Introduction
Strategic analysis is one of the fundamental management elements and it involves evaluating an organisation’s business environment in order to be effective in formulating business goals. Conversely, strategic planning is long-term oriented and it focuses on the entire organisation.
Strategic planning involves setting long-term organisational goals and formulating plans that aid in attaining pre-determined ends. Besides, strategic planning enhances optimal resource allocation, thus increasing the likelihood of realising organisational goals and a high competitive edge.
Grunig and Kuhn (2011, p. 8) argue that the ‘process concentrates on determining the future success potentials’.
Organisations base their long-term planning process on the hypothesis that the prevailing environment will persist for a prolonged period. However, Marvell (2009) is of the view that achieving strategic goals is a demanding task due to the turbulent business environment in which firms operate.
Thus, organisational managers must evaluate the emerging issues progressively and adjust their operational strategies accordingly.
British Airways has attained market position by operating as a full service global airline. The airline has established a broad global route network. These aspects have provided the firm with optimal market leadership in the UK. Furthermore, its extensive network has provided a global market presence.
The airline intends to achieve long-term sustainable competitive advantage. However, this goal will depend on the effectiveness in aligning the firm’s operations with the changing business environment such as fluctuating oil prices (Ringbeck, Gautam & Pietsch 2009).
Purpose
This paper involves a critical strategic analysis of the British Airways. The analysis considers a number of elements, which include a resource audit, value systems, product/service portfolio, and the potential future strategic growth.
Resource audit
Effective resource management is essential in organisations’ pursuit for competitive advantage. Resources include an organisation’s competencies and assets. Assets include the diverse resource endowments such as equipments, plants, brand equity, and location that an organisation has developed or accumulated over time.
Conversely, competence includes the abilities, skills, and knowledge within an organisation that enable the firm to transform inputs into outputs directly or indirectly (Sahaf 2008). One of the strategic management aspects that organisational leaders should consider entails adopting a resource-based view [RBV].
The approach accentuates that firms can derive competitive advantage from optimal utilisation of the internal capabilities and resources. However, an organisation’s ability to develop and sustain the competitive advantage from its assets depends on the superiority of its resources and capabilities (Stonehouse & Houston 2003).
British Airways has adopted the RBV in its operation, as evidenced by the resources that the firm has developed individually and through partnership.
British Airways has nurtured diverse business resources, which include technological capabilities, physical resources, financial resources, organisational systems, human resources, and intangible resources.
Technological capabilities
British Airways is committed to meeting and exceeding the customers’ experience. The firm considers technological capability as one of the fundamental operational aspects in attaining total flight reliability.
British Airways undertakes careful planning and resources, which is made possible by the firm’s investment in tooling and training (British Airways 2015b). By developing adequate engineering capabilities, the firm undertakes the right diagnostic and testing on the aircrafts, hence sustaining the condition of its modern commercial aircrafts.
The firm’s technological capability is also enhanced by its extensive aircraft maintenance facility located in the UK. Moreover, a team of over 2,000 skilled engineers undertakes aircraft maintenance. The team undertakes different maintenance activities such as structural repairs and other major aircraft maintenance.
Due to its technological capabilities, British Airways has entrenched its commitment to customer safety, which is a vital element in strengthening customer trust (Bartsch 2012).
In addition to the above aspects, the company collaborates with Original Equipment Manufacturers [OEMs] such as Boeing in its aircraft maintenance process. The partnership enables the airline to undertake effective aircraft maintenance by implementing emerging technologies.
In 2015, British Airways acquired the right to utilise Boeing’s Electronic Logbook [ELB] and Boeing Airplane Health Management software, which enables the organisation to diagnose technical problems electronically in its aircrafts.
Through the partnership, British Airways has remarkably improved its ability to undertake aircraft maintenance. Moreover, the firm is in a position to share expertise and knowledge on aircraft maintenance with Boeing (Payler 2015).
Physical resources
The intensity of competition in the global airline industry has grown considerably due to different factors such as increasing demand for air travel and reforms within the industry such as liberalisation of the airspace (Flouris & Oswald 2006).
Surviving in such an environment is quite challenging and it requires the industry players to develop a high level of operational efficiency. In a bid to achieve this goal, British Airways has integrated a number of physical resources. First, the firm owns and operates the largest hi-tech fleets.
The fleet is comprised of different types of aircrafts such as Airbuses, Boeings, and Embraer. The airline has a fleet of over 2,000 aircrafts (British Airways 2015a).
The airline has also integrated effective ground handing technologies, which enable the firm to handle the customers’ luggage effectively and efficiently. Every week, the airline handles over 250,000 bags, which is made possible by different equipments and facilities (British Airways 2015a).
Due to its effective ground handling services, British Airline sustains operational efficiency at Heathrow Airport, which ranks amongst the busiest airports in the world. This aspect has contributed to the company’s high competitive advantage.
Human resources
British Airways has integrated employee training as one of its strategic management elements. Training is performed on different aspects such as aircraft training, which is undertaken using state-of-the-art facilities (Katie 2010).
The airline has integrated a program referred to as ‘airmanship’, which focuses on training employees on how to handle customers and luggage by focusing on safety.
This move has enabled the company to develop an effective working culture. Moreover, the company’s physical resources have led to the development of a high level of trust among different customers such as individual and business customers.
Financial resources
British Airways has developed adequate financial strength, as evidenced by its attractive profit margins. It is projected that the firm’s profitability will reach £1.3 billion in 2015 (Whiterow 2013).
The company profitability is expected to arise from the establishment of new routes, hence serving a large number of customers. Due to its financial strength, British Airways sustains its competitiveness by acquiring new technologies and new aircrafts.
Value systems
British Airways is focused on achieving and sustaining an optimal market position. In a bid to achieve this goal, the airline has invested in a number of activities that culminate in value addition to its products and services. The firm’s value adding activities do not focus on the internal operations exclusively.
On the contrary, the firm management team appreciates that its ability to develop a value system that culminates in the desired level of synergy depends on the extent to which effective linkages are established between the internal and external activities.
Evans, Stonehouse, and Campbell (2012) affirm that value addition can be achieved by changing the customers’ perception regarding the products and services offered. Consequently, the firm influences the consumers’ decisions to consume its air travel services.
The company’s commitment in delivering value to its target customers is illustrated by the value chain analysis below.
Primary activities
Inbound logistics
The Heathrow International Airport serves as British Airway’s hub. Moreover, according to British Airways (2015a par. 6), ‘the airline has also established operations at other airports such as London Gatwick and London City airports’.
At Heathrow Airport, British Airways operates in three main terminal, viz. Terminal 1, Terminal 3, and Terminal 5. The airports have considerably improved the airline’s seamless operations.
Operations
Ensuring seamless operations is a critical element in sustaining competitive advantage in the airline industry. British Airways has taken into consideration a number of elements, which include check-in, service desk, effective baggage and handling, bounding and lounge services, and airport pushback.
The check-in, bounding and lounge services, baggage, and handling operations ensure that customers are served efficiently and cargo is handled effectively. Conversely, effective airport pushback using tractors ensures that passengers board the aircraft easily at the established terminals (British Airways 2015c).
Outbound logistics
The company intends to achieve and sustain adequate competitiveness in the global airline industry. Consequently, the firm focuses on offering diverse air transport services such as passengers and cargo services.
The firm has established the British Airways World Cargo hence ranking the firm amongst the leading cargo airline companies. The airline offers courier services in over 200 destinations located in over 80 countries (British Airways 2015a).
By establishing the British Airways World Cargo, the firm has improved its efficiency in offering customers different cargo services around the world.
Marketing and sales
It is imperative for firms’ managers to develop adequate brand loyalty in order to enhance the development of repeat purchase behaviour amongst customers.
British Airways has developed adequate level of brand awareness, which has been enhanced by the adoption of different techniques such as offering customers loyalty programs, effective pricing, and market communication through different mediums such as point of sale materials and online marketing.
The firm undertakes online marketing through different platforms such as social media networks. Moreover, the firm has integrated public relations, as evidenced by the participation in different charitable activities and sponsoring different cultural and sporting events.
These marketing approaches have influenced the customers’ perception positively regarding the services offered by the firm.
Service
The company has integrated a number of after-sale services such as customer service, which is available for 24 hours per day. Efficient customer service delivery have also been promoted by the integration of online support portals that customers can use in seeking clarification and raising complaints regarding the firm’s services.
