Introduction
Despite the stiff competition in the information sector, the newspaper industry remains one of the largest information outlets in the US with a growing influence. The industry has seen tremendous growth in recent years, increasing in value in every phase, and is anticipated to experience a further increase. Print media is the most used form and the largest revenue stream in the industry, even though the development of the internet has seen it adopting digital subscriptions. As in other industries, American newspapers’ demand and supply are not constant but continuously experience changes as influenced by price and income among other factors such as preference, price of related products, consumer expectation, and several producers in the market.
Demand and Supply Analysis of the Newspaper Industry
In the context of the newspaper industry, demand is the amount of newspaper services readers desire to purchase and can pay for at various prices. Since there are several substitutes in the information sector, the demand for newspapers and associated services is influenced by several factors (Blassnig and Esser, 2022). Supply on the other hand refers to the number of newspapers and associated services the industry provides in the market. Likewise, the supply of newspapers is affected by numerous factors in the market. Demand and supply in the newspaper industry are intertwined with each influencing another.
Until the early 20th century, the demand and supply of print news in the US were high since it was the major source of information. The supply of newspapers was high as the American population depended on print media for information and news. The industry did not face competition as many media platforms and alternative information sources such as the internet, television, and radio news had not become popular. The majority of the people in America got news largely from print sources, with only and mostly in remote areas relying on alternative sources such as radio news (Blassnig and Esser, 2022). However, this trend changed when other alternative sources of information grew popular, especially with the advent of digital media and internet services facilitated by smartphones. The majority who owned smartphones and other electronic gadgets began searching for information and news from the internet and digital media, reducing the demand and supply for newspaper and print news.
To maintain popularity, the newspaper industry has been trying to adopt digital subscriptions to supplement print news media. Most newspaper firms such as The Street Wall Journal, New York Times, and Gannet Co. Inc. have embraced digital media, introducing digital readership and subscriptions for online consumers, even though print sources remain the largest revenue stream and practice in the industry (Firmansyah et al., 2022). Some of the factors affecting demand and supply in the industry include:
Digital Media
Following COVID-19, most news consumers resorted to online media for fast and up-to-date news. The majority of the American population with smartphones and other electronic gadgets began looking for news from the internet and digital media. As a result, the demand for print news went down, reducing the supply of newspapers (Blassnig and Esser, 2022). The demand for print sources such as newsletters, journals, and magazines among others took a downward trajectory in both demand and supply.
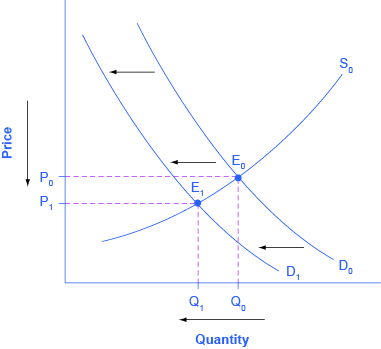
The Print News Market: Demand and Supply Curve
A change in taste from print news to digital media leads to a leftward shift in demand for print sources, resulting in the decrease of both the equilibrium price and quantity of newspapers as shown in figure 1 below.
Price of Related Products
Digital media remains the top rival of the newspaper industry, affecting its demand and supply. Digital sources of information such as the internet and social media are cheaper and more efficient, making several information consumers embrace them (Leroch, 2022). Unlike newspapers, digital media provides summarized news at a cheaper cost, requiring only bundles. In addition, digital media is more convenient in providing news as the information can be easily saved and stored for future reference. The cost and convenient advantages of digital media have led to a decrease in the demand and supply of print news, affecting the general demand and supply in the newspaper industry.
Elasticity
Elasticity refers to the change in demand that results from the price change. Usually, when the price of a commodity reduces, the demand for the item increases as many people can afford it, such products are said to be elastic or to have elastic demand. However, some commodities’ demands are not affected by price changes, and thus do not experience any change when their price is raised or lowered, and thus considered inelastic (Ma, 2022). Newspapers are inelastic or have inelastic demand and supply since the changes in their prices do not affect them.
The fall in the demand and supply for print sources in the newspaper industry is caused by the emergence of digital media which are considered more convenient, and not by their prices. Lowering the prices of newspapers cannot increase the demand and supply for print sources, but will only affect the profit in the industry, since the consumers of digital news will continue to subscribe to online media, leaving the newspaper industry to incur losses (Ma, 2022). Similarly, Americans who depend on television and radio for news will continue to use these sources regardless of the decrease in the prices of newspapers. Thus, lowering the prices of newspapers will only affect the revenue stream in the industry but not increase the demand.
