Introduction
This paper is about the effects of food capitalism on people’s diet. The paper is limited to a discussion of human dietary effects that arise from regular consumption of industrial and artificially processed foods. Further, the paper suggests effective solutions to eliminate identified health threats. The report will be of direct relevance human population consuming processed foods. They will be informed about the effects of food capitalization, and how to avoid its negative impacts.
Background
Definition
Food capitalism can be defined as the radical shift in development and production of food for human consumption. It is a worldwide phenomenon whose effects is felt by millions of people. Food capitalism has brought about new changes in the human diet and has changed the nutritional value of foods eaten by human beings. This has contributed to the erosion of healthy diets.
History
Food capitalism dates its history from the industrial and agrarian revolution that brought about massive changes in the agricultural system. Agricultural systems changed from small and subsistence food production to large export production. Also, land ownership changed from small scale ownership, and large scale ownership was introduced. As a result, new methods of farming were introduced to encourage production.
Current Situation
Currently, industrial food production is mainly a profit making business that has created a global crisis. Also, industrial food production overwhelming effects to human health. The western world has devised inappropriate models of food production that rely on industrialization. As a result, processed foods rich in; calories, fat, carbohydrate and sodium dominates most diets today (Anderson, 2013, para. 23). Processed foods account for lifestyle diseases, especially in the American society. In fact, Americas population is exposed to heart diseases, cancer, Type 2 diabetes and cancer, all linked to changes in eating habits (Crossfield, 2009, para. 8).
Causes
Changes in Agricultural Practices in Third World Countries
Developing countries are subjects of agricultural adjustment programs that impose strict conditions in exchange of low interest loans. Therefore, governments in third world countries create open markets to exports, among them food exporters. This leads to fluctuation of food commodities in domestic markets. As a result, farmers experience fluctuation in food commodities and are unable to compete with introducing prices (Avakian, 2008, para. 17).
Industrialization of Agriculture
Today, agricultural production depends on modern technology for cheap and tight labor. Agricultural manufacturers have improvised new technologies of preserving food products with chemicals and transporting them to other continents. Consequently, there has been continuous growth of food capitalism. Also, industrialization has led to the growth of corporations that continuously dictate the types of food grown and prices. As a consequence, developing nations abandon domestic products for export products. Afterwards, they consume processed products made available by industrial corporations. The manufacture of farm inputs among them fertilizers and pesticides to boost yields has negative effects on foods consumed by human beings.
Increased Production of Biofuels
Production of bio-fuels has created shifts in farming practices. Industries that produce biofuels continue encouraging farmers on the growth of sugarcane and other foodstuffs. Consequently, and used for agricultural production is now utilized for non-agricultural production. This has contributed to food shortage and malnutrition. Consequently, people turn to the world market for cheap and affordable processed food commodities (Avakian, 2008, para. 19).
Effects and Problems
North America and Europe
Health effects caused by food capitalism are shocking. In America, deadly diseases among them, diabetes, stroke, cancer and heart illnesses all linked to the “Western diet” (Anderson, 2013, para. 25). Food capitalization has also created race and social classes among the American citizenry. Foods with high nutritional values are expensive and can be afforded by a certain class of people in the guild. Consequently, there are races that are more prone to obesity and diet related illnesses than others. Minorities also face higher risks of suffering from obesity and diet related disorders.
Asia
In Asia, the continuous growth of food for export has lead to hunger. For instance, the Indian population suffers from chronic hunger. Colombia’s population has suffered malnourishment with the produce in exports increasing Angus (2008). Few people suffer from obesity, diabetes and heart complications.
Africa
Food capitalism has created food crisis characterized by hunger, famine and increases in food process. The rate of indigenous and highly value nutritious food products has decreased, and exports have increased. Examples of illnesses caused by processed foods also exist in the continent with high blood pressure, obesity and cancer affecting parts of the population (Magdoff, 2012, para. 15).
From the discussion above, health impacts caused by food capitalization on diets are felt in all continents. However, Europe and North America are the worst affected continents. The figure below illustrates the prevalence of obesity rates in selected areas. From the figure, the effects of food capitalism of people’s diet have impacted people’s health with America leading to obesity relates illnesses.
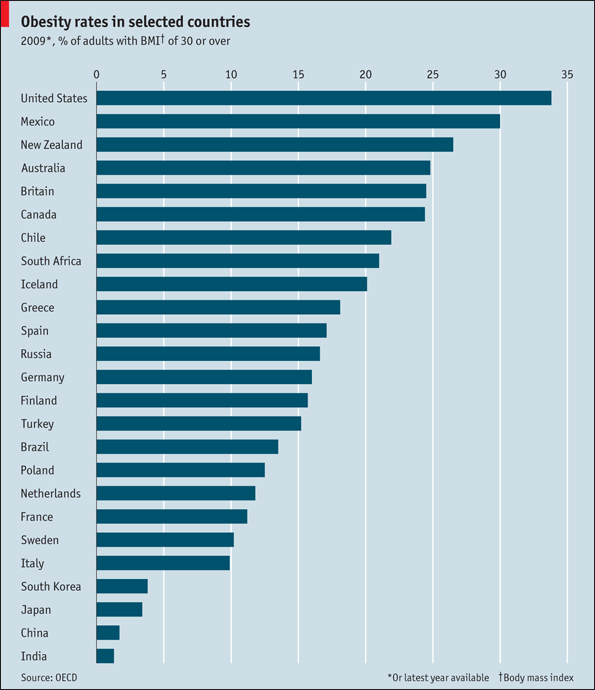
Discussion
Today, cities are parked with fast foods cafes and hotels. Many people feed on food products that lack nutritional value. Supermarket stands have beautiful displays of canned and refrigerated foods from different companies. It is interesting to note that, the product’s contents may be of equal quality and quantity, but of different manufacturers. This is what defines capitalism in the food chain. Multinational companies are rushing to introduce cheap and new processed food products into the marketplace.
