Introduction
Starbucks Corporation is a private limited company that was established in 1971. The firm operates within the specialty eateries industry. Upon its inception, the firms’ operation entailed roasting and retailing ground and whole coffee beans, spices, and tea. Its operations were solely based at Seattle’s Pike Place market.
Due to its focus to attain an optimal market share both domestically and internationally, the firm currently operates approximately 18,000 retail stores, which are located in 60 countries. The firm has adopted a unique mission that entails inspiring and nurturing the human spirit. In an effort to position itself in the market, Starbucks has adopted a unique market strategy, which entails product differentiation and growth.
The firm has achieved this goal by dealing with specialty products. Over the years, Starbucks has continued to provide a wide range of beverage products such as coffee, tea, and juices. The firm also deals with a variety of fresh food items such as pastries, salads, and oatmeal.
Its product differentiation strategy has enabled Starbucks to incorporate premium-pricing strategy. In line with its differentiation strategy, Starbuck has adopted a unique marketing strategy. The firm has attained this objective by adopting unconventional marketing strategies. The firm does not engage in aggressive marketing strategies such as advertising, but instead it focuses on branding and high-level marketing using alliances, partnerships, and word of mouth (Larson 2009).
Some of the most effective marketing strategies that the firm has adopted include provision of high quality coffee products, ensuring a high level of customer satisfaction, and establishing itself as the 3rd place for consumers to patronise between home and work, brand marketing, and establishing a Starbucks’ community.
By adopting the unique marketing strategies, Starbucks has positioned itself as a market leader in an industry that is increasingly becoming very competitive. In a bid to develop a better understanding of Starbucks, the paper entails a detailed analysis of Starbucks internal and external environment. An analysis of the internal environment comes out clearly in the process of undertaking a comprehensive strategic management analysis.
Starbucks Strategy Analysis: PESTLE analysis of the UK market
Firms face numerous factors emanating from the external business environment, which makes it paramount for firms’ management teams to develop a comprehensive understanding of the environment in which they operate (Kotter & Schlesinger 2008, p. 136). Market environment analysis should take into account the macro-environment such as the economic, political, legal, social-cultural, and technological environments (Gilligan & Hird 2008, p. 36).
The analysis should also incorporate microenvironment analysis, which entails evaluating the industry in which a firm operates. The micro and macro environments vary across countries. Thus, it is paramount for firms’ management teams to conduct an analysis of the macro-environment of the country in which they operate.
Macro-environment analysis
One of the models that firm’s management team should undertake is the PESTLE model in a bid to undertake market environment analysis effectively. In its UK market, Starbucks’ operations are impacted by changes in the macro-environment.
PESTLE analysis of the UK market
Political environment
The UK has continued to experience a high level of political stability. Consequently, most local and foreign investors perceive the UK as an attractive investment destination. The UK is a member of a number of economic integration and trading blocs such as the G20 and the Euro Zone.
This aspect increases the probability of Starbucks marketing its products to a large number of countries in Europe. Companies operating in the UK benefit from the tariff-free market because of being a member of the European Union. The UK is also in a free trade agreement with Liechtenstein, Switzerland, and Norway.
The UK is also a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). As a multinational company, Starbucks sources its raw materials from different countries through importing. One of main challenges that the firm experiences in its importing process relates to the existence of international trade regulations and tariffs. These tariffs may adversely affect the firm’s competitiveness in the UK market.
Economic environment
The global economic environment has become very dynamic over the past one decade. The changes in the economic environment have adversely affected firms in different economic sectors. The 2007/2008 economic recession stands out as one of the worst economic recession of the 21st century.
Due to the recession, Starbucks experienced a decline in its sales revenue, which occurred due to decline in the consumers’ purchasing power. The recession led to an increment in the rate of unemployment thus reducing the consumers’ ability to purchase, and thus there was a change in the consumers’ consumption behaviours.
For example, consumers who previously afforded Starbucks’ products became unable to purchase the same products. Most consumers adjusted their spending habits by being very cautious in their discretionary spending. As a result, consumers became more concerned with purchasing necessities rather than luxuries. The consumers’ regarded specialty products as luxuries.
The 2012 sovereign debt crisis being experienced in the Euro Zone is also adversely affecting business operations in the UK. Following the crisis, the UK has experienced an increment in the rate of unemployment to 11.2 per cent (Cha 2012). Consequently, the consumers’ spending has declined significantly.
The crisis has thrown UK consumers into deep uncertainty with reference to their economic future. In response to their uncertainty, consumers have reduced their spending on both big and small items such as cars and a cup of coffee. The severe nature of the crisis has forced the Moody’s (credit rating agency) to consider downgrading the country’s rating from its current AAA. This move will adversely affect the country’s competitiveness and attractiveness (This Money 2012).
