Introduction
- Technology is:
- A practical application of knowledge in a specific area;
- A way of accomplishing tasks with the use of technical knowledge, methods, and processes;
- Devices and machinery developed through research.
- Educational technology is:
- A practice of enhancing knowledge and improving learning by using technologies;
- An approach to theory and practice associated with machinery use.
With the abundance of new technologies and advancements that occur every year, integrating innovative solutions into education has become paramount. As students are more proficient in technologies than some teachers, their integration is often successful. Ranging from various devices such as tablets to services such as online conferencing, the process of education can be significantly enhanced. However, in order to truly enrich learning, educators should align theory with practice and act as facilitators.

Overview of research
- Classroom technologies have evolved from PC labs to integrated solutions;
- The scope of educational technologies is vast;
- New developments are occurring every year;
- Students receive immense support from technologies;
- Teacher education is essential;
- Technologies improve collaboration and communication;
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning may make the classroom smarter.
Research studies about technologies in education have revealed that new tools are developing each year. In the beginning, simple PC labs existed. Today, however, even the use of virtual reality headsets is available. As most students grow in a technology-oriented environment, they receive immense support from new tools. Teachers are not as advanced and thus require further education and training to enhance their lessons and offer value to students. Moreover, machine learning and artificial intelligence exhibit significant potential for education.

Why does education need technology?
Technology in education is needed for:
- Accelerating and deepening learning;
- Empowering teachers and learners;
- Facilitating information;
- Providing smart solutions;
- Helping learners and teachers overcome existing barriers.
A variety of applications of technologies are available in education. However, prior to implementing them, it is important to understand the aims for technologies in the classroom. It is expected that technologies will deepen and accelerate the learning of new skills and concepts. Also, new solutions are designed in a way to empower teachers in their practice as well as support learners when it comes to developing new competencies and knowledge. Smart solutions such as interactive whiteboards make it easier to navigate through lessons and offer platforms for collaboration between teachers and parents. Teachers and learners also expect to overcome barriers that exist within the sphere of education.
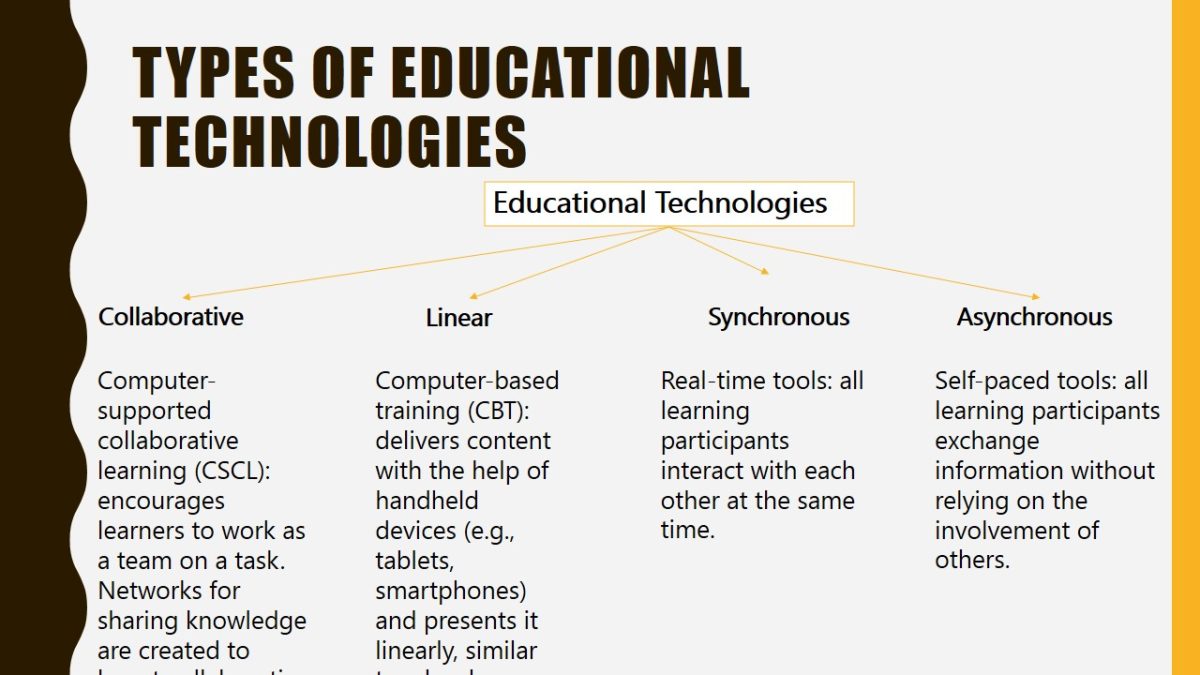
Types of educational technologies
- Collaborative:
- Computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL): encourages learners to work as a team on a task. Networks for sharing knowledge are created to boost collaboration.
- Linear:
- Computer-based training (CBT): delivers content with the help of handheld devices (e.g., tablets, smartphones) and presents it linearly, similar to a book.
- Synchronous:
- Real-time tools: all learning participants interact with each other at the same time.
- Asynchronous:
- Self-paced tools: all learning participants exchange information without relying on the involvement of others.
Educational technologies are differentiated into linear, collaborative, synchronous, and asynchronous. Their implementation depends on the needs of teachers and their students and can range from one classroom situation to another. For example, asynchronous technologies make it possible for students to follow their own schedules and be more independent.
Educational technologies
Linear
- Computer-based training (CBT):
- Tablets or smartphones are the devices most commonly used in linear learning;
- Content is presented in a linear way;
- Predominantly used for teaching static processes (e.g., software development or completing mathematical equations);
- The assessment of learning – scoring – can easily be done with the help of computers;
- Assessments are scored, recorded, and shared with the help of computers;
- Instant end-user feedback is available about one’s accomplishments during learning.
Computer-based training is a subset of linear technologies, which present new material in a way in which books lay it out. Linear technologies are best applied in learning static procedures such as resolving mathematical problems. In CBT, the assessment of learning can be easily completed with the help of standardized tests, which are then recorded and shared. Also, they offer immediate feedback on learning effectiveness.

Collaborative
- Computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL):
- Combining the cooperative and collaborative learning of students at different locations;
- Supporting students’ learning in sharing information and ideas;
- Allowing for the collaborative access to information, documents, instructor feedback, and other data;
- Facilitating group processes and group dynamics that are not possible during regular communication;
- Improving thinking skills, problem-solving ability, collaborative processes, and epistemic fluency.
Collaborative technologies are targeted at enhancing communication between students no matter where they are located. Such technologies can include Skype conferences in which learners work together on group assignments or just share some information about their class. Collaboration is expected to improve problem-solving and thinking skills because it encourages learning from the example of others. Combining multiple ideas from different sources will yield the most effective results.

Synchronous
- Takes place in real time and is led by the instructor;
- Participants are expected to interact simultaneously;
- Students share information and exchange ideas within a specific time period;
- For example, face-to-face discussions, Skype conference calls, and chat rooms, and real-time teaching instruction can all be used;
- This type of learning increases students’ online awareness along with improving students’ writing and speaking skills.
Synchronous technologies are used when learners need to develop new skills and gain knowledge in real time. Usually, this learning is guided by an instructor who encourages students to participate and make their contributions at the same time. Ranging from face-to-face classes to chat rooms, synchronous learning with the help of different technologies is a widely applied approach. It is especially useful for increasing everyone’s online awareness along with enhancing their interpersonal skills.

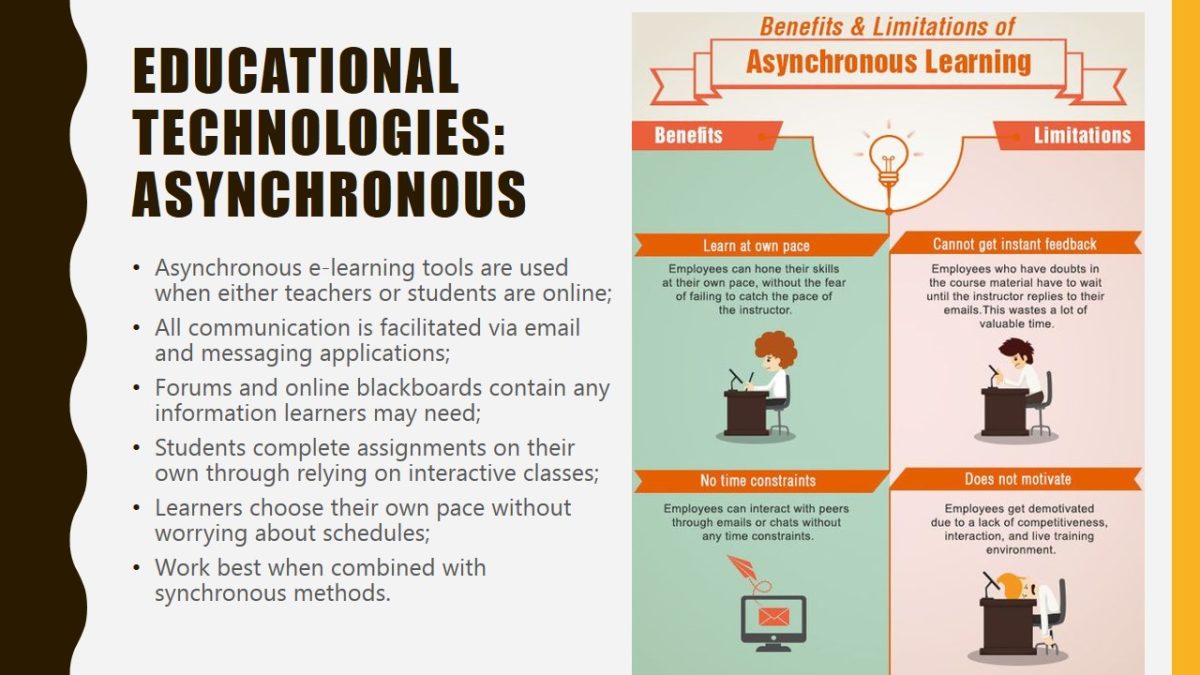
Asynchronous
- Asynchronous e-learning tools are used when either teachers or students are online;
- All communication is facilitated via email and messaging applications;
- Forums and online blackboards contain any information learners may need;
- Students complete assignments on their own through relying on interactive classes;
- Learners choose their own pace without worrying about schedules;
- Work best when combined with synchronous methods.
The asynchronous use of technologies is effective when students have flexible schedules and need to complete assignments remotely. While asynchronous use may be less effective than synchronous methods, learners still develop communication skills by connecting via email or any other messaging tools. This method promotes independence among students who are also welcome to interact with each other without being constrained by a time limit. Asynchronous learning will work best when combined with synchronous.
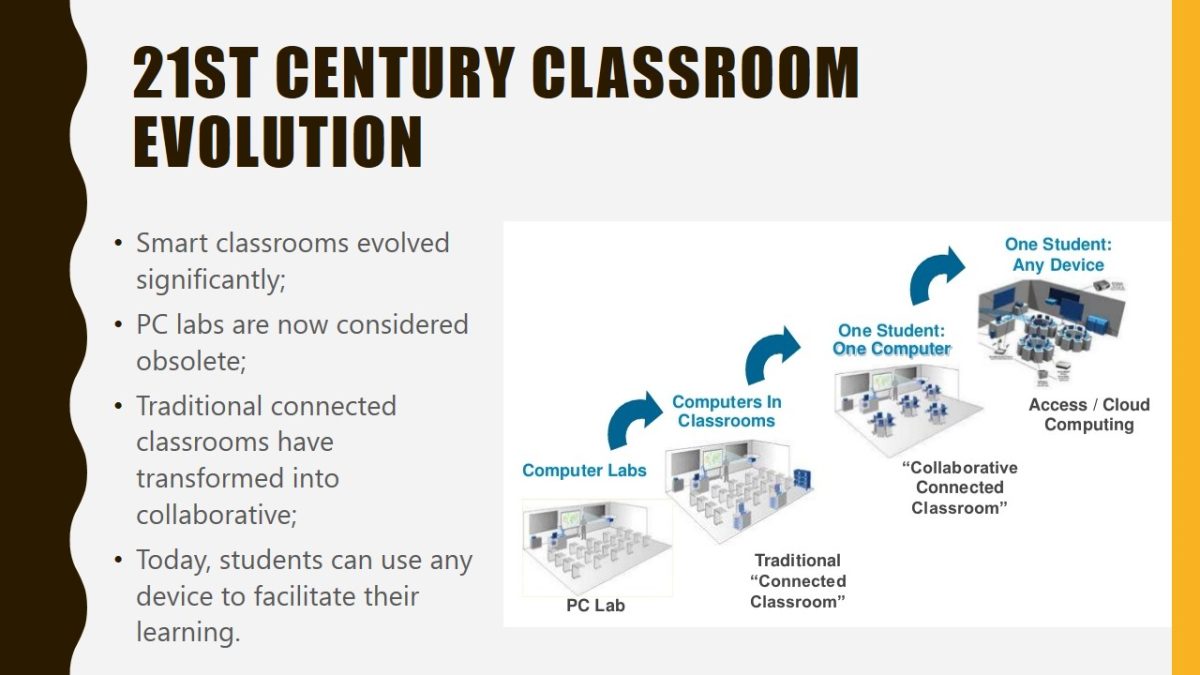
21st century classroom evolution
- Smart classrooms evolved significantly;
- PC labs are now considered obsolete;
- Traditional connected classrooms have transformed into collaborative;
- Today, students can use any device to facilitate their learning.
As seen from the graph presented on the slide, the 21st-century classroom has undergone some significant changes. In the late 20th century, students could attend simple computer labs where each assignment was guided by a specialized PC instructor. Connected classrooms were the next step in the evolution, but they were still ineffective. Next, collaborative, connected classrooms were developed and entailed one computer for one student so that everyone could get involved in the process of learning. Today, with wide access and cloud computing, a student can use any device for his or her convenience and use technologies to enhance the learning process.
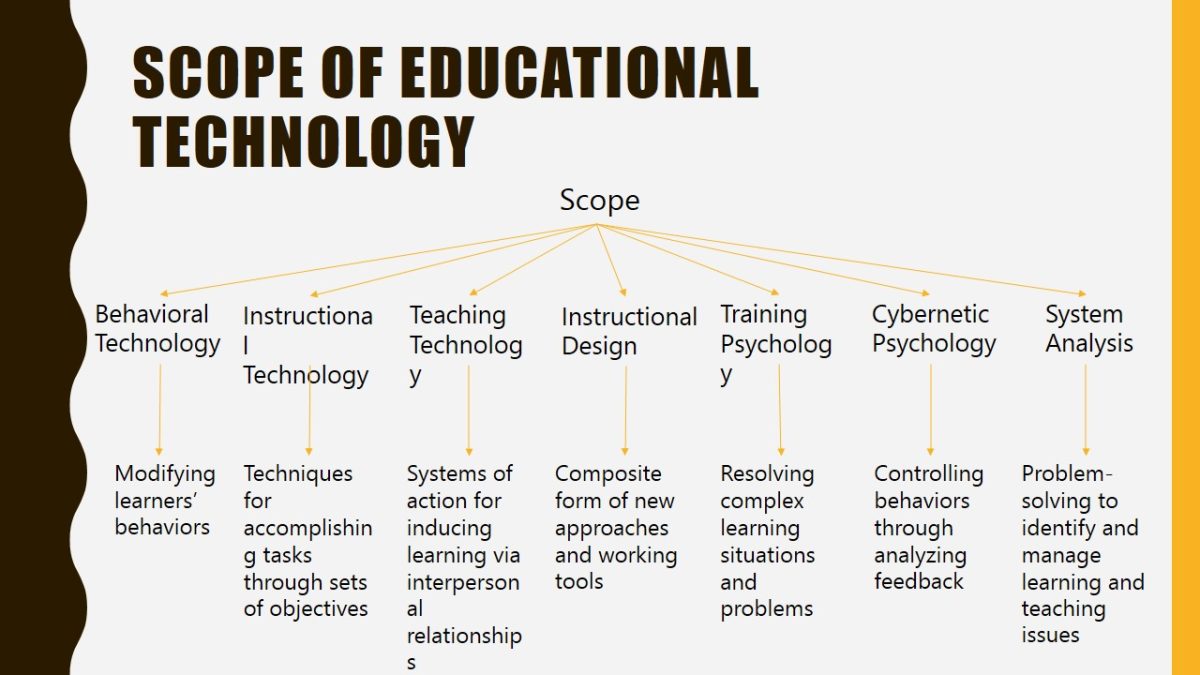
Scope of educational technology
- Behavioral Technology → Modifying learners’ behaviors.
