Introduction
It is challenging to deny the claim that the Covid-19 pandemic has become one of the most unpredictable events in the world’s history. The crisis and governments’ attempts to mitigate its consequences have impacted the whole globe, making lockdown, social distancing, and other preventive measures “new normal.” This state of affairs refers to the fact that multiple spheres of the world economy experience problems resulting in decreased revenue, higher unemployment rate, and others. However, one should also admit that the pandemic has helped some industries face growth. That is why the given research paper is going to present a detailed overview of how Covid-19 had impacted the economy.
In covering the idea above, the paper will demonstrate that the pandemic has differently affected world countries. Even though the US financial markets were in decent conditions during the pre-crisis period, the nation has suffered one of the most noticeable economic downturns in its history (Patton, 2020). Furthermore, the country is underperforming in equity disbursement compared to other First World countries. Since this financial concept describes the distribution of money from financial institutions, it can be useful in assessing how and why the economy suffers from the crisis. Thus, analyzing this information is significant because it can reveal that some countries undertake more successful approaches in managing such situations. These results can become guidance for other nations to mitigate the coronavirus’s negative impact and recover from financial problems.
It is also reasonable to make a point concerning the information above. A thesis statement is that Covid-19 has brought mainly adverse consequences for the world economy, while the inefficiencies in the US are present because the nation failed to offer an adequate response to the pandemic. This idea demonstrates that political decisions and social events have contributed to economic issues in the United States during the Covid-19 pandemic. In an attempt to support this thought, the paper will rely on logical argument and scientific evidence. In particular, the given study will use charts and graphs from credible sources to justify the ideas.
Research Question
A specific research question is necessary to guide the scientific activities of this study. The present paper will focus on the following: To what extent have poor political decisions and social unrest led to the fact that the US economy showed worse results compared to other First World countries? This question demonstrates that there can be a direct and substantial connection between financial markets’ performance and external conditions. It means that the government’s decision to introduce lockdown measures or limit businesses’ activities can influence a country’s economic indicators. Simultaneously, massive demonstrations and strikes also bring uncertainty to the market, making numerous industries experience losses and other problems. That is why there is evident reasoning behind suggesting that the variables above can explain the United States’ poor performance regarding equity disbursement. Furthermore, answering this question is expected to reveal that various economic spheres have witnessed different consequences after the pandemic.
The research question above allows for offering the study’s hypothesis. This statement implies that poor political decisions and social unrest in the USA have become the leading events that can explain why the US is underperforming in equity disbursement compared to other First World countries. In an attempt to prove or disprove this hypothesis, one should identify economic indicators for the United States and other developed nations, including Norway, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, Germany, and Canada. This approach will bring more scientific value to the study. It is so because relying on such indicators will allow for identifying whether there is a statistical correlation between the variables under analysis and equity disbursement in the US. Consequently, the determined and synthesized data will help generate credible conclusions that will demonstrate whether the proposed hypothesis is valid.
Thesis
As has been mentioned above, the current paper focuses on a specific thesis statement. It is that Covid-19 has brought mainly adverse consequences for the world economy, while the inefficiencies in the US are present because the government failed to offer an adequate response to the pandemic. The following paragraphs will present some logical reasoning to justify the claim above. They will mention original thoughts, while scientific evidence will be introduced in the Literature Review section.
When it comes to assessing the Covid-19 pandemic’s impact on the world economy, many people tend to highlight its adverse consequences, and there is an evident rationale behind such claims. It is so because the disease has reshaped many phenomena and processes that were considered unchangeable and undeniable. For example, the freedom of movement and travel was a characteristic feature of every developed society, and no nation could deprive individuals of this liberty unless it was required to protect public order and health. However, the whole globe now understands that such a measure can be justified under some conditions.
There is no doubt that the “new normal” living situation has significantly affected the world economy. Governments’ preventive measures resulted in the fact that most businesses were temporarily closed because people were only allowed to leave their homes for a limited set of reasons. This decision has brought the most significant problems for those industries that focused on direct contact with customers and promoted gatherings of many people in the same place. For example, it refers to entertainment establishments, tourism, transportation services, and others. Some of these businesses found themselves on the verge of bankruptcy because of the widely-accepted preventive measures.
Even though it can be surprising, some industries have experienced growth during the pandemic. It relates to those organizations that do not need to establish physical contact with customers to run business. For example, multiple online companies and firms have witnessed a much higher demand against the pandemic’s background. Furthermore, various digital businesses became successful in the Covid-19-era because they have managed to offer timely and practical solutions to the new challenges. Since people were forced to stay at home, they were still required to deal with numerous vital activities. That is why online retailers, remote working solutions, video conferencing services, and others became demanded in such a society. This suggestion demonstrates that even the dangerous virus cannot be assessed unequivocally. No one would neglect the pandemic’s adverse consequences on people’s health and the world’s economy in general. However, it is also reasonable to consider that the negative event provided some businesses with growth and development opportunities.
When it comes to assessing how the Covid-19 pandemic has affected various countries, it appears that the US has witnessed more adverse consequences. Since the country has the highest number of confirmed coronavirus cases in the world, it is not a surprise that its economy is also subject to significant adverse effects. This information makes it rational to identify why this state of affairs is found in the United States. The present research overrides the claims that the US’s underperformance in equity disbursement is because the country’s economy is weak. It is so because the United States did not experience any significant economic or financial issues before the pandemic. That is why it is reasonable to suppose that some other phenomena have contributed to this negative outcome.
As has been mentioned above, the research paper tries to answer a specific question. It refers to whether poor political decisions and social unrest have led to the fact that the US economy showed worse results compared to other First World countries. The proposed thesis statement implies that these events are the leading causes of the economic issues under analysis. However, in an attempt to answer this question and justify or deny the hypothesis, the current study should rely on a scientific approach. That is why the research paper will look for statistical data and experts’ commentaries to assess the relationships between the study variables, including political decisions, social unrest, and economic indicators. Thus, the thesis is going to be defended by identifying adverse consequences of the phenomena under analysis on the American economy.
It is reasonable to conceptualize the meaning of social unrest and poor political decisions within the scope of this research. The former term refers to Black Lives Matter demonstrations that took place across the country against the pandemic’s background. These events included many thousands of people who gathered outdoors to express their dissatisfaction with police brutality and white supremacy. Since Covid-19 is a highly infectious disease, some people believe that these demonstrations contributed to its spread, leading to adverse economic consequences for the nation. The latter concept refers to those government decisions that were made or not made to help the country overcome the crisis. For example, it relates to specific measures to prevent employers from firing their employees, support small businesses, provide local governments with monetary support, and others.
It is expected that the two concepts above contribute to the fact that the American economy loses its position. On the one hand, Black Lives Matter demonstrations are considered to increase the number of confirmed Covid-19 cases in the nation. It leads to the fact that the economy is left without a significant part of the workforce. On the other hand, the poor government’s decisions do not offer effective measures to address unemployment rate increase, provide financial support, and others. The combination of these two factors is considered to result in the fact that the United States’ economy is underperforming in equity disbursement.
The information above has introduced the topic, answered the research question, and explained how the thesis is going to be defended. That is why the following section will present and synthesize scientific evidence on the topic to confirm or deny these ideas. Attention will be drawn to scholarly papers, newspaper articles, government agencies, and reputable organizations. These sources can provide the research paper with valuable information to assess the American economy’s state against the pandemic’s background. Furthermore, other First World countries’ economic indicators will be analyzed to find whether it is true that they show better performance when compared to the United States. This approach will allow for proving or disproving the research hypothesis.
Literature Review
The present section will introduce and synthesize scientific findings to answer the research question and test the hypothesis. In the beginning, it is reasonable to focus on the Covid-19 pandemic’s overall impact on the world’s economy. It is impossible to ignore the vast adverse consequences of the event under consideration. Pak et al. (2020) confirm this claim and demonstrate that the crisis has resulted in an essential decline in oil prices. This fact denotes that various world economies faced significant losses because of this fact. Abel and Gietel-Basten (2020) emphasize that adverse consequences occur since international borders were closed, which created substantial issues in the globalized world. Simultaneously, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) (2020) demonstrates that the Covid-19 pandemic has differently affected multiple industrial sectors. This organization analyzed the indicators of numerous economic spheres and concluded that most industries witnessed negative consequences, either protracted or lagged, while others witnessed recovery. Computer electronics, machinery, leather, furniture, and apparel industries are among those that saw growth during the pandemic (UNIDO, 2020). This literature demonstrates that the pandemic’s overall impact is negative, while some positive features are still present.
Since it has been suggested that social unrest in the United States became one of the leading causes of the nation’s poor economic performance, it is reasonable to identify what reputable and credible sources mention. Even though it is possible to expect a connection between the protests and an increased Covid-19 incidence, scholars and experts deny this claim. For example, Neyman and Dalsey (2020) have conducted a scientific study and identified that the protests resulted in a socially insignificant increase in the Covid-19 rates. The scholars investigated the data from two databases to arrive at such findings. Lazer et al. (2020) conducted another survey to track a connection between the massive protests and the disease spread. The researchers identified that Washington, DC, saw the highest participation percentage of 13.7% (Lazer et al., 2020, p. 10). However, the capital did not witness any significant increase in the coronavirus cases during the period of protests. Thus, no scientific grounding supports the claim that the Black Lives Matter events intensified the pandemic’s adverse effects on the American economy by reducing the workforce.
The next step is to find a connection between economic consequences and the United States’ political decisions to address the crisis. Numerous credible sources admit that the pandemic has severely affected the US because its administration failed to take adequate and timely measures. Zamarripa (2020) states that it took 55 days for the country “to reach a daily testing rate of one test per 1,000 residents after surpassing the milestones of 1,000 total confirmed cases” (para. 8). In comparison, it took one day for Iceland, eight days for Norway, and 45 days for Australia (Zamarripa, 2020). This example demonstrates that President Trump and his administration postponed taking specific efforts. This strategy resulted in the fact that the country has witnessed a significant rise in its unemployment rate. Patton (2020) demonstrates that in late 2020, there were almost seven million unemployed workers more than it was in early 2020 before the pandemic. It denotes that the American economy was losing its position because it has an insufficient labor force.
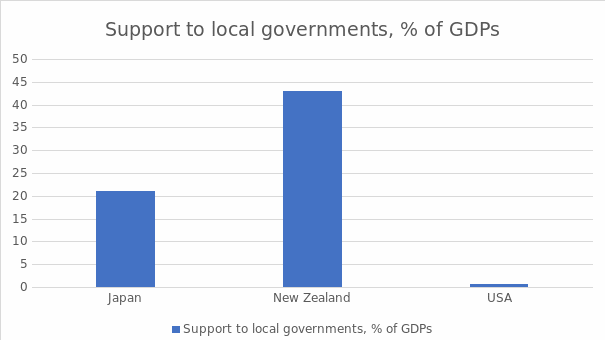
Furthermore, Trump’s administration also failed to provide state and local governments with adequate monetary support. For example, Burns (2020) stipulates that slightly less than 100% of American cities with a population of 50,000-more than 500,000 citizens anticipated a revenue shortfall. The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act was initiated to address the situation above. This step provided the governments with $150 billion, but this sum only constituted 0.7% of US 2019 GDP (Zamarripa, 2020, para. 19). Other developed nations allocated more resources to assist their economies. In particular, Japan used 21% of its 2019 GDP, while New Zealand spent more than 40% of its 2018 GDP to support their local governments (Zamarripa, 2020, para. 19). This fact highlights that the economic inefficiencies in the USA are present because of insufficient aid to local and state governments.
Finally, it is reasonable to explain that a failure to help small businesses also intensified the pandemic’s adverse consequences. In April 2020, every fourth small business reported temporarily shutting down (US Chamber of Commerce, 2020). Zamarripa (2020) demonstrates that Trump tried to provide companies with assistance, but the CARES Act offered aid to large firms, while minority-owned, women-owned, and rural businesses were suffering significant losses. In comparison, the German government took certain efforts to allow most offices and factories to work, while South Korea kept its entire economy open (Zamarripa, 2020). The information above presents an evident reason to explain why the US is underperforming in equity disbursement compared to other developed nations.
Methodology
This section will explain the details of how the research has been conducted. The Literature Review has presented the findings from multiple credible sources, including government agencies, newspaper articles, and scholarly journals. In addition to theoretical details, these sources offered percentages, statistics, and other numerical data to demonstrate what is happening to the American economy during the Covid-19 pandemic. That is why it is reasonable to present these economic indicators in a detailed manner and explain how they were acquired. A suitable approach is to deliver appropriate visuals from the sources used to compare the United States’ economy with that of other First World countries.
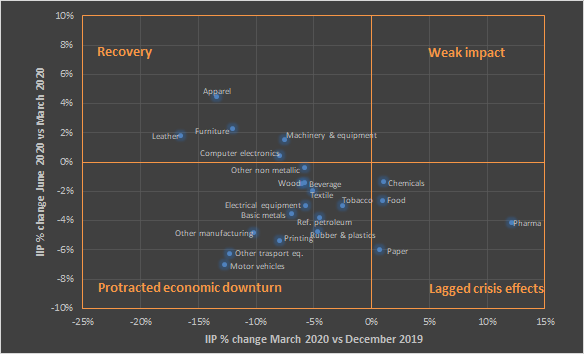
Firstly, it has been mentioned that the Covid-19 pandemic has brought various consequences to different industries. It is so because some economic spheres were more prepared to run their operations against the background of preventive measures. Thus, Figure 1 by the UNIDO (2020) demonstrates how the crisis affected various industries worldwide. In particular, the organization focuses on the adjusted Index of Industrial Production (IIP) that reflects production volumes (UNIDO, 2020). Thus, the visual below allows for stating that the majority of industries experienced adverse effects because their IIPs became significantly lower in 2020 compared to the indicators of late 2019. However, fewer economic spheres faced recovery during the pandemic because they managed to provide their services to customers. Furthermore, the preventive measures increased the demand for products from such industries. For example, the lockdown made it necessary to work remotely, which explains the computer electronics sphere’s recovery.
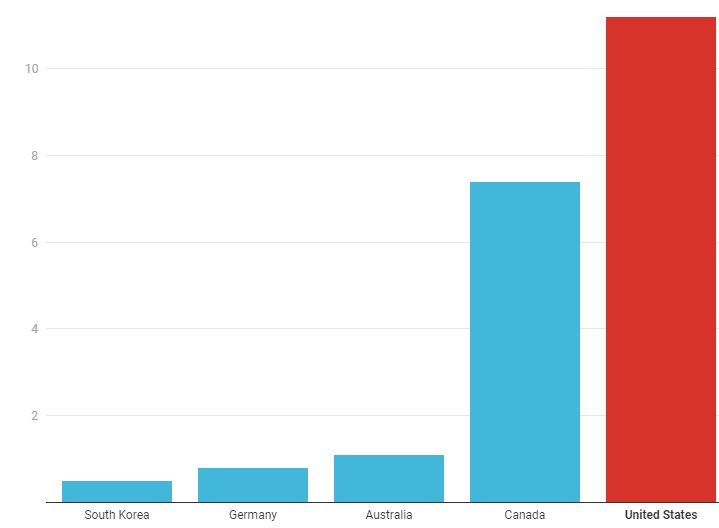
Secondly, it is reasonable to present evidence to justify that the American economy is suffering losses because of a high unemployment rate. Figure 2 by Zamarripa (2020) demonstrates that the United States has a much higher portion of unemployed individuals than other developed nations, including South Korea, Germany, Australia, and Canada. The given graph can be considered reasonable and credible because it relies on the data offered by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (Zamarripa, 2020). There is no doubt that this state of affairs adversely affects the whole American economy. Since Figure 1 has demonstrated that the severity of the pandemic’s consequences depends on a specific industry, it is impossible to suppose that this United States’ inefficiency occurred because of American economy properties. That is why one can suggest that the American government failed to find an adequate response as distinct from other developed nations.
Thirdly, it is essential to consider what actions the United States has taken to mitigate the pandemic’s economic consequences. Figure 3 has specifically been created for this research to exemplify this issue. This graph relies on the data by Zamarripa (2020), who comments on the amount of assistance that various countries around the world offered to their local and state governments. Thus, Figure 3 demonstrates that the American government provided monetary support that was significantly lower when compared to other First World countries. The graph reflects the amount of assistance in connection to the country’s GDP. The United States’ CARES Act provided local governments with $150 billion, but this sum was insufficient considering the proportion of this assistance to the nation’s 2019 GDP. The data from Japan and New Zealand reflect that these countries allocated a higher part of their resources to cope with the crisis.
Analysis
This section will present the analysis of the information that has been mentioned above. Attention will be drawn to whether the data from the Literature Review support the thoughts from the Thesis section. The following paragraphs will rely on scientific evidence and logical reasoning to arrive at conclusions. This analysis will help answer the research question and identify whether the hypothesis has been proved or denied.
The thesis statement mentioned that the Covid-19 pandemic had mainly adverse impact on the world, and the research paper has proved this claim. Sufficient scientific evidence has demonstrated that lower oil prices and decreased production volumes provided numerous industries with losses. However, one should admit that the crisis has changed the world, meaning that the demand has also shifted. That is why some businesses were experiencing growth during the pandemic. Since people were forced to stay at home and perform their work duties, the computer electronics sphere was enhanced to meet these new requirements. Furthermore, individuals became more involved in online shopping activities, which explains the reasons for the recovery of leather, furniture, and apparel spheres worldwide. Consequently, it is challenging to offer a unanimous appraisal of the Covid-19 pandemic when it comes to its economic effects throughout the world.
The present research has not managed to find credible evidence to state that the Black Lives Matter protests intensified adverse impacts on the American economy by increasing the number of Covid-19 cases. Neyman and Dalsey (2020) identified that the median coronavirus rate was 0.0049 in protests counties and 0.0041 in control ones. Even though the difference was considered statistically significant, the researchers assure that it should not be overestimated because protest counties were more populous. In other words, a higher Covid-19 rate among protesters was found because more people attended these events. This information denies the effect of the Black Lives Matter demonstrations on the US economic inefficiencies because the social unrest did not reduce the nation’s workforce by increasing coronavirus incidence. Since these events did not contribute to the fact that the American economy fell short of workers, it is not reasonable to blame the demonstrations for economic issues.
The situation is the opposite when it comes to assessing the role of the government’s decisions. The crisis is unprecedented, meaning that an immediate and adequate response is needed. However, the identified data have demonstrated that the United States failed to cope with this task. On the one hand, Trump’s administration was not hasty in implementing measures because it took much more days for the US to increase testing volumes compared to other countries. Since there were no actions to respond to medical issues, it is not a surprise that the economic sphere did not face any essential interventions. On the other hand, when some monetary support was finally offered, it was significantly smaller compared to that in other developed nations. That is why one can claim that the US administration provided its local and state governments with insufficient monetary aid. Thus, this fact can be considered one of the leading prerequisites of a high unemployment rate in the United States.
At this point, it is reasonable to comment on how the data above relate to the research question. Its first part received a positive answer because a significant correlation between poor political decisions and the American economy’s inefficiencies has been identified. A failure to take timely measures and the provision of insufficient support has led to the fact that the United States economy suffers from many issues, and a high unemployment rate is among them. Since many industries are deprived of their workforce, they have difficulties meeting the customers’ demand. However, the second part of the research question did not receive sufficient evidence to be considered correct. It is so because no direct connection has been found between Black Lives Matter demonstrations and increased coronavirus incidence. Since the protests did not lead to more Covid-19 cases, it is impossible to tie these events to economic issues.
The findings above also allow for commenting on the research hypothesis. The situation is the same as with the research question. In particular, the first part of the hypothesis has been proved, while the second one has been denied. This claim refers to the fact there was no statistical dependence between Black Lives Matter demonstrations and the increase in Covid-19 cases, while a connection between poor political decisions and economic inefficiencies could be found.
However, some people can oppose the argument above by stating that Trump’s administration could not cope with the crisis and its challenges because the American economy was weak when the pandemic arrived. Specific economic indicators are suitable to deny this statement and avoid disclaiming the government’s responsibility. It relates to the fact that the unemployment rate was at a 50-year low, while inflation was below 2% before the pandemic (Patton, 2020, para. 7). That is why it is not reasonable to refute the argument of this research and claim that Trump’s administration could not find any effective solutions because of previous problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is rational to comment on the significance of the findings. Firstly, they demonstrate that even though the pandemic has brought mainly adverse consequences, it is still possible to grow in this environment. Such a result is possible if industries offer products and services that are more required during the pandemic. Various businesses can use this information to identify how they can overcome new challenges and stimulate their development. Secondly, the research paper has demonstrated that political decisions can have a significant impact on economies. Thus, a failure to take timely and sufficient actions can result in the fact that the country witnesses adverse consequences because of the Covid-19 pandemic. Even though this information relates to the American context, representatives of other nations will also find it helpful. It is so because the conclusions reveal that poor decisions can subject one of the strongest economies to adverse effects.
The findings allow for concluding regarding whether the research question has been answered. Its first part was confirmed, while identified scientific evidence was located to state that the second part of the question about the effect of the Black Lives Matter demonstration has been denied. This information implies a significant meaning for the bigger picture. Since the Covid-19 pandemic is not over, it can create fundamental problems for many economies worldwide. Thus, the given research paper has demonstrated that governments should bear leading responsibility in finding practical solutions to mitigate the pandemic’s effects. When it comes to identifying proper responses, governments should avoid repeating the mistakes of Trump’s administration. It refers to taking late actions and offering insufficient monetary support because such a strategy can lead to adverse economic indicators, and the increased unemployment rate is a suitable example.
References
Abel, G. J., & Gietel-Basten, S. (2020). International remittance flows and the economic and social consequences of Covid-19. Environment and Planning A: Economy and Space, 52(8), 1480-1482.
Burns, D. (2020). The economy and cities: What America’s leaders are seeing. The United States Conference of Mayors.
Lazer, D., Santillana, M., Perlis, R. H., Ognyanova, K., Baum, M. A., Druckman, J., Quintana, A., Volpe, J. D., Chwe, H., & Simonson, M. (2020). The state of the nation: A 50-state Covid-19 survey. Report #10: The pandemic and the protests (PDF document).
Neyman, G., & Dalsey, W. (2020). Black Lives Matter protests and Covid-19 cases: Relationship in two databases. Journal of Public Health (Oxford).
Pak, A., Adegboye, O. A., Adekunle, A. I., Rahman, K. M., McBryde, E. S., & Eisen, D. P. (2020). Economic consequences of the Covid-19 outbreak: The need for epidemic preparedness. Frontiers in Public Health. 8(241).
Patton, M. (2020). The impact of Covid-19 on U.S. economy and financial markets. Forbes.
United Nations Industrial Development Organization. (2020). Coronavirus: The economic impact.
US Chamber of Commerce. (2020). Special report on coronavirus and small business – April.
Zamarripa, R. (2020). 5 ways the Trump administration’s policy failures compounded the coronavirus-induced economic crisis. Center for American Progress.