Introduction
Globalization has had a lot of impact on the world in various aspects, which include exchange of cultures, development of language, faster spread of information and international financial and economic growth. This paper will analyze the economic and business effect of globalization on Turkey as well its position in the global economy.
The economy of the Republic of Turkey is primarily driven by the services and industrial sectors but still the agricultural sector plays an important role, and it accounts for 30 percent of the state’s employment. Privatization undertaken by the government has led to the minimization of government’s participation in basic sectors like industry, financial and transport and communication.
There are several emerging industries like automotive, construction and electronics, which contribute significantly to the economy. The government has been implementing different monetary and fiscal policies after the financial crisis of 2001.
From the turn of the 21st century, Turkey has consistently enjoyed a period of uninterrupted economic growth; varied reforms have been under implementation as part of the requirements of joining European Union. Turkey’s economy has benefited from its geostrategic location of being at a point between Middle East and Europe; this makes Turley a strategic location for transit of petroleum and gas.
Turkey demonstrated that it can weather any economic storm when it overcame its domestic fiscal meltdown in 2001. Following the economic turmoil in 2001, Turkey implemented several stability and structural reforms, which eliminated various macroeconomic policies that were deemed unsuitable for economic stability.
The economic growth rate of Turkey has been steady from 2001 to 2006, and it was comparably higher than that of most countries in the EU. Turkey is favorable to foreign investment, and it is considered as a country of opportunity.
It is worth mentioning that Turkey’s economy can be a heavy casualty in the event of global financial crisis; the economy of the country can be affected by three main factors namely: collapse in the external demand of its commodities, distress in international capital markets and uncertainties in the global economy (Alp and Elekdag 3).
The Preliminary Hypothesis
The preliminary hypothesis is that globalization has had its share on the unstable condition of the Turkish economy thus leading to a possibility of future crisis on the same. This hypothesis will lead to conduction of a study case on the Turkish economy in a bid to justify it.
Sources of Information
In order to gather as much information as possible on the topic, the sources of information need to be diversified. In addition to the study books, other books such as The Global Crisis and the Turkish Economy by Ercan Uygur will be used.
Journals and other periodicals on topics related to the topic of study will also be used for reference. Lastly, electronic sources, including web pages and electronic magazines will be used to acquire information on the topic.
Overview of Essay on Turkey’s Economy
For a long time, the economy of Turkey experienced a high and stable growth until in 2008 and 2009 when it suffered a severe blow as a result of the global financial crisis (The Economist 1).
This affected the key indicators of the Turkish economy, including inflation rates and employment opportunities just to mention a few (Uygur 12). This paper will therefore look at how the effects that came about and globalization will affect the economy of Turkey. An analysis of the expected changes in the Turkish economy within the next five years will also be made.
In order to make an assessment of how the Turkish economy has responded to the global crisis and effects, this paper will explore the changes that have taken place in the monetary and fiscal policies (Alp and Elekdag 17).
This will then be used as a measuring tool to forecast the position of the Turkish economy within the next five years. In conclusion, the measures and strategies to be put in place in order to stabilize the Turkish economy will be recommended (Hill 19).
Current Economic Situation in Turkey
The economy of Turkey has been on the decline for the last three years from 4.3 percent in 2007 to 3.0 percent in 2009. Employment has also increased to a high of 9.4 percent. This slow growth rate was necessitated by the decrease in domestic credit and skyrocketing interest rates of domestic saving aimed at curbing inflation.
The external financing of Turkey’s massive deficit has been hampered due to the reduction of capital inflows and global financial crisis. Turkey’s macro environment is increasingly becoming complicated for the banks due to weakening growth of the economy and the volatilities in the financial market.
The main risk that needs to be addressed in the banking sector is asset quality, which is deteriorating at an alarming rate. The banking sector has witnessed default in loan payment and credit cards. The underestimation of asset quality have also made the loan books of many Turkish banks to remain untested via a full economic cycle hence making them vulnerable and victims of abrupt increases in interest rates.
Turkey has been undergoing various economic problems and restructuring. There was the foreign debt crisis that was experienced in 1979, which prompted liberalization of the economy in 1980. In 2008, Turkey was hit hard by the global financial crisis which prompted the government to reduce interest rates and implement various economic stimulus programs, which were aimed at lifting the budget deficits.
Capital Inflows
Insufficient capital inflows and reduced domestic savings are and will be the key determinants of the prosperity of the Turkey’s economy. The current economic structure highly depends on capital inflows for growth, and this brings up the question of whether or not the capital inflows will continue into the future. This is one of the dilemmas regarding the Turkey’s economy that needs to be addressed (Uygur 5).
