Introduction
The analysis of the environment in which a healthcare institution operates reveals the characteristic factors and drivers that determine the success and effectiveness of activities and highlights the key barriers and challenges, including those related to competition. The Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital, used as a target facility for analysis, is a respected institution that is part of the Jackson Health System and offers important services to the public in addressing mental problems associated with substance abuse, behavioral deviations, and other forms of mental disorders. This institution is reputable in its professional field, and the assessment of the external and internal operating environments can help determine how competitive the hospital is and what developments its administration is promoting to provide high-quality services to patients. As relevant tools, a PESTL analysis, a SWOT analysis, a core competencies technique, and a gap analysis will be engaged. These assessment instruments are relevant approaches to evaluating external and internal operating environments and may contribute to identifying the individual characteristics of the hospital in question.
Internal Environment
As part of the vast Jackson Health System, the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital offers targeted services to narrow populations. The key mission of this healthcare institution is to promote recovery through the provision of qualified care and professional support (“Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital,” 2021). As Kowalski (2020) notes, this approach is in line with the basic principles of mental health care. As a vision, the idea is highlighted that an individualized approach to rehabilitation, whether at the family or group level of interaction, is a positive initiative to encourage patients to recover. The Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital pays particular attention to vulnerable populations, such as members of the LGBTQ community, those who have experienced suicidal thoughts, and many other people whose psyche has been exposed to dangerous conditions for certain reasons (“Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital,” 2021). Therefore, an opportunity to return targeted patients to normal and self-directed life is one of the main values promoted in the hospital in question.
Core Competencies
To assess the internal operating environment of the healthcare facility under consideration, a core competencies analysis can be performed. According to Mallidou et al. (2018), this tool implies evaluating two key criteria – resources and capabilities, which, in turn, include additional factors to take into account. In relation to the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital, these aspects determine the sustainability of the financial base, the occupancy of professional staff, and some other significant indicators.
Resources
From the perspective of the resource base, the healthcare institution has sufficient potential to provide comprehensive assistance to the target populations. The hospital is the biggest facility of its type in Florida, and as part of a wide network, it has a sustainable facility base. According to the official report, in 2020, $77,025 was received as grant funds (“Jackson County DHHS,” 2021). Additional funds also come from official partners; for instance, at the end of 2020, $15,000 was transferred to the hospital account from one of the banks (“Jackson County DHHS,” 2021). Despite the restrictions caused by the current COVID-19 pandemic, the healthcare institution is organizing campaigns and open projects to engage patients and promote the clinic’s services to expand its coverage. Hellmann (2020) argues that today, financial assistance from the government is limited for institutions of this type because most funds go to fight the consequences of the pandemic. However, due to a strong partner base, the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital can count on sufficient resources to realize its capabilities.
Capabilities
Targeted work with patients in the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital is carried out in different directions. The clinic provides child and adolescent services, inpatient and outpatient assistance, and organizes regular therapeutic sessions (“Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital,” 2021). High staffing allows for a multi-disciplinary approach to interacting with patients, which, as Reiter et al. (2018) note, allows for improving primary care and utilizing employees’ skills effectively. The full continuum of supportive care is achieved through the effective practice of coordinators who compile flexible work plans and make daily patient appointments possible. The hospital team consists of a large number of professionals, including social workers, nurse practitioners, therapeutic recreation specialists, counselors, and other employees (“Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital,” 2021). Such a wide range of specialties allows for addressing a wide range of tasks and makes the healthcare institution a leader in its region.
Gap Analysis
The internal operating environment of the clinic in question, despite a sufficient resource base and professional staffing, can be considered in the context of some barriers. One of them is the restriction on direct interaction with patients during group sessions due to the current COVID-19 pandemic. According to Moreno et al. (2020), in the field of mental health care, such a deterrent is critical because face-to-face contact is a prerequisite for targeted care for patients with mental disorders. While the management at the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital is doing its best to minimize the implications of this barrier to productivity, sanitary restrictions prevent the clinic from operating as it did before the pandemic. Thus, when taking into account this factor, the hospital needs to optimize its activities and create more flexible conditions for interaction with patients.
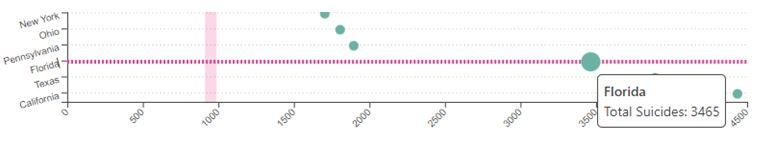
Although the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital provides both in-person and remote communication, which is realized through telehealth technologies, the institution fails to address the issue of research activities. This is particularly true for the suicide case study since, as shown in Figure 1, Florida has the third-highest rate of suicides in the country (“Suicide rates by state 2022,” 2022). This may mean that the clinic in question cannot address this problem as effectively as possible because, as one of the leading healthcare institutions in its field in the state, the clinic is involved in working with patients who experience suicidal ideation or have experienced unsuccessful suicide attempts. An organizational structure should be optimized to enhance activities in this direction and embrace diverse populations by analyzing social determinants (Rockett et al., 2022). Since high workforce occupancy allows this task to be realized, the clinic’s management should create dedicated research teams and direct resources towards solving the issue and improving the health indicators of the vulnerable population.
