Introduction
British Airways has been in the air business travel since its inception in 1947. This has been coupled with a strong international brand name and good economic performance. However, new and emerging trends have continuously subjected to the airline industry’s management to tough challenges in decision making in the face of turbulent economic times and other global challenges. These challenges include cabin crew strikes, strike threats, adverse global economic conditions, declining profits, financial losses, and reduced consumer spending.
Therefore, management decisions, strategic plans and innovative approaches to addressing these issues could have a long term impact on the company’s financial performance and position in the market. These will be the determining factors for the continued survival of the company’s as an air carrier in the turbulent economic times and unfolding global trends. One of the radical, controversial, and high profile decisions made by the company’s management has been massive job cuts.
This decision has led to massive industrial strikes which have translated to a loss of business, declining revenue, and a damaged brand name. Management decisions have taken the company through periods of industrial disputes and dispute resolutions. The research was conducted to identify the commercial and managerial problems and challenges facing the company, evaluate the challenges, and design possible solutions to the problems plaguing the industry. In addition, the research was designed to investigate how management decisions and approaches have impacted the company’s revenue and the effects on the economy (Brother 1).
The research critically evaluates the impact of management decisions on employee productivity, company revenue, and investigates the appropriate solutions and approaches to addressing these problems and challenges. The report analyses the key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats affecting the company and looks at possible approaches for addressing these issues (Bazerman and Moore 2).
Statement of the problem
Managerial problems experienced by the British Airways have variably been affected by rising fuel costs, international insecurity, job layoffs and salary cuts, industry competition, management plans, strategic decisions, and an uncertain economic environment, leading to a decline in employee productivity, loss of business and declining company profits.
, The company has over time experienced declining profits due to increasing oil prices over the years, coupled with a downturn in consumer spending. Clark (1) argues that industrial action by the cabin crew coupled with Iceland’s volcanic eruptions have caused severely impacted on the company’s revenue adding to the massive financial losses it has been experiencing more recently. These unfolding conditions have challenged BA management’s approach to decision making in overcoming these problems.
The article, Strategic Management (1) argues that an efficient
Management should ensure that company resources are effectively and efficiently utilized, and effective controls are applied to align it to its vision to achieve their goals and objectives. Management strategy should identify and integrate appropriate approaches to profit maximization and sustainability in an environment prone to changing consumer behaviour, changing market forces and trends, and a dynamic business environment.
Management should tailor dynamic business plans to address the ever-changing business needs and requirements in achieving customer satisfaction and improving employee productivity to sustain revenue generation while maintaining a strong business position in a turbulent market. Specifically, companies sustain their business operations when profits are sustainably sufficient.
A case in point “The Unite trade union is pushing ahead with the industrial action that will see the start of three five-day strikes next week unless the two sides reach an 11th-hour settlement” (Clark 1). “The group was also hit by industrial action from its cabin crew in March, costing the business £43m” (Clark 1). Lack of contingency plans to address employee discontent and strikes reflects on the management’s failure to address employee concerns and to create a good working environment, directly negating on profit realization.
Significance of the Study
The company faces a number of commercial and management problems. These have revealed themselves in the form of declining profits, rising operational costs, and employee strikes, which have turned the prestigious airline industry to a loss-making business organization engulfed in a damaged brand name. These problems are directly linked to managerial approaches to decision making and conflict resolution. The organization’s management called upon the researcher to conduct research and critically evaluate the effects of job layoffs, rising fuel prices, and global economic trends on the company and design an appropriate strategy that could help steer the company from a loss-making to a profit-making business organization.
The report was found to be vitally important as it analyzed company position, key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and provided strategic solutions to managerial plans in performance enhancement and profit generation. The report also addressed employee concerns on job layoffs. Thus it will benefit current employees, the management of the company and revive the company’s strategic position.
In effect, a managerial plan and strategy could help the company maintain its strategic position in the Airline industry in the face of competing forces such as unfolding economic downturns, global recession and employee discontentment.
Aims
The aim of this project is to identify and provide an in-depth description and analysis of the pertinent factors or critical issues and commercial challenges facing the British airways. In addition to that, the project aims at analyzing strategic management plans designed to make the organization competitive in the market in line with its goals and objectives. The report analyzes the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats’ contributions to its current position in the market and how solutions to these problems could impact positively on the well being of the company.
Objectives
The research objectives seek to:
- Determine the effect of management decisions on employee productivity.
- Determine managerial approaches and strategic plans in countering the effects of global trends on the financial performance of British Airways.
- We are identifying managerial approaches to employee discontent and strikes.
- Identify and evaluate managerial plans in addressing competitive forces in the business industry.
- To critically analyze the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Identify strategic management plans for placing the company in a strong position in the market.
- To identify a sustainable approach to employee dispute resolutions.
Research Questions
Research questions to be answered include:
- What managerial decisions affect employee productivity?
- How do these decisions affect the organizations profits?
- What are the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats?
- What strategic plans are in place to exploit the company’s key strengths and available opportunities?
- How does the company plan to overcome its weaknesses?
- How do global economic events affect the airline financial performance?
- How can employee disputes be sustainably resolved without resorting to strikes?
- What strategic plans are in place to steer the company to sustainable profits?
- What managerial plans are in place to handle employee conflicts plaguing the company?
Incumbent upon the researcher was a call to answer the research questions by emphasizing on the need to identify appropriate strategic options for solving business problems identified in the research questions for economic sustainability and positive financial performance.
Background
The British Airways has been in the business of air travel since 1947. Over the years, the industry has been experiencing unprecedented growth until it started experiencing a decline in passenger traffic, employee strikes and a decline profits.
BA’s management has forecast a downward trend in the earnings from profits if contingency measures are not put in place to overcome this trend. This is in addition to the effects of controls that are put in place by the governments. In addition to that, these controls prevent the company from growing. These places the company in a difficulty position in dealing with situations that arise due to various environmental factors such as a decline in profits, competition from principal stakeholders, environmental factors, and global economic conditions.
More importantly, strikes have in the recent past enormously contributed to the enormous losses the company has incurred and as the company continues to suffer a bad image. The trend is discouraging.
A more recent trend has had the company make losses in its operations as a result of employee strikes directly resulting in managerial decision to adapt and implement deep cost cutting measures by cutting employee salaries and the size of its workforce.
Compounding the above problems with the current business trends called upon the researcher to conduct a research on the commercial challenges and management problems facing the industry and seek for practical solutions to the problems. Of interest were the drastic rates at which the airline’s profits were declining, frequent strike threats, and the impact of managerial decisions on the operations of the airline industry.
The airline industry has suffered from lengthy strikes translating to loss of business, low customer retention, low employee morale, and a poor market image. Employee layoff translates to fear and uncertainties, reduced productivity, anxiety, and strikes. Therefore the researcher felt justified to conduct this research to identify the best options and approaches to addressing the problems plaguing the industry. In addition to that, if the problems lead the industry to stall, the consequences of massive employee layoffs, grounded aircrafts and revenue generation could be disastrous.
Researching on the British Airways was a topic of interests since it could expose the researcher to the approaches managers used in making high profile and critical decisions and the impact of those decisions on the operations and sustainability of giant companies like the British airways. In addition, that could enhance the researcher’s skills in decision making at the managerial levels when faced with challenging business environment. The researcher could learn the long term impact of those decisions and innovative and alternative approaches to better and sustainable solutions for the problems and challenges facing the giant company.
Literature Review
Managerial decisions have diverse impacts on any organization and may lead a company’s operations to register massive profits or massive losses in addition to attracting large fines from legal authorities and instruments. That was what happened with the British Airways. According to Wardell (1), British Airways management executives endeavored to gain an economic upper hand by fixing fuel prices for its fleet of aircrafts against its competitors. “a total of around $550 million by British and U.S. authorities for colluding on fuel surcharges between August 2004 and January 2006, but Virgin and its executives were granted immunity after bringing the matter to the attention of the OFT” (Wardell 1).
The rise in fuel prices resulted in the adjustment of the cost of air tickets which resulted in a shift in demand for short distance customers. “For example, the number of short haul European business class trips from the UK has fallen dramatically from nearly 65% in 1991, to 25% in 2003. It is forecasted that as few as 15% of short haul business trips will be taken in business class by 2006” (Changes In Demand For Air Travel 1).
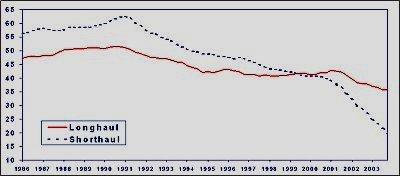
The effects of fuel prices on the cost of travelling and demand for the service are further illustrated in the above chart. The management should have strategic plans to convince customers to take longhaul flights. Thus BA’s executives should exercise their marketing skills and ability to justify price rises in air travel. A timely intervention could stem a drop in passenger traffic on longhaul flights. Accumulated effect of world’s economic recession was a further challenge on managerial approaches on averting further losses (Changes In Demand For Air Travel 1).
An annual report by the British Airways indicates drastic changes in the demand for air travel which at times was far much worse than predicted. “the economic recession that has followed has been severe, far more than most had predicted. It has hit demand for air travel significantly, particularly premium business. That coupled with record fuel prices in the early part of the year, has meant that we posted an operating loss of £ 220 million for the year, down from 1098 million and pre-tax loss of 140 million down 1323 million from the previous year” (British Airways 2008/2009 Annual Report and Accounts 13). These grim figures led the British Airways executives to design a plan to cut back on expenditure.
This was in addition to what Jakubal (1) describes as “The results raise the possibility that a rebounding economy may end up hurting carriers if it forces raw material costs up faster than it restores consumer confidence or travelling.” In addition to that Brothers (1) in her report argues that “The leading trans-Atlantic airline in Europe, British Airways, said Friday that its earnings collapsed over the past spring, in another indication of the havoc being wrought on the industry by a surge in the cost of fuel.” According to Brothers (1) an estimated 8 million pounds was spent each day in keeping the company’s fleet of aircrafts operational. These expenses could translate to millions of pounds in losses in a year.
The Economist (1) reported the possibility of a strike by British Airways cabin-crew in addition to the woes trailing the company. With a big volume of passengers using the airline in the recent past, the strikes could have a detrimental effect in the company’s earnings. According to the Economic Basics (1) previous strikes had reduced the carrying capacity of the airline by 25%, directly reducing revenue earnings drastically.
This effect was a direct result of the management’s decision to dismiss some staff members. According to Bono and Heller (4) these was a management problem that clearly revealed the management’s incompetence in amicably resolving employee conflicts. According to the Economist (1) “Indeed, staff are to be balloted again to assess their reaction to the dismissal of five staff members and the removal of flight perks from 55 others who took strike action earlier in the year.” Providing a clear picture of how BA is struggling “for its own continuing existence within the company’s workforce, the chances of its backing down remain thin. And with BA in the red, smarting from ash-cloud difficulties and doubtless casting jealous” (Economist 1).
Further still, BA’s woes do not end there. The management is faced with the challenge of keeping the company afloat in terms of its strategic positions by aligning it with its strategy and vision. These call into question the management’s strategies and functional approaches to solving the company’s problems.
The strengths of the airline industry have been its strong international brand name, a strong market position, well trained and skilled cabin crew and technicians, and a well maintained fleet of aircrafts on longhaul and shorthaul routes (Strategic Management 1). A SWOT analysis and competitive industry analysis was conducted on the company to identify various factors the management needed to embrace to avert the giant company from collapsing.
Research Methodology and Approaches
The purpose of the research was to determine managerial approaches to decision making in keeping the giant company operational in the face of competition, global economic trends, insecurity, and the impact of management decisions on employee productivity and strategic plans in aligning it to its vision.
The information was intended for the management of British airways executives to assist them make strategic plans to overcome and address emerging problems and economic challenges and formulate enhanced ways of addressing declining employee productivity, conflict resolution, and plummeting profits. Quantitative and qualitative approaches to data collection formed the basis of the research study. A SWOT analysis of the company was integrated in the study in addition to a study of the economic challenges facing the company.
These analyses could bring to light the effects of global economic trends including recent global recession, rising oil prices, insecurity such as the attack on the world trade center, recent volcanic eruptions over Iceland, the spiraling economic crisis in Greece, and frequent strikes due to job layoffs and management’s approach to tackling those problems.
Primary Sources
Primary sources of data included conducting interviews with the company’s management, line managers, and company employees. In addition to that, the researcher planned to administer structured questionnaires to customers, line managers and company employees. According to the article, Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources (1) primary sources of data form an important supplement to secondary sources and are advantaged by current information which is direct and accurate. (Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources 1).
Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources (2) clearly outlines various primary data collection methods. These include interviews, questionnaires, phone interviews, and one on one interviews were conducted. This formed an important part in accumulating expert information on various aspects of the research objectives and questions. Another approach to primary data collection included observations. These could be in line with employee productivity on a limited scale.
According to the article, Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources (3), the researcher planned well before hand on the research questions and determined how to identify responses to the questions. Ethical issues including seeking for permission to conduct interviews with an approach that caused minimum disruptions were factored (Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources 4).
The data collected from the interviews was analyzed for relevance to the research questions by going through the interview documents and selecting the relevant data to the questions (Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources 13).
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources of data included prints, abstracts, online sources, and review articles and other relevant issues. Among the most important secondary sources included the Wall street journal, The journal of Commerce, and radio stations including the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC).
These sources provided up to date information on unfolding events affecting the company in addition to providing various aspects on the effect of those events on the running of the company by the managements’ executives.
The British Airs Annual Report was an important basis for analyzing the company’s financial position and performance.
These sources also assisted the researcher in identifying the company’s market position and in identifying current strategies and how they impact on the company’s profitability and its image in the market.
Schedule
Due to the spiraling economic trend and other effects that have impacted on the company as a whole, the management assigned a period of two weeks for the researcher to conducts the research and present a complete report about the findings, conclusion and recommendations on the best course of action. Activities covered included, planning, collecting information from customers, conducting and interview and administering structured questionnaires with some line managers and employees.
Validity and Reliability
The internal validity will effectively demonstrate whether management decisions have a direct effect on employee unrest. In addition to that, the test validities could determine the effects of global, souring oil prices, and economic down turn specifically the current trends of global recession, spiraling effects of Greece’s economy in the Euro zone. Validity tests will rest on a comparison between previous profits and current figures and projecting on them out for a period of time to come.
These tests will clearly demonstrate the relationships between recession, strikes, oil prices, and current economic trends and the relationship between these variables with management decisions and how they impact on the performance of the airline company.
In addition to that, pretest and post test analysis will be conducted on the collected data to validate the findings. According to the article Sekaran (1), controls will be put in place to ensure no biasness affects the research by inclining towards the perceived courses in decreased profitability of the airline industry, frequent strikes, and other economic down turns.
To avoid bias characteristics defined ad demand characteristics, the article Sekaran (1) asserts that the subjects of study should not be given a cue on the outcome of the study. This reduces the possibility of “sure that subjects are not aware of anticipated outcomes (referred to as a blind study) reduces the possibility of this threat.
Scope and Limitations
The scope of the research will evaluate the relationship between the impacts of managerial decisions on employee productivity, how international oil prices have had an impact on the performance and profitability of the airline in relation to the current global economic crisis, and other environmental factors affecting the operations of the airline company. In addition to that, the study will concentrate on interviewing a small number of employees. The casual relationship between the employee strikes and managerial decisions to layoff certain employees and the effect of those layoffs on employee productivity were critical.
The research was however limited in scope. These limitations were directly as a result of management refusal to divulge some sensitive information to the researcher on issues such as management views on the laid off employees, the casual relationships between the strikes and the productivity of other employees and management view and plans to deal with such unrests. In addition to that, the approaches by management to deal with economic crisis was treated as confidential information especially with regard to the competition the company was facing from the Asian airlines and rising oil prices.
Description of Findings
BA’s brand name has been on the decline as its profits have experienced a downward trend. While the company’s management has on several occasions introduced cost cutting measures to maintain its position, the company does not seem to recover from the effects of the forces affecting its performance.
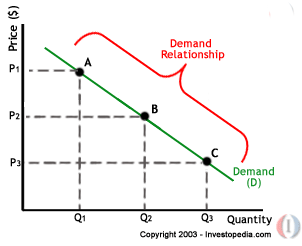
A case in point illustrates business decisions and their effects based on a report by the Milmo (1) “From Thursday, the surcharge on flights lasting more than nine hours will rise by £30 to £116 for a return ticket, while the levy for sub-nine-hour long haul flights to destinations such as New York will increase by £20 to £96. The surcharge on return short-haul flights will increase by £4 to £20”. The management decision to appreciate flight charges directly reduced customer flow that lead to a decline in company revenue. This management decision can be analyzed on the demand curve illustrated below (Wardell 1).
According to article on Strategic Management (1), an internal and external analysis of the company revealed a weak strategic position. The Value Based Management (1) asserts that despite the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats faced by the British Airways, the management has no strategic plans to analyze the company’s internal and external SWOT.
The management of BA should embrace the five stages identified in the Value Based Management (1) as setting long-term performance targets, forming the right product matrix, and a right marketing mix. By investing on the activities correctly, the company may realize an upper hand against its competitors in the market as is determined in (Strategic Management 1). Management should reduce employee discrimination and grant them equal opportunities. Reducing employee discrimination could lead to motivation, improved performance and a better image.
Employees
A managerial decision to scale down employee salaries and layoff some others resulted in cabin crew strikes. These resulted in the loss of business, a bad image and reduced customer traffic leading to low customer retention, poor company image, and huge financial losses. This action led customers to opt for alternative and cheaper means of transport.
Employee satisfaction is one of the motivating factors to their productivity and retention. Employees who remain satisfied in their jobs and have a guarantee of a secure job positively contribute to an organization’s performance. To the contrary, discontented employees tend to undermine an organization’s activities. Worries and anxieties associated with retrenchment, salary reduction, and any other form of lay offs, be they temporary or long term influence employee productivity.
Resolutions of worker’s grievances need timely attention. Management may engage employees in speedy grievance resolutions that would curb scenarios like mass industrial action that translates to loss of income in the way of profits. BA management has to make deliberate efforts to listen to employee disputes and create excellent channels of communicating their grievances to the management in a timely manner to avoid disputes spiraling out of control (Strategic Management 1).
New entrants
One strategy of competitively dealing with new entrants is providing incentives to customers, use of hard selling concepts, luring customers by offering price discounts at a competitive rate to the new entrants, and establishing long term relationship particularly with those customers who use the airline frequently. Customer needs need to be assessed to tailor make air travel needs, to suit customer needs. Good listening to customers is also another important marketing strategy.
Substitute routes exists such as road and rail transport. These need critical evaluations. According to Bono and Heller (1) the marketing and administrative management need to identify the need that drives customer to use alternatives of rail and road transport as opposed to air travel. According to the findings, the report recommended that the company conduct a SWOT analysis to determine its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (Edward & Heller 4).
According to the report, the key strengths of the company revolved around a strong brand name, strong customer focus, experienced staff, and use of modern technology.
According to the report Management executives, had to ask questions about newcomers, and their potential to cause a stir in the market. New entrants might be more powerful and create greater competition in the market. In addition, research established that the SWOT analysis called upon executives in the company to identify technology related issues of its fleets.
New Markets
According to Value Based Management (1) on marketing, various opportunities existed for the company to exploit in addition to new markets. A new market comes with its own challenges. Inclusive are legal requirements and other stringent rules by the host market. In addition, old competitors in that environment of newfound opportunities, tax requirements, and other hurdles may present a challenge for the airline in exploiting them particularly in the Asian markets.
Value Based Management (1) asserts that BA should have strategic plans to quickly and adapt to the changing environment. Their plans emphasized on operational management (Bono and Heller 1). It however was recommended that the company establish plans of action flexible to the rapidly changing customer and the environment and embrace business process reengineering concepts (Value Based Management, 1).
Discussion
To appreciate the cost of travelling shifts the right side of the demand curve downwards. It leads to a deeper decline in the flow of customer consequently affecting revenue generation and consumer confidence. This analysis assumes other variables remained constant. When new variables such reduced personal incomes, uncertain operating environment such as the eruptions of volcanic ash, and employee dissatisfaction are introduced, then the gradient of the curve becomes more negative. These results in a worse economic performance and a steeper decline in revenue generation coupled with a loss in consumer confidence.
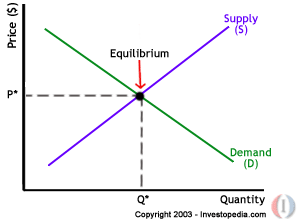
According to the article, Economics Basics (1) a more recent trend has had the company make losses in its operations resulting from employee strikes which are a direct result of management’s decision to adapt and implement deep cost cutting measures by unjustifiably laying off a number of employees. Other factors that have placed the management in a dilemma and contributed enormously to the losses the company has been making include the effects of September 11th 2001 attack on the world trade center in the US, recent global economic recession, Iceland’s volcanic eruptions, current economic crisis facing Greece, and frequent cabin crew strikes.
Competition from upcoming airlines with specific emphasis on the Asian shorthaul airlines has also placed the British Airline on a competitive edge. These have resulted in reduced profits, high operational costs, sliding business traffic, and frequent employee strikes, and a poor organizational image.
A hypothesis was formulated to test the effects of management decisions on employee productivity and company losses experienced in the form of striking cabin crew and layoffs.
A small sample of employees was interviewed and an analysis done on their responses. Of the number of the Cabin crew, X was assumed to be the number of cabin crew discontented with management decisions. Modeling the findings on a binomial distribution, where X- B (12, p). 12 was the sample population.
Then: H0 (null hypothesis), p= 0.35 (Management Decisions do not affect Behavior)
H1 (Alternative hypothesis), p# 0.35 (Management decisions solely affect employee Behavior).
If there is any truth in the null hypothesis, then X- B (12, 0.35) is valid.
A 5% distribution of a significance test on an even distribution indicates that the value of X lies within the critical region of the distribution. Therefore with a test value of X=1, on a binomial distribution, P (X≤1) = 0.04244, approximating to 4.2%. P (X≤1) <5%, implying the management of British airways critically contributed to the unrests by employees.
Conclusion and Recommendations
From the above discussion, the management of British Airways is in a quagmire. The research clearly indicates that urgent measures to save the company from imminent collapse are critically vital. The consequences of BA collapsing could include massive job losses that could spark a chain of events due to the loss of income for thousands of employees and their dependants. The country could loose one of its revenue sources which could further affect the economy. Others to be adversely affected could be business partners and those who indirectly depend on a functional airline as a source of income (Economics Basics 1).
The report recommends that the company’s executives should continuously conduct an internal and external SWOT analysis and seek to capitalize on the weaknesses of their competitors, eliminate the weaknesses that plague the company, seize the available opportunities to turn it round once more (Value Based Management 1).
The report recommends that the management should ensure the channel of communication between them and the employees are effective and alternative means of sending redundant employees agreed upon accompanied with sufficient benefits for the laid-off employees. That could make those employees retained in the workplace more productive and innovative. That could lead to improved work quality, teamwork, making it easily for retained employees to adapt to the changing economic environment. Such approaches could result in customer satisfaction, retention and increased return on investment over time. These could be reflected in increased profits, improved customer flow, and a better company image.
The report also recommended that the company’s management should identify non-profitable routes and critically analyze alternative options, such as partnering with other airlines, taking more cost effective routes, or dropping the routes entirely.
Further, the report recommended that the company establish a strong relationship with reliable fuel suppliers on a longer term basis with special discounts for the fuels to cushion it from the adverse effects of unpredictable price rises in a turbulent global economy.
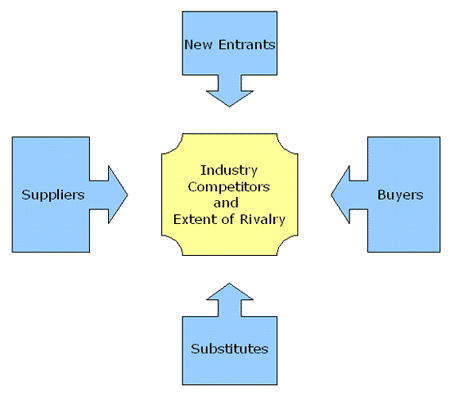
The management should design a strategic plan to identify reliable and long term suppliers particularly for fuel, identify new entrants to the airline industry and the likely effects on the competition from them, and substitute means of travelling in addition to strategically identifying new routes and customers. The plan should identify industry competitors and provide a detailed analysis of the effects of the above factors on industry competition in addition to external rivalries in the business industry as illustrated in the chart below.
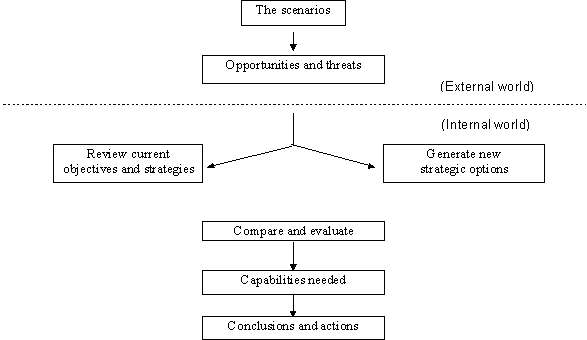
The report recommended that the organization critically analyze the current scenarios in terms of internal and external environmental factors affecting the profitability of the company and design a strategic plan and measures to counter the effects of these factors. In addition to that, the report recommends that the executives of the company should continuously review its current strategies and objectives and continuously endeavor to device comprehensive methods to align the company to its vision.
A number of options should be placed on the table regarding employee discontent regarding their layoffs plans and salary cuts to avert the consequences of perpetual strikes and arrive at an amicable solution that caters for the interests of the cabin crew.
Interview with one of the line managers
- Which company do you work for? British Airways
- What is your position in the company? Relationships Manager
- How long have you worked for the company? 10 years
- How long have you been in your current position? 2 years
- When hiring a new employee what do you look for? I look for personality, originality, creativity and able to effectively under pressure.
- Who do you report to? Zonal Director.
- How many people report to you and what are their position? 100 people
- What are your job duties and responsibilities? Ensure employee working environment is conducive and any grievances are communicated to the management in time.
- What is you salary range? If they will answer? N/A
- What is the most important part of your job? Ensuring employees remain productive in their workplace address their concerns and grievances?
- What do you spend the most time on? Ensuring employees are up to date and ensure that managerial decision and plans are communicated effectively.
- What is the most difficult part of your job and why? Convincing employee not to go on strike but listen to managerial deliberations.
Interview with an Employee
- Which company do you work for? BA
- How long have you worked for the company? 10 years
- In what capacity have you worked for the company? Cabin Crew
- What is your salary? N/A
- Are you happy in your work? No
- Why? Constantly in fear of being laid off
- Who wants to lay you off? Management
- Why? To cut costs as they say
- Do see that as an important step for the company? No
- Why? They have not explored other alternatives
- Like? Restructuring the company, cutting on salaries across the whole workforce and not just the cabin crew only.
- What do you intend to do? We have all agreed to go on strike and the strike has been received a court consent to go on.
Interviewing the Management
- What is your position in this company? Executive director
- What are the company’s most challenging problems? Profits have been going down over the years, employees have frequently gone on strike, fuel prices have been souring, and the general economic environment has been quite turbulent.
- How do these elements affect the company’s operations? The company has been experiencing a downturn in customer flow, profits have declines, and it has become expensive maintaining the current workforce.
- What is the company’s position right now? Growing worse
- What contingency plans do you have to save it from making further losses and steer it to profitability? Cutting the workforce, cutting back on the cabin crew, and others.
- Do you think these radical steps will arguer well with the current cabin crew? For now those are the available alternatives.
- What are your plans to counter the current strike threats? We shall continue to negotiate with the union representing the cabin crew.
Time allocated for the interview elapsed and the busy executive had to leave for another appointment on urgent company issues.
Works Cited
Bazerman, M. H., and Moore, D.A. Judgment in managerial decision making 7thedn. 2010. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
British Airways 2008/09, Annual Report and Accounts / 55 (2009) Management Board. 2010. Web.
Brothers, Caroline. The New York Times Company: Business: British Airways posts huge loss and blames rising fuel prices. 2008. Web.
Changes In Demand For Air Travel. Airport International: 2009. Web.
Clark, Nick. The Independent: British Airways suffers record loss as more strikes loom. 2010. Web.
Economics Basics: Elasticity. Investopedia. 2010. Web.
Economist. The Economist Newspaper Limited 2009. Looming strife. Web.
Bono, Edward de and Heller, Robert. Thinking Managers. Assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your business with SWOT analysis. 2006. Web.
Jakubal, M. Environmental Economics& sustainable development. 1998. Web.
Milmo, Dan. British Airways raises fuel surcharges. 2007. Web.
Nature and Uses of Primary Data Sources. 2009. Web.
Strategic Management. SWOT analysis. 1999-2010.
British Airways raises fuel surcharges Sekaran, U. Research methods for business: A skill building approach (4thed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2004.
Value Based Management, 2009. SWOT analysis. 2010. Web.
Wardell, Jane. Associated Press. British Airways Fuel Price-Fixing Trial Collapses. 2010. Web.