The major adjustment that is needed to bring to an end the effect of global crisis in Turkey is to eliminate the global imbalance, but still it can be impossible since it is this global imbalance that has been the engine of capital inflows that drive the economy. Turkey has heavily benefited from the capital inflows. Making this adjustment will come at a substantial cost, especially if capital inflows are to be slowed.
It would imply that countries like Turkey would have to receive limited or less capital than what it received in the period 2002-2007.
Failure by these adjustments to materialize will lead to the continuation of the global imbalance and hence putting into serious risk currencies like the dollar and sterling pound, and this will in turn precipitate chaos in the global payment system which will have an adverse effect on international trade and capital inflows. This may lower the economic growth rate for the global economy in short and medium term (Uygur 51).
Turkey’s Economic Forecasts
According to the Medium-Term Program (MTP) forecasts which were published recently and according to the IMF’s World Economic Outlook for the period 2009-2012 forecast which are illustrated by table 1 below, MTP based its assumption on the fact that global economic growth rate and rate of capital inflows are instrumental in predicting the future of Turkey’s economy.
The forecast by the two institutions, the IMF and MTP are unanimous on the fact that Turkey’s economy is likely to decline in the period 2009-2012 when it is juxtaposed with 2002-2007.
Table 1
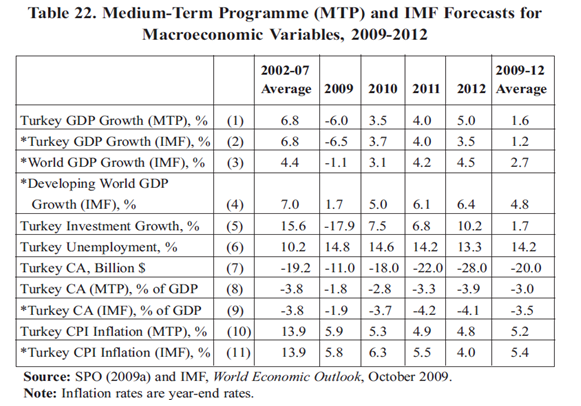
(Uygur 52)
From the above forecast, it is evident that the economic growth rate of Turkey will fall below the average growth rate of developing countries as well as below that of the global economy unlike in the period 2002-2007 where the economic growth rate of Turkey was nearly equal to that of developing countries but above that of the global economy.
Other optimistic projections in respect to the global economy are increased in investment rate while unemployment will remain at an average of 14 percent (Uygur 53).
From the above projections, Turkey will not make an adjustment in the above parameters, but it will likely pursue an unsustainable growth strategy only on the medium term. The strategy will succeed but only for a particular period of time, unless there is no global investment. The inflation ratio in Turkey will depend on the global inflation (Uygur 54).
Globalization and Turkey’s Economy
It has been proven from the past crises that Turkey’s economy is vulnerable to the whims of international economy and in the event of collapse in the global economy, the Turkish economy becomes affected. This is because a collapse of the global economy will lead to a situation of the contraction in the demand of Turkish exports, which is the major contributor to the country’s economy as well as the collapse of the country’s assets.
Turkey’s integration into the world economy and emergence of foreign direct investment as a core component of the Gross Domestic Product is gaining momentum but Turkey has not maximized gains from these two factors, it has not utilized foreign direct investment over the inflows of capital. These are among the changes that need to be effected in order to steer Turkey’s economy forward.
Just like other emerging markets, Turkey faces problems like defining its exchange rate regime, the problem of eliminating inflationary milieu and minimizing of political uncertainties. These are the obstacles that Turkey needs to address in order to attract direct foreign investment as well as to integrate itself into the global economy (Aguilar and Gita 74).
Globalization enabled Turkey to borrow a lot of money to make it finance trade deficits as well as to fill the financial gap between savings and investment. However, growth strategies that are financed by debts are not sustainable.
The liberalization of the financial markets in Turkey has experienced the effects of financial globalization. The country has been frustrated by its policy of liberalization and deregulation of financial markets, which have led to deficits in the public sector and high debt volume.
After the weakening of the economy in 2009, Turkey has speedily recovered from it and in 2010, it recorded high economic growth rate as compared with the G20 countries where it belongs. No financial institution failed, and inflation rate was well managed. The main concerns, if the pace of economic growth rate is to be maintained are inflation and deficit in the current account.
There are also the expectations that there will be a lot of pressure on the government to tighten the fiscal policies and the central bank will as well be under pressure to increase the interest rates. To curtail the ever increasing capital inflows, the central bank must be in a position to lower the interest rate and simultaneously increase the reserve threshold for both foreign and local banks.