- Instructional Technology → Techniques for accomplishing tasks through sets of objectives.
- Teaching Technology → Systems of action for inducing learning via interpersonal relationships.
- Instructional Design → Composite form of new approaches and working tools.
- Training Psychology → Resolving complex learning situations and problems.
- Cybernetic Psychology → Controlling behaviors through analyzing feedback.
- System Analysis → Problem-solving to identify and manage learning and teaching issues.
The scope of educational technologies is vast and includes a variety of aspects that can be applied for different purposes. For example, behavioral technologies are used for monitoring and changing the behaviors of students. Instructional technologies allow teachers to disseminate learning objectives and develop strategies for their accomplishment. It should be mentioned that these technologies are designed to support the teaching/learning process, which means that training in their application is needed.
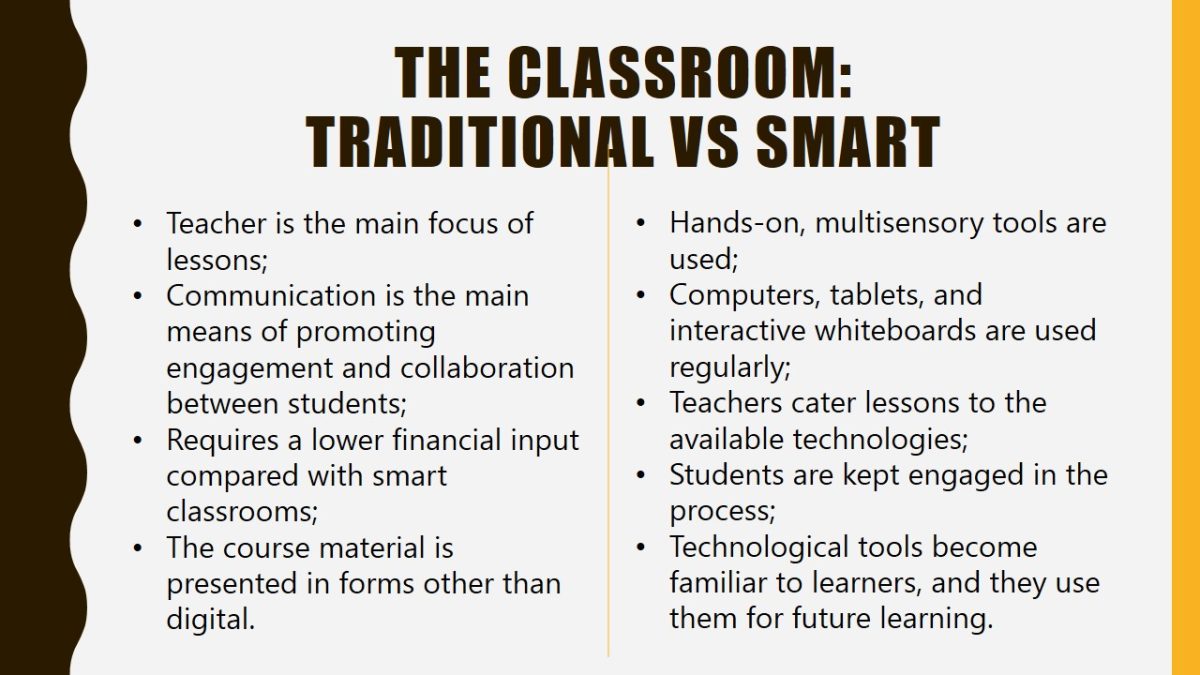
The classroom: Traditional vs smart
- Teacher is the main focus of lessons;
- Communication is the main means of promoting engagement and collaboration between students;
- Requires a lower financial input compared with smart classrooms;
- The course material is presented in forms other than digital.
- Hands-on, multisensory tools are used;
- Computers, tablets, and interactive whiteboards are used regularly;
- Teachers cater lessons to the available technologies;
- Students are kept engaged in the process;
- Technological tools become familiar to learners, and they use them for future learning.
When comparing traditional and smart classrooms, several important differences should be noted. While a traditional classroom is teacher-oriented, technologically oriented lessons make teachers act as facilitators. Smart classrooms are more flexible and can always include aspects of traditional lessons, while the latter are limited to the information available to teachers and in textbooks.
PROs of traditional classrooms
Why are traditional classrooms effective?
- Complete participation of students and the ability to ask questions: nothing prevents students from communicating.
- Direct, face-to-face interactions during collaborative assignments: learners are free to share opinions and information.
- Established responsibility of students to comply with instructions and established deadlines: learners rely on themselves rather than technologies.
- The option to learn with the help of real examples.
- The promotion of wide knowledge and increased achievement.
Traditional lessons still present a variety of positive aspects. For example, students are expected to be responsible for their work and rely solely on their own knowledge. Despite not being flexible, traditional classrooms teach learners to adhere to a strict schedule, which disciplines them. Also, offline face-to-face communication promotes the development of social skills and competencies that are hard to develop online.