Similarly, raising the prices of print sources in the newspaper industry will not affect the demand in the industry. American population depending on print sources for information are loyal consumers who are not motivated by the cost, therefore, increasing the prices of the print sources will not chase them away from newspapers (Wang, 2022). Being inelastic, raising the cost of newspapers will lead to an increase in revenue stream in the industry.
Despite the inelastic nature of demand in the print media industry, price affects the demand for advertisement in the newspapers. The cost of advertisement is relative, and thus consumers will always choose the cheaper option (Firmansyah et al., 2022). Therefore, if the prices are increased, the demand for advertisement services will go down as customers will choose the cheaper alternative, thereby reducing the revenue stream from the advertisement sector. Likewise, reducing the prices of advertisements will raise the demand for the services, thereby increasing the revenue stream for the industry.
Market Structure
American newspaper industry relies on both local and international markets with consumers streaming from all regions. The industry shares the market with other rivals in the larger information industry such as television, radio, and digital media (Chen, Su, and Tai, 2022). Various firms in the industry are focusing on strategies such as innovations, popularity campaigns, new product launches, and originality to survive in the market (Garz and Rickardsson, 2022). Since most businesses in the industry are old in the market, they are trying to maintain originality and conducting popularity campaigns to compete with the newcomers the in the information and media industry and remain afloat.
Among the services offered in the industry, print news remains prevalent with the largest share. In recent, due to the shift to online media with the emergence of the internet and smartphones, the industry has been inclining towards and embracing digital options, introducing digital subscriptions for online consumers (Firmansyah et al., 2022). Firms such as The Wall Street Journal have developed online subscriptions, providing consumers with digital readership.
The Wall Street Journal is the largest firm in the industry with the highest subscribers both locally and internationally, both print media and online subscriptions. It is followed closely by Gannet Co. Inc. which boasts of being the largest publisher (Garz and Rickardsson, 2022). Other notable firms in the market include New York Times Company, Tribune, and MediaNews Group. Inc., News Corporation, The Washington Post, Los Angeles, New York Post, and News Day which serves both local and global markets. In addition, other small firms serve only the local market.
Even though it is fighting stiff competition to remain afloat, the industry is not doing badly. The newspaper industry is valued at USD 19.6 according to the latest ranking in 2021 and is projected to rise even higher in the coming years (Firmansyah et al., 2022). The annual growth rate is predicted to be higher between the periods of 2022-2030, showing its potential (Leroch, 2022). With the adoption of digital subscriptions and online options, the industry will likely recapture the market. Advertisements and news are the most valuable news, fetching the largest revenue. Newsletters form the largest driver of both print and digital subscribers across all the firms. The businesses in the industry have invested in newsletters, recruiting the top experts to produce the best-selling creative and entertaining content for both online and print subscribers.
Conclusion
The American newspaper industry has experienced growth, overcoming the stiff competition in the larger information and media industry by digital journalism which almost saw its decline. The industry is affected by the forces of supply and demand as influenced by factors such as preference, price, and convenience created by rival digital journalism. To survive in the market, it has embraced online media by introducing digital subscriptions for consumers who are quickly shifting to online media. The industry has an inelastic demand, less impacted by the changes in price. The Wall Street Journal is the firm enjoying the largest market share, followed by other big print media outlets such as the Los Angeles, and The Washington Post.
Reference List
Blassnig, S. and Esser, F. (2022) ‘The “audience logic” in digital journalism: An exploration of shifting news logics across media types and time,’ Journalism Studies, 23(1), pp.48-69. Web.
Chen, M., Su, F. and Tai, F. (2022) ‘Major league baseball marketing strategies and industry promotion approaches,’ Frontiers in Psychology, 13. Web.
Firmansyah, F. et al. (2022) ‘How the print media industry survived in the digital Era,’ Jurnal ASPIKOM, 7(1), pp.1-15. Web.
Garz, M. and Rickardsson, J. (2023) ‘Ownership and media slant: Evidence from Swedish newspapers,’ Kyklos, 76(1), pp.18-40. Web.
Leroch, M. (2022) ‘Market power and journalistic quality,’ European Journal of Law and Economics, 53(1), pp.109-124. Web.
Ma, J. (2022) ‘Defining the relevant market for data monopoly: In regulating data monopolies: A law and economics perspective edited by Ma, J. (pp. 109-123). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. Web.
Newspapers and the Internet(n.d.) Web.
Wang, X. (2022) ‘The impact of IoT on news media in the smart age,’ Mobile Information Systems, 2022. Web.