Introduction
Decision-making is a critical process that has to be undertaken by any leader in the management of an organization. A systematic approach is required to take charge of the business. In some cases, it is necessary to consult and reach a consensus. In the case of a highly valued venture, decisive action is appropriate. For effective leadership and management to take place, the process of making decisions should be systematic and procedural. There are several models that can be used by leaders to make decisions. One of them is the Vroom-Yetton framework. According to Vroom (1976), the model is preferred when consistency and order are necessary.
In this paper, the author will discuss the decision that should have been made by Masayoshi Son with regards to the merger between Sprint and T-Mobile. The Vroom-Yetton model will be used to analyze the decision-making process. In addition, the significance of the model to contemporary corporate executives will be highlighted.
The Decision-Making Style that is Appropriate to the Masayoshi Son’s Case
A company merger is an important decision in the business world. Companies like T-Mobile are highly valued and their acquisition, as a result, is important to the competitors, such as Sprint. If it succeeds, the merger will increase Sprint’s market value and its income base (Gelles & Merced, 2014). As Masayoshi’s son, I would need to respond to the questions posed in the Vroom-Yetton model to determine the best style to use in making decisions for the company. The questions and their responses are highlighted below:
The quality of the decision
In the case of Masayoshi, it is important to take into consideration the quality of the decision made. The reason is that the merger is a huge risk that involves a lot of money and input from the team led by Masayoshi (Yao, 2014). A venture like this will determine the future of the company in terms of its market share and profit margins.
The importance of team commitment to the decision
The commitment of the team is necessary. However, at times, a decision from one individual makes more sense. All the decisions made in the company are carried out by the team. As such, without the commitment of the team, the decisions made cannot be actualized (Merced, 2014).
Information required to make the decision
There is scanty information regarding the merger. The situation makes it hard to make some decisions, especially those involving a risky venture like this merger (Merced, 2014). Government regulations and the ability of the other firm to provide the necessary documentation are crucial to the success of the resolution made.
Structuring the problem
The structure of the problem involving the acquisition of such a big company is complex. In this case, the structure required to make the decision-making process easy is lacking (Gelles & Merced, 2014).
The likelihood of the team to support the decision
The involvement of the team in the decision-making process is important to the business. With regards to the merger between Sprint and T-Mobile, the support of the team is assured even if the resolution is made by one person. The single managerial decision highlighted by Vroom (1976) is needed in this case. Reliable and committed leaders will have the support of the team even in cases where decisions are made by one party.
The link between the organizational goals and the team
Organizational goals bring the team together. As such, they need to take part in the process. To meet the organizational goals and mission, the team should work together even when crises arise (Rigolosi, 2005).
Conflicts between the team members
Conflicts between the team members over the decision made are more likely. According to Merced (2014), there is a government regulation that is opposed to the merger. The regulation may lead to an uproar among the workmates.
The Decision-Making Style Recommended for Masayoshi’s Son
A merger is a technical process and it involves serious decisions. In the case of Masayoshi, the son should involve the team in discussions to get their suggestions. However, the final decision should be his (Vroom & Yetton, 1973). The answer to this question is not surprising. The reason is that a critical analysis of the questions posed in the Vroom-Yetton model reveals that the decision made regarding the merger was inevitable. The process needs a clear mind and the information required should include the input of the team and other relevant agencies interested in the merger (Rigolosi, 2005). The figure below was used to arrive at this decision:
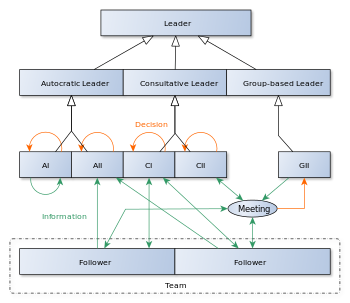
Figure 1. Vroom-Yetton’s decision-making model. Source: Rigolosi (2005).Decision-making takes place on a daily basis on all organizations. The choices arrived at have significant impacts on the operations and growth of the business (Stanford, 2007). A leader should make sound decisions that take into account the quality of the suggestions made by the team (Stanford, 2007). According to the diagram above, the type of decision-making process undertaken by the leader as per the response to question 7 is consultative (Rigolosi, 2005). Based on the existing information and the evidence regarding the quality of the merger, it is advisable to recommend this type of decision-making model to Masayoshi’s son in relation to their negotiations involving the acquisition of T-Mobile. It is the most appropriate model given the situation (Rigolosi, 2005).
The Significance of the Vroom-Yetton Model to Corporate Executives
According to Stanford (2007), managing an enterprise requires leaders to have skills in all the decision-making models. Executives play an important role in decision-making. As such, their input is crucial to the success of the firm. The parameters that determine the success of leaders include the commitment of other members of staff and the resources used in making decisions (Vroom & Yetton, 1973). Leaders are expected to assess the work environment and take into consideration the interests of the team they are leading.
It is recommended that corporate executives should be trained on the Vroom-Yetton model. However, the framework can be improved by including parameters that factor in a time constraint and lack of resources in the process of making decisions. In its efforts to acquire T-Mobile, executives at Sprint took the time to analyze the deal. A lot of resources were used to come up with a suitable deal (Gelles & Merced, 2014). Progressive decisions are required to improve the relationship between the managers and the employees.
Conclusion
The success of most business organizations is entirely dependent on the ability of the managers and the team they lead. Leadership plays a critical role in decision-making and the management of resources. As indicated in the case study analyzed in this paper, the growth of enterprises is determined by the decisions made on a daily basis by the managers and the employees. As such, all managers should have the skills required to make decisions. The Vroom-Yetton model can help them to achieve this. Masayoshi’s son and the entire team at Sprint can use this framework to make a sound decision with regards to the acquisition of T-Mobile.
References
Gelles, D., & Merced, M. (2014). T-Mobile and Sprint zeroing in on a $32 billion merger. The New York Times. Web.
Merced, M. (2014). Sprint ends its attempt to purchase T-Mobile: Board abandons plans, fearing antitrust concerns would derail any merger.International New York Times. Web.
Rigolosi, E. (2005). Management and leadership in nursing and health care: An experiential approach (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
Stanford, N. (2007). Guide to organization design: Creating high-performing and adaptable enterprises. Mason, OH: Bloomberg Press.
Vroom, V. (1976). Can leaders learn to lead?. Organizational Dynamics, 4(3), 17-28.
Vroom, V., & Yetton, P. (1973). Leadership and decision-making. New York, NY: University of Pittsburgh Press.
Yao, D. (2014). Moody’s: Sprint/T-Mobile merger faces negative free cash flow until at least 2018. Web.