HELOC refers to a cyclic bank loan where the lending institution offers to grant a sum within a specified period or duration, where the debtor’s assets serve as security. A home equity line of credit is guaranteed mostly by the equity in the households. Figure 1 below shows how HELOC works: the firm has dynamic mortgage rates where monthly repayments will change based on the current rate and the amount users borrow. However, the home equity line of credit has advantages and disadvantages over other bank loans.
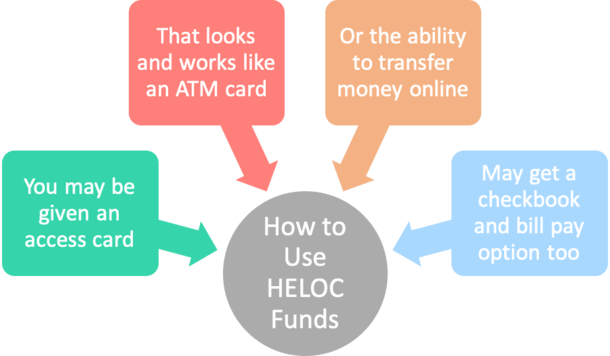
The advantages of HEVOC are that it offers accessible installment loans for an emergency and fluctuating borrowing rate, which means that overall mortgage and repayment rates can decrease if reputation increases or lending rates decline. In addition, HELOC allows customers to decide how much or the least of their bank loan to utilize (Fontinelle, 2022). Additionally, it offers reduced interest rates compared to other ways to borrow money, such as credit cards and consumer lending loans. However, a Home equity line of credit has its drawbacks. Despite the fluctuation of interest rates, which might decrease repayment rates, it makes it difficult for lenders and debtors to budget.
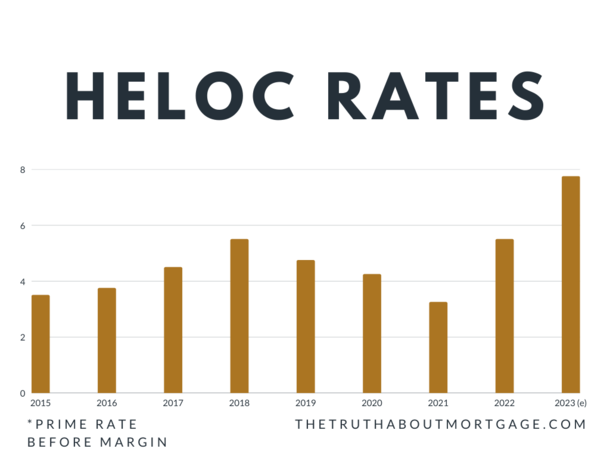
The fluctuation of interest rates is shown in graph 1 below between the years 2015 to 2022. Moreover, one can lose their homes to HELOC if loans are not repaid on time. In addition, the variability of interest rates can go up depending on the inflation rate rise, increasing payment interests. Because of this, there may be better options than a HELOC for people with limited incomes who struggle to handle significant changes in overall monthly spending. Consequently, it is simple to spend impulsively up to one’s available credit due to the fluctuating interest rates.
The U.S. bank is the best overall bank that offers the HELOC program. This is because U.S. bank offers convenient accessibility. One can withdraw on your HELOC using convenient checks from anywhere. Furthermore, visa access cards can be used anywhere. Likewise, U.S. bank has no transaction charges or processing fees, and the interest can be revenue deductible. Additionally, they give customers multiple payment choices, including involvement payment if they meet the requirements.
HELOC can increase mortgage payments since its interest rates are unpredictable. The range that the bank decides is added to a reference rate, such as the cash rate, to determine the lending rate; hence, as loan rates rise, so will mortgage repayments. In addition, repayments with a HELOC might vary greatly when interest rates fluctuate, much such as with an expandable mortgage. When one cannot forecast their monthly payments or overall borrowing costs, creating a budget or establishing long-term financial planning can take time and effort (Kim, 2020). In addition, consolidating large amounts of debt, such as credit card transactions, may seem as a wonderful idea when done with a low-interest HELOC. Refinancing debts such as vehicle loