Introduction
Sustainable development generally refers to the balanced advancement of society regarding social, environmental, and economic aspects. Some experts believe that development and sustainability are highly interrelated concepts and cannot be addressed separately (Klarin 69). Therefore, efficient progress in most industries should take social and environmental components into account and should not sacrifice these aspects for economic prosperity. The food industry has a severe impact on the environment, and a large number of business companies in the field tend to ignore sustainable development. Therefore, it is essential to critically analyze the trends in the food industry regarding sustainability and provide efficient solutions to the problem.
Food Industry Overview
The food industry includes businesses that supply provisions for customers. It is a highly complex network and comprises agricultural groups, distributing organizations, academic departments, etc. Therefore, the circular-flow diagram takes the canonical shape and is illustrated below:
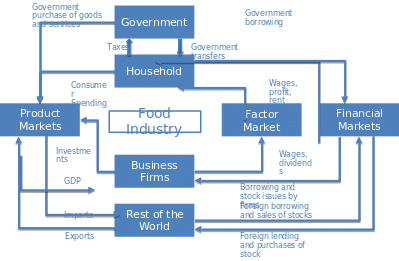
As seen from the chart, the food industry has a profound impact on all the aspects and stakeholders of the economy, such as government and households, product, factor and financial markets, and business groups. The food industry is frequently referred to as the “world’s largest industry” due to the immense impact on all components of sustainable development and significance to the lives of individuals (Jeffries par. 4). On the global level, the food industry is one of the most influential markets with more than a billion workers (Jeffries par. 4). With such a vast impact on the universal state of business, sustainability issues are highly prevalent as well.
The food industry has an immense impact on the environmental and social components of sustainable development and directly influences the population. At the moment, the industry is responsible for more than 25% of greenhouse emissions with livestock being the major factor (Ritchie and Roser par. 22). The authors of the research provide the following diagram to illustrate the impacts of the food industry on the environment:
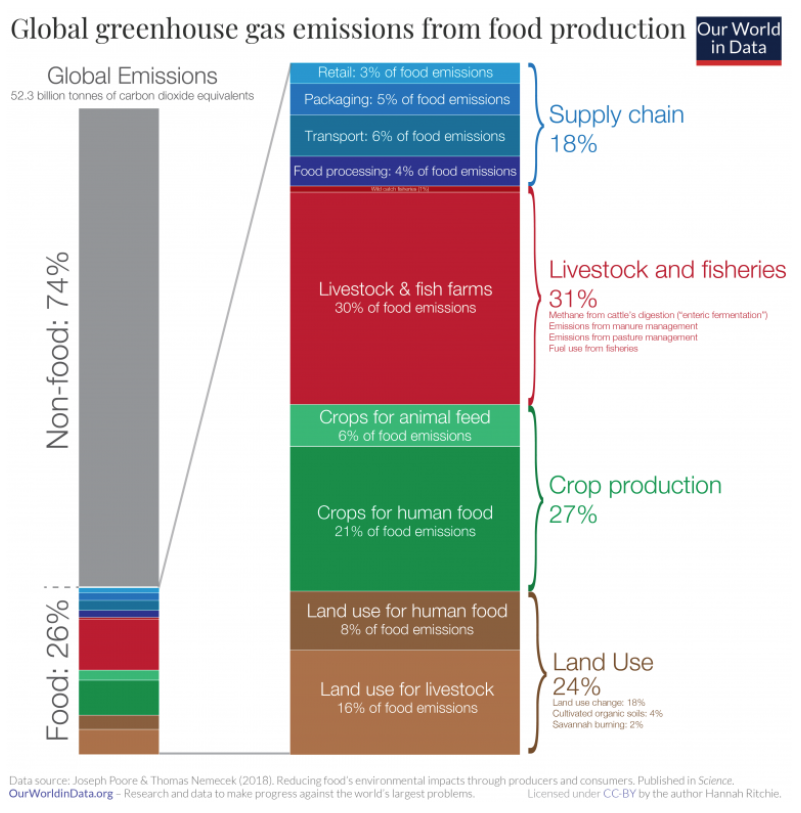
The food industry also accounts for land and water scarcity, ocean eutrophication (nutrient-rich pollution of waterways), and endangerment of wild animals (Ritchie and Roser par. 4). Nevertheless, due to the extents of the industry, a large number of people are provided with jobs and sufficient earnings that account for social and economic aspects of sustainable development. Therefore, the sustainable development vastly affects global levels of economy, including the government, business groups, and financial markets.