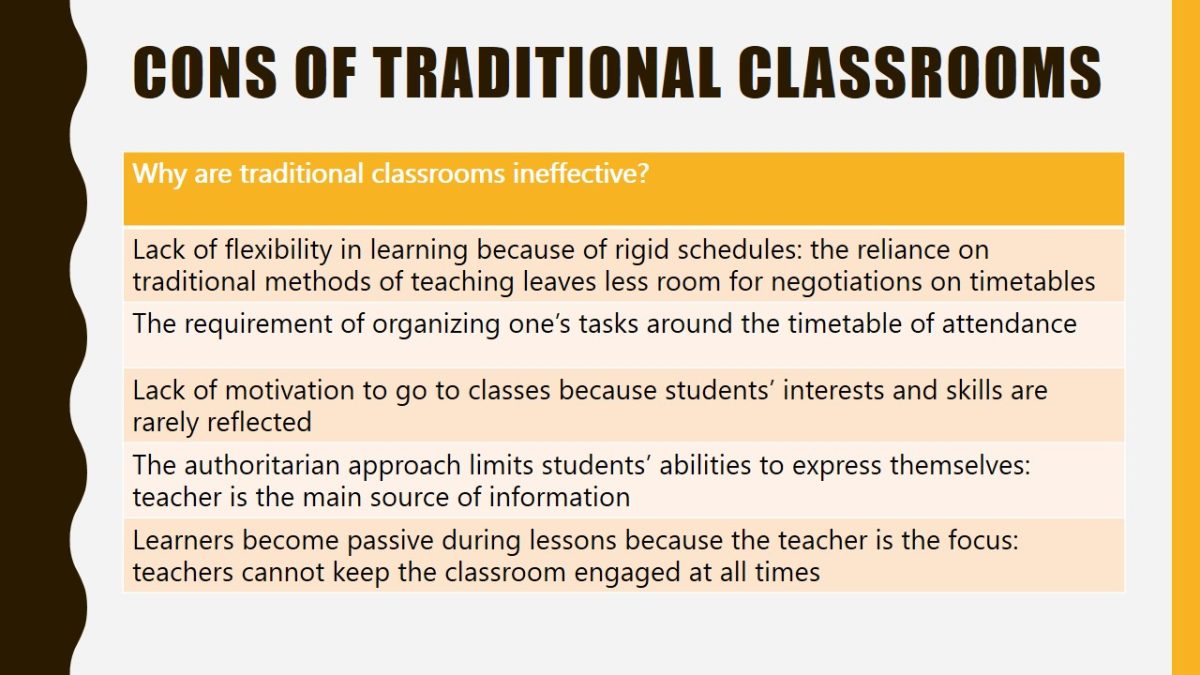
Cons of traditional classrooms
Why are traditional classrooms ineffective?
- Lack of flexibility in learning because of rigid schedules: the reliance on traditional methods of teaching leaves less room for negotiations on timetables.
- The requirement of organizing one’s tasks around the timetable of attendance.
- Lack of motivation to go to classes because students’ interests and skills are rarely reflected.
- The authoritarian approach limits students’ abilities to express themselves: teacher is the main source of information.
- Learners become passive during lessons because the teacher is the focus: teachers cannot keep the classroom engaged at all times.
Barriers such as a lack of flexibility make traditional classroom learning not as effective as it could be. Students may not have enough motivation to go to classes because their knowledge and skills are rarely reflected. During lessons, students may become passive and lazy.
Pros of using technologies in classrooms
- Advantages of using technologies:
- Experimenting with pedagogy and getting immediate feedback
- Ensuring full participation of all students: technologies are interesting and engaging
- Providing multiple resources for making learning effective, fun, and interactive: a variety of tools and solutions are available
- Automating tedious tasks: less time needed for assessments
- Offering instant access to relevant information to supplement the learning process: the quick speed of the Internet
- Training students for the future use of technologies: any career will be connected to some technologies.
As seen from the list of advantages of using technologies in the classroom, most of them are associated with automation, engagement, and experimentation. Because there are no strict guidelines for using technologies in the classroom, both teachers and learners are welcome to offer new ideas and research new tools.

Cons of using technologies in classrooms
- Challenges to using technologies:
- Being a distraction to students: games, social media, and so on.
- Disconnecting learners from social interactions offline: e-based communication becomes the main way of interacting.
- Fostering cheating on home assignments and during class work: available technologies make cheating tempting.
- Unequal access to resources among students: some can afford new gadgets while others cannot.
- Difficulties with filtering through high- and low-quality information.
- Lesson planning becomes more complicated: teachers are challenged by new technologies.

New teaching aids and technologies: Interactive whiteboards
- An interactive whiteboard (IWBs) is a large white display that:
- Has a touchscreen capability to enhance the completion of tasks;
- Has the option to be controlled remotely with the help of computers or tablets;
- Allows information and images to be shown on the IWB through a projector;
- Allows streaming presentations & videos and providing supplementary material to teachers’ lessons;
- Offers a large variety of data sharing and inter-connectivity with mobile devices.
Interactive whiteboards represent a new replacement for traditional blackboards. They include a variety of tools and features that make the presentation of information more interactive and flexible. Teachers can control the whiteboards remotely and project PowerPoint presentations, videos, and images on the screen. As some whiteboards have direct access to the Internet, teachers and students can look up any necessary information straightaway.

Benefits of Interactive whiteboards
- Touchscreen option: information can be altered with one’s fingers;
- Online help: the ability to access the Internet without using other tools;
- High-quality imaging: videos, graphs, and tables are clearly visible to all students;
- Smart tools: a variety of options to enhance the process, such as screen capture, a pointer, a magnifier, markers, a spotlight, and so on;
- Collaboration: teachers can help students, while students can show teachers how to use technologies.
Such technologies as interactive whiteboards can be helpful for teachers and students because of personalization and management options. Also, high-resolution images provide better illustrative material, thus enhancing the learning process. IWBs are highly collaborative: while teachers can ask students about the way in which the technology should be used, students receive new information from teachers with the help of the new tool.

Limitations of interactive whiteboards
- Price: not all educational facilities will be able to afford IWBs;
- Technical inabilities: teachers who are used to traditional methods of teaching may find it hard to use IWBs;
- Training: when a school invests in an IWB, it must invest in teacher training to make sure that the technologies enhance the process;
- Reliance on power/Internet: in cases when there is no connection to electricity or the Internet, IWBs will not work;
- Distractions: as with any other technologies, students will get distracted from the topic by paying more attention to the tool.
While interactive whiteboards are becoming very popular, they still have numerous limitations. Price, training, and reliance on other technologies all limit the effective delivery of information through IWBs. High costs are especially important because of recent budget cuts.

New teaching aids and technologies
- Artificial intelligence, educational software, and machine learning have the potential of being integrated into education;
- Learning models can become personalized with the help of technologies;
- Philosophical shifts in education are also expected to occur;
- Teachers will remain important and act as facilitators;
- AI can become tutors, helpers, and diverse companions of learning;
- More responsibility will be assumed by students;
- Final roles of education remain to be determined (Bernard, 2017).
With 2019 around the corner, technologies continue to capture the sphere of education as developers design new products for enhancing learning. Traditional methods are being substituted for cloud computing, AI, machine learning, and educational software. New aids and techniques have been shown to provide a new look on education and collaboration between teachers and their students.

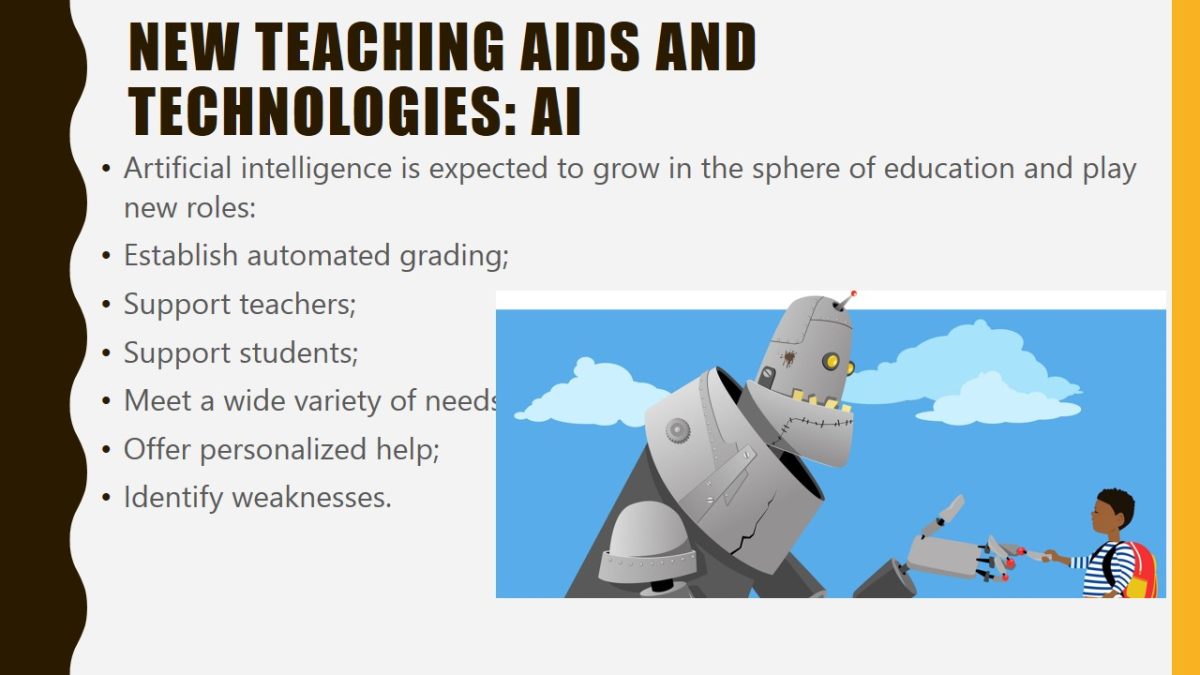
New teaching aids and technologies: AI
- Artificial intelligence is expected to grow in the sphere of education and play new roles:
- Establish automated grading;
- Support teachers;
- Support students;
- Meet a wide variety of needs;
- Offer personalized help;
- Identify weaknesses.
As already mentioned, AI is becoming an important part of the learning process. When it comes to establishing automated grading, teachers will not have to assess assignments manually. In supporting teachers, AI can enhance online communication with students and act as assistants. In supporting students, AI is expected to take on the role of learning companions that know students’ and schools’ histories. The new tools can also reinforce students’ skills and help them master these skills along with assessing classrooms to determine areas in which learners are less proficient. They can also help students with special needs adapt, can act as facilitators, and manage paperwork.
Examples of AI in the classroom
- Thinkster Math: an application that assigns each student an online tutor to help him or her solve math problems;
- Brainly: a social media website that uses machine learning for classroom questions;
- Content Technologies, Inc.: an AI solution that creates customized textbooks to cater to students’ needs;
- Netex Learning: helps create digital lesson plans with the aid of a learning cloud solution;
- Mika: AI-based tutoring tool for a personalized approach.
The examples of AI solutions presented in the slide point to the fact that these technologies are developing at a rapid pace. Ranging from solving mathematical problems to personalized tutoring, AI can provide both teachers and students with opportunities to make learning easier and more efficient. It is recommended for everyone to research available solutions to find the most appropriate apps and try to use them in each lesson.

New teaching aids and technologies: Machine learning
- The new field of computer science can:
- Support teachers: mine data to offer the most valuable information for classes;
- Predict the performance of students: identifying possible weaknesses and suggesting improvement methods;
- Test learners: standardized tests and other assessments;
- Fairly grade students: remove human bias in grading;
- Offer customized learning: catering to each learner;
- Improve retention: identify “at risk” students and teachers.
Machine learning is another sphere of technologies that can support the learning of students and help teachers. Examples of its benefits include predicting performance, offering the most relevant information, testing the knowledge of learners, grading students automatically, or even identifying students who are likely to drop out. The integration of machine learning into education requires skills and knowledge, which means that teachers should receive training on this topic.
New teaching aids and technologies: educational software
- New applications and tools facilitate students’ learning. They include:
- Courseware: educational material in digital formats;
- Classroom aids: projectors, IWBs, and other tools;
- Assessment software: decreasing the amount of human labor when checking assignments;
- Reference software: dictionaries and encyclopedias in digital form;
- Custom platforms: learner-friendly devices and hardware that do not have distractions;
- Problem-solving, math applications, small dictionaries, calculators, and other apps.
Educational software represents an abundance of new tools and applications that students and teachers can use in classrooms and while doing homework. For example, reference software can be used to quickly search for relevant information and share it with others. Students and teachers can download applications that help with mundane tasks such as finding a new word in a dictionary or solving a math problem.

Future of smart classrooms
- The Internet of Things spreading across educational facilities;
- Intelligent spaces for an interactive experience: technologies adapting to teachers and students;
- Always-on experience: technologies being available anywhere and at any time;
- Augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR) solutions becoming common in classrooms;
- Location-awareness solutions: technologies adapting to where students and teachers are located;
- Dense environments’ multiplication: sensors, lighting, tablets, and other smart devices work together.
A look at the future of technologies in education suggests that innovation will spread across the majority of educational facilities, from kindergartens to universities. Students will get an “always-on” experience wherever they are: technologies will always be available. Virtual reality and similar technologies will provide an immersive experience and make learning more engaging. Gadgets ranging from tablets to smart whiteboards are expected to become the norm.

Challenges to address in the future
- Overload of networks: issues with handling different devices;
- Using social media instead of looking for relevant information;
- Security breaches: ensuring control over stored data;
- Cheating: students should be prevented from cheating;
- Gaming: apps and games that students can access online are distracting;
- Damaged devices: in the classroom, any hardware can break.
Despite the bright future of technologies in the sphere of education, there are still some challenges that should be addressed. For example, teachers should prevent students from getting distracted by social media and other websites. Also, cheating is a significant issue, especially with a wide availability of completed assignments posted online. In the case when schools invest in tablets or computers, there is also a need to prevent expensive equipment from getting damaged.

Barriers to including technologies in education
- High costs of integration:
- Technologies requiring significant investment;
- Solutions becoming obsolete quickly;
- Budget problems at schools;
- Inability to cater to different devices;
- Overall educational underfunding.
- Absence of training:
- Need to invest money in teacher training;
- Proper training rarely available;
- Older teachers not familiar with new tools;
- Steep learning curves.
- Resistance to change:
- Lack of training and education;
- Absence of time to dedicate;
- Inefficient support of teachers;
- Parents think that there are too many.
- Insufficient infrastructure:
- Lack of network infrastructure for supporting technologies;
- Challenging with establishing Internet connections;
- Tech companies asking too much for introducing technologies;
- their solutions into classrooms.
- Unequal support:
- Low-income students are at a disadvantage;
- Teachers assign homework that requires tech;
- Missing opportunities for using advanced tools;
- Students feel shame due to financial issues.
- Red tape (bureaucracy):
- Tech providers produce too many tools;
- Short sales cycles for educational tech;
- Sign-offs from different parties;
- Companies focus their efforts on sectors other than education.
Barriers to implementing technologies in the sphere of education include a variety of aspects. For example, high costs for new equipment require institutions to make significant investments, especially since new tools become outdated as newer ones emerge. Overall underfunding makes it harder for schools to keep up with technological progress. New advancements also make it hard for teachers to understand how to use them, and the learning curves are usually steep, especially for older teachers.
Other barriers to implementing technologies in education include teachers’ resistance to change as well as the lack of relevant infrastructure to sustain new advancements. Dedicating more time to education and the support of teachers who are not ready to replace their traditional methods with technologies is recommended. Schools should be aware of the need to establish effective infrastructure and collaborate with tech companies to introduce new tools and improve the learning process.
Bureaucracy and a lack of support for underserved students also limit the benefits of technologies in classrooms. Students whose parents or caretakers cannot afford to purchase new tablets or computers can be at a disadvantage because teachers may assign tasks requiring new solutions. When it comes to bureaucracy, educational facilities are at a disadvantage because not many companies are willing to collaborate with schools. Businesses are more profitable, and thus, more attention is given to them.

