Introduction
The supply chains of any organization should be safeguarded. Many times, the supply chains are compromised by trust issues, interdependence, and information sharing. The ascending of expense for working together is another challenge and this can be ascribed to numerous reasons. One reason being the new regulations from the health division that for the most part oblige the medical centers to keep up a given measure of assets. The cost of developing and acquiring medical products and equipment has become too high due to globalization and fast-paced development. There is a shortage or lack of sufficient medical personnel to tend to the hospitals.
The doctor-patient ratio is very low, whereby one doctor tends to an overwhelming number of patients. Trust and standard practices should guarantee that the medical facilities are very much ensured and their part to the general public is recognized. There is the problem of mismanagement, whereby the hospital proprietors misuse the organization’s resources for their gain. This creates a problem of misplaced priorities and lost needs. Another issue is how to understand and deal with manageability measurements and natural concerns and its connection to productivity (Cho & Pucik, 2005). This paper will seek to analyze the effectiveness of trust, interdependence, and information sharing on the performance of Sheikh Khalifa Medical City.
Impacts of Trust, Interdependence, and Information Sharing
Any given supply chain network relies on trust among the partners to be successful. Besides trust, sharing of information and interdependence among the partners is very beneficial.
Trust
In the field of business, firms have much of the time made intentional attempts to build up more grounded associations with suppliers and clients. As a method for decreasing expenses, expanding productivity, enhancing quality and innovation, and keeping in tow with the competitors, numerous organizations are moving far from customary ‘safe distance’ business connections and are manufacturing closer and more shared ties with supply chain accomplices (Cho & Pucik, 2005). Rivalry from international producers, mechanical developments, and shorter life cycles of products has changed the purchaser-seller connections. The conventional safe distance contractual connections no more suffice, yet closer community-oriented methodologies are required. The advancement of organizational connections is a methodology that consolidates the merits of vertically incorporated distribution frameworks (control, coordination, and data preparing) with the benefits of frameworks using free chain members (adaptability, scale economies, proficiency, and low overheads) (Crossan & Dusya, 2004).
Be that as it may, the organizational connections have related expenses and dangers. Medical facilities like Sheikh Khalifa Medical City (SKMC) are for the most part thought to be subordinate and defenseless in such connections as a result of asset imbalances, corruption, and the misuse of unbalanced authority to seize restrictive resources and acquire concessions from the other accomplice. The trust exists if one partner trusts that the other partner is straightforward or big-hearted. The desire weakens the suspicion that one partner in the transaction will act artfully. In this way, if there is trust in a contract, the contracting partners will be persuaded that they will not be casualties of conduct, for example, unfriendly determination, moral hazard, or any kind of contractual peril (Haley, 1986).
Interdependence
Interdependence has just been managed in supply chain management to an extremely constrained degree and as a rule in an intra-hierarchical setting, examining how works inside of a firm rely upon each other. The level of interdependence in the supply chain network has to some extent been managed regarding how the included firms are successively dependent. Along these lines, the firms need to facilitate their exercises while the relationship among the supply chains has just been somewhat touched upon in the supply chain management literature. One unequivocal idea of this sort of relationship non-part connections can be of significance to consider (Cho & Pucik, 2005). The non-part connections are portrayed as connections between individuals from the central organization’s supply chain network and non-individuals from the production network that are of significance to the central organization. For instance, a supplier of the central organization can likewise be a supplier to its principal rival; this is why this connection gets to be essential to think seriously about (Haley, 1986).
What is fascinating is that these sorts of connections have not been further considered in the supply chain management of SKMC. Additionally, when contemplating the types of reliance that exist, the role classifications, for example, contenders get to be tricky to apply because they may likewise tackle a few different parts in connection to diverse firms in a specific supply chain network.
Moreover, in connection to a specific firm in this chain, a contender may add to the central company’s productivity if their exercises use normal assets. Considering reliance similar to the instance of SKMC, supply chains cannot be streamlined (Haley, 1986).
Attempts to advance individual supply chains without checking the association among chains may affect the productivity in the system, which may need responses. Moreover, exercises, assets, or items can be viewed as given when supply chains are composed and overseen since conditions for movement coordination and asset use continually change. Different firms, specifically or in an indirect way associated with a specific supply chain network may transform the courses in which they compose and deal with their portions of the supply chains. Hence, firms are never in full control of the parts of the unpredictable examples of supply chains they are included in (Crossan & Dusya, 2004).
Information Sharing
Data sharing can drastically enhance the way worldwide organizations and their accomplices work together, particularly in the wake of progressive globalization and outsourcing, which has and will keep on profoundly affecting store network operations. By trading data, for example, stock levels, estimating information, and deals patterns, organizations can decrease process durations, satisfy the orders all the more rapidly, save much money in overabundance stock, and enhance prediction exactness and client administration (Crossan & Dusya, 2004). Data sharing can be connected to all the central areas of corporate operational exercises. Beginning from the improvement chain process where data sharing can happen in the item outline stages and item life cycle administration exercises with both inner and outer accomplices (Cho & Pucik, 2005).
