People of the 20th century saw the technological revolution, with many companies shifting from manual labor to efficient machinery that accelerated the process many times. Yet, the revolution has not stopped in the previous century and proceeded to introduce new innovations and breakthroughs that changed the lives of people and markets. Among such facilitators of innovation is Tesla Inc., which specializes in matters of renewable energy and artificial intelligence. In the past decade, the firm introduced a vast range of products that many people considered impossible. For this reason, this organization is among the highest-valued firms not only domestically but internationally. In the following years, Tesla will possibly focus on its three significant opportunities, which involve the introduction of new products, the creation of new markets, and international expansion.
Description of the Organization
First, it will be vital to give an overview of the corporation and its main scope of expertise. Tesla is a green energy and electric automobile firm run by entrepreneur Elon Musk. According to one of the biggest financial news agencies, Reuters (n.d.), the firm creates not only completely electric automobiles but provides energy production and storage equipment and distributes and rents them. The company then additionally provides services relating to the mentioned goods. The firm’s automotive sector sells automobile regulatory credits in addition to designing, developing, producing, renting, and selling electric cars (Reuters, n.d.).
Services, as well as other products, that include non-warranty after-sales automobile maintenance, used-car sales, commercial product sales, revenues by its acquired companies to third-party clients, and car insurance, are also included in the automobile category (Reuters, n.d.). In its power storage systems section, items for solar power generation, battery storage, and support products are designed, manufactured, installed, sold, leased, and subject to relevant business initiatives (Reuters, n.d.). Therefore, Tesla is not merely an organization that manufactures renewable energy goods.
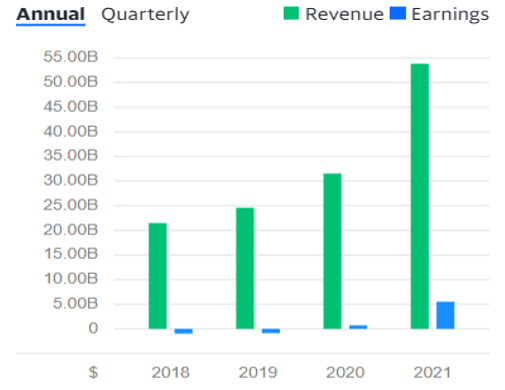
For the purposes of global market presence, Tesla operates in different factories around the globe. The company has six extensive, vertically integrated facilities that it runs over three continents from the Texas headquarters (Tesla, n.d.). The teams internally create, manufacture, market, and support the goods with the help of over 100,000 workers (Tesla, n.d.). According to the business agency Fortune (n.d.), a significant achievement for the company was established in 2003 as Tesla Motors, which was the sale of its one-millionth vehicle in 2020. What is noteworthy is that Tesla produces and distributes solar panels, rooftop solar tiling, and other associated goods and services via Tesla Energy (Fortune, n.d.). In addition to being a significant operator of photovoltaic energy-producing equipment within the U.S., Tesla Energy is among the top global providers of battery power storage systems (Fortune, n.d.). Therefore, the company has subsidiaries that play a crucial role in production and marketing. As can be seen from Figure 1, Tesla’s sales have been increasing with the help of the mentioned services and products.
Organization’s Structure
Type of Ownership
Still, it is necessary to remember the given company’s organizational structure that additionally plays a vital part in the estimates of its success. Tesla Inc. is a public company with 21,143,862 outstanding shares (Reuters, n.d.). The company has a market capitalization of $576,131.90 billion, which makes the company among the most high-valued entities in the market (Reuters, n.d.). Therefore, such figures, notably the shares and market capitalization, indicate that the company has the confidence of both institutional and retail investors.
Organizational Hierarchy
The second essential aspect when analyzing the structure is the organizational hierarchy. Here, Max Weber’s bureaucratic management theory can be used to characterize the business management of Tesla. According to the theory, a company must have a strict hierarchy with a specific division of labor among the employees who constitute the firm (Schermerhorn & Bachrach, 2019). Here, a structured organization with elements of a hierarchical system best describes Tesla (Tesla Investor Relations, n.d.). For all company operations, covering financial administration, selling, advertising, information technologies, manufacturing, and design, as well as the C-suite offices, Tesla does employ workable units. Among the most critical people in Tesla are Elon Musk, the CEO; Zachary Kirkhorn, CFO; and Andrew Baglino, SVP (Tesla Investor Relations, n.d.). Therefore, with such strict rules and structures, Tesla can be considered a bureaucratic system
The Tesla, Inc. Board of Directors has high expectations for all of the Company’s employees, executives, and members. This concept makes the value of good company governance apparent. The Board of Directors has a duty to supervise corporate management for the organization and to act as a responsible fiduciary for stakeholders. The Board of Directors adheres to the practices and standards outlined in these policies in order to carry out its duties and meet its obligations. These rules may be modified on a regular basis as the Board of Directors sees fit in the corporation’s best interests or as necessary by relevant laws and regulations.
Business Model
The last aspect of the organization’s structure is the business model. Tesla Motors and its distinctive business strategy are primarily responsible for the general public’s excitement and adoption of electric vehicles. Elon Musk, the chief operating officer of Tesla and the company’s creator, said of the company’s mission: “Our goal when we created Tesla a decade ago was the same as it is today: to accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass market electric cars to market as soon as possible” (Tesla, n.d.-d). The foundation of Tesla’s lucrative business strategy is this objective. Instead of using licensed outlets, Tesla’s business strategy relies on direct product selling and servicing (Tesla, n.d.-d). Tesla’s business strategy places a strong emphasis on expanding its network of charging stations. Tesla has expanded the scope of its business model to include both residential and commercial energy storage technologies (Tesla, n.d.-d). As can be seen, the business model emphasizes the revolutionary approach to green-energy products and the introduction of such goods to the markets.
A Range of External Influences that Might Impact Growth
New Market
As for the external influences that might impact the growth of Tesla, the first is the new market. For instance, Tesla Bot is developing the next generation of automated processes, which includes a general-purpose, bipedal, humanlike robot capable of carrying out dangerous, monotonous, or repetitive duties (Tesla, n.d.-b). Furthermore, in Tesla, deep neural systems are trained on issues ranging from observation to regulation by utilizing cutting-edge technologies (Tesla, n.d.-b). These algorithms gather iterative data from the collection of millions of automobiles in real time to learn from the complex and varied events in the world (Tesla, n.d.-b). The 48 systems that make up the whole build of the Autopilot neural networks require 70,000 GPU hours to learn. At every timestep, they produce 1,000 different tensors (predictions) collectively (Tesla, n.d.-b). As a result, with the growing demand for artificial intelligence, a new market will be introduced specializing in robotics, and Tesla will be able to seize the opportunity, although not immediately.
Product Range
Another opportunity for growth is the introduction of a new product range, represented by batteries. Tesla is aiming to produce its battery cells internally, which will reduce production costs and add a large number of new employees while providing time. The Gigafactory 1 battery manufacturing facility became the world’s highest-capacity battery facility in the middle of 2018, achieving a yearly pace of around 20 GWh (Tesla, n.d.-c). Tesla’s price of battery cells will drastically decrease when the Gigafactory accelerates production owing to economies of scale (Tesla, n.d.-c). Tesla will, in the long run, expand the market for its products by lowering the price of batteries, which will enable the company to have the greatest potential influence on the shift to the planet of renewable power.
Internation Expansion
Lastly, the purpose of the firm’s cars’ design is quite well matched to the European market. Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla Motors, stated that Tesla’s objective is to blend style, technology, and efficiency with a forward-looking direction toward renewable energy and sustainability (Tesla, n.d.-a). The organization’s most significant markets in Europe, notably Germany, Switzerland, Norway, and the Netherlands, are the most beneficial options for the business (Tesla, n.d.-a). As a result, with its emphasis on developed countries that promote green energy, Tesla will ultimately be able to relocate its sales to more lucrative regions.
Conclusion
Hence, Tesla may concentrate on its three key opportunities in the following years, which are the launch of new products, the development of new markets, and global expansion. At the moment, the company provides services and designs and manufactures goods in the vehicle and green energy industry. Tesla is a public company and has a hierarchical organizational system, and its market capitalization indicates shareholder confidence. In the following years, it will be able to seek growth when introducing the new market of artificial intelligence with its innovative robotic products, extend its product range with the development of batteries, and expand internationally.
Reference List
Fortune. (n.d.). Tesla, Inc. Web.
Reuters. (n.d.) Tesla Inc. Web.
Schermerhorn, J. R., & Bachrach, D. G. (2020) Management. Wiley.
Tesla. (n.d.-a) About us. Web.
Tesla. (n.d.-b) Artificial intelligence & autopilot. Web.
Tesla. (n.d.-c) Tesla gigafactory. Web.
Tesla. (n.d.-d) Mission. Web.
Tesla Investor Relations. (n.d.) Corporate Governance. Web.
Yahoo Finance. (n.d.) Tesla, Inc. Financials. Web.