Supply of iPhones in UK
The iPhone is a smartphone that is manufactured by Apple Inc. The company developed the product to diversify the product range. Apple has penetrated the electronics industry to improve on the profits of the company. The iPhone brand was technologically developed to match the innovativeness of the company. The product has gained high market demand in the global market.
Apple Inc. applied modern technologies to develop the iPhone brand, and the product has competed successfully in the UK, the US and other global markets (Walker, Stanton, Jenkins and Salmon, 2009).
There are about five different types of iPhones, with the technology employed in each of them being the main distinctive feature. The iPhone was first invented in the year 2007 as part of the revolution in the global telecommunication industry. The brand has found its way into the entire world market (Wright, 2012).
The electronics industry has experienced intense competition, and this has forced all players to develop quality products. Quality is a crucial consideration in the marketing of technological products. Consumers in the global markets have become very sensitive about the quality of products they purchase.
Therefore, companies in the industry have applied the best technologies to improve the quality of products they offer to the global markets (Boyer and Verma, 2010). For the iPhone, consumers consider the high quality, efficiency and effectiveness of using the product. Apple Inc. has considered all these product aspects when developing the iPhone brand (Bloomberg Businessweek, 2011).
Apple Inc. has developed various generations of the iPhone brand to improve the quality. This strategy was applied to overcome the competition in the global markets. For instance, Blackberry and Samsung among other competitors have introduced similar products in the market (Mohr, Sengupta & Slater 2010).
When the iPhone brand was first introduced to the market, it attracted many customers, creating high expectations in the products. To meet the expectations of the customers, Apple has conducted continuous research to change the features of the brand. This strategy has improved the demand of the iPhone brand.
Therefore, the demand for iPhone has been growing with time despite the existence of many competitors in the market. Apple has developed cost reduction strategies during the manufacturing process to ensure that the company benefits from the sales of the product. Quality management in the manufacture of iPhone has led to increased sales and profits to Apple Inc. (Cohen & Roussel, 2005).
Importance of product innovation to the supply chain
The iPhone hit the market with a bang because of innovation that went into its production. During the early stages of introduction to the market, iPhone recorded exceptionally high sales. Just like innovations that preceded the iPhone, the Apple Company utilized the new product development process in making the iPhone brand (Hitt, Ireland and Hoskisson, 2007).
There are many benefits of continued innovation in products. The main aim of supply chain management is seeing that the products get to the market and meet the needs of consumers and consumer expectations. Product innovation is a means of making the product in the supply chain. Innovation in products entails the creation of economic, social and environment value by using new ideas (Wilding, 2007).
The ideas that led to the development of the iPhone were remarkably advanced. As soon as the iPhone was released into the market, it immediately captured the customers’ needs. The brand has advanced tools, which ease communication compared to other brands in the market. The demand was automatically created by the value with which the users attached to the iPhone.
The iPhone has undergone several changes, with each change being aimed at adding value to the product. This is achieved by adding an application that does not exist in previous products. There are five generations of iPhone: iPhone, iphone3G, iPhone 3GS, iPhone 4 and the iPhone 4S. This denotes an improvement on innovation for each of these products.
Each generation of iPhone has a different design and taste that is different from the others. The latest generations are more advanced in terms of design and quality, and these are key aspects in fulfilling the demand of customers (Jefferson, 2011).
Supplies for Delivering IPhones
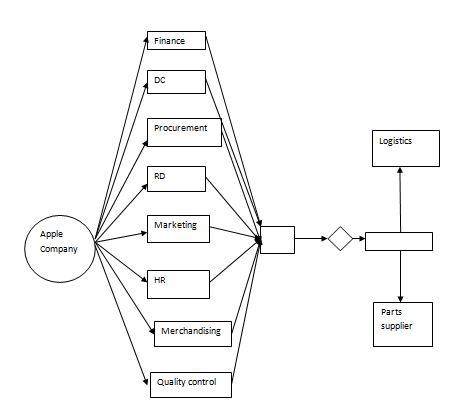
The iPhone is manufactured in different countries, with considerable manufacturing centers being in China and the United States. The two main stores are found in the two countries. The supplies to the subsidiaries in the United Kingdom are obtained from the United States. Therefore, a lot of logistical procedures are involved in the supply of the raw materials during the manufacturing process.
The supply of iPhone is guided by the demand for the products in a country. However, it is the responsibility of the management of the company to ensure that customers get the products at the time they need them (Moren, 2010).
The manufacturers of iPhone depend on other suppliers, who supply with materials that are used in processing the iPhones. The quality of iPhones in the market depends on the quality of the material that is used in making the iPhones. The iPhone manufacturers work closely with the suppliers of the products materials to ensure that total quality management is attained in the final products.