In the supply chain process, data sharing can offer in figuring clients some assistance with experiencing methodologies; expand client administration viability and operations. The mental obstructions around data sharing are genuine and basic. Some of the time there is genuine and legitimized dread that data sharing over the corporate limits can transform into an aggressive hindrance. By detailing successful business approaches, understandings, and strategies for success that a venture can use to build up rules and standards for the trade of data with inventory network accomplices can alleviate those hindrances. This will at last moderate the trepidation of data sharing and enhance productivity and make new open doors for all partners (Haley, 1986).
Data sharing can be best and minimum problematic for all concerned when done by executing the accessible innovative devices, which would achieve the procedure in a controlled and secured way along these lines streamlining the worldwide production network operations. Cooperative planning, prediction, and replenishment work processes and arrangements are present in the inventory network procedure (Crossan & Dusya, 2004). They aim to upgrade the supply chain network joining and information sharing among enterprises; however, not very many organizations successfully utilize it to their upper hand. The present difficulties that associations face in actualizing these work processes truly spin around non-incorporated procedures and frameworks with retailers and makers working out of their storehouse and diverse information planning. This produces unreasonable reaction times, expenses, and stock because of incorrectness in prediction. Retailers on one side deal with stock shortages, raw material deficiencies, lost deals, and poor client administration. Then again producers get tormented by out of date quality and stock expenses affecting the profit margins (Crossan & Dusya, 2004).
History and Profile of the Sheikh Khalifa Medical City
The principal objective of any business is to expand the shareholder’s riches. In this undertaking, we have picked the health segment and contemplated Sheik Khalifa Medical City as an illustration. Because of globalization and high specialized improvement in the area and intense rivalry between opponents in this part, we will investigate the difficulties that meet this hospital conglomerate. These challenges apply to any medical facility around the globe. One challenge that medical centers face is meeting a legitimate level of income for the speculators. The standard measure of profit for value is at least 12%. There is a genuine challenge for the hospital facilities to pull in extra capital to perform their part in undertaking monetary development (Barney, 1991).
Sheikh Khalifa Medical City started in the year 2005. The medical city was formed as a merger of all the health facilities that are in Abu Dhabi. The entities that were merged include the Abu Dhabi Central Hospital, which was established in the 1960s. It started as a hospital with 200 beds before it was later down-scaled to be just an outpatient emergency center. The second entity was the Abu Dhabi Psychiatric Hospital, which was established as a 120-bed medical facility. The third entity was the Abu Dhabi Rehabilitation Center, which was established as a nursing home for vulnerable individuals like the elderly or people with special needs. It had 88 beds. The fourth entity was the Al Jazeera Hospital which was a 300-bed facility established in the 1970s. It was mainly open for emigrants who dwelled in Abu Dhabi. The other remaining three entities included the Preventive Medicine Clinic, Primary Healthcare Clinics (9 in number), and the Sheikh Khalifa Medical Center which was established in 2000 with 250 beds (Crossan & Dusya, 2004).
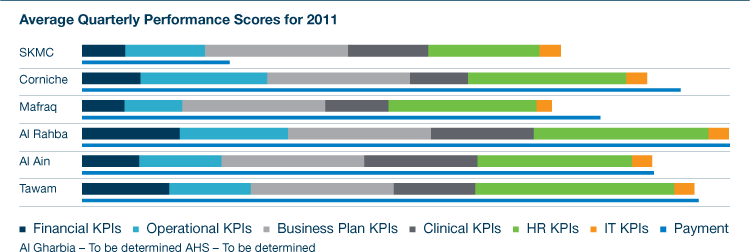
The new merger of the entities was called the Sheikh Khalifa Medical City (SKMC). The name was a representative of the real nature of the hospital. As a result of the merger, various transformational changes came about intending to make the merger stronger and solid. The Cleveland Clinic took over the management of SKMC in 2007. Cleveland Clinic is a top Hospital in the United States. In 2008, SKMC received an award from the Joint Commission International as recognition of its outpatient facilities and surgical pavilions. Figure 1.1 below summarizes the SKMC financials.
Literature Review
Building Trust
There are three sorts of trust. These are contractual trust, capability trust, and goodwill trust. Contractual trust lays on a mutual good standard of positivity and guarantees keeping while ability trust requires a common comprehension of expert behavior, specialized and administrative norms. Goodwill trust exists when there is an accord on the standard of objectivity. There is a chain of the importance of trust whereby satisfying a base arrangement of commitments incorporates contractual trust while respecting a more extensive set incorporates goodwill trust. In this way, a development from the contractual trust to goodwill trust includes a steady extension in the consistency of convictions about what is adequate conduct (Cho & Pucik, 2005).
The more one party controls the organization together through power advantage, the more prominent the probability that the cooperation would perform inadequately. The communication in the middle of trust and power demonstrates that the presence of trust influences the relationship between power equalization and execution. On account of the relationship between power parity and execution, it is demonstrated that trust houses a positive relationship (Haley, 1986). Trust and power parity serve to some degree as intermediaries for one another in the expectation of relationship execution. Where a firm can believe its accomplice, the adjusting of power is not as basic for upgraded execution. Trusting connections are seen to advance union execution and the vicinity of PowerPoint of preference negatively affects collusion execution, which is further exacerbated by the lack of trust (Crossan & Dusya, 2004).
Trust cannot turn a bad relationship to be better; however, everything it can do is improving a decent relationship. The SKMC underlines that sound monetary standards decide the long-haul eventual fate of their contribution to the suppliers. Essentially, the mediators who are included in the supply chain network with the medical facility showed that they would just keep on supplying equipment and products so long as it reflected the most successful assignment of their assets, in regards to their inclination. The trust union between the suppliers and SKMC raises their net revenue because it decreases their exchange costs. In any case, the extension for expense diminishment is constrained and cannot adjust for wasteful asset use. Trust, along these lines, is an aftereffect of the advantages the people acknowledge in the relationship (Haley, 1986).
However, organizational connections have related expenses and dangers. Medical facilities like Sheikh Khalifa Medical City (SKMC) are for the most part thought to be subordinate and defenseless in such connections as a result of asset imbalances, corruption, and the misuse of unbalanced authority to seize restrictive resources and acquire concessions from the other accomplice. The trust exists if one partner trusts that the other partner is straightforward or big-hearted. The desire weakens the suspicion that one partner in the transaction will act artfully. In this way, if there is trust in a contract, the contracting partners will be persuaded that they will not be casualties of conduct, for example, unfriendly determination, moral hazard, or any kind of contractual peril (Haley, 1986).
Effectiveness of Sharing Information
Sharing Information among production network individuals may convey various advantages to commercial ventures. Among these advantages, the noteworthy points of interest of data sharing are in two ways; either expected expense diminishment or stock decrease. If data sharing is utilized proficiently, the producers can decrease the stock expenses by 5% to 35% when the administration level may be kept up or expanded to the retailers (Barney, 1991). At the point when extra data gets to be accessible inside a supply chain inventory network, accomplices may profit by this enhanced reflectivity to modify existing plans or detail future operations. Case in point, sharing demand data empowers each of the store network individuals to make precise expectations because of genuine demand. Individuals may achieve flawless data about them in a supply chain, yet will not have such immaculate data about the other individuals (Lundberg, 2001).
Vulnerabilities may emerge as an aftereffect of this absence of data about the other individuals. When an individual has the capacity and eagerness to impart data to other individuals, instabilities can be altogether decreased. The bullwhip impact may be brought on by the absence of information balance in distributed frameworks. The stream of information inside of supply chain network individuals might essentially diminish or even dispose of the negative effect of the bullwhip impact (Lundberg, 2001). The preferences that accompany effective sharing of data include 1) Efficient stock administration through enhanced correspondence, 2) Cost lessening in requests administration through proficient correspondence, 3) Increased profitability and benefit through the most productive finish of requests, and, 4) Improved asset usage through the better administration of the work distribution (Barney, 1991).
By sharing information between the partners inside of the supply chain system, or production network administration, a business can be made. Data sharing inside of a production network causes an incredible change in the business associations. The mutual data constructs and reinforces connections and social bonds among the data collectors and suppliers. Hierarchical effectiveness and execution are other advantages that come with information sharing (Lundberg, 2001; Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991).
There are some difficulties associated with information sharing in a supply chain network. Among these hindrances is the classification of the data shared, lack of proper incentives, the high cost of the ICT equipment, restrictions by anti-trust policies, Inaccuracy and lack of reliability of the information, lastly the complexities caused by the innovation and advancement of new ways of sharing information among partner companies. One of the fundamental hindrances of interpersonal data sharing may be worried about data security. A trusted system ought to be made for people to share data (Barney, 1991). Association individuals may need trust in one another which may obstruct data sharing. Figuring out how to utilize IT frameworks for people in an inventory network is expensive and time-consuming. The introduction of easy-to-understand IT applications may enhance data sharing. A wasteful and non-easy-to-use framework would negatively affect data sharing bringing about fewer data and information to be shared (Lundberg, 2001).
The center of the exploration in the supply chain management territory has been on monetary perspectives and particularly on proficiency. Likewise, one region of interest has been the estimation of the execution of the supply chain. Thus, there has been an emphasis on the upgrading of the supply chains with a specific end goal to enhance effectiveness. In connection to this, one central region has been that of how to choose the most proper supply chain network. This suggests a perspective of the individuals of the supply chains as free and compatible. Critical fundamental confidence in this sort of point of view on supply chain management is that it is conceivable to recognize and set up the most effective supply chain network by selecting the best group of individuals. Moreover, the attention has been on firms utilizing long-linked advancements, i.e. every phase of the generation utilizes as its inputs the output of the preceding phase (Lundberg, 2001).