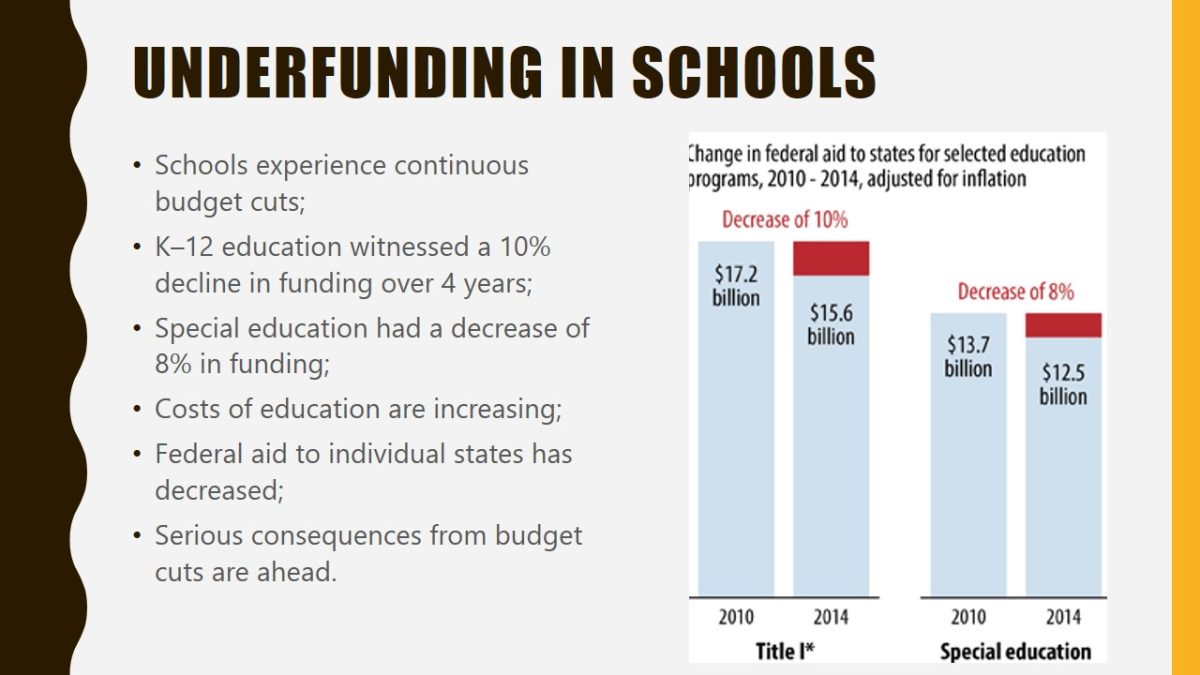
Underfunding in schools
- Schools experience continuous budget cuts;
- K–12 education witnessed a 10% decline in funding over 4 years;
- Special education had a decrease of 8% in funding;
- Costs of education are increasing;
- Federal aid to individual states has decreased;
- Serious consequences from budget cuts are ahead.
Underfunding is a massive barrier in the context of technologies and education because financial support for schools is on the decline. For example, compared to 2010, the funding of education for K–12 classrooms with a lack of family support decreased by 10% in 2014. For special education, funding dropped by 8%. These figures show that the government will be unable to support the technological advancements in education, and many students will have to invest in new solutions themselves. However, even this solution is only possible for wealthy families.
Absence of teacher training
- TPACK is the goal of technological teacher training;
- Combining content, pedagogical, and technological knowledge;
- Program-wide and program-deep training is needed;
- Older teachers struggle the most: they did not grow up with technologies;
- There are no sufficient standards, credentials, or frameworks to guide teachers’ practice in regard to technologies.
As the lack of teacher training is another barrier to implementing technologies in education, it is important to achieve a unified framework to address all concerns. TPACK – technological pedagogical content knowledge – combines the three most important aspects of teaching to help instructors to effectively interact with technologies. The expertise associated with the framework helps teachers to become proficient in their special disciplines through being creative and using technologies. Therefore, teachers are encouraged to implement various aspects of their knowledge and be bold in their choices.

Addressing teacher preparation issues
- General:
- System-wide planning and implementation of educational technologies;
- Instructors:
- Focus on teachers’ skills and knowledge when preparing them to use technologies;
- Provide exposure to the technologies and strategies relevant to teaching.
- Accreditors:
- Offer a timeline of standards and skills for educational technologies that teachers can use in their practice;
- Plan the ongoing development of competencies and knowledge to align with innovation.
- Teachers:
- Collaborate with each other to facilitate co-learning opportunities.
To address the problem of poor teacher preparation, several recommendations have been suggested. Overall, there is a need to plan for the integration of technologies in advance. Instructors should assess teachers’ skills and knowledge to identify areas for improvement. Teachers should not resist changes and should collaborate with each other to facilitate their learning and adherence to new technologies.

Tips for incorporating technologies into classrooms
- Letting students become teachers:
- Students possibly being more technologically-advanced;
- Teachers seeking the advice of the younger generation;
- Allowing learners to use new tools;
- Promoting collaboration and the mutual exchange of information;
- Making sure that there are no gaps in technology use.
- Teachers championing digital citizenship:
- Safe and friendly environments for technology use;
- Responsible behavior regarding technologies;
- Refraining from sharing personal and sensitive information online;
- Ensuring to communicate the negative effects of cyberbullying;
- Exploring their digital footprints.
- Smart ways of using phones and social media:
- YouTube for searching information;
- Newsletters for sending assignments;
- Encouraging the reporting of news;
- Discussing the latest news found online.
- Using technologies that let students learn from each other:
- Recording technologies to improve speaking/listening skills;
- QR and other technologies to facilitate research and access to information;
- Shooting short videos of classroom interactions for students to analyze later;
- Creating classroom forums for information exchange.
As seen from the list of recommendations, incorporating technologies into classrooms is possible through collaboration and attention to maintaining a safe environment. Both teachers and students should share information and develop ways that technologies can fit into their classroom settings. Safety and privacy are key – the rights of each student and teacher should be preserved.
It is always important to look at new ways to use conventional technologies. For example, social media can be employed for sharing information on classroom learnings. Recording technologies can enhance the learning process by boosting creativity as well as helping students educate themselves on the use of different supplementary tools.