According to Vivas (2009), human beings consume food that “no longer responds to the nutritional needs of people” (par. 1). This is due to capitalists’ models of maximizing profits and exploiting labor force in production. The revolution of agricultural methods has eroded small scale farming that sustains the production of subsistence food, and introduced large scale farming to increase export production. Developing nations continue to nurture and export unprocessed food products and importing more processed food products.
Nutrition is the latest crisis brought about by changes in capitalism. The introduction of processing in the food supply chain has introduced health complications to consumers. Industrial processing of food has led to mass production of food products that lack nutritional value. Human beings knowingly and unknowingly continue to eat these processed foods with little or no knowledge of the immense effects on their health. Guthman (2011) claims “the neighborhood makes people eat what is available (p. 66)”. Food manufacturers create neighborhoods that have ready and affordable processed foods. This, in turn, has changed the eating lifestyles of human beings.
Agricultural corporations have for the last few years managed to increase earnings by producing cheap food products, and dominating the production of processed foods. As consumers search for new meanings of food products in the marketplace, manufacturers continue making success and huge profits. It is interesting that such corporations do not have interests in the effects caused by their end products.
As a matter of fact, capitalism of the food chain has demonstrated the inability of human beings to cater for their own basic needs. It is a painful fact that even in the 21st century ordinary people are facing food shortages and instability in food prices. Also, huge populations suffer from obesity, type 2 diabetes, cancer and heart diseases. Obesity cases related to consumption of processed food high in calorie levels, especially in America are increasing day by day. In addition, millions of people are dying from hunger and malnourishment. All due to consumption of processed foods brought about by capitalization in the food supply chain.
However, some states are making significant steps towards the eradication of the evils introduced by food capitalism. Both private and public organizations are funding domestic agricultural projects aimed at producing high nutritional value food. For instance, in Africa, The Alliance for Green revolution funds projects aimed at producing in Africa’s crops. If all continents adopted healthy food production measures, human beings would live a life free from heart disease, cancer, obesity, diabetes and other food related illnesses. A continent cannot work alone in eradicating food capitalism since it is a worldwide problem. The international community is mindful of the challenges and hopefully, good mechanisms will be produced.
Conclusion
To conclude, food capitalism is a serious problem facing the human population globally. Developed countries so far feel the effects of food capitalization. Organizations concerned with human health have mostly embraced the issue and people are slowly becoming aware of the dangers exposed by consumption of processes foods. Luckily, some organizations have taken actions towards the eradication of food capitalism.
Recommendations
Solving the problems caused by food capitalism is not easy. Large agricultural corporations control food economies and people face difficulties in changing diet lifestyles. However, the following recommendations will help to improve the situation for ordinary people. For their implementation to be effective, governments, international economic agencies, and health agencies need to adopt strong and active stands.
- Governments need to put mechanisms in place and ensure that all its citizens have access to enough cultural and highly nutritious food.
- Governments need to oppose strict policies aimed at facilitating control of agriculture by multinational corporations. This will include taking firm stands against exploitation of international forces like the International Monetary Fund.
- Governments need to impose strict rules on use and conservation of natural resources. This can be accomplished through the formulation of conservation policies.
- Health authorities need to implement research on the impacts caused by processed foods and engage in discussions with the relevant authorities to moderate the vice.
- Publicity campaigns using the media should be started to alert ordinary people on the impacts and educate them how to live healthy lives
- The health sector needs to provide authoritative information on health risk factors to ordinary people. This can be done through the provision of free training on health risk factors caused by lifestyle.
- Ordinary people should enhance their diets with domestic foods and if necessary, work hard to retain them in their farms.
References
Anderson, Katie. 2013. The Greatest Threat to Global Food Security: Capitalism. Web.
Angus, Ian. 2008. Capitalism, Agribusiness and the Food Sovereignty Alternative Global Research. Web.
Avakian, B. 2008. The Global Food Crisis and the Ravenous System of Capitalism. Web.
Crossfield, Paula. 2009. Why Unfettered Capitalism is bad for Your Health. Web.
Guthman, Julie. Weighing In: Obesity, Food Justice, and the Limits of Capitalism. London, England: University of California Press Ltd, 2011. Print.
Magdoff, Fred. 2012. Food as a Commodity. Web.
Vivas, Esther. 2009. Food crisis Causes, consequences and alternatives. Web.