What is left out is the fact that each of the included firms is additionally included in numerous other supply chains through its trade associations with different partners, in this manner framing a one of a kind connection to every supply chain network. Besides, that medical facilities frequently adjust to one another’s assets and exercises, and in this manner make partnerships (Barney, 1991). If this had been recognized as a focal viewpoint, the rearrangement of supply chains would seemingly have been viewed and examined as riskier than what is regularly the case. Considering the association inside and among supply chains infers that all supply chains should be managed as exceptional. Following this, there is no most ideal approach to overseeing supply chains (Lundberg, 2001). This is because of the way that the physical structures of supply chains are altogether different. Every case shows generally pretty many degrees of many-sided quality, with an assortment of stages and with wide differences of members at every production network stage. There are additionally fluctuating degrees of the dispute over the assets that must be given at every phase of the physical inventory network, and noteworthy contrasts in the capacity of medical facilities to proper quality from their position inside of the chain (Barney, 1991).
Success of Interdependence
While having concentrated on auxiliary parts of supply systems, the speculations alluded to might likewise give further direction to managing administrative angles in these structures. This kind of movement is bland to its character and helps to characterize or delimiting the change exercises of importance for any production network (Lundberg, 2001). This is because sorting is the choice part of showcasing that guides items in supply chains to distinctive assets used to perform change exercises. Sorting consequently is the fundamental element that connects the supply chains. For instance, exercises, for example, sales prediction, planning of production, and medical facility of collections are firmly identified with how sorting is done (Barney, 1991).
What are the suggestions for further investigations of supply chains and administration? To start with, where investigations of structures are concerned this paper recommends investigations that begin from specific exercises, assets, or items keeping in mind the end goal to recognize and examine their reliance on different exercises, assets, and items (Lundberg, 2001). Investigations of this kind license investigation of structures and examination of reliance patterns reaching past the firm and dyadic levels of investigation. Where investigations or procedures in these structures are concerned this paper recommends attention on connection designs as investigations of this kind may enhance the comprehension of firms’ effort to impact their partners.
Thus, even though there are no straightforward arrangements accessible in these mind-boggling structures, lessons from attempts to effectuate change in them are crucial to building up the comprehension of their motion. Henceforth, top to bottom contextual investigations of structures and procedures considering association inside and crosswise over supply chains, by making utilization of the hypothetical ideas proposed, would ostensibly add to the improvement of the field of independence in the supply chain network administration (Lundberg, 2001).
Attempts to advance individual supply chains without checking the association among chains may affect the productivity in the system, which may need responses. Moreover, exercises, assets, or items can be viewed as given when supply chains are composed and overseen since conditions for movement coordination and asset use continually change. Different firms, specifically or in an indirect way associated with a specific supply chain network may transform the courses in which they compose and deal with their portions of the supply chains. Hence, firms are never in full control of the parts of the unpredictable examples of supply chains they are included in (Crossan & Dusya, 2004).
The expanding level of coordination among organizations in supply chains has prompted attention to the courses in which organizations connect. Connections and organizations between organizations included in supply chains have in this manner getting to be highlighted and examined by a few works of literature (Barney, 1991). An expanding spotlight on connections and organizational connection rather than vertical integration and the market connection is focused on numerous works of writing. Market coordination is portrayed by control, taking into account systems administration and reconciliation of procedures across practical, geographical, and authoritative interfaces. This perspective is altogether different from the perspective of control because of order.
Since the transaction cost approach can clarify why these connections or hybrid structures happen, this methodology has of late been broadly utilized as a part of the supply chain management range. The utilization of this methodology may likewise be a legacy from supply chain management’s roots in logistics as exchange expense methodology is, for the most part, acknowledged among logistics analysts as a helpful hypothetical structure for examining vital logistics choices. In the writing, there are a few cases of hypothetical and experimental studies, in light of benefits specificity, administration structures, and elimination of opportunism (Lundberg, 2001).
Be that as it may, the transaction cost approach may not be instrumental with an end goal to distinguish reliance across supply chains attributable to its attention on dyadic connections. To manage circumstances where a few firms in distinctive ways are included, a system that allows for an examination of more extensive structures is required. Most models of complex associations accept the relationship of hierarchical parts. There are three sorts of relationships: (1) pooled, (2) successive, and (3) proportional to facilitate the activity of associated components inside of an association (Lundberg, 2001). A pooled relationship is a circumstance in which every part renders a discrete commitment to the whole. A successive relationship occurs when direct reliance can be pinpointed between segments and the request of that association can be determined. The third type of reliance can be marked as proportional, alluding to the circumstance in which the yields of each get to input for the others. Diverse parts inside of an association should be joined given the relationship among their operations. The relationship can be overseen inside of the association (Barney, 1991).
With a pooled relationship, coordination by institutionalization is suitable. With corresponding reliance coordination by shared modification is essential. This reliance system identifies with various types of advancements: (1) ling-linked, (2) intervening, and (3) serious. The long-linked innovation encompasses serial association as in act Z can be performed strictly upon fruitful finishing of act Y, which, thus, depends on act X (Lundberg, 2001). In this manner, long-linked innovation is firmly identified with the large scale manufacturing mechanical production system, which is regularly found in the car business. The attention is on changing inputs (e.g. crude materials and transitional items) into yields as items that are sent to clients. The sequential construction system is intended to deliver standard items, fully and at a consistent rate, in this way gaining economies of scale.
The intervening innovation is the connecting of customers or clients who wish to be reliant. Samples of such associations are banks (connecting investors and borrowers), phone organizations, and so on, who encourage connections among distinctive clients dispersed in time and space. The interceding innovation requires working in institutionalized ways, which infers that clients can be arranged into totaled gatherings and joined (Lundberg, 2001). This third assortment named escalated to connote that an assortment of methods is attracted upon request to accomplish an adjustment in some particular article; yet the determination, blend, and request of use are controlled by criticism from the item itself. The concentrated innovation is represented with samples from healing centers and the development business, where a customer or a client issue is illuminated by a particular blend of exercises and assets (Barney, 1991). A fruitful utilization of the serious innovation plays both on the accessibility of the entire limit conceivably required, yet just as on the suitable blend of limits as required by the particular task. The ideas advanced in supply chain investigation are versatile past the conventional assembling connection to which its depiction and sequencing of exercises are most appropriate (Lundberg, 2001).
Implications of Trust in Operations
Trust can be portrayed in a lot of ways. These different portrayals rely upon the zone of specialization under study. Trust is addressing the needs of the present era without trading off the capacity of future eras to address their issues. It includes enhancing the nature of human life while living inside of the conveying limit of supporting biological systems. Trust involves financial development that gives decency and chance to the majority of the people in the world, not only the special few without further annihilating the world’s restricted common assets. It is, in this manner, consistent to say that trust incorporates various needs and measurements, for example, ecological stewardship, protection of assets, lessening of carbon pollutants, money related saving and suitability, and social obligation (Haley, 1986).
The medical centers and additionally other medical foundations are taking an amazing look after executing the above measurements in their operation and production network. Medical centers, for example, Sheik Khalifa Medical City can empower trust improvement. The medical center contributes to a great extent by appending higher value and rates and applying premium separation on the organizations that are not executing trust arrangements and not ecological situated. The fundamental motivation behind why medical facilities ought to do that is because ecological dangers will be related by money related danger that may emerge because of distinctive reasons, for example, changing government strategies and high movement to the urban communities because of globalization.
Also, security may decrease in quality if there were environmental dangers. At long last, the significant impact will be reflected as a reputation danger which is an imperative component in the success of the operations of the hospitals.
Executing the trust will expand mindfulness towards objective utilization of assets and decreasing the waste which will be translated into lessening the expense and expanding the productivity. Sheik Khalifa Medical City possesses a gigantic space and expends a considerable measure of materials and vitality which can be controlled and streamlined by adjusting the maintainability policies (Lundberg, 2001).
Sharing of information can be problematic for all concerned when done by executing the accessible innovative devices, which would achieve the procedure in a controlled and secured way along these lines streamlining the worldwide production network operations. Compliant planning, prediction, and replenishment work processes and arrangements are present in the inventory network procedure. They aim to upgrade the supply chain network joining and information sharing among enterprises; however, not very many organizations successfully utilize it to their upper hand (Lundberg, 2001). The present difficulties that associations face in actualizing these work processes truly spin around non-incorporated procedures and frameworks with retailers and makers working out of their storehouse and diverse information planning. This produces unreasonable reaction times, expenses, and stock because of incorrectness in prediction. Retailers on one side deal with stock shortages, raw material deficiencies, lost deals, and poor client administration. Then again producers get tormented by out of date quality and stock expenses affecting the profit margins (Lundberg, 2001).
Methodology
The methodology is the process of instructing the ways to do the research. It is, therefore, convenient for conducting the research and for analyzing the research questions. The process of methodology insists that much care influences the kinds and nature of procedures to observe in accomplishing a given set of procedures or an objective (Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991). The purpose of this research was to analyze the trust in Sheikh Khalifa Medical City. The exploratory research study provides researchers an opportunity to assess areas that do not have extensive research. Therefore, engaging in exploratory study contributes to the development of additional knowledge on the issue or phenomenon under investigation. This goal comes by testing the stipulated hypotheses. To undertake the research study, a comprehensive research methodology is necessary. This part includes the research design, the sample, and the methods used in gathering information. It also contains the data analysis methods, validity and reliability of data, and the limitation of the study.
Quantitative Approach and ANOVA
The quantitative research approach refers to the use of statistical techniques, mathematical methods, and calculation techniques to analyses data (Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991). The quantitative methodology aims at utilizing mathematical and statistical theories and models to analyze the data. The quantitative method validates the hypotheses and conclusions that stem from the qualitative methodology. The scientific procedures and processes that help in quantitative methodology encompass deriving models and theories; designing instruments for data gathering; controlling the variables empirically; and analyzing data using models.
The quantitative approach is mostly concerned with human motives and the reasons behind such motives (Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991). The main questions that come with the qualitative approach are ‘why?’ and ‘how?’ in addition to ‘what?’, ‘where?’ and ‘when?’ Concerning this, a researcher utilizing the qualitative approach will tend to use smaller samples rather than larger samples. The qualitative approach strictly generates only information that applies to the designated case study; any additional information is guessed. Once the hypotheses stem from a qualitative approach, they filter through the quantitative approach.
Research Design
There are three types of research design: exploratory research, descriptive research, and causal research (Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991). This study utilized the exploratory research design. The exploratory research design mainly explores the nature of the problem to draw inferences. In this scenario, the researcher is in a good position to understand the problem under investigation. The flow of exploratory research involves identifying the problem and seeking to find the appropriate solutions and new ideas. Exploratory research is mostly applicable in circumstances where the structure of the research problem is not definite. The interview is a good example of the methods that help to gather information in this kind of research.
Considering the exploratory nature of the research study, the research will adopt a mixed research design. The study will take into account qualitative and quantitative research designs. The choice of mixed research design has arisen from the need to improve the quality of the research study. First, the integration of the qualitative research design will aid in the generation of adequate data from the field to support the study. Moreover, the research will have an opportunity to collect data from the natural setting, hence improving the relevance of the research study. In the course of implementing the qualitative research design, the study will take into account the grounded theory.
Subsequently, incorporation of the grounded theory in the qualitative research design will enable the research to elucidate the issue under investigation. For example, the research study will contribute to a further understanding of the importance of adopting a multi-dimensional approach in formulating employee compensation policies. Conversely, the quantitative research design will aid in improving the effectiveness with which the research data are analyzed and interpreted by the target research audience such as organizations’ human resource managers.
Population and Sampling
There are two popularly used procedures for sampling. The sampling procedures include prospect sampling and non-prospect sampling. In a probability sampling procedure, the samples are representative of the population. This is because all the entries have a chance of selection. On the other hand, items in the non-probability sampling do not have an equal chance. In this scenario, not all the items in the population have equal chances of selection. The data for the study came from the employees of the organization’s understudy. The employees had profiles that fit the context of this study. Therefore, the employees were an excellent choice because many of them have had the organization experience. Because not all the employees could be accessible, a non-probability sampling procedure was important in this study.
A pilot test was needed to ensure that the questionnaires were reliable and valid. After the pre-test, questionnaire editing was important to remove and change some words. Another pre-test was then important to be sure that the questionnaire was now very reliable and very valid. Conducting a study on the entire population is not manageable due to the high cost and the amount of time required. Consequently, the research study will take into account the sampling technique. To make the study manageable scholars found that the research will integrate the simple random sampling technique in constructing the research sample (Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991). This technique will ensure that there is no bias in conducting the study.
Data Collection and Instrumentation
In any research, there are basic stages that are involved in regards to the shaping of the research. These stages include understanding the research problem, the conceptual framework of the research, data collection, data analysis, and interpretations, and drawing inferences, and making recommendations. In this study, the quantitative research method helps to test the hypotheses formulated. The quantitative research method is very instrumental in harnessing mathematical models that are enshrined in natural facts. The existing theories construct a conceptual framework that measures this type of research.
The adoption of primary sources played a fundamental role in improving the relevance of the research findings. The integrated interviewing technique helped to collect data from the field. Consequently, a set of questionnaires was developed. The questionnaires acted as a guide in conducting the interview. The questionnaires were mainly composed of open-ended questionnaires to provide the respondents an opportunity to answer the required issues based on their opinion. The respondents received the questionnaires directly via online media. Thus, the data collection method entailed an online survey. Adopting this method of administration validates the need to minimize the cost of the study. This is because respondents stay sparsely.
Questionnaire Survey
Questionnaires are a pre-formulated set of questions that require the respondents to record their answers usually within closely defined alternatives. The respondents can receive the questionnaires from the researcher via mail or through personal delivery. Before designing a questionnaire, there are three principles to pay attention to, these principles include principles of wording, principles of measurement, and the general set-up of the questionnaire. The principle of text entails the content and purpose of the questions, for instance, the researcher needs to understand the nature of variables to consider. If a variable is subjective such as satisfaction where it measures a respondent’s beliefs, perceptions, and attitudes, the questions should draw the dimensions and elements of the concepts. Besides, when tapping the objective variables such as age and income, a single direct question would be appropriate. The wording and language are other elements of the principle of text, for instance, the language of the questionnaire should approximate the level of understanding of respondents. Consequently, the choice of words should depend on the degree of education of the respondents.
