Abstract
This report entails an analysis on the financial performance of banks in the Gulf region. The GCC is comprised of a number of countries. However, the report focuses on six banks operating in Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Qatar. The analysis entails evaluating the performance of one big and one small bank from each country. In a bid to gain a better understanding of the banks’ financial performance, the analysis focuses on a number of financial ratios. Some of the ratios considered in this form of analysis include “return on average assets, return on average equity, net interest margin, and cost to income ratio” (Golin & Delhaise, 2013, p.102). Moreover, the paper evaluates the performance of the six banks based on liquidity ratio, capital ratio, asset quality ratio, and operations ratio. The analysis shows that the big banks have a relatively strong performance compared to the small banks.
Introduction
Economies in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) have a number of commonalities. Most GCC countries are oil exporters and they have adopted a fixed exchange rate regime. Subsequently, their economies are exposed to change in international oil prices (Bikker, 2008). The banking sector forms a fundamental component of the GCC economies. The sector dominates the GCC financial sector and it is comprised of both Islamic and non-Islamic banks. The banking sector in the GCC countries has undergone significant growth over the past decades.
A report by Global Research released by Global Research in September 2013 shows that the industry has experienced a double-digit year-on-year growth with regard to profitability (Statt, 2013). However, the level of profitability varied from one country to another. Banks in Kuwait had highest increment in net profit at 23.1% while that of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Qatar averaged 13.4%, 20.8%, and 3.5% respectively (Oxford Business Group, 2007).
The sector also experienced a significant growth in the size of loan issues (Baker & Powell, 2005). The Qatar banking sector registered the highest growth with regard loan books at 23.1% while the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia experienced a 13% growth. This paper attempts to compare the performance of banks in the GCC countries. Considering the large size of the sector, the report focuses on three countries, which include Qatar, the UAE, and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Two banks [one large and one small] are selected from the three countries.
Background information of the big banks
Qatar National Bank
The bank was established in 1964 in Doha. Currently, the bank serves 26 countries through its affiliate and associate companies. Fifty percent of the bank is owned by the private sector and 50% by the Qatar Investment Authority. QNB has undergone steady growth over the years hence positioning itself amongst the largest banks in the MENA region. The QNB is the largest bank in the Qatar. The banks total assets is estimated to be over $ 101 billion and accounts for 45% of the total assets in the country’s banking sector and 6.9% of the total assets in the region’s banking sector.
QNB offers customers different products such as mutual funds, investment management, insurance, commercial deposits, loans, commercial and private deposits accounts, and credit cants. Currently, QNB has established over 50 branches in Qatar. The bank’s competitiveness has grown over the past years because of its excellent reputation, local branch and ATM network, large capital base, and its strong financial position.
National Commercial Bank (AlAhli Bank)-Saudi Arabia
The NCB was established in 1953 in the Saudi Arabian Finance industry. The bank’s headquarters is located at Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The bank mainly focuses on Islamic banking. Over the years, NCB has also earned its place in the Arab’s world financial institutions. By the end of 2013, NCB managed 512 branches located across Saudi. Moreover, the bank has also established branches in Bahrain, the United Kingdom, Beirut, Seoul, and Singapore. Its customer base is estimated to be over 3.3 million and a human capital base of over 9,631 employees.
In its pursuit to maximize the shareholders wealth, NCB is committed to position itself as the leading Islamic bank and the market leader in the provision of consumer finance. The bank has achieved consistent growth over the years. Its growth has emanated from the management’s focus on core growth, geographical expansion, and expansion of the bank’s scope.
Initially, the bank operated as a General Partnership. However, it was restructured in 1997 to operate as a Joint Stock Company. Today, the bank’s ownership is divided into private and public institutions. Since its inception, NCB has managed to establish over 264 branches, 10,750 point-of-sale terminals and a network of 1,180 ATMs. The bank is cognizant of the importance of operating in an effective and efficient manner. Subsequently, it has invested in mobile phone banking and internet banking. NCB has established a number of business segments, which include Islamic retail banking, business banking, wealth management, investments and consumer finance (National Commercial Bank, 2014).
Emirates National Bank of Dubai
The bank was established in 2007 after a merger between the National Bank of Dubai PJSC and the Emirates Bank International PJSC. NBD has positioned itself amongst the largest banking institutions in the Middle East. The bank operates in three main industries, which include the Banking, Insurance, and the Financial Services. Its headquarters is located at Dubai, the UAE (Statt, 2013).
