Abstract
The report compares two banks one is Saudi NCB and Societe Generale. Saudi NCB is located in Saudi Arabia and Societe Generale is in France. Societe Generale is one of the leading financial institutions in euro zone. Its operation is scattered with corporate and investment banking. It is the 1 retail banking in France, 3rd largest corporate and investment bank in eurozone, and 4th largest asset management bank in euro zone. In 2007 its net income is EUR 3.1 billion and return on equity is 18.9%. Saudi NCB is the first established bank in Saudi Arabia. In terms of capital Saudi NCB is the largest bank in Arab world. It is also biggest financial asset management in Arab world. Different type of principle is maintained by the bank. Societe Generale is based on interest rate and Saudi NCB is based on commission rate. Both banks operational strategy and maintenance is same. Both are diversified in asset and liability management, finance additional fund from derivatives.
Introduction
Augmentation of civilization and modernization is based on availability of funds. So, short-term and long term loan is necessary for establishing a firm and to meet its current demands. So, banks are the best solution for these criteria. Before approaching towards any bank it is necessary to understand the financial structure of the bank and how the interest the interest rate is differs, the cost of capital, and procedure of utilization of funds. This report is designated with a view to clarify these information and structure and compare of two banks.
Methodology
To compare between two banks several points should be considered. These are: the operating structure of the financial institution, board powers, management structure, Bank risk management processes and internal controls, Regulatory supervision and reporting, Market penetration/segmentation/strategy/product mix, Asset/liability management, PL trends and analysis, Competitive analysis, technology usage/branching-domestic and international, strategic alliances, Loan/loss provisions and policies, Asset/liability diversification, Derivative product risk management, and Off balance sheet management. The differences and relationship have been evaluated between two banks. The recent published annual reports of respective banks are used.
Theoretical Aspects
To illustrate the comparative study, various terminologies are used and clarified here. To analyze bank risk management country risk, liquidity risk, market risk, business risk, commission rate and interest rate risk should be taken into consideration. By changing the pattern of these risks overall transaction pattern and business strategy pattern are changed and these have direct influence over its financial condition. To show the marketing and promotional strategy marketing planning, strategy and segmentation and positioning have been conducted. Both of the banks are operating off balance sheet activities to generate revenue to meet internal finance and the procedure to maintain off balance sheet management is described here by using several financial instruments. According to Mishkin, F. S. (2003), ‘Off balance sheet involves trading financial instruments and generating income fees and loan sales activities that affect banks profit but do not appear on bank balance sheet.’ Competitive analysis has been conducted with the comparison of Citi bank, UBS Pvt etc. The asset liability management has been shown with a view to show the gap between assets and liabilities. The asset liability management is a procedure to find out the gap of assets and liabilities to verify the firm’s ability to meet its current obligations.
The Operating Structure of the Financial Institution, Board Powers, Management Structure
The operational structure of Societe Generale is given below:
- France (57%)
- Europe (Outside of France) (24%)
- Asia and Oceania (4%)
- Americans (5%)
- Africa and Middle East (10%)
The percentage above shows the concentration of activities. The bank is more concentrated in France as it is home and not inclined to expand its major activities outside of Europe.
Retail banking outside of France is concentrated as follows:
- Europe: Bulgaria, Cyprus, Greece, Czech Republic, Romania, Russia, Serbia Montenegro, Slovakia, Slovenia
- Mediterranean Basin: Algeria, Egypt, UAE, Jordan, Lebanon, Morocco, Tunisia
- Africa: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameron, Ghana, Guinea, Madagascar, Senegal, Chad
Asset Management Service is Concentrated to The USA, UK, Continental Europe, and Asia
Saudi NCB is operated within Saudi Arabia, Middle East and GCC countries.
Management Structure of Societe Generale
With a view to operate the overall banking activities the whole management system of Societe Generale is divided into several groups. The designations are listed below:
- Board of directors
- Chairman and chief executive officer of Societe Generale
- Chief executive officer of group
- Chief executive officer of Societe Generale
- Company director
- Honorary chairman of Societe Generale
- Member of the council economic at social
- Chairman of the management board of company financial
- Global head of securities services for investors
- Head of group communication
- Deputy global head of corporate and investment banking
- Chief financial officer
- Global head of private banking
- Deputy Head of retail banking
- Head of strategy and marketing-Retail banking
- Chief executive Investment banking- Europe
- Head of international retail banking
- Senior advisor to the chairman and chief executive officer
- Head of specialized financial service
- Head of corporate strategy
- Global head of equity derivatives
- Head of SOCIETE GENERALE payment services
- Head of information systems in retail banking
CEO of Societe Generale Americans
- Directors
- Audit committee
- Nomination committee
- The management structure of Saudi NCB is given below:
- Chairmen
- Management director
- Board member s
- Deputy managing director
- Representative of general organization for social insurance
- Chief financial officer
- Assistant general manager
- Chief operating manager
- Head of corporate banking group
- Head of retail banking group
- Chief compliance officer
- Corporate human resource manager
- Head of group treasury
- Personal financial services manager
- Inspector general and Audit division manager
- Investment services division manager
- Chief credit officer
- Financial and accounting control division
- Information technology division manager
- Corporate operations division manager
- Western regional manager
- Central regional manager
- Eastern regional manger
Board Power
The board of directors enumerates its strategy and prepares the guideline for implementation. Its internal rule is to examine the group’s strategy and take action against any misleading. The decision of acquisition, merging and takeover are implemented by the board of directors.
Bank Risk Management Processes and Internal Controls
Internal Controls
Societe Generale and Saudi NCB have some common internal control principles.
Alleviation of bank risk by internal control system is a major issue. Both banks design the process with stable and durable plan.The internal control system has cleanness and can be understood by the staffs. Caution and warning in the state of progress is a major cause for controlling of the administration efficiency. Any misleading or fluctuation from standard is managed by taking influential steps and a special committee is maintained. So, it ensures the dependability and instant course of action. The internal system is separated from the execution committee. Bank’s management and board have the controlling power to maintain the internal control procedures. The controlling procedure evaluates the current misleading and course of action. Two types of control activities are used in Societe Generale. First one is the formation the internal control system and compliance of the procedure. Both the bank applied their internal control system at various levels and functions.
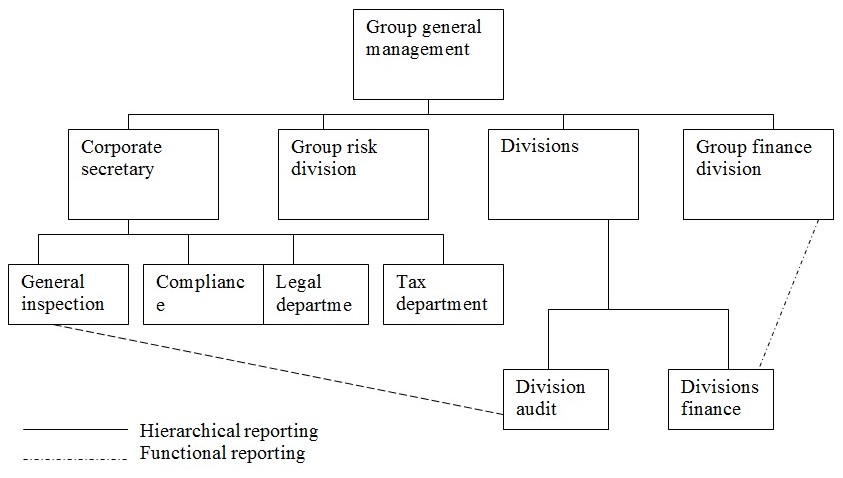
The department involves in internal control of Societe Generale are:
- The risk division
- The group finance division
- The division finance department
- The group compliance department
- The group legal department
- The group tax department
- The internal audit department
- The general inspection department
All these department report directly to the group general management except finance and audit division. Below an organizational chart involved in internal control department is given:
Risk Management Procedure
Risks arises form changes in the economical conditions. Societe Generale and Saudi NCB control these risks by forming a specialized team with essential tools. The risk management is same for all group divisions; the bank deals with credit, liquidity, market, operational, business, legal structure and capital risk.
Societe Generale bank is facing the following risks:
Credit Risk
The risk arises from the possibility of occurrence of default. It can be Default risk and Country risk. Default risk is when the borrower can not pay and country risk is when there are substantial changes in the pattern of invested country’s economy. The mitigated country risk in 2007 in Societe Generale is 2.1 billions of euros and Standard country risk is 3.2 in billions of euro. In Saudi NCB , for loans and advances and off balance sheet financing , the bank estimates the chance of default of borrowers using internal rating model. Societe Generale mitigates or lowers its risks by diversifying of loans, using collateral, internal grading and using derivatives. The table below shows the consumer and credit cards has more risk exposure.
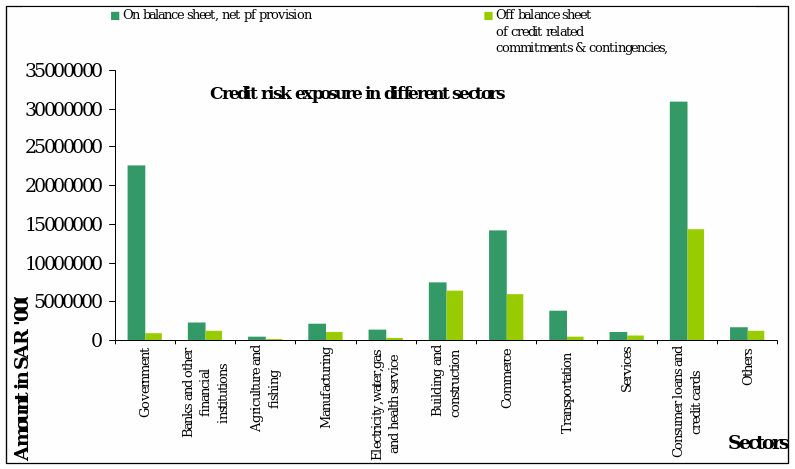
The table shows the amount in consumer and credit card sectors has more risk exposure as investment is higher. The second position is taken by government means more cash balances are maintained with SAMA and it is risk free.
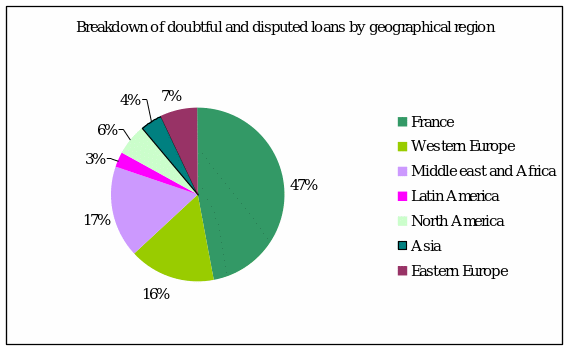
Societe Generale has more doubtful and distributed risks in France and second place is leaded by Western Europe.
Liquidity Risk
From unavailability of enough fund liquidity risk is arisen. For managing the credit risks several tools are used. By managing monitoring on loan, identifying probable of risky loan, stipulate terms, setting the level of amount, independent auditing liquidity risk is measured and mitigated.
Country Risk
For managing the country risks total counterparty exposure, Transfer risk exposure, highly stressed event risk scenarios, Country risk rating, Country risk limits, and Monitoring country risk tools are used.
Market Risk
Market risk can be derived from interest and commission rate risk, exchange rate risk, equity rate prices. The banks always maintain the limits of interest rate and commission rate by considering risk premium and market rate of return. Exchange rate risk arises when the country’s currency rate fall below than expected level. For managing the exchange and interest or commission rate risk derivatives are used.
Business Risk
Business risk can be arisen due to client behavior, market environment and technological changes.
To manage the above risk both of the bank uses some approaches like economic capital, historical data analysis, value at risk and stress testing.
Regulatory Supervision and Reporting
Long term decisions are taken by the supervisory board. Both of the banks has established a supervisory board to ensures the laws and regulation are operated smoothly. Audit and management committee are formed to establish the risk management process and administrative efficiency.
Saudi NCB is complied with SAMA, Saudi Arabia monetary agency. Regulatory and supervision board maintains the soundness of financial affairs. In the following way the procedure is established.
Under regulatory and supervision banks are obliged to following reports to its central bank:
- Asset and liabilities
- Risk management
- Investments and deposits
- Credit exposure
- Financial instruments
- Capital adequacy
- Asset liability management
- Loan classifications
Minimum capital requirement is a stipulated law for all banks. Currently cash balances with SAMA is and Societe Generale maintains 5206 million euros.
Both of banks are required to comply with the bank principle. The key principles of two banks are not similar. One is interest based bank and another is commission based bank. So, the distinction between interest and commission is maintained rigorously in Saudi NCB.
Under the central bank’s prescription the regulatory ratios are reserved:
The adequacy capital is maintained by Saudi NCB and the figures are given below:
Market Penetration/Segmentation/Strategy/Product Mix
The strategies followed by Saudi NCB are not diversified enough. It is only concentrating only customer and business banking. Though he global banking has been started, lacks of global braches hamper it.
Market can be segmented into geographical and services basis:
Geographical Segmentation
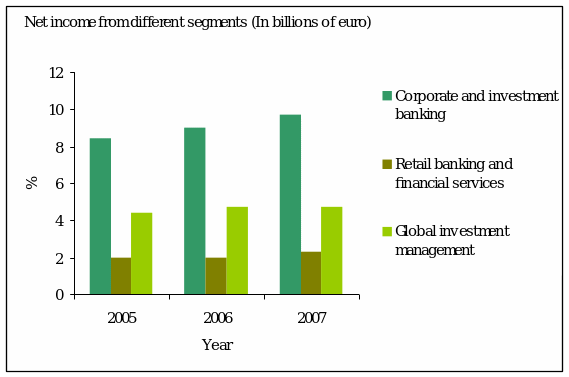
The main activities of Societe Generale is concentrated on corporate and investment banking, retail banking and financial services, global investment management, corporate banking.
Product Mix
The product mix is consisting four components: Product, price, place, promotion. Currently Societe Generale is operating g various kinds of products. Money management services are provided to meet up the requirement of working capital. Besides these regular functions it is also working as advisory, the advisory services include mergers and acquisition, financial sponsor, industry specialist.
Asset/Liability Management
Asset liability management means to keep balance between assets and liabilities to maintain enough liquidity to meet short term and long term obligations. The on balance sheet and off balance sheet gap is estimated and derived out the fluctuation. This is determined to set a tolerance level and for monitoring process. By using gap model the present scenario of asset liability management of Saudi NCB is shown below:
The bank is not able to meet its short term obligations as the figures are negative within 3 months. This means the total amount of short term asset in compare with liabilities are limited.
From the asset and liability management chart of Societe Generale it is seen that the bank cannot meet its short term obligations. This may happen for if customers are not willing to deposit in bank so much rather they spends more.
Profit and Loss Analysis
Analysis of profit and loss is based on ratio analysis and DuPont system. The significance ratios of Societe Generale and Saudi NCB are presented below by trend lines:
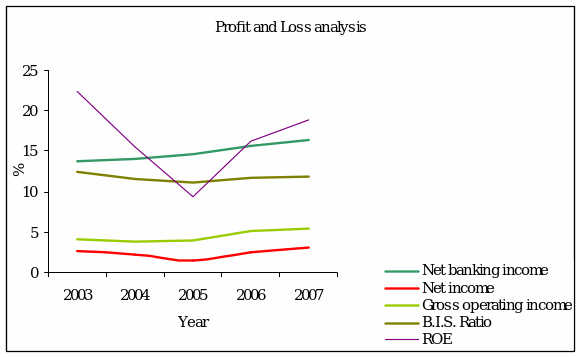
From the above graph the Net banking income is increasing over the year though ROE has not any standard level. The net income over the years is stable. The administrative efficiency is high as the net income gap with gross income is in a standard level. Firm attain in these income level as the group income level income is higher. The overall income level and cost to income ratio is quite satisfactory. Below the shares related structure is presented. It is satisfactory news for shareholder that the dividend payout ratio is increasing over the years. The earnings per share is also increasing over time. So, investors find it potential.
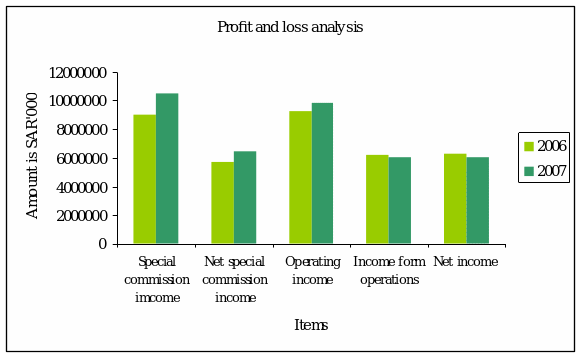
Below the graph of Saudi NCB is presented. The graph shows the relationship between two years. It is seen that between special commission and net income there is enough gap. So, the management efficiency is high. The bank is able to earn more income besides its normal banking operations as operating income is higher and in 2007 it is slightly increasing. The Earning share in 207 is 4.01 decreased form previous years 4.18.
Competitive Analysis, Technology Usage/Branching-Domestic and International, Strategic Alliances
Competitive Analysis
The competitive performance is varying with perfectly competitive movement. The commercial banks should concentrate on market niche. The most commercial banks are involved with large corporate borrowers and does no t concentrate on the small and medium enterprise. So it’s a lucrative opportunity for Societe Generale. Here the competitive pressure is reasonable. The slot is gainful. As the large banks are facing problems to finance in the industrial area the small sized banks are getting more advantages as large amount of financing are done form direct finance. Form the picture below the scenario can be comprehended:
On the other hand Saudi Arabia banks are facing more advantages in lending in industrial financing. The largest banks are making more profit through financial services and trading securities
Technology Usage/Branching-Domestic and International
In technology using Societe Generale is in ahead than Banque Saudi NCB. It is equipped modern technologies like internet, extranet, intranet, ATM, e-payment system, online banking, cellular banking and etc.
Loan Loss Provision and Policies
The criteria for identify the impaired loans and advances include: Recognized with accounting period and balance sheet, the impairment of loan will affect the overall cash flow pattern and the amount off loan loss can be estimated. To recognize the loan loss as independently, all the relationships of counter party are assessed. The major conditions are whether there is violation of contract, financially distraction or misbehavior in interest rate or principle payments. The collectively loan loss is determined by evaluating impairment of loan is individually significant but there is no significant evidence. The risks are recognized and an allowance is estimated. Based on historical data on homogeneous group a probable loss and allowance are estimated.
When deutsche Societe Generale sees any damaged loans the previous accrual interest is considered as interest income and a separate provision of loss is shown in the income statement. When it is manifested that the certain loan is irrecoverable the amount is charged off against loan loss provision
The following table shows the allowance for loan loss for each component.
Allowance for credit losses of Saudi NCB is given below:
The majority allowance goes to commercial loans and maximum loan is written off against consumer loan.
For different sectors the loan loss allowance is given below:
Societe Generale is more concerned in France and Western Europe as investment is more over there. So a specific and special provision is maintained.