The principle of measurement encompasses the principles to ensure that the data collected are appropriate to test the hypotheses. These principles include categorization, which entails the adjustment of negative questions to become positive issues, coding, using scales and scaling techniques, and reliability and validity. Reliability indicates how stable and consistent the instrument taps the variable. The general set-up of the questionnaire encompasses the introduction to respondents, length of the questionnaire, instructions for completion, and the overall appearance of the questionnaire.
Data Analysis and Presentation
The collected data will be analyzed quantitatively. This goal comes by incorporating quantitative data analysis tools such as tabulation, use of graphs, percentages, and charts. Because the research study has integrated the qualitative research design, the data analysis and presentation method will entail the adoption of the textual presentation technique. This technique comes about by using statements that comprise numerals. One of the textual presentation tools that are important in analyzing the research data entails the Likert scale. By using this tool, the research will be in a position to evaluate the qualitative data using point scales such as the 5-point Likert scale. In addition to the above technique, the research will integrate the Microsoft Excel data analysis technique. The adoption of this technology played a fundamental role in improving the effectiveness and efficiency with which the collected data will be analyzed using tables, charts, and graphs. Moreover, the incorporation of the Microsoft technique played a fundamental role in improving the ease with which the research data translates.
Findings, Data Analysis, and Interpretation
This section covers the analysis of the data, presentation, and interpretation. The results were analyzed using SPPS, ANOVA, regression, and correlation analysis.
Sample Characteristics
The sampling procedures include prospect sampling and non-prospect sampling. In a probability sampling procedure, the samples are representative of the population. This is because all the entries have a chance of selection. On the other hand, items in the non-probability sampling do not have an equal chance. In this scenario, not all the items in the population have equal chances of selection. The data for the study came from the employees of Sheikh Khalifa Medical City. These three individuals were chosen because they are the core staff implementing the Hong Kong Rugby Seven 2014. They were involved in the named three stages, preparation, process, and evaluation of the event.
This technique will ensure that there is no bias in conducting the study. The study had a sample of 4 respondents for data collection. The study will take into account both males and females in constructing the research sample. The study assumes that the selected research sample will be representative of the workforce perception of the relationship between pay and performance. The choice of these regions has arisen from the need to understand the impact of social and cultural diversity on employee perception and hence performance. To understand the demographic information about the participants, the distribution of gender, age, education level, income, and period employed in the organization are in the following sections.
Reliability Analysis
Reliability analysis evaluates whether the multiple instrument items are measuring the same variable or concept (Haspeslagh & Jemison, 1991). In SPSS, the Cronbach’s Alpha value measures the reliability of the various variables. The minimum requirement for the value of Cronbach’s Alpha is 0.7 to ensure that the items are internally consistent and reliable. In the exploratory study, Cronbach’s Alpha value of 0.6 is valid. In this study, the various measurement items are from previous studies, thus, the minimum value is set at 0.7. The corrected-item total correlation (CITC) is also included to evaluate the reliability of the individual item. If the CICT is below 0.5, then the item cannot reliably measure the corresponding variable and is invalid for further analysis. The Cronbach’s Alpha if item deleted indicate whether the Cronbach’s Alpha value goes up or down after excluding this item. Thus, if this value is above Cronbach’s Alpha value for the variable, the item is invalid for further analysis. Table 4.6 summarizes the results.
Table 4.6. Reliability Analysis for Variables.
According to the results, the Cronbach’s alpha value of the trust, interdependence, information sharing, external factors, sustainable supply chain, workplace management, and economic performance are 0.836, 0.817, 0.761, 0.739, 0.898, 0.833, and 0.837, which are all above the minimum requirement of 0.7. Also, the CICT for individual items is all above the minimum requirement of 0.5, and the Cronbach’s Alpha, if deleted for individual items, are all below the Cronbach’s Alpha value. These results demonstrate that these items are internally consistent and reliable, and are valid for further analysis.
Frequency Analysis
Trust
Table 4.7. Trust frequency analysis.
Table 4.8. ANOVA results for Trust.
As can be seen from Table 4.7 and Table 4.8, more than half of the participants are familiar with trust. There are 52.1% of the participants indicate, “Supply chain relationships are based on mutual trust” and 46.2% of the participants indicate, “When making decisions, supply chain partners consider our welfare as well as their own”. From the total score of these three items measuring Trust, a large group of participants has a score of 11 or 12. To gain a clearer picture of the participants’ Trust, there was the aggregation of the items measuring Trust. The aggregated mean value was 3.69, suggesting that participants have a medium level of trust.
Interdependence Frequency Analysis
Table 4.9. Interdependence frequency analysis.
Table 4.10. ANOVA results for Interdependence.
Table 4.8 shows the overall responses to the interdependence among participants. According to the results, the mean value of all measurement items was between three and four. Thus, the participants’ attitude, concern was at a medium level. By analyzing the frequency, more than half of the participants have expressed their concern regarding the trust of Sheikh Khalifa Medical City. To gain a more detailed picture of the level of interdependence, the aggregate mean score was classified into three levels: low (below 2), medium (2-4), and high (4-5). The aggregate mean score was 3.76, suggesting a medium level of interdependence. There was a summary of the overall scores of the items measuring interdependence. The results reveal the range to be 16, with scores ranging from five to 20. The majority of the participants have an overall score between 14 and 16.