Social environment
The prevailing social trends in the UK present an opportunity for Starbucks to market its products. Most UK consumers spend a substantial amount on coffee. It is estimated that approximately 511 million cups are consumed in the UK every week. The largest percentage of coffee consumption takes place in shopping malls and franchises such as Starbucks. UK consumers greatly enjoy relaxing as they drink a cup of coffee (Walsh 2011).
Therefore, there is a high probability of the firm increasing its sales revenue. Changes in consumer tastes and preferences can adversely affect Starbucks’ sales. Consumers may shift to specialty coffee products offered by its competitors. The high rate at which consumers are becoming health-conscious in their consumption patterns may affect the firm’s future operations. Therefore, to align itself with these changes, it is critical for Starbucks’ management team to conduct a continuous analysis of the prevailing social environment.
Technological environment
The UK has experienced a wave of technological advancements over the past decades, and to benefit from these changes, it is important for Starbucks to implement the necessary technological changes. UK consumers have become technologically shrewd in their purchasing patterns. In an effort to exploit this phenomenon, Starbucks has embraced a new mobile phone payment system.
The system has played a vital role in reducing queuing at its outlets especially during peak times. Additionally, the emergence of social networks also presents an opportunity that the firm can exploit. Through these social networking sites, Starbucks can engage its customers through communication.
Legal environment
In a bid to improve the country’s competitiveness, the UK government has implemented a number of measures, which make the UK very attractive to local and foreign investors. One of the ways through which the UK government has attained this goal is by recognising intellectual property rights such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks. By ensuring an effective legal environment, Starbucks has managed to operate effectively in the UK.
The UK government has also established 21 new enterprise zones. The zones aim at stimulating economic growth in some areas in the UK. Moreover, to attract investors in such areas, the UK government has implemented a 5-year tax holiday amounting to GBP 275,000. The UK government has not incorporated any exchange control that would affect remittance of royalties, patent fees, and dividends (Deloitte, 2011).
Microenvironment analysis
Porter’s five forces
In an attempt to succeed in their respective industries, it is paramount for firms’ management teams to understand the prevailing industry dynamics. One of the ways through which a firm can understand the industry in which it operates is by taking into account the Porter’s five forces model (Grundy 2006, p. 215).
The model evaluates the characteristics of a particular industry by evaluating the potential entrants, the buyers and suppliers’ bargaining power, existence of substitute products, and degree of industry rivalry. The chart below illustrates the prevailing characteristics of the UK specialty eateries industry.
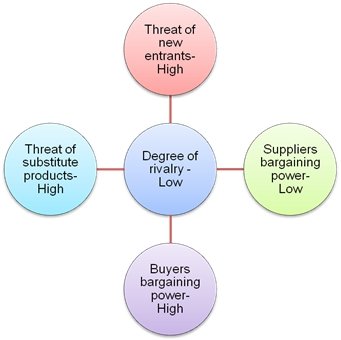
The industry is characterised by low supplier bargaining power because of the numerous coffee beans exported into the UK from other countries such as Brazil and Indonesia. The profitability potential of the UK specialty eateries industry has made most investors to consider the possibility of venturing in the industry.
One of the most common modes of entry that these firms are adopting is importation. The low capital requirement coupled with the fact that no special knowledge is required to venture into the industry has increased the attractiveness of the industry. Emergence of other beverage products such as hot chocolate and tea has led to an increment in the number of substitutes available to consumers.
The UK specialty and eateries industry continue to experience an increment in buyers’ bargaining power due to the low-switching cost associated with the industry.
The occurrence of the recent global economic recession coupled with the sovereign debt crisis has increased the degree of price sensitivity amongst consumers (Miller 2009). Consequently, Starbucks will be required to adjust to these industry dynamics.
The industry is characterised by a high degree of rivalry due to the large number of industry players. Some of the major firms in the industry include Costa, Nero, Caffee Ritazza, BB’s, and Pucchino. Despite this aspect, Starbucks has managed to attain an optimal market position.
Critical success factors
The success of every business organisation is dependent on the effectiveness with which it adheres to the critical success factors. These factors vary across firms and industries. In its operation, Starbucks has incorporated a number of critical success factors, which include attaining global dominance, offering a high level of customer service, and brand development. These factors have played an important role in the success of Starbucks over the years.
Starbucks Strategic Management Analysis
Effective strategy development is one of the ways through which a firm can attain coherence between its internal abilities, resources, skills, and the external factors affecting the firm’s operations (Srinvasan 2005).