Examples of using technologies
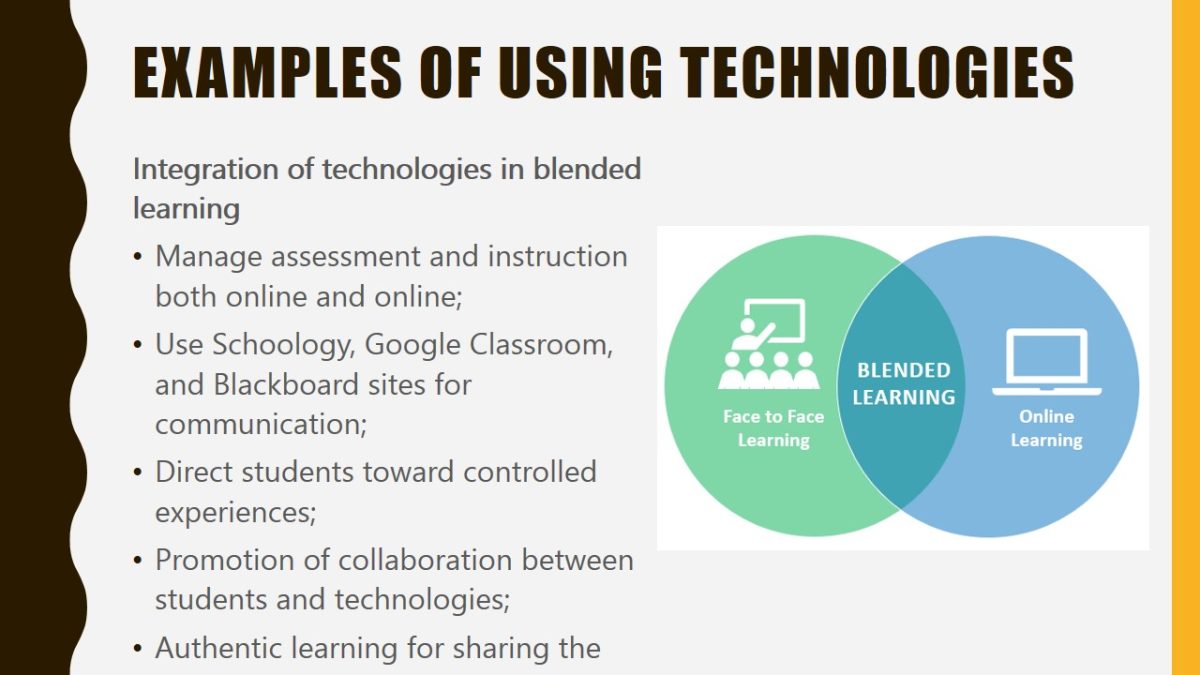
- Integration of technologies in blended learning:
- Manage assessment and instruction both online and online;
- Use Schoology, Google Classroom, and Blackboard sites for communication;
- Direct students toward controlled experiences;
- Promotion of collaboration between students and technologies;
- Authentic learning for sharing the results of learning.
- Getting students outdoors with the help of technologies:
- Project Noah and Journey North: websites to encourage the reporting of natural phenomena;
- Project Squirrel: reporting squirrel sightings to track environmental changes;
- iNaturalist: taking and submitting photos of nature to get more information about plants and animals;
- Project FeederWatch: bird observation tool to study migration patterns.
- Student-created videos:
- Learning product videos: filming to demonstrate student learning;
- Response videos: filming to respond to a question or prompt;
- Reflection videos: filming to talk about one’s learning experience;
- Tutorial videos: filming to demonstrate a skill, concept, or practice;
- Experience videos: filming to boost collaboration and teamwork.
- Class Twitter Chats:
- Hosting: a teacher is a moderator who invites students and guests to study course content;
- Privacy: communicate the importance of nondisclosure to students and parents;
- Aims: establish the objective of a chat;
- Access: offer several dates for chats, provide tutorials, and demonstrations;
- Students: ask learners about their ideas, evaluate their behaviors;
- Preparation: develop prompts that will be discussed during each lesson.
- Game-based learning:
- Benefits STEM subjects;
- Embodies understandable principles of modeling and learning through games;
- Represents effective and meaningful contexts for simulating skills;
- Aligns with Piaget’s theory of learning and development;
- Allows for assimilation and accommodation to real-life situations;
- Provides cognitive, social, motivational, and emotional benefits.
- BrainNook: a website focused on Math and English with a teacher portal;
- Creativity Games: a resource with an abundance of brain training tasks;
- Sheppard Software: free educational games for early learners;
- Arcademic Skills Builders: games for language arts, vocabulary development, thinking, and math skills;
- Primary Games: over a thousand game titles along with curriculum guides for instructors;
- Poptropica: a virtual world in which students can learn and play safely.
Blended learning has become the most common way of combining traditional and online learning. On the one hand, students interact with each other in real life, thus developing interpersonal communication skills. On the other hand, their learning is supported by online resources that help them collaborate and conduct research. Such tools as Google Classroom have been shown to foster the team spirit without taking away from personal interactions. Overall, blended learning promotes authenticity through offering the “best of both worlds.”
Because technologies often lead to students staying indoors behind their computers, promoting the use of interactive applications can be useful for motivating them to go outside. The list of applications presented in the slide is not limited to them only. They can be interesting to both younger and older students because observing the environment can be fascinating to people of all ages. Teachers should especially promote the use of such apps because they enhance students’ overall knowledge.
Student-created videos are another way of using technologies in the classroom. They promote creativity and collaboration through encouraging students to come up with innovative ways of recording information. These methods can be used by both younger and older students because video tutorials or reflections have gained massive attention with the worldwide popularity of YouTube. The most important thing to consider in the case of student-created videos is privacy. It is essential to maintain the filmed materials as educational tools.
Class Twitter chats represent a convenient way for teachers and their students to share information wherever they are. Because Twitter is available on smartphones, this example of using technologies shows that complex and sophisticated tools are not always necessary to make the learning process effective. Teachers should prepare for these chats and establish objectives for the classes and give freedom to students to collaborate and exchange knowledge.
Despite some skepticism, game-based learning is another way in which technologies can be used for education. Games have shown to be effective because they encourage students to accommodate to new contexts and situations. Such games model understandable environments and offer a platform for learning. In addition, when playing, learners can develop their emotional, cognitive, and social skills by being creative regarding finding necessary solutions to problems within games.
The list of educational games presented in the slide is applicable to younger students because they are the ones to be the most interested in learning while playing. These games promote the development of memory, logic, creativity, math skills, and language competencies. Teachers should show their students that educational games are available and that they can be used as supportive methods.




Conclusion
- Technologies are advancing at an exponential rate;
- Students are more familiar with technologies than teachers;
- New tools include IWBs, machine learning, and AI;
- Cuts in educational funding prevent technologies from being implemented;
- The training of teachers is imperative for success;
- Educational technologies require significant investment;
- Shortages and cuts in funding contribute to an unequal distribution of technologies.
In conclusion, technologies represent a new way for teachers to engage students in the process of learning. With new advancements developing every year, it may be hard to keep up. However, the use of supportive tools should be guided by the needs of students and the abilities of teachers to navigate technologies and use them to their advantage. Schools are required to make significant investments, but shortages in funding make this challenging.
Reference
Bernard, Z. (2017). Here’s how technology is shaping the future of education. Business Insider. Web.