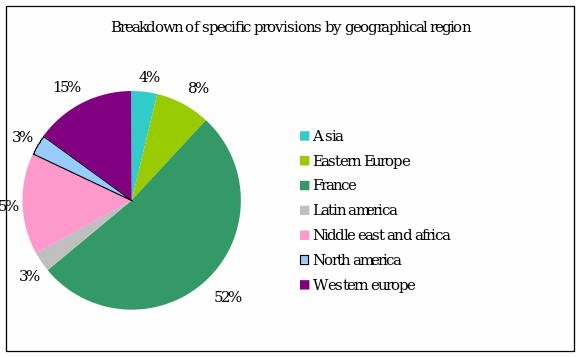
Asset/Liability Diversification
Asset Diversification
Asset diversification is superior enough for Saudi NCB as it holds more liquid asset for meet its current obligations but Societe Generale is maintaining better than Saudi NCB. Saudi NCB is containing conventional procedure of maintaining assets. The significant portions of Societe Generale asset classification are:
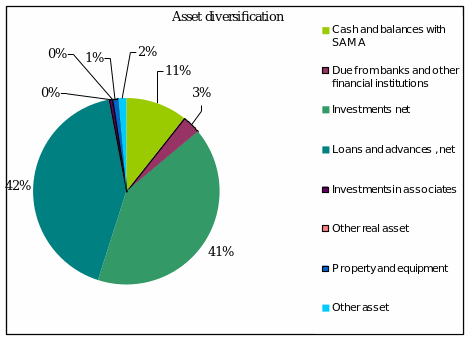
Liability Diversification
Societe Generale is diversifying its liabilities it’s on a maturity basis. There are five segments of classifying liabilities. The short term liabilities are maintained for matching with operating assets. On the other hand long term deposits for more than 5 years are not funded enough. It can be inferred that customers are not willing to go for long term benefits. The item below is the diversification of liabilities:
The shareholders and liabilities diversification of Saudi NCB is given below:
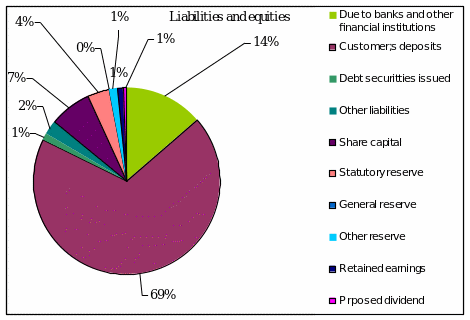
Derivative Product Risk Management
Every bank conducts various derivatives to reduce the risks. These derivatives include swaps, hedging, forward contract, provision and etc. To determine the derivatives management the following g steps are taking:
- Based on the spread and volumes, traders bids for quote to other participants.
- Managing risk position is important for setting the limits of carrying risk or the estimation of risk from probable return
- Engage in trading when price or interest rate belongs to a expected level
To manage the future rate of interest hedging is used. This will fix the interest rate and avoid uncertainty of both parties. The summary of derivatives of Societe Generale is given below:
The summary of derivatives of Societe Generale is given below. The bank is more involve in notional amount. IN over 5 years it has less uses of derivatives.
Off-Balance Sheet Management
Saudi NCB
Significant Off-Balance Sheet Items
Bank’s commitments and contingencies of the contractual maturity structure are given below:
The commitments and contingencies are given below:
The main problem arises for these two banks is principal agent problem. One might bet for more risk and another for less. So, a debacle between two may hamper the operational and decision making activities. To prevent this, the trading activities and book keeping activities must be separated. The risk tolerance has been set by these firms.
The Societe Generale has developed a statistical model which can estimate the loss may occur. So, from this statistical model the diversification of off balance sheet item can be determined.
Another approach is developed by Societe Generale, is stress testing. This tool tastes the extreme level of tolerance at full default. So, what amount of provision should be kept can be estimated.
Web Source
finance.yahoo.com
finance.google.com
sama.gov.sa
www.socgen.com
Bibliography
Brigham, E. F., & Houseton, J. F. (2004), Fundamentals Of Financial Management, 10th Edition, Thomson south-western, Singapore, ISBN:0-324-17829-8, pp. 244-294, 350-378.
Ball, L., (1999), Policy Rules for Open Economy, Taylor, J., ed., Monetary Policy Rules, University of Chicago Press, pp.120-145
Clarida, R., J. et al (2000), Monetary policy rules and macroeconomic stability: Evidence and some theory, Quarterly Journal of Economics 115(1), pp. 150–172.
Mishkin, F. S. (2003), Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets plus MyEconLab Student Access Kit, 7th ed., Addison Wesley, Ition, ISBN-10: 0321200497.
Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc. (2008), Accounting Encyclopedia, Ultimate Reference Suite. Pp. 560-561.
Societe Generale Group (2007), Annual Report and Accounts- 2007, Paris, France.
Saudi NCB Group (2007), Annual Report and Accounts- 2007, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Kotler, P., and Armstrong, G. (1999), Principles of Marketing, Prentice Hall of India, 07 (P194-233).