The logistics of shipping the goods to the UK poses another challenge in the supply of iPhones within the UK market. There are different models of iPhones, and the demands for each of the models vary. The most demanded models are the latest models of iPhone 4S. Sales orders are placed by different wholesalers, who get the products directly from the company.
Apple has its own supplies and logistics departments, which guides in taking orders and ensuring that products are delivered safely to the distributors. Within the United Kingdom, there are many suppliers of iPhone products.
The importing companies deal directly with iPhone manufacturers. There are several importing companies that are engaged in the import of the iPhones. The UK has many distributors and wholesalers of iPhones. They get the products from the importing companies (Moren, 2010).
Apple takes part in the entire supply of iPhones to ensure that quality in the supply of the iPhones in the UK is applied. Follow-ups are made in the retail stores, which are the final points of supply before the iPhones get to the consumers. Furthermore, active communication between the manufacturer of Apple and consumers is maintained to taste the level of utility which guides future supplies of iPhones (Sako, 2011).
Making supplies sustainable
Apple has more than ten companies that supply with materials or different parts that are used in the manufacturing of the iPhones. If problems exist with any of suppliers and supplies, a problem will be imminent in the quality of products (Taylor and Brunt, 2001; Pegasus Software, 2009). The company must ensure that all quality considerations are met in all supplies.
Apple has put mechanisms of managing the supplies of the raw materials. One thing that is notable on the list of its suppliers is that most of them come from Taiwan. This shows that it is easy to assess the supplies and gain trust with the companies making the supplies. In addition, the standards of quality in production for a country are often standardized. The types of material and production processes are often similar (Abilla, 2007).
Apple must initiate healthy and mutual strategies to ensure sustainability of supplies from the supplying companies. These strategies have to ensure that all the companies benefit reasonably from the supply and sales of iPhones. This will enhance trust that will extend into quality in supplies (Beheshti, 2010). Apple invests a lot in quality checks, which is the reason why the company can come up with high quality products.
One key objective of service–chain management is ensuring that customers get quality products. Through quality checks, Apple managed to keep the quality of iPhones according to the expectations of their customers (Hugos and Hulitzky, 2010).
As part of the expanding its supplies of iPhones due to the risen demand for the products, Apple needs to select more outsourcing vendors in the UK. The outsourcing vendors will reach a significant number of customers creating increased demand for iPhone supplies (Beheshti, 2010).
How to ensure sustainability in supplies
The supply chain of iPhones can be made sustainable by capturing the relevant areas of supply management (Tillon, et al, n.d). In dealing with the manufactures, the suppliers of products used in manufacturing iPhones, three things have to be kept in mind.
These are time, transparency, and trust between the suppliers. Trust enhances transparency and timely delivery of supplies. When this relationship is embraced, the supply chain of will be effective and efficient thus sustainable.
Reference List
Abilla, P. 2007, The Apple iPhone Supply Chain. Web.
Beheshti, H. M. 2010, “A decision support system for improving performance of inventory management in a supply chain network”, International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 452 – 467.
Bloomberg Businessweek 2011, Apple’s Supply-Chain Secret? Hoard Lasers. Web.
Boyer, K. K. & Verma, R. 2010, Operations & supply chain management for the 21st century, South-Western/Cengage Learning, Mason, Ohio.
Cohen, S. & Roussel, J. 2005, Strategic supply chain management: The five disciplines for top performance, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D. & Hoskisson, R. E. 2007, Strategic management: Competitiveness and globalization: concepts, South-Western, Mason, OH.
Hugos, M. H. & Hulitzky, D. 2010, Business in the cloud: What every business needs to know about cloud computing, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ.
Jefferson, G. 2011, Apple profit nearly doubles as sales of iPhones surge. Web.
Mohr, J., Sengupta, S. & Slater, S. F. 2010, Marketing of high-technology products and innovations, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Moren, D. 2010, “Apple Cleans up Its Supply Chain”, Macworld, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 14-15.
Pegasus Software 2009, An FD’s guide to Supply Chain Management. Web.
Sako, M. 2011, “Technology Strategy and Management Driving Power in Global Supply Chains”, Communications Of The ACM, vol. 54, no. 7, pp. 23-25.
Taylor, D. & Brunt, D. 2001, Manufacturing operations and supply chain management: The LEAN approach, Thomson Learning, London.
Tillon. P., et al. n.d, Improving Sustainable Supply Chain Efforts among Retail Leaders. Web.
Walker, G., Stanton, N., Jenkins, D., & Salmon, P. 2009, “From telephones to iPhones: Applying systems thinking to networked, interoperable products”, Applied Ergonomics, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 206-215.
Wilding, R. 2007, How to engineer a supply chain to improve competitiveness. Web.
Wright, A. 2012, “Analyzing Apple Products”, Communications Of The ACM, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 27.