Therefore, it is important for firms’ management teams to identify the external and internal factors that may affect their firms’ overall performance (Ghani, Nayan, Ghazali, Shafie, & Nayan 2010, p. 52). Different analytical tools can be used to conduct internal analysis of a firm. An example of such a tool is the strategic factor analysis summary matrix.
The chart below illustrates internal factor analysis summary of Starbucks.
Starbucks core capabilities/competencies
Starbucks has been committed to attaining a high level of competitive advantage, and to attain this goal, the firm has nurtured a number of capabilities that aim at improving the level of customer satisfaction.
Over the years, the firm has nurtured the capability of offering high quality specialty coffees and eateries. Starbucks has developed its stores in such a way that customers can enjoy and relax to enhance the level of customer satisfaction. Its ability to develop these capabilities arises from the fact that it has developed a sufficient financial and human resource base.
In the process of offering its products and services to customers, Starbucks greatly emphasises on good business practices and ethics. In 2011, Starbucks was ranked as one of the most worlds’ most ethical company (Environmental Leader 2011). Considering the intense competition in the specialty coffee market, Starbucks has developed a strong competence with regard to product innovation.
Since its inception, the firm has developed sufficient competence with regard to market and customer innovation process. The objective of its innovativeness is to enable the firm to meet the needs of various market segments. Additionally, innovation contributes towards the firm being effective in addressing the changing consumer tastes and preferences.
Strategic Fit Analysis
Starbucks’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
In the course of its operation, Starbucks has managed to attain a number of strengths. However, its operations have not been without some weaknesses. From the above analysis, a number of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in relation to Starbucks are evident as shown below:
Conclusion
In the course of its operation, Starbucks has managed to position itself as the market leader within the specialty and eateries industry. Its success has arisen from the adoption of effective market strategy, which entails product differentiation and growth. An analysis of the market environment depicts the UK as an attractive market.
The macro environment analysis shows that the UK has managed to ensure a high level of stability with regard to the political and legal environment. The stability established in the UK has made it possible for Starbucks to implement its aggressive expansion strategy. However, the recent global economic crisis coupled with the current sovereign debt crisis presents a major challenge for the firm. Through the Porter’s five forces, it is evident that the UK specialty and eateries industry is very attractive.
Consequently, Starbucks should implement effective strategies to exploit the presented market opportunities. Starbucks’ success in the UK market has emanated by the fact that it has nurtured a number of unique resources, core capabilities, and competences. With regard to resources, Starbucks has nurtured a strong human resource base. As a result, it has managed to offer sufficient customer service. Other capabilities that the firm has developed relate to product innovation and adherence to quality.
These capabilities have made Starbucks a favourite amongst many customers. The capabilities have also enhanced the firm’s strengths. In an attempt to survive in the future, it is paramount for Starbucks to assess its threats and weakness and make the appropriate adjustments. The firm should also exploit the opportunities available in the external business environment.
Reference List
Cha, A. 2012, European financial crisis has ripple effect on US businesses. Web.
Deloitte: Taxation and investment in United Kingdom 2011. Web.
Environmental Leader: Ford, Starbucks, among most ethical companies. Web.
Ghani, K., Nayan, S., Ghazali, S., Shafie, L. & Nayan, S. 2010, ‘Critical internal and external factor that affect firm’s strategic planning’, International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, vol. 3 no 51, pp. 50-57.
Gilligan, C. & Hird, M. 2008, International marketing: strategy and management, Taylor and Francis, New York.
Grundy, T. 2006, ‘Rethinking and re-inventing Michael Porter’s five forces model’, Strategic Change, vol. 15 no. 5, pp. 213-229.
Kotter, J. & Schlesinger, L. 2008, ‘Choosing strategies for change’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 2, pp. 130-150.
Larson, R. 2009, Marketing strategy and alliances; analysis of Starbucks Corporation, Liberty University, New York.
Miller, C. 2009, Will the hardcore Starbucks customer pay more? The chain plans find out. Web.
Srinvasan, L. 2005, Strategic management, the Indian context, PHI Learning PVT, London.
Theodore, S. 2002, Expanding the coffee experience; Starbucks keeps sales brewing with new products, innovation and global expansion, Beverage Industry, vol. 1, issue 3, pp. 57-62.
This Money: Moody’s could downgrade UK’s ‘AAA’ credit rating in early 2013 if the economy fails to shape up. Web.
Walsh, J. 2011, Britain’s caffeine boom: Why can’t we wake up without smelling coffee. Web.