behavior, Information System Research, 13 (2): 205-223.
Thomson, A., Peteraf, M., Gamble, J., & Strickland, J. (2008). Crafting & Executing Strategy: Concepts and Readings with Connect. Alabama: McGraw-Hill Companies.