Information Sharing Frequency Analysis
Table 4.11. Information sharing frequency analysis.
Table 4.12. ANOVA results for Information sharing.
Table 4.11. summarizes the frequency analysis for items measuring information sharing. According to the results, the majority of the participants agree or strongly agree that “Inventory data are visible at all partners in the supply chain”, “Actual sales data are visible at all partners in the supply chain”, “Performance metrics are shared across the supply chain” and “Demanding forecasts are shared across the supply chain”. The aggregated mean value of information sharing is 3.98, nearly 4, suggesting that participants have a positive attitude towards the information sharing of the services. Table 4.12 summarized the score of the items measuring information sharing. As can be seen from the results, the majority of the score ranged between 10 and 15, indicating a relatively higher-level positive attitude towards information sharing.
Conclusion
Sheikh Khalifa Medical City started in the year 2005. The medical city was formed as a merger of all the health facilities that are in Abu Dhabi. The entities that were merged include the Abu Dhabi Central Hospital, which was established in the 1960s. It started as a hospital with 200 beds before it was later down-scaled to be just an outpatient emergency center. Medical centers, for example, Sheik Khalifa Medical City can empower trust improvement. The medical center contributes to a great extent by appending higher value and rates and applying premium separation on the organizations that are not executing trust arrangements and not ecological situated.
The supply chains of any association ought to be shielded. Quite often, the supply chains are traded off by trust issues, interdependence, and information sharing. The rising cost for cooperating is another test and this can be credited to various reasons. One reason being the new regulations from the medical sector that generally oblige the health facilities to keep up a given measure of advantages. The expense of creating and obtaining therapeutic items and equipment has turned out to be too high because of globalization and quick-paced improvement. There is a deficiency or absence of an adequate medicinal workforce to tend to the doctor’s facilities.
The doctor to patient ratio is low, whereby one doctor tends to a staggering number of patients. Trust and standard practices ought to ensure that the medicinal offices are all that much guaranteed and their part to the overall population is perceived. There is the issue of corruption, whereby the medical facility proprietors abuse the association’s assets for their increase. This makes an issue of misplaced priorities of needs. Another issue is the way to comprehend and manage reasonability estimations and common concerns and its association with profitability (Cho & Pucik, 2005). This paper will look to break down the adequacy of trust, association, and data sharing on the execution of Sheik Khalifa Medical City.
SKMC has actualized ISO 9001 and 14001 while much emphasis is given to executing ISO 27001. This may be credited to the way that the data is the most basic component and can be liable to numerous risks from numerous segments. The danger and harm came about because entering the data framework would have a high effect on the organization’s picture and would prompt high money related misfortunes. The results of the study revealed that trust, interdependence, information sharing, external factors, sustainable supply chain, and workplace management all affected economic performance.
Rivalry from international producers, mechanical developments, and shorter life cycles of products has changed the purchaser-seller connections. The conventional safe distance contractual connections no more suffice, yet closer community-oriented methodologies are required. The advancement of organizational connections is a methodology that consolidates the merits of vertically incorporated distribution frameworks (control, coordination, and data preparing) with the benefits of frameworks using free chain members (adaptability, scale economies, proficiency, and low overheads).
Sharing of information can be problematic for all concerned when done by executing the accessible innovative devices, which would achieve the procedure in a controlled and secured way along these lines streamlining the worldwide production network operations. Compliant planning, prediction, and replenishment work processes and arrangements are present in the inventory network procedure. They aim to upgrade the supply chain network joining and information sharing among enterprises; however, not very many organizations successfully utilize it to their upper hand. The present difficulties that associations face in actualizing these work processes truly spin around non-incorporated procedures and frameworks with retailers and makers working out of their storehouse and diverse information planning. This produces unreasonable reaction times, expenses, and stock because of incorrectness in prediction. Retailers on one side deal with stock shortages, raw material deficiencies, lost deals, and poor client administration. Then again producers get tormented by out of date quality and stock expenses affecting the profit margins.
References
Barney, J. (1991). Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. Journal of Management, 17(1), 99-120.
Cho, H., & Vladimir P. (2005). Relationship between Innovativeness, Quality, Growth, Profitability, and Market Value. Strategic Management Journal, 26(6), 555-575.
Crossan, M., & Vera, D. (2004). Strategic Leadership and Organizational Learning. The Academy of Management Review, 29(1), 226-227.
Haley, J. (1986). Economic Dynamics of Work. Strategic Management Journal, 7(1), 459-471.
Haspeslagh, P., & Jemison, D.B. (1991). Managing Acquisitions: Creating Value through Corporate Renewal. New York: Free Press.
Lundberg, C. (2001). Toward Theory More Relevant for Practice. Current Topics in Management, 6(1), 15-24.