This policy did not materialize, and the banking sector has been forced to reverse its decision and increase the interest rates. Capital inflows have become a menace in the Turkish economy, and this threatens the monetary strength; the continued increase in capital inflows has made the monetary conditions of the country to be weak and loose.
Raising the reserve requirement has demonstrated no tendency of slowing down consumer lending. It is predicted that if the developed economies, particularly the United States of America increase their interest rates, Turkish external finance will diminish.
The current account market also needs to be addressed. Though the country has solid public finances, there are notoriety and abnormality in its current account crisis, which is a sign of economic flaws.
Among the austerity measures that needs to be implemented for future economic prosperity include making amendments to the high minimum wages and trimming unregistered sectors of the economy as well as increasing market economy, which can reduce operational and consumer costs (The Economist 1).
With the political and economic fragility and uncertainty witnessed in the Arab region following the current series of uprisings, it is imperative that Turkey revives and repairs its trade relations with the European Union, which is the primary market for its exports.
Turkey suffered some losses following revolutions in the Arab spring, for example, it had several of its construction contracts canceled in Libya, and its deals with Syria have been stopped or left unconcluded (The Economist 1).
Structural Reforms to be implemented to Strengthen Future Economy
Turkey has realized a microeconomic stability due to the implementation of the reform program. For the future of Turkish economy and to foster its potential economic growth, the government needs to implement various structural reforms to make the economy flexible and allow individual firms to react immediately to the incentives. Among the important changes that need to be made are:
Inflation
Inflation has been a chronic problem in Turkey’s economy just like in any other global economy. Inflation had minimized the country’s economic growth rate. A fall in the rates of inflation leads to uncertainties in all sectors of the economy as well as undermining the macroeconomic stability of a country.
The government, therefore, needs to develop effective counter-inflation policies. Low rates of inflation led to an accelerated global economy in the 1990s, and lower inflation rates resulted in the financial turmoil witnessed in Turkey in 2001-2002. Lower inflation leads to flexibility in the exchange rates and realistic interest rate. In the recent time, Turkey has witnessed a decrease in inflation that is associated largely to fiscal consolidation achieved in the country.
The government needs to keep inflation in check to enhance the credibility of its monetary policy. Consequently, government’s commitment to curb any rise in inflation will enhance the credibility of its policy-making and fiscal policies, in particular (IMF 1). Minimizing inflation will help in moderating the consumer prices and especially in the provision of services.
Fiscal Policies
Failure by the government to stem from fiscal imbalance has led to the inflation problem. It is therefore, necessary for the government to effectively manage its fiscal situation in order to end any future economic crisis, minimize inflation and restore macroeconomic stability. The government, furthermore, needs to meet and maintain its surplus target to reduce debt burden of the country.
The current country’s high public debt is considered to be a result of short-term interest rates and foreign currencies. The reduction of the country’s debt ratio will enhance its debt profile hence reducing vulnerability to ever dynamic global interest and exchange rate volatility (IMF 1).
It is imperative for the government to have a strong fiscal policy that will enable it to strengthen its economic growth while minimizing the distorting aspects of a country’s tax system.
Structural Reforms
It is evident that the economic growth rate of the country is growing at a steady and sustainable rate. The government’s duty is to further increase the economic growth rate without triggering any inflationary pressure. This will enhance individual incomes, which will result in the reduction of poverty.
The government needs to implement various structural reforms that can make the economy stable, flexible and market force oriented. Though the government has been traditionally implementing these structural reforms, for example, free market and reforms in the banking sector, in financial sectors and in regulation of business, still the tightening of these reforms and introducing others will make the economy effective.
Among the reforms that need to be implemented are in the business and investment environment to make the country favorable to foreign investment, privatization of government assets to enhance competition and reduce the burden state sector and other banking reforms (IMF 1). The labor market needs to be reformed.
This will assist in reducing obstacles to formal employment, and this will enable firms to move from informal to the formal sectors of the economy.
Positive forecasts have continued to raise the profile of Turkey. There is a projection by analysts of a growth of five percent for the coming three years, which has enabled Turkey to attract a lot of investors. The country was rated as BB+ in 2010 by the Moody’s, an international rating agency due to the faster recovery of its economy, increased market confidence and enhanced market finance.
There is growing investor nervousness caused by the poor performance of the Istanbul stock exchange. This has prompted the majority of the investors to move their investments to countries like Germany and Poland where the economic growth is healthy.
There is a need, therefore, to revamp the country’s stock exchange to attract investors. To deter short-term investments flaws in investment, the central bank has extremely reduced its lending rates and consumption by rising reserve demands and reducing interest rates. This policy has proven controversial and more so it has never addressed its intended purpose (Champion and Parkinson 1).
The resilience of Turkey’s financial markets was overshadowed by decreased global demand and reduced international capital flows, which adversely affected the economy of the country. The OECD has predicted Turkish economy to be one of the fastest growing with a projected estimate of 6.7 percent between 2010 and 2017. This is illustrated by the graph below.
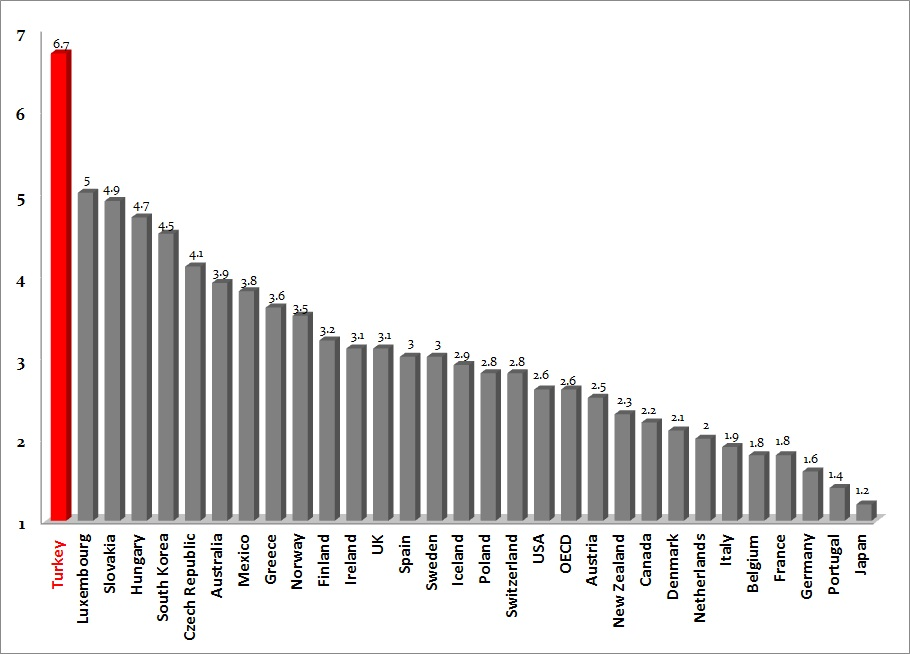
(Invest in Turkey 1)
Conclusion
A country can only benefit from the globalization of economy if its macroeconomic policies are strong and there exists liberalized market and sound monetary system, in particular.
Globalization has made the management of economies easier as well as difficult and hence countries should exercise caution when designing and implementing economic policies. Turkey has enjoyed a period of considerable success in creating a liberalized economy, consequently, making its economy open for international competition.
To realize stable economic growth and sustainability, Turkey has devised export oriented economic strategy based on the real and reasonable exchange rate (Alp and Elekdag 4). Just like in other countries, structural reforms in Turkey will speed up the country’s economic growth. Turkey is among the few countries that suffered heavily from the global financial crisis but managed to come out of it without much damage at a time when other countries were seriously affected.
The long-term economic prospects of Turkey is slowly increasing but still there is a lot of demand for reforms in the labor market, raise in education spending, transparency in handling and spending public finances and credibility in monetary policy.
These are necessary for the country to maintain a steady economy. The economic growth rate of Turkey is primarily driven by financial, retail and construction sectors and its banking sector is stable but it is only the consumption of the country that is low.
Works Cited
Aguilar, Mark and Gita, Gopinath. “Emerging Market Business Cycles: The Cycle is the. Trend,II” Journal of Political Economy 115.1 (2007): 69–102. Print.
Alp, Harun and Elekdag, Selim. “The Role of Monetary Policy in Turkey during the Global Financial Crisis.” International Monetary Fund, 2011. Web.
Champion, Marc and Parkinson, Joe. “Turkey’s Economy Surged 11% in Quarter.” The Wall Street Journal, 2011. Web.
Hill, Charles. (2007). International Business: Competing in the Global Marketplace. New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Print.
IMF. “Turkey’s Economy: A Future Full of Promise.” International Monetary Fund, 2005. Web.
Invest in Turkey. “Economic Outlook.” Invest, 2011. Web.
The Economist. “The Turkish Economy Overheating.” The Economist, 2011. Web.
Uygur, Ercan. “The global crisis and the Turkish economy.” Third World Network, 2010. Web.