The bank falls under the ownership of the Government of Dubai [56%] and the public [44%]. Emirates NBD operates as a fully-fledged commercial bank and offers diverse financial services. The bank has established a number of business segments, which include personal banking, specialized services, wholesale banking, priority banking, private banking, and business banking. Personal banking provides individual customers with a broad range of personal banking packages such as loans, accounts, cards, and insurance. The bank commands approximately 20% of the UAE’s banking industry.
On the other hand, specialized services is comprised of activities, which are aimed at assisting customers meet their asset management needs, global markets and treasury, global markets and treasury. Currently, the bank has over 140 branches in Dubai. However, the bank is formulating expansion policies in an effort to establish branches in other emirates. In addition to domestic operations, the firm has also established branches in the United Kingdom, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar (Statt, 2013).
Financial performance
The financial performance of an organization can be determined using various performance measures. Financial ratios are one example of such measures. Needles and Powers (2005) argue that financial ratios aid in evaluating the performance of an organization on different platforms. Subsequently, firms’ management teams can be able to understand an organization’s strengths and weaknesses (Baker & Powell, 2005).
There are different critical financial ratios that an organization can use in evaluating the financial statement elements. The financial ratios are classified into the return on investment or profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, leverage ratios, and efficiency ratio. Below is a comparative analysis of the three big banks based on the various financial ratios.
Analysis of the big banks
Qatar National Bank
Return on average assets
This ratio is used to determine the effectiveness of an organization in deploying its assets. The ratio is calculated by dividing the net income by the total assets (Carlberg, 2001).
The bank has experienced remarkable year-on-year growth with regard to its profitability. The firm’s return on average assets has increased significantly from 2009 to 2013 as illustrated by the chart below. The ratio “is calculated by dividing the total net income by the average total assets” (Golin & Delhaise, 2013, p.119).
Return on average equity
The ROE is calculated by dividing an organization’s net income by the total shareholders’ equity (Doumpos, 2008). The ratio shows how effective an organization is in generating profit using the shareholders’ investment.
Net profit margin
This ratio is used to determine the overall profitability of an organization (Leach & Melicher, 2012). This ratio illustrates the effectiveness of an organization’s management team. Despite its growth, Qatar National Bank has experienced a decline in the level of its net profit margin over the past years. The chart below illustrates the banks trend with regard to net profit margin.
The chart below shows that Qatar National Bank has experienced a steady decline in the size of its profitability over the past five years. However, the rate of decline has been relatively low.
Cost to income ratio
This ratio is used as a proxy in determining an organization’s operation efficiency (Luna-Martinez, 2000). The ratio is mainly used in the process of determining the financial performance of banks. According to Emirates NBD (2014), the ratio indicates the effectiveness of banks in managing their costs in relation to their income. The ratio is determined by dividing the total operating cost by the operating income within a particular financial year. The table below shows the cost to income ratio in Qatar National bank.
The chart shows that Qatar National Bank has been very effective in sustaining its cost to income ratio at a low level as illustrated by the minimal change in the cost to income ratio over the years under consideration. The slight change in the level of cost to income ratio indicates the banks effectiveness in managing its costs (Gibson, 2012).
Net Interest Margin
Qatar National Bank (2014) is cognizant of the importance of effective loan management. Subsequently, the bank has implemented effective loan management strategies. This has led to a significant decline in the level of net interest margin over the years. The effective loan management strategies have shielded the bank incurring losses emanating from interest expenses. The table below illustrates the trend in the banks NIM.
Liquidity ratios
These ratios exhibit “an organization’s ability to meet its current financial obligations” (Golin & Delhaise, 2013, p.94). Subsequently, liquidity ratios depict how effective an organization is in managing its assets in order to cover its liabilities such as short-term debt and accounts payable. There are different liquidity ratios that an organization can utilize. Current ratio is one category of liquidity ratios. The ratio is used in evaluating an organization’s ability to meet its near-term financial obligation. The general rule is that the ratio should be 2:1.
The ratio is calculated by dividing an organization’s total current assets by the total current liabilities (Zopounidis, 2002).The chart below shows the banks current ratio.
The chart above shows that Qatar National Bank has been able to manage its current assets and current liabilities over the past five years. Subsequently, the firm has been able to meet its financial obligation.
Debt-to-equity ratio
This ratio is used in evaluating an organization’s financial leverage. The ratio “is calculated by dividing the total debt by the total shareholders’ equity” (Golin & Delhaise, 2013, p.121). Qatar National Bank has sustained a positive trend with regard to its debt to equity ratio as illustrated in the chart below.
National Commercial Bank (AlAhli Bank)-Saudi Arabia
Return on average assets
National Commercial Bank has also experienced significant growth with regard to return on average assets. The chart below shows the trend in the banks’ performance.
Return on average equity
AlAhli Bank appreciates the importance of effective utilization of the shareholders’ equity. Subsequently, the bank has been able to sustain a steady growth with regard to return on average equity. The table below illustrates the growth in the banks ROAE from 2009 to 2013.
Net profit margin
The bank is committed towards attaining leadership with regard to Islamic banking and finance. Subsequently, the National Commercial Bank has invested a substantial amount of resources in popularizing Islamic banking the GCC region. The table below illustrates the growth in the institutions net profit margin over the past few years.
The chart shows that the National Commercial Bank has undergone a steady growth with regard to the level of its profitability.
Cost to income ratio
AlAlhli Bank ensures that its cost to income ratio remains at a low level in an effort to sustain its operations into the future. The chart below illustrates the change in the bank’s cost to income ratio.
Current ratio
National Commercial Bank has been able to sustain its current ratio at an acceptable margin indicated by the chart below. The banks current ratio is relatively similar to that of Emirates NBD. The chart below shows the banks current ratio.
Debt-to-equity ratio
The National Commercial Bank recognizes the importance of effective debt-to-equity management. The bank has maintained its debt-to-equity ratio at a relatively low level as illustrated below.
Net interest margin
The national commercial bank has also sustained its net interest margin at a relatively low level over the past few years as illustrated in the chart below.
Emirates National Bank of Dubai
Return on average assets
Emirates National Bank of Dubai is one of the biggest banks in the UAE with regard to total assets. The bank has been very effective in utilizing its assets to generate revenue. The table below shows the trend in the bank’s return on average assets.
Return on average equity
Emirates National Bank of Dubai has implemented effective strategies on how to utilize its equity. The chart below shows the bank’s performance over the past five years. The chart shows that the bank has experienced a steady growth with regard to its return on average equity.
Net profit margin
The chart below shows Emirates NBD trend with regard to net profit margin. The banks trend with regard to net profit margin.
Cost to income ratio
This ratio is used as a proxy in determining an organization’s operation efficiency.
Liquidity ratios
Current ratio
Emirates NBD performance over the past few years has been enhanced by optimal management of current assets and current liabilities. Similar to the National Commercial Bank and the Qatar National Bank, Emirates National Bank of Dubai has maintained a stable current ratio as illustrated by the table below.
Debt-to-equity ratio
Emirates NBD has sustained a positive trend with regard to its debt to equity ratio as illustrated in the chart below.
Net interest margin
Emirates NBD has also sustained its net interest margin at a relatively low level over the past few years as illustrated in the chart below.
Comparative analysis of the big banks financial performance
The financial ratios above shows that the National Commercial Bank, the Emirates NBD, and the Qatar National Bank have managed to attain significant market dominance in their respective industries. However, Qatar National Bank’s performance is relatively strong compared to the other two banks. The difference in the performance of the three banks is illustrated by the graph below, which compares the banks’ performance with regard to return on average assets and return on average equity.
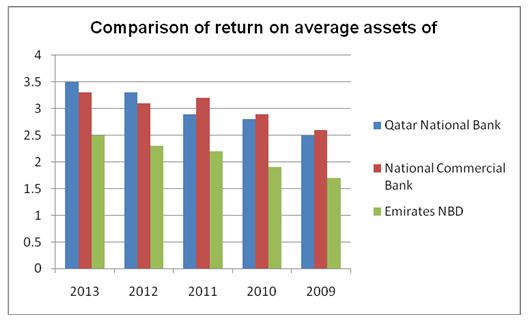
Similarly, the banks have portrayed positive performance with regard to return on average equity as illustrated by the chart below.
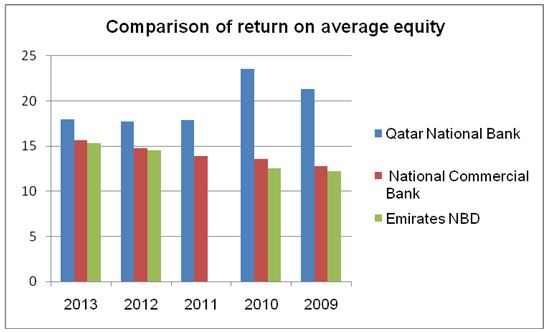
From the graph above, Qatar National Bank has a relatively high return on equity. This indicates that Qatar National Bank has a high level of profitability compared to the other banks. Moreover, the bank has been able to add value to the shareholders’ equity compared to the other two banks.
The difference in the banks’ financial performance is also illustrated by their variation with regard to net profit margin. Qatar National Bank has a relatively high net profit margin compared to the National Commercial Bank and the Emirates National Bank of Dubai as depicted in the chart below.
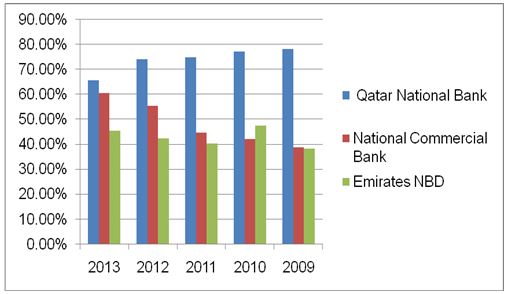
The three banks have managed to maintain their current ratio at an acceptable level. Subsequently, one can assert that the banks can be able to meet their current financial obligation without difficulty. With regard to the debt-to-equity ratio, the banks have been able to rely on the shareholders’ equity compared to borrowing. Subsequently, the banks are characterized by low debts. One of the factors that have contributed to the low debt-to-equity ratio is the managements’ ability to maximize the value of their equity. According to Sheeba (2011), a low debt-to-equity ratio eliminates financial distress in an organization.
Analysis of the small banks
Background information of the small banks
Noor Bank
This bank was established in 2008 in the UAE. Fifty percent of the bank falls under the government of Dubai ownership, 45% by individual investors, and 5% by the Emirates Investment Authority. The bank is managed by the Sharia board, which is largely comprised of Islamic scholars. The bank operates as a subsidiary to Noor Investment Group. Its headquarters is located in Dubai, UAE (Noor Bank, 2014).
The bank has positioned itself as an innovative and creative bank, which is evidenced by the introduction of attractive banking products tailored to meet personal and business customer needs. The bank’s commitment towards creativity and innovation is motivated by the desire to attract new customers. The bank is focused towards being ranked amongst the most innovative financial institutions in the UAE by 2010.
Saudi British Bank (SABB)
SABB was established in 1978 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The bank operates as a Joint Stock Company and an associate of HSBC Group in the United Kingdom. Over the years, the bank has developed a wide range of financial products and services. The banking services offered include ATM Cards, private and Islamic banking, personal banking, corporate and commercial banking. The company’s total asset has increased significantly over the years. For example, the total assets increased from SAR 125.4 billion in 2010 to SAR156.7 billion in 2012 (SABB, 2014).
Barwa Bank
This bank operates in Qatar and it has been licensed by the Qatar Central Bank. The bank has an estimated issued capital of QAR 3 billion and an additional authorized capital of QAR 4 billion. In the course of its operation, Barwa Bank provides diverse Shariah compliant banking products. Some of the products offered include real estate finance, structured finance, asset and investment management, structured finance, private banking, retail and corporate banking. The bank is committed towards positioning itself as the leading Islamic bank in the world. Subsequently, its operations are guided by excellent service provision, adherence to progressive ethos and positive contribution to the society (Barwa Bank 2014).
Analysis of the small bank’s financial performance
Noor Bank
Return on average assets
Despite the competitive nature of the banking industry in the UAE, Noor Bank has managed to attain a positive financial performance over the past five years as illustrated by the table below. The growth in the level of the bank’s return on average assets depicts the management team’s commitment to exploit the assets fully in order to attain the desired level of profitability.
Return on average equity
Noor Bank has also been effective in utilizing its shareholders’ equity. This is well illustrated by the organization’s return on average equity, which has been on an upward trend from 2009 to 2013. Subsequently, the bank has been in a position to maximize the shareholders’ investment hence generating high returns. The chart below shows the bank’s performance with regard to ROAE.
The chart shows that the bank has experienced steady growth with regard to its ROAE over the years.
Net Interest Margin
Noor Bank has sustained a positive improvement in its net interest margin as illustrated below.
Net profit margin
The net profit margin depicts the effectiveness of an organization in achieving its profit maximization objective. Subsequently, the ratio can be used to judge the effectiveness of an organization’s management team. The table below depicts the bank’s performance with regard to net profit margin from 2009 to 2013.
The chart above shows that Noor Bank has experienced a steady increment in the size of its profitability over the past five years.
Current ratio
Noor Bank’s management team appreciates the significance of effective asset and liabilities management. The bank has managed to increase the size of its loans significantly over the years. As a result, Noor Bank has improved its financial returns through accumulated interest on loan issued. On the other hand, the bank’s management team has maintained the level of its current liabilities at a low level. The bank’s effectiveness in managing current assets and current liabilities is illustrated by the current ratio in the chart below.
The chart shows that Noor Bank has been able to manage its current assets and current liabilities over the past five years.
Debt-to-equity ratio
Noor Bank has sustained a positive trend with regard to its debt to equity ratio. The bank has largely relied on equity in undertaking its operations. Subsequently, the size of banks debt has remained low over the years. The table below illustrates the percentage change in the banks debt-to-equity ratio. From the char, it is evident that Noor Bank has managed to lower the size of its debt to equity ratio.
Saudi British Bank (SABB)
Return on average assets
SABB has also experienced significant growth with regard to return on average assets as illustrated by the chart below.
Return on average equity
SABB’s management team and the board of directors are cognizant of the importance of effective utilization of the shareholders’ equity in order to maximize their wealth. Thus, the bank mainly depends on the shareholders in the course of undertaking its investment activities. The table below illustrates the growth in the banks ROAE from 2009 to 2013.
Net profit margin
The profitability of an organization is a key determinant of its attractiveness to individual and institutional investors. SABB is committed towards positioning itself as the leading bank in Saudi Arabia. Subsequently, the institution’s management team ensures that every dollar earned is translated into profit. Over the years, the banks’ management team has been focused towards managing the cost of its operation. Its effectiveness in controlling cost and utilizing the earnings is well illustrated by the growth in the level of its net profit margin (SABB, 2014).
Cost to income ratio
In the course of its operation, SABB has managed to sustain its cost to income ratio. Subsequently, the ratio has been characterized by minimal change in its cost to income ratio as illustrated by the table below.
Current ratio
Over the years, SABB’s management team has maintained its current ratio at an acceptable level of 2:1. Consequently, the firm’s management team is able to meet its short-term financial obligation without major hindrance.
Debt-to-equity ratio
SABB recognizes the significance of sustaining a low debt to equity ratio. Consequently, the bank is increasingly focusing on how it can utilize the shareholders’ equity in generating profit. The chart below depicts the change in the organization’s level of the debt-to-equity ratio from 2009 to 2013. From the table, it is evident that the bank has managed to lower the debt to equity ratio remarkably.
Net interest margin
Similar to Noor Bank, SABB has maintained its net interest margin at a low level. Its effective management has culminated in a decline in the level of its net interest margin as indicated in the chart below.
Barwa Bank
Barwa Bank is ranked as the fastest growing Islamic banks in the Qatar. Its growth is associated with effective utilization of the organizations assets in order to generate revenue. The bank has managed to sustain a growth with regard to return on average assets as illustrated by the table below.
The table above shows that the bank has experienced a positive and steady growth in the size of its return on average assets. From this trend, one can assert that the bank will sustain a growth in the future.
Return on average equity
Similar to the other small banks, Barwa Bank is committed towards ensuring that the shareholders’ equity is effectively utilized. Over the years, the bank has managed to improve its return on equity as illustrated by the table below.
Net profit margin
Barwa Bank appreciates the importance of sustaining a growth with regard to net profit in order to meet its cost obligations. The bank’s management has implemented effective cost control measures, which have culminated in growth in the firm’s level of net profit over the years. The chart below illustrates the percentage change in the institution’s level of profitability.
Cost to income ratio
The management team of Barwa Bank appreciates the significance of developing effective cost and income management strategies. Subsequently, the bank has been able to sustain an acceptable change in its cost-to-income ratio. The chart shows that Barwa Bank has managed to lower the cost to income ratio subsequently.
Current ratio
The firm’s effectiveness in managing current assets and current liabilities has enhanced its capacity to meet the short-term financial obligations. The table blow illustrates the banks current ratio over the past five years.
Debt-to-equity ratio
The bank has also maintained its debt to equity ratio at an acceptable level. In the course of its operation, the bank mainly relies on both equity and debt sources of finance. However, the level of debt is relatively low as compared to equity. The chart below illustrates the change in the bank’s debt-to-equity ratio over the past five years. From the chart, one can assert that the bank has been committed in lowering its dependence on debt finance over the years.
Net interest margin
Barwa’s bank management is cognizant of the importance of effective management on the loans. Loans provide a source of revenue to banks through the interest that they generate. However, poor management of loans can culminate in a significant decline in the level of profitability emanating from interest expenses. Barwa Bank is committed towards reducing the net interest margin at an acceptable level. The chart below shows the trend in the performance of the banks’ NIM from 2009 to 2013.
Comparative analysis of the small banks financial performance
From the above analysis, one can assert that the small banks in Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and Emirates are committed towards attaining high and sustainable financial performance. The financial ratios show that Noor Bank is more effective as compared to the other small banks under consideration. The strength of Noor Bank is well illustrated by the various financial ratios evaluated. For example, the bank’s return on average assets and return on average equity have grown substantially over the years. The graph below compares the performance of Noor Bank, SABB and Barwa banks’ ROAA.
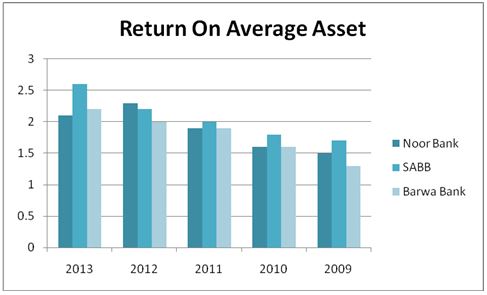
The small banks have also portrayed a positive trend with regard to return on equity as depicted by the chart below.
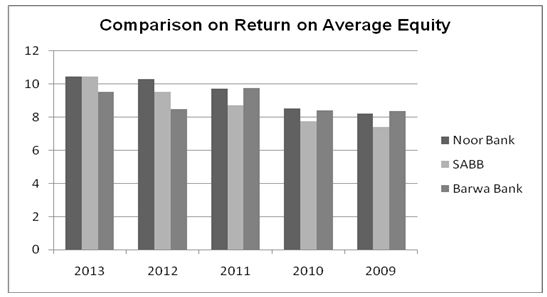
From the graph above, Noor Bank has a relatively strong return on average equity compared to SABB and Barwa Bank. Subsequently, one can assert that the bank is more effective in managing its shareholders’ equity compared to the other small banks. This has greatly improved the banks effective in generating a high level of profitability and hence adding value to the shareholders’ wealth (Khan& Jain, 2007).
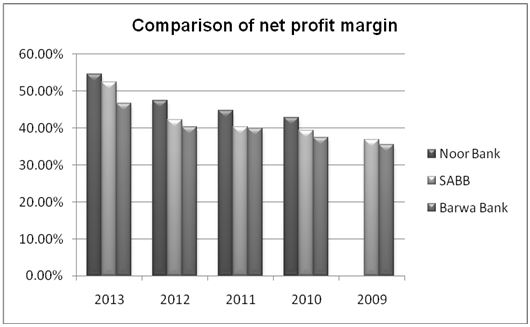
Noor Bank financial strength is also illustrated by the difference in their level of net profit margin. Noor Bank has managed to sustain a growth with regard to the level of profitability. Similarly, Barwa Bank and SABB have undergone a growth with regard to their profitability. However, their growth has been relatively low as depicted in the chart below. The high level of net profit margin in Noor Bank shows that the firm is in a position to withstand challenging economic conditions. According to Khan and Jain (2010), the net profit margin is very effective in illustrating an organization’s effectiveness in managing and sustaining its operations.
With regard to the current ratio, the three small banks have maintained the level of their current ratio at an acceptable level of 2:1. This shows that the bank has been very effective in meeting its current financial obligations.
Evaluation of Bankscope’s strengths
Bankscope provides a wide range of data on the financial performance of banking institutions. Financial analysts can therefore utilize the database in conducting analysis on the financial performance banks across different countries over a period. Thus, the credibility of the financial analysis using data from Bankscope is high. The database covers over 30,000 banks distributed in different parts of the world. The database is effectively developed in order to improve its usability.
Conclusion
The banking industry is one of the most important components in a country’s economic growth. Banks act as financial intermediaries, which enhance transfer of finances between the demand and the supply sides. However, the effectiveness with which banks undertake their operation is dependent on how well they are managed. Countries in the GCC region have undergone significant growth over the past few years. Subsequently, most of the countries in the GCC region are categorized as emerging economies. Some of these economies include Saudi Arabia, Qatar and the United Arabs Emirates. These economies have undergone significant growth over the past decade. The growth has been greatly supported by the banking industry, which is dominated by both big and small banks.
Qatar National Bank, Emirates NBD, and the National Commercial Bank are amongst the largest banks in Qatar, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia respectively with regard to total asset. The three banks have experienced significant growth with regard to financial performance over the past five years. The ratio analysis shows that Qatar National Bank has a strong financial performance compared to Emirates National Bank of Dubai and the National Commercial Bank of Saudi Arabia. The strength of the three banks is illustrated by the growth in their return on average assets and return on average equity.
Moreover, the banks’ financial performance is also illustrated by the growth in their level of net profit margin. This shows that they have been effective in managing their operating cost, which is further illustrated by the cost-to-income ratio that has declined steadily over the years. Thus, one can argue that the big banks have been effective in maintaining their cost of operation at a low level. Thus, the banks are able to invest their income in areas that culminate in maximization of the shareholder’s wealth.
The analysis also shows that the big banks have been very effective in managing their net interest margin. The three banks have a relatively low net interest margin compared to the small banks. Subsequently, the banks have been able to avoid losses emanating from interest expenses. The small banks should learn from the big banks’ strong financial performance and implement effective operational strategies. This will enable the small banks to gain substantial market share in their respective industries.
References
Baker, K., & Powell, G. (2005). Understanding financial management; a practical guide. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishers.
Barwa Bank: vision and mission. (2014). Web.
Bikker, J. (2008). Bank performance; theoretical and empirical framework for the analysis of profitability. New York, NY: Routledge.
Carlberg, C. (2001). Business analysis with Microsoft excels. Indianapolis, IN.: Worldcat.
Doumpos, M. (2008). Handbook of financial engineering. Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Emirates NBD: Emirates NBD announces its 3rd quarter 2013 results. (2013). Web.
Gibson, C. (2012). Financial reporting and analysis. New York, NY: Southwestern Publishers.
Golin, J., & Delhaise, P. (2013). The bank credit analysis handbook: A guide for analysts, bankers and investors. Solaris, Singapore: John Wiley & Sons Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Khan, M., & Jain, P. (2007). Financial management. New Delhi, India: Tata McGraw-Hill.
Khan, M., & Jain, P. (2010). Management accounting; text, problems and cases. New Delhi, India: Tata McGraw Hill Education.
Leach, C., & Melicher, R. (2012). Entrepreneurial finance. Singapore: Cengage Learning.
Luna-Martinez, J. (2000). Management and resolution of banking crisis; lessons from the republic of Korea and Mexico. Washington, DC: World Bank.
National Commercial Bank: AlAhli online. (2014). Web.
Needles, B., & Powers, M. (2012). Financial accounting. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.
Noor Bank: Islamic finance. (2014). Web.
Oxford Business Group: The report; emerging Qatar. (2007). London, UK: Oxford Business Group.
Qatar National Bank: QNB. (2014). Web.
SABB: About SABB. (2013). Web.
Sheeba, K. (2011). Financial management. Noida, India: Pearson.
Statt, F. (2013). Emirates NBD posts Dh 2.6 billion profit. Web.
Zopounidis, C. (2002). New trends in banking management. Heildelberg, OH: Physica- Verl.