External Environment
To assess the external factors affecting the competitiveness of the hospital in question and its productivity, a PESTL analysis can be performed. This tool aims to evaluate political, economic, social-cultural, technological, and legal factors influencing operations (Himawan & Wening, 2021). In the context of the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital, such aspects involve evaluation based on the specifics of the field, namely the effectiveness of mental health care.
PESTL Analysis
The results are summarized in Table 1, where the relevant implications for the work of the clinic are indicated.
Table 1. PESTL analysis for the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital
While taking into account the information collected from a PESTL analysis, one can note that the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital is experiencing some challenges, most of which relate to socio-cultural and legal aspects. The clinic is forced to adhere to national standards for the provision of appropriate medical care, which requires a series of clinical examinations to determine and confirm a specific diagnosis in a patient. At the same time, one can highlight the stable financial support and coverage of most public insurance plans, which allows the hospital to provide a wide range of services to target populations, thereby maintaining competition and remaining a leader at the state level.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is another handy tool to assess the characteristics of the external environment of the hospital in question while considering both positive prospects and risks. Sameh et al. (2022) explore the mental health area and use this analysis to identify relevant “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats” regarding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people’s psychological states (p. 55). In Table 2, a SWOT analysis is given for the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital, and the clinic’s characteristics are described based on the above criteria with a particular emphasis on opportunities and threats as critical external factors and forces governing competition.
Table 2. SWOT analysis for the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital
Conclusion
The analysis of the internal and external factors influencing the development and competitiveness of the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital allows highlighting relevant areas to pay attention to when planning strategic growth. As the tools for an internal evaluation, the mechanisms for identifying core competencies and gaps are involved, and for an external assessment, PESTL and SWOT analyses are utilized. The results show that, despite the advantages and strengths, for instance, a leadership position at the state level and a developed technical base, some barriers complicate sustainable activities, particularly an increase in the number of admissions of patients with mental health problems, the need to adhere to inflexible standards of care, and unstable funding. To avoid losing its competitive position and become a nationally and internationally recognized healthcare institution, the Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital should strive for greater freedom in conducting activities, expanding partnerships, and strengthening its research base.
References
Hellmann, J. (2020). Mental health, addiction services clamoring for coronavirus funds. The Hill, 27(36), 11-12.
Himawan, N. S., & Wening, N. (2021). On health care sector, what external environment that important? A review literature.Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology, 15(4), 2036-2042. Web.
Jackson Behavioral Health Hospital. (2021). Jackson Health System. Web.
Jackson County DHHS: 2020 annual report. (2021). Jackson County Public Health. Web.
Kowalski, M. A. (2020). Mental health recovery: The effectiveness of peer services in the community. Community Mental Health Journal, 56(3), 568-580.
Mallidou, A. A., Atherton, P., Chan, L., Frisch, N., Glegg, S., & Scarrow, G. (2018). Core knowledge translation competencies: A scoping review. BMC Health Services Research, 18(1), 1-15.
Moreno, C., Wykes, T., Galderisi, S., Nordentoft, M., Crossley, N., Jones, N., Cannon, M., Correll, C. U., Byrne, L., Carr, S., Chen, E. Y. H., Gorwood, P., Johnson, S., Kärkkäinen, H., Krystal, J. H., Lee, J., Lieberman, J., López-Jaramillo, C., & Arango, C. (2020). How mental health care should change as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic.The Lancet Psychiatry, 7(9), 813-824. Web.
Reiter, J. T., Dobmeyer, A. C., & Hunter, C. L. (2018). The primary care behavioral health (PCBH) model: An overview and operational definition.Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings, 25(2), 109-126. Web.
Rockett, I. R., Jia, H., Ali, B., Banerjee, A., Connery, H. S., Nolte, K. B., Miller, T., White, F. M. M., DiGregorio, B. D., Larkin, L., Stack, S., Kõlves, K., McHugh, K., Lulla, V. O., Cossman, J., De Leo, D., Hendricks, B., Nestadt, P. S., Berry, J. H., … & Caine, E. D. (2022). Association of state social and environmental factors with rates of self-injury mortality and suicide in the United States.JAMA Network Open, 5(2), e2146591. Web.
Sameh, M. S., Fozal, F. B., Shuvo, T. H., Farhath, M. J., & Oyshi, T. H. (2022). Psychological impact of COVID-19 described with SWOT analysis.International Journal of Science and Business, 7(1), 53-66. Web.
Suicide rates by state 2022. World Population Review. Web.