According to IMF (2012), the Reform Agenda of 2012 has a number of goals regarding financial-regulation; for example, it aspires to modify the entire monetary system into a reliable and secure arena, plans to take the system at the correct track by making marketplaces or organizations further translucent, additionally uncomplicated, free, fair, and consistent, and completely uninfluenced from powerful bodies. Reorganizations are largely at banking-segment; these inflict elevated expenses for persuading them for internalising expenses of some uncertain-activities; it is believed that the needs and goals of the agenda for further improved-quality assets and liquidity-buffers must facilitate bodies to better-endure miseries; banks would regulate fresh-expenses in different methods and the latest banking-standards could promote certain-activities to be moved to non-banking-sector.

With intention of carrying out all these goals to ensure a global financial reform, a number of initiatives were undertaken – a brief illustration of the initiatives is given in the following tables:
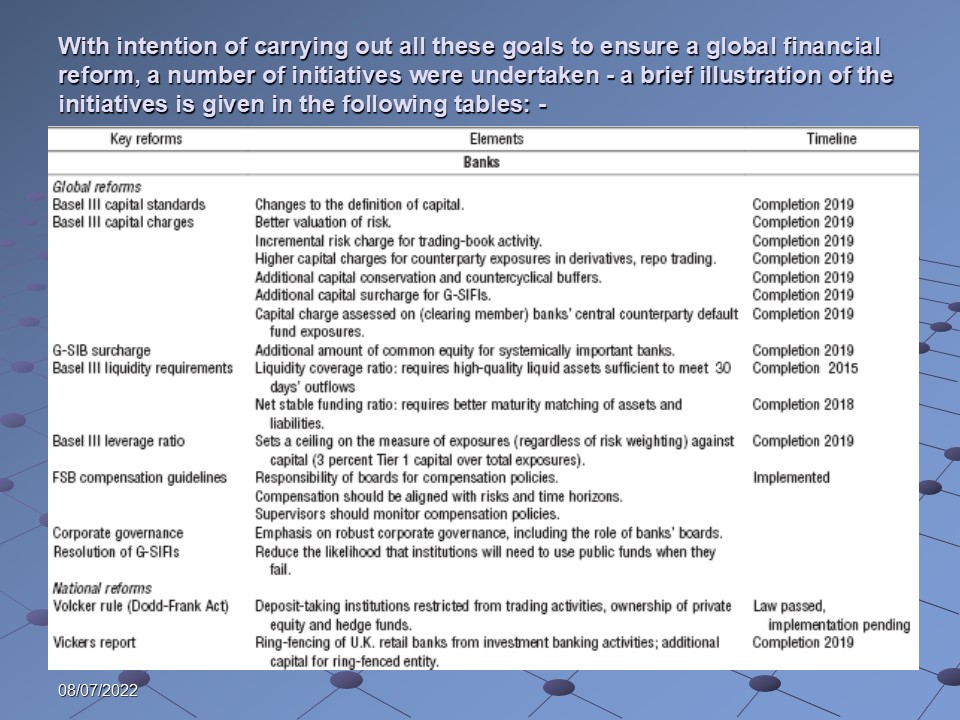
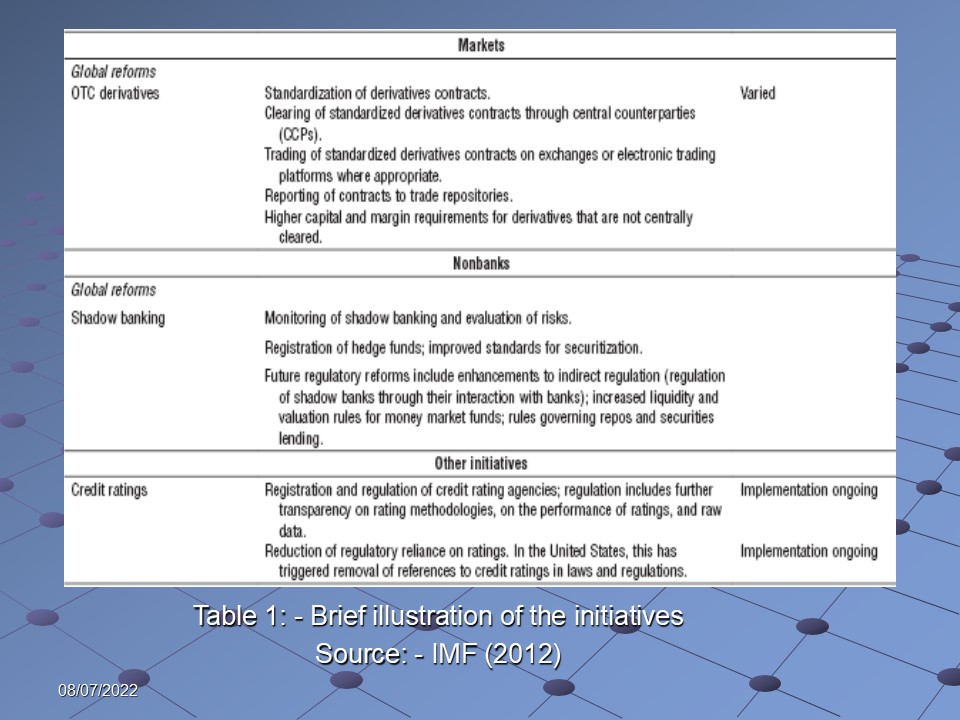
Nevertheless, glimpse of the recent international regulatory proposals is illustrated below:

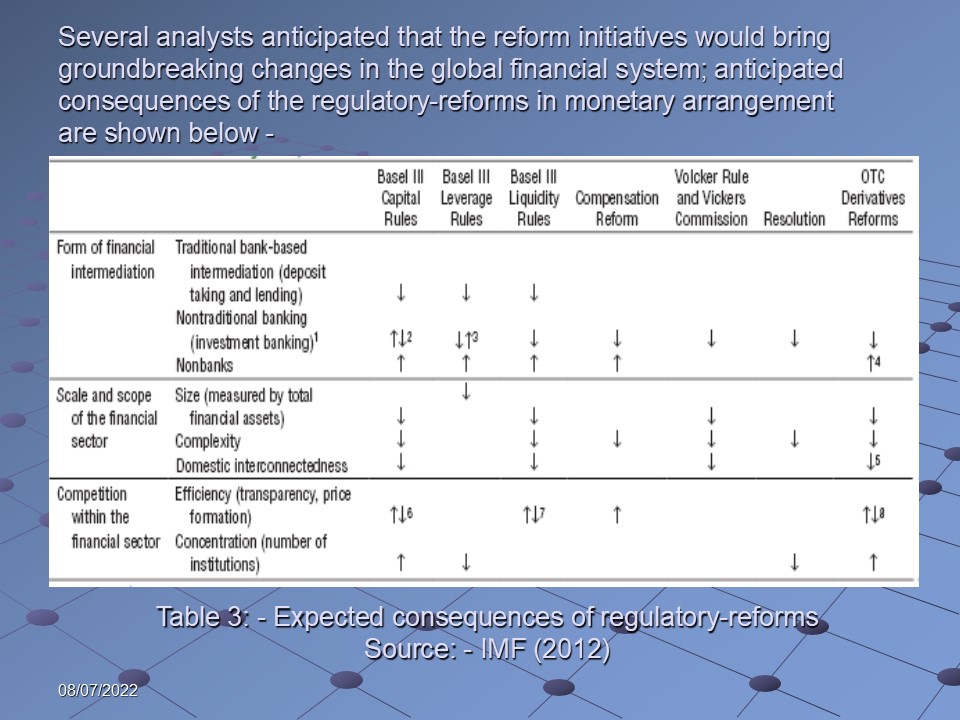
Several analysts anticipated that the reform initiatives would bring groundbreaking changes in the global financial system; anticipated consequences of the regulatory-reforms in monetary arrangement are shown below:
Critical Assessment of the Effects of the Global Financial Reform
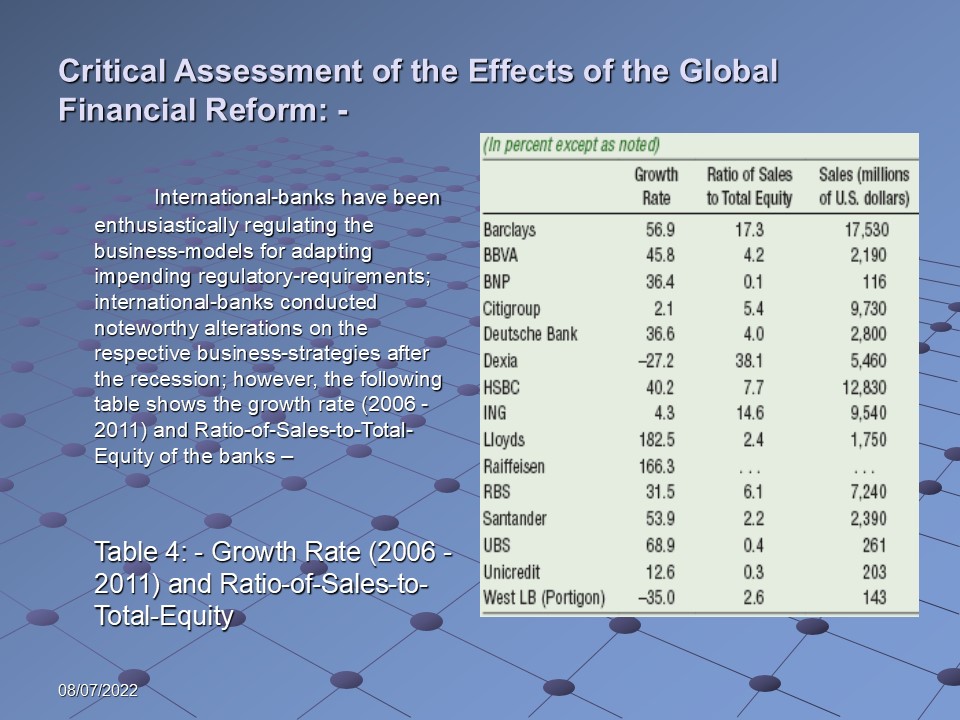
International-banks have been enthusiastically regulating the business-models for adapting impending regulatory-requirements; international-banks conducted noteworthy alterations on the respective business-strategies after the recession; however, the following table shows the growth rate (2006 – 2011) and Ratio-of-Sales-to-Total-Equity of the banks:
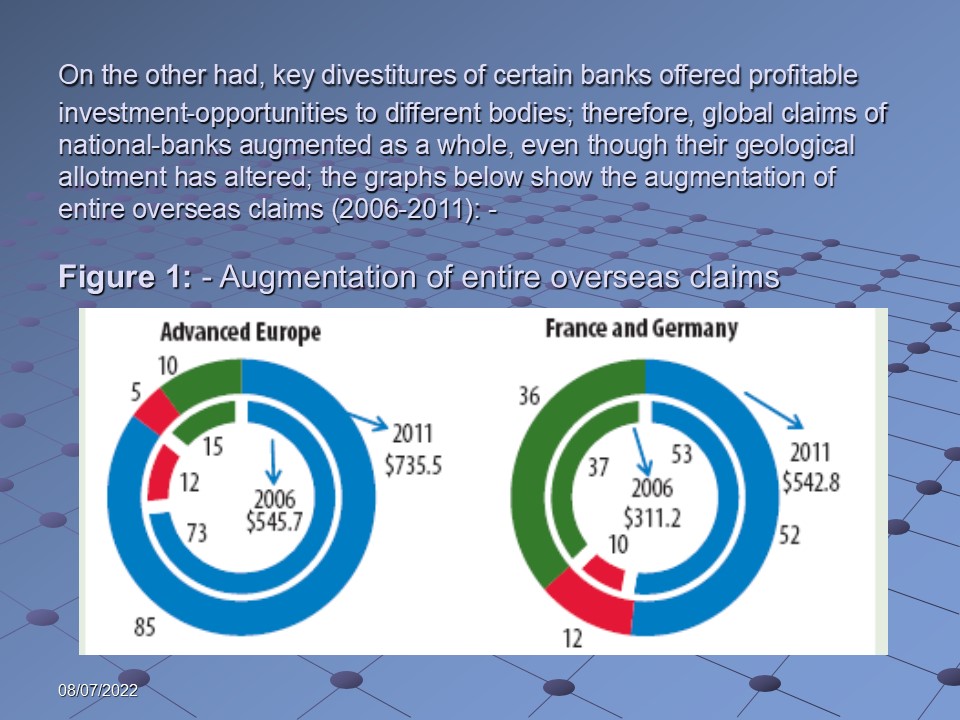
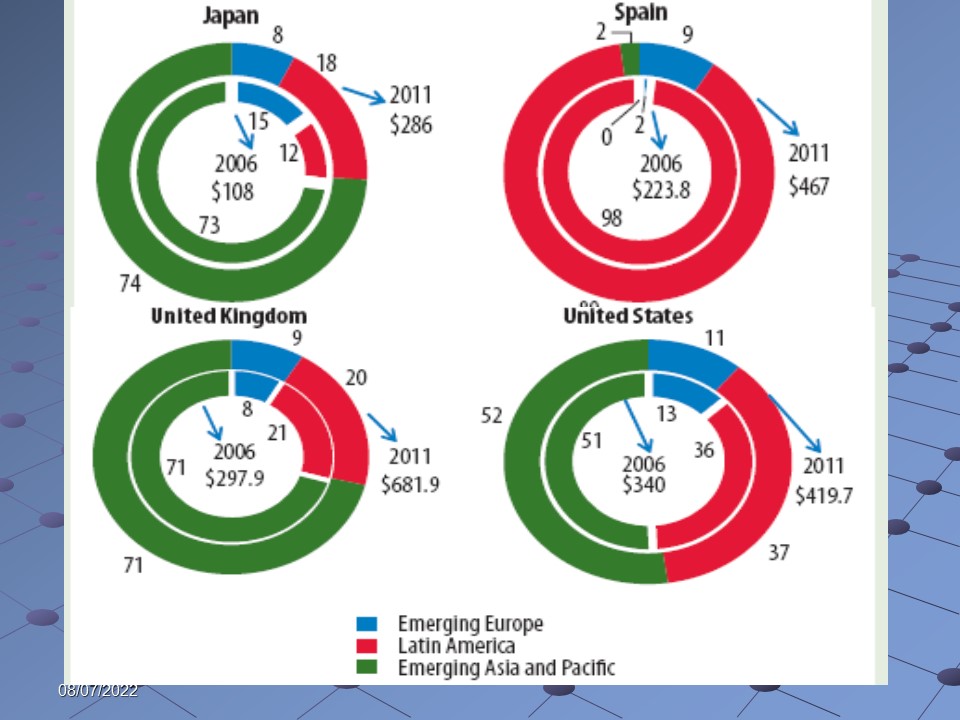
On the other had, key divestitures of certain banks offered profitable investment-opportunities to different bodies; therefore, global claims of national-banks augmented as a whole, even though their geological allotment has altered; the graphs below show the augmentation of entire overseas claims (2006-2011):
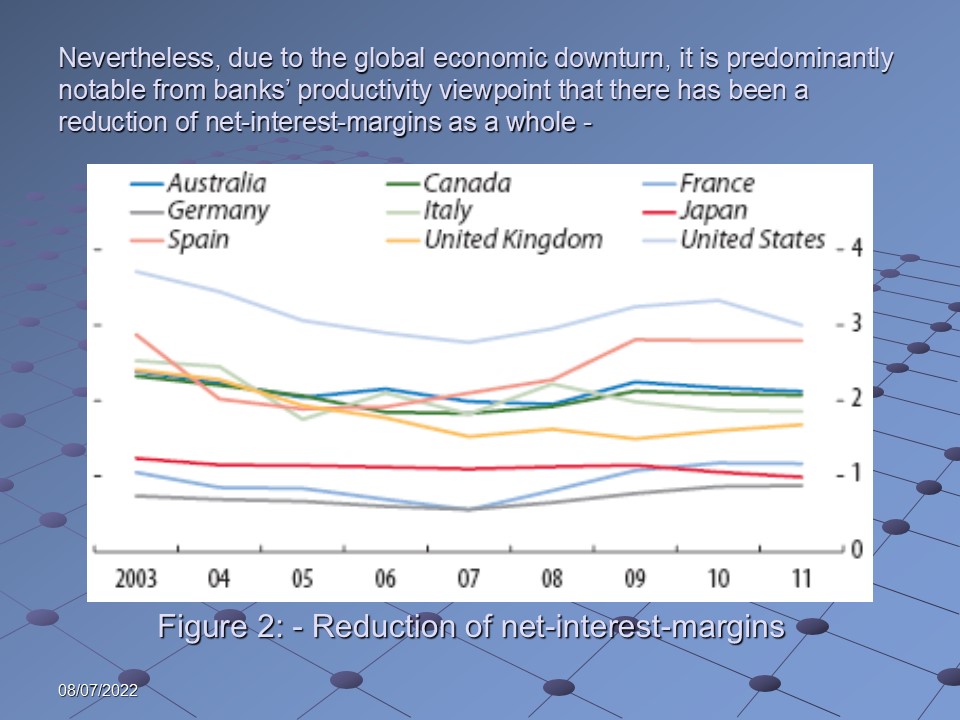
Nevertheless, due to the global economic downturn, it is predominantly notable from banks’ productivity viewpoint that there has been a reduction of net-interest-margins as a whole:
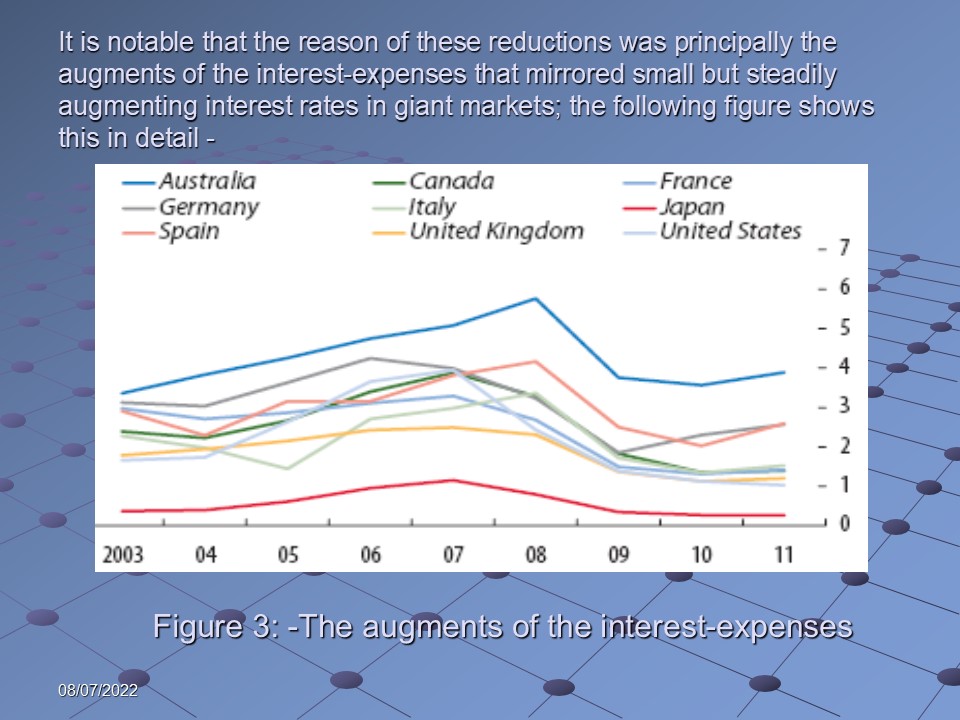
It is notable that the reason of these reductions was principally the augments of the interest-expenses that mirrored small but steadily augmenting interest rates in giant markets; the following figure shows this in detail:
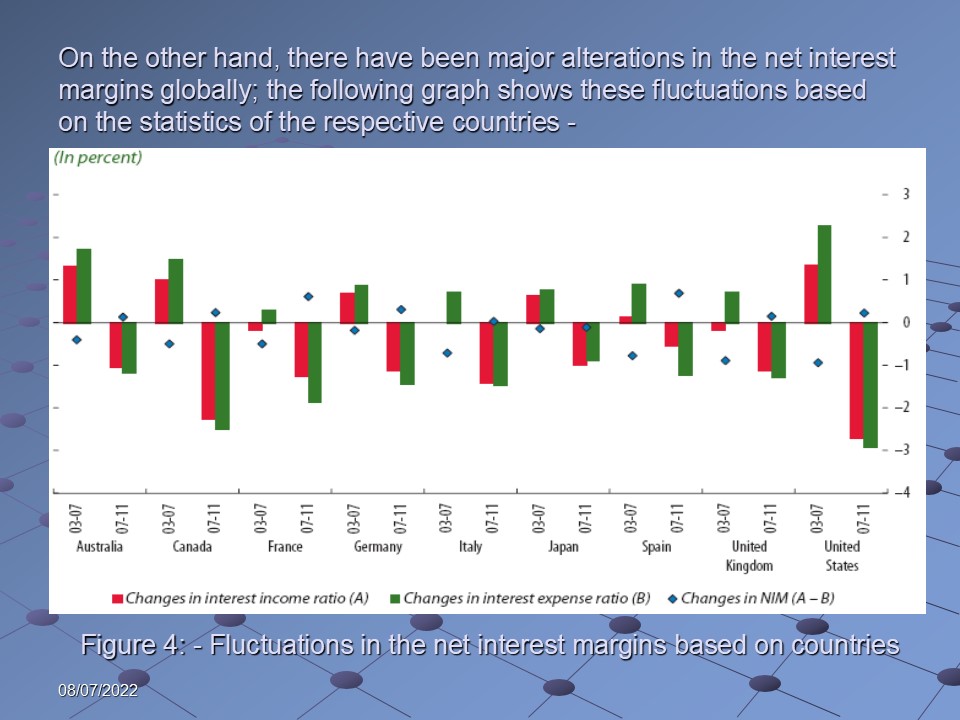
On the other hand, there have been major alterations in the net interest margins globally; the following graph shows these fluctuations based on the statistics of the respective countries:
Critical Assessment on the Account of Progress towards the Goals
IMF (2012) has noted that even though the purposes of the official decision- makers were comprehensible and optimistic, the account of progress of the reforms are not impressively significant due to a number of factors – the reforms are not quite widespread in some financial systems across the world, as these still require to result in safer-set of monetary arrangements.
As a result, it is necessary for the reform agenda to get further infallible in order to ensure secure financial regulations; in addition, at certain international markets, the involvement activities (as part of the reform-agenda) require to handle long- term disaster more efficiently, as it still causes hindrance and delay in disaster management and in resetting the arrangement on safer-path. In addition, further critical evaluation about the account of progress towards the goals of the IMF report is pointed out below:
- It is notable that research indicates that in spite of development in certain extents and in a few regions, the configuration, or set up of the financial-systems are still mostly unaffected;
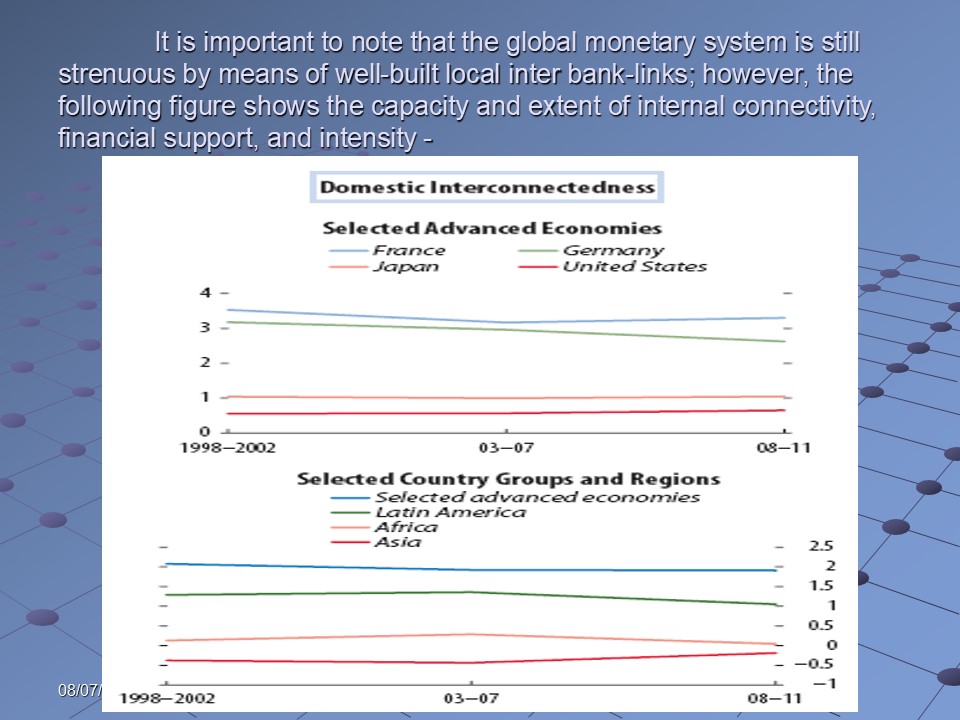
- On the other hand, according to IMF (2012), certain reliable statistics imply that financial-systems are excessively intricate even after the reforms; moreover, banking-assets are strenuous through tough national inter-bank-linkages, whilst the imperative subject matters are unsettled even today;
- There is evidence that fresh financial services are created with intention of avoiding the strictness of a number of latest laws; however, the alarming concern lies behind the fact that such kind of acts were performed earlier as well, which had resulted in the global financial crisis, and this indicates that the financial systems are still enough susceptible; the following figure shows the resultant effects of the accelerating rate of creation of fresh financial services –


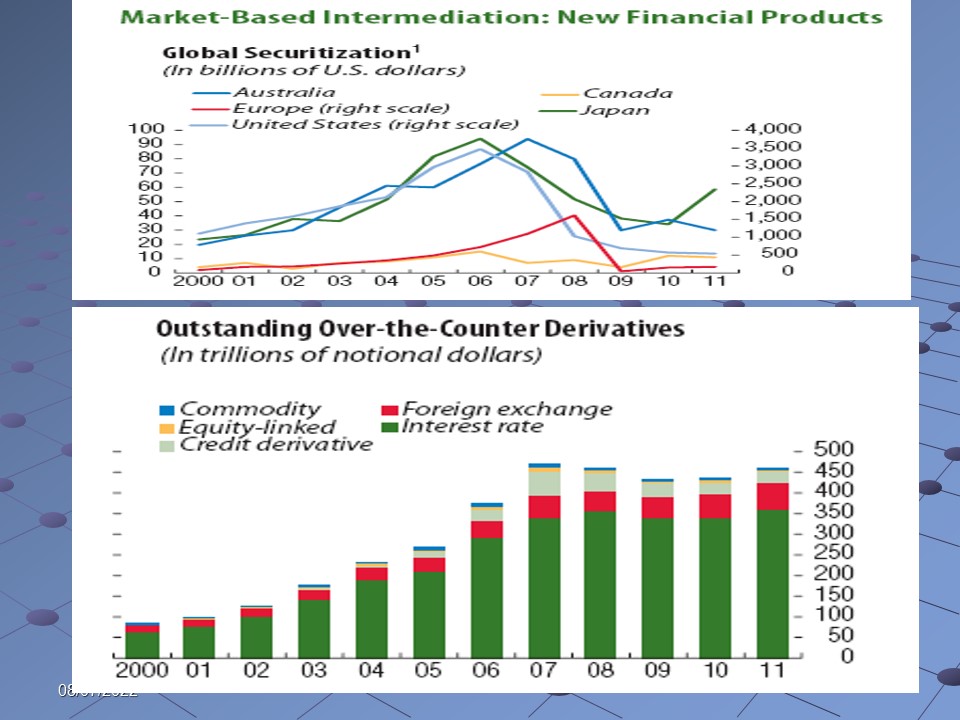
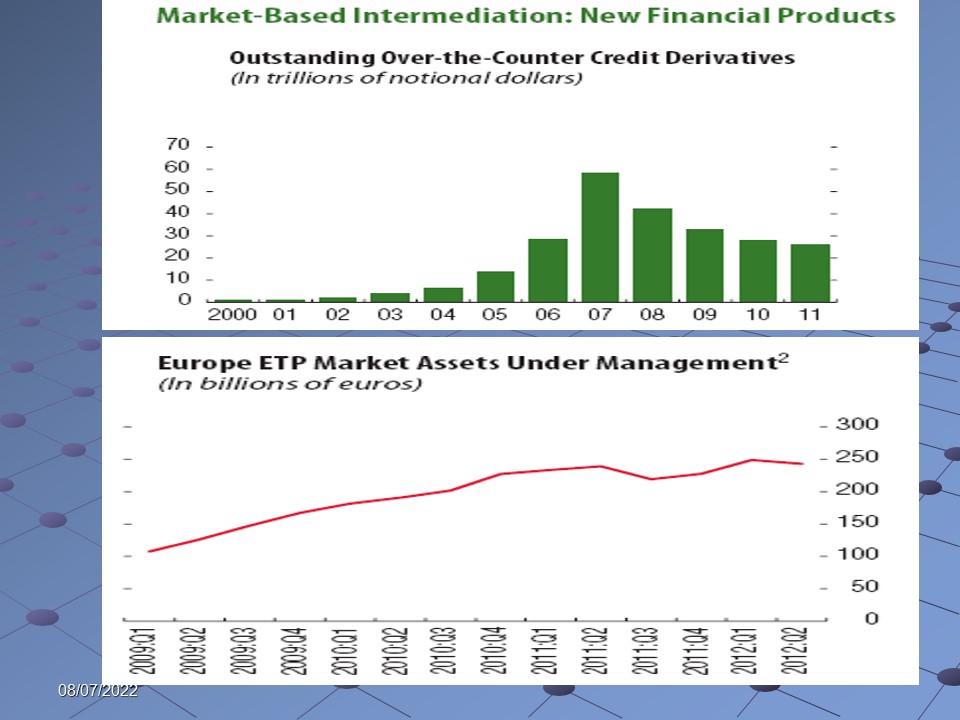
It is significant to consider the fact that monetary bodies of developed countries persist to depend profoundly over wholesale-financial support, although under certain situations such activity results in profound dependence over central-bank-liquidity backing; at all situations, the IMF report indicates that susceptibilities of financial support exist.
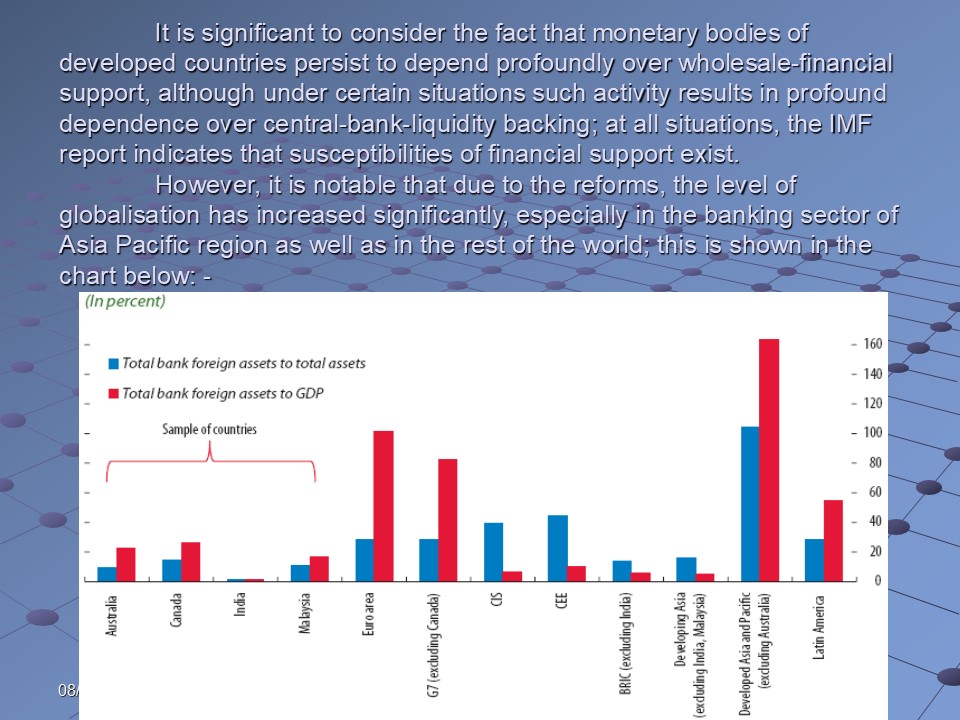
However, it is notable that due to the reforms, the level of globalisation has increased significantly, especially in the banking sector of Asia Pacific region as well as in the rest of the world; this is shown in the chart below:
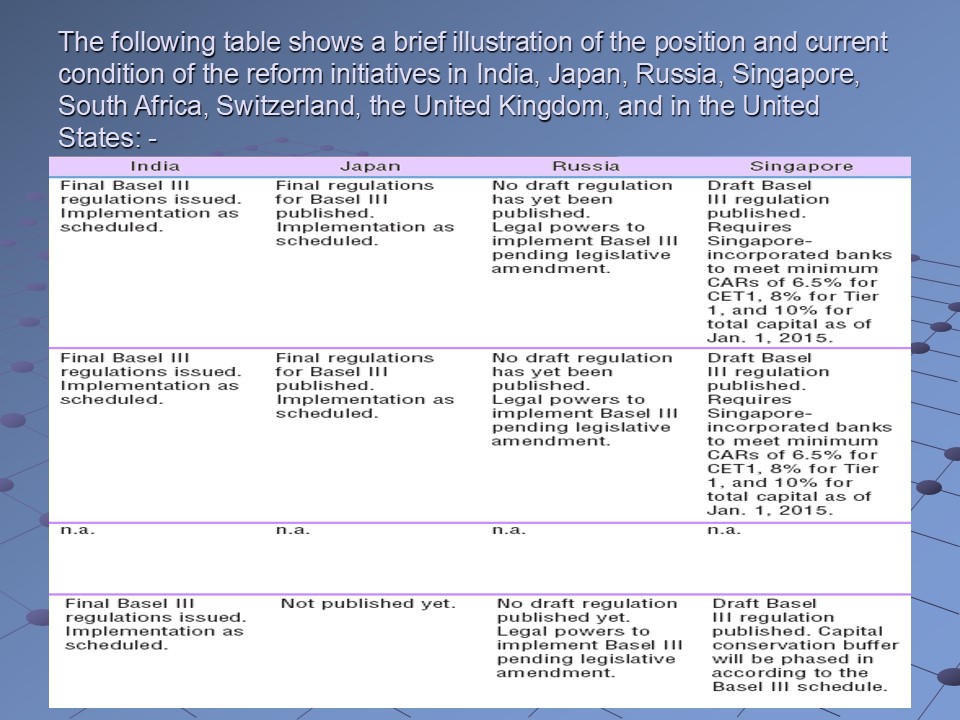
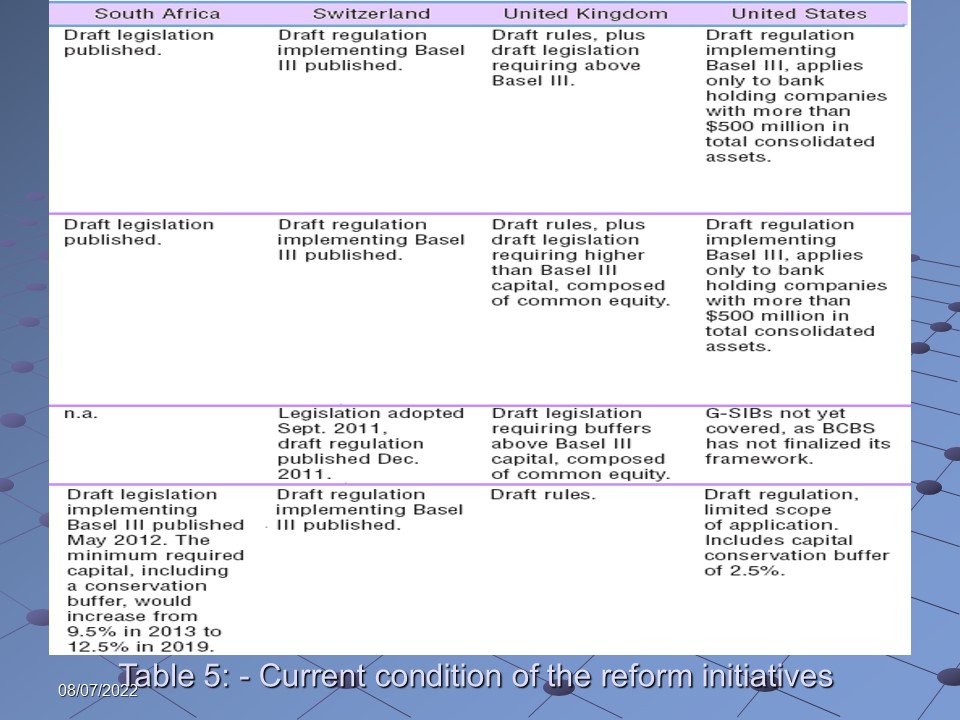
The following table shows a brief illustration of the position and current condition of the reform initiatives in India, Japan, Russia, Singapore, South Africa, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and in the United States:
It is important to note that the global monetary system is still strenuous by means of well-built local inter bank-links; however, the following figure shows the capacity and extent of internal connectivity, financial support, and intensity:
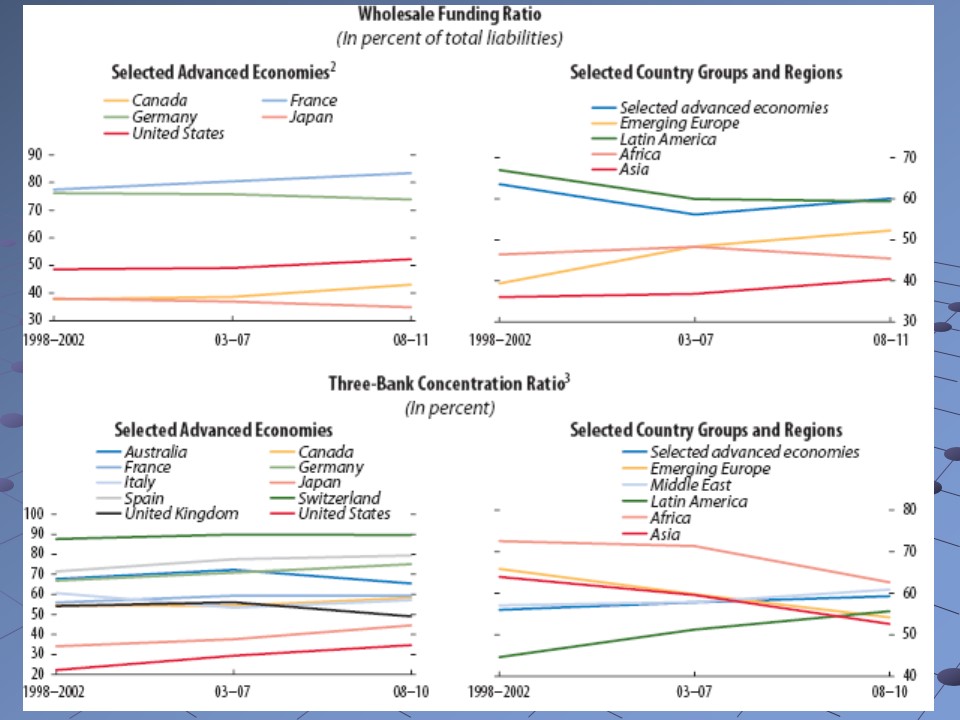
Irrespective of the fact that until now that global financial reform agenda has not been able to bring groundbreaking success vastly, the recent report of International Monetary Fund suggests that the current global financial downturn has indicated some guidance regarding where financial systems need fixing; with this experience, it hopes the goals of new financial regulations to be established soon.

Reference list
IMF, 2012, The Reform Agenda: An Interim Report on Progress Toward a Safer Financial System. Web.