Food Industry in Tampa, Florida
Naturally, the business groups in the industry affect the local communities as well. For instance, uncontrolled distribution of unhealthy food might affect the well-being of residents in the community. In Florida, the number of street food vendors is continually expanding, and safety issues are frequently overlooked and underestimated by independent business owners (Okumus and Sonmez 3).
While the availability of food trucks and small fast-food restaurants is highly convenient for customers, it might have a deteriorating effect on sustainable development. Furthermore, the low level of hygiene and improper management in the food establishments might directly influence the environmental situation. The supply chains account for approximately 18% of greenhouse gas emissions in the food industry (Ritchie and Roser par. 24). Therefore, it is essential to minimize the number of harmful emanations to meet the contemporary requirements of sustainable development.
Nevertheless, the small business groups in the industry provide occupations and places to work for citizens with lower levels of education. In Tampa, approximately half of the employers claim that there is a shortage of qualified workers (Robertson 456). Therefore, the increasing number of food trucks and small business start-ups create occupations and account for social and economic aspects of sustainable development. Overall, the current state of sustainable development provides both negative and positive impacts on local, national, and global levels.
Solutions
The presented information transparently demonstrates the need to address the issue of sustainable development in the food industry, and there are several solutions that might improve the environmental situation. As mentioned before, sustainable development implies the proper balance between social, economic, and environmental aspects; therefore, the changes in one segment might cause externalities and unintended developments in others. Therefore, it is essential to analyze both the solutions to the problem and the consequences of the implementations.
The three solutions to the issue of sustainable development in the food industry are the following: product innovation, supply chain improvement, and governmental support of independent business groups. The first implementation implies the increasing quality of food products. For instance, the meat-free and gluten-free policies might greatly reduce the agricultural demand in the industry and improve the environmental situation (Leon-Bravo et al. 5). The second solution refers to the development of logistics, distribution, packing, tracking, and other aspects of retail chains (Leon-Bravo et al. 5). The last implementation might improve the quality of food trucks and small business enterprises in the local community and reduce the environmental and social risks.
Due to the associated economic profit losses, some people might be against the policies aimed at the improvement of the environmental situation. For instance, the cost of healthy food is higher than its processed counterparts; therefore, it might provide negative connotations regarding changes in sustainable development. Particularly, it is evident on the local level for households with low income. In such cases, both product innovation and supply chain improvements might have negative effects due to economic fluctuations.
Nevertheless, sustainable development is an influential incentive for individuals, business groups, and governments; thus, the first two solutions are justified in terms of economics. The third alternative is vastly supported on local and business levels; nevertheless, it might be challenging for the government to allocate additional finances to support small organizations.
Personally, I believe that the first solution, product innovation, is the most appropriate choice for improving sustainable development. As seen from figure 2, the agricultural aspect of the food industry is responsible for 82% of greenhouse emissions, and product innovation might greatly reduce this number. Nevertheless, while this perspective is supported by government incentives, business organizations and individuals might object to the change. Therefore, it is essential to change the perspectives of the business groups in the food industry and address the environmental issues even if it means decreasing revenue growth. Currently, the trends for healthy and organic food are continually progressing in terms of influence making it possible to achieve high levels of sustainable development.
Conclusion
The current work demonstrates that sustainable development is a serious issue in the food industry and proposes three solutions to the problem, product innovation, supply chain improvement, and small business support. The three alternatives can reduce the harmful environmental impacts; nevertheless, some people might object to the solutions due to economic reasons. Overall, product innovation proves to be highly effective in the model of sustainable development, and, according to my personal evaluations, is the best solution to the issue.
Works Cited
Jeffries, Nick. “A Circular Economy for Food: 5 Case Studies.” Circulate. 2018. Web.
Leon-Bravo, Veronica et al. “Innovation for Sustainable Development in the Food Industry: Retro and Forward-Looking Innovation approaches to Improve Quality and Healthiness.” Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management. 2019, pp. 1-14.
Okumus, Bendegul, and Sevil Sonmez. “An Analysis on Current Food Regulations for and Inspection Challenges of Street Food: Case of Florida.” Journal of Culinary Science & Technology, 2018, pp. 1-15.
Ritchie, Hannah, and Max Roser. “Environmental Impacts of Food Production.” Our World in Data. 2020. Web.
Robertson, Robert. “Local Economic Development and the Skills Gap: Observations on the Case of Tampa, Florida.” Higher Education, Skills and Work-Based Learning, vol. 8, no. 4, 2018, pp. 451-468.