Other services offered include catering and hospitality services and lounges. These aspects have contributed to development of a high level of customers’ satisfaction.
Support activities
British Airways has considered a number of support activities that aim at enhancing the effectiveness of its primary activities. Some of the support activities that the firm has taken into consideration are evaluated herein.
Human resource management
Developing a strong human capital base is a vital element in establishing a strong competitive edge (Hill & Jones 2010). British Airways recognises human capital as one of the critical organisational asset. Thus, the firm has integrated efficient human resource management practices.
Some of the HRM aspects that the firm has considered entail employee reward and training. The firm’s reward system is comprised of monetary and non-monetary rewards. Conversely, the training programs enhance the employees’ knowledge, skills, and expertise, hence their ability to execute their roles and responsibilities optimally.
By adopting these approaches, the firm has improved the employees’ level of job satisfaction significantly due to fair and equitable remuneration and the career progression opportunity.
The ultimate effect is a high rate of employee retention, which further fosters the firm’s ability to achieve and sustaining its long-term competitiveness (Riege 2005).
Firm infrastructure
British Airways has designed its operations into a number of functional departments, which include marketing, finance, legal, quality, and public relations. The respective departments have the discretion in making decisions associated with their operations.
However, it is essential for the departmental heads to ensure that the decisions made contribute to the attainment of the overall organisational goal. Furthermore, the functional departments must operate synergistically, for example by sharing information in order to enhance the entity’s operational effectiveness.
Technological development
The company invests in continuous research and development in order to promote its market dominance. However, the firm’s research and development initiatives are undertaken collaboratively between British Airways and Original Equipment Manufacturers [OEMs] such as Boeing.
Furthermore, the airline collaborates with ICT companies in implementing digital technologies such as in-flight entertainment systems coupled with computerised reservations system.
Additionally, the airline has integrated a flight scheduling system. These aspects have enhanced the firm’s innovativeness, hence its capacity to undertake new product development.
Product and service portfolio [BCG Matrix]
British Airways intends to attract a substantial number of customers by offering attractive products and services. Currently, the airline offers two main products, which include cabin and cargo services.
The British Airways World Cargo has improved the airline’s capacity to offer cargo services to diverse customer groups such as the corporate and individual customers. The firm ensures a high level of professionalism in handling cargo.
Moreover, handling of cargo services is promoted by the integration of advanced automated freight handling technology. Thus, the airline handles million tonnes of freight. Furthermore, the firm has designed its flight schedule effectively, hence improving its reliability to customers.
With regard to cabin services, British Airways has designed its cabin services into different classes in an effort to meet the travel needs of the different customer groups. The main classes include the short haul, mid-haul, and long haul.
The short-haul unit is further divided into economy and business class while the long haul unit is comprised of the first class, club world, world traveller, and world traveller plus. The respective business units are instrumental to the firm’s performance.
However, their contribution varies and likelihood of adding to the firm’s long-term growth differs as illustrated by the BCG matrix below.
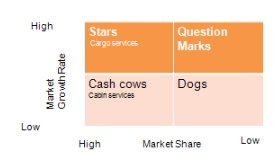
Figure 1: [BCG Matrix]
The cabin services can be categorised as source of income due to their ability to generate sufficient cash flow to the firm. Through the cabin service, British Airways serves a large number of customers. However, the potential for growth is relatively low due to the intense competition within the industry (Uddin & Akhter 2011).
Moreover, the entry of low-cost airlines companies has increased the intensity of competition. Conversely, the cargo services can be considered within the ‘star’ category due to high market growth potential.
Currently, growth in international trade between the UK and other countries has increased demand for cargo services. By developing efficient cargo services, British Airways will be in a position to enhance its attractiveness in the global airline industry.
Potential future strategic growth
Demand for air travel has increased considerably over the past decades. This trend has been spurred by the recognition of air travel as one of the most efficient method of transportation (IATA 2014). This aspect presents a notable opportunity for airlines to enhance their profitability.
However, the airlines’ efficiency in tapping the market opportunity will depend on the adopted strategies. British Airways can stimulate its growth by adopting a number of strategic growth options.
- Strategic alliance – Despite the fact that the firm is a member of OneWorld, which is one of the leading global alliances, the firm can enhance its competitive edge in the global airline industry by collaborating with other well-established airline companies. However, the alliance should not only be limited to airline companies, but also OEMs. This approach will enable the firm to develop sufficient competitiveness by developing its tacit and explicit knowledge. Furthermore, the airline will benefit from code sharing (Das & Teng 2002). Subsequently, the firm will attain a high operational efficiency. However, the firm should conduct a comprehensive strategic fit analysis before forming the alliances in order to determine the likelihood of attaining a high competitive edge by collaborating with the identified airline companies (Kale & Singh 2009).
- Market expansion– Another strategic option that the firm should consider in its pursuit for market growth entails market growth. The firm should enter the emerging economies such as the BRIC, which are considered as some of the most attractive markets due to their high rate of economic growth and volume of trade (Holloway 2003). These countries are increasingly liberalising the industry through the open-sky policy, which presents an opportunity for the firm to establish its market operations successfully (Petrick-Felber 2014).
Conclusion
The above analysis shows that British Airways has invested in effective strategic management practices. First, the firm has focused on developing its internal strength by exploiting different organisational resources such as human capital, physical, financial, and technological resources.
The firm has integrated both internal and external stakeholders in operations, which has led to the development of an effective value system. In addition to the above aspects, British Airways has diversified its product offering, hence maximising its cash flow. Moreover, the firm meets the diverse customer needs.
Recommendations
In a bid to improve and sustain sufficient competitiveness, it is essential for British Airways to take into consideration the following elements.
- The airline should focus on improving the customers’ perception regarding its products, services, and operation by investing in comprehensive value addition processes. In a bid to achieve this goal, the airline should develop sufficient market knowledge by investing in market research in order to understand the market trends.
- The company should invest in technological development by implementing emerging airline innovations. Some of the issues that it should focus on in its technological development relate to implementing fuel-efficient innovations and in-flight systems.
- The firm should invest in extensive continuous employee training on different operational aspects, customer safety, and security. These aspects will aid in strengthening the company’s brand.
Reference List
Bartsch, R. 2012, International aviation law; a practical guide, Ashgate Publishers, Burlington.
British Airways: About British Airways 2015a. Web.
British Airways: Engineering and maintenance services 2015b. Web.
British Airways: World Cargo 2015c. Web.
Das, T. & Teng, B. 2002, ‘Alliance constellations; A social exchange perspective’, Academy of Management Review, no. 27, pp. 445-456.
Evans, N., Stonehouse, G. & Campbell, D. 2012, Strategic management for travel and tourism, Routledge, New York.
Hill, C. & Jones, G. 2010, Strategic management theory: an integrated approach. Houghton Mifflin, Boston.
Holloway, S. 2003, Straight and level; practical airline economics, McGraw-Hill, Burlington.
Grunig, R. & Kuhn, R. 2011, Process based strategic planning, Heidelberg, New York. Flouris, T & Oswald, S 2006, Designing and executing strategy in aviation management, Ashgate, Aldershot.
IATA: The economic benefits generated by alliances and joint ventures 2011. Web.
Kale, P. & Singh, H. 2009, Managing strategic alliances; what do we know now and where do we go from here, . Web.
Katie, J. 2010, Strategic management; British Airways, Grin Verlag, London.
Marvell, A. 2009, GCE as travel and tourism double award for excellence, Heinemann, London.
Payler, A. 2015, British Airways wins CAA approval to use Boeing’s ELB. Web.
Petrick-Felber, N. 2014, Liberalising Europe’s skies, Anchor Academic Publishing, London.
Riege, A. 2005, ‘Three dozen knowledge sharing barriers managers must consider’, Journal of Knowledge Management, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 18-35.
Ringbeck, J., Gautam, A. & Pietsch, T. 2009, Endangered growth; how the price of oil challenges international travel and tourism. Web.
Sahaf, M. 2008, Strategic marketing; making decisions for strategic advantage, PHI Learning, London.
Stonehouse, G. & Houston, B 2003, Business strategy, Routledge, London.
Uddin, M. & Akhter, B. 2011, ‘Strategic alliance and competitiveness; theoretical framework’, Journal of Arts Science & Commerce, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 44-55.
Whiterow, P. 013, British Airways owner ups profit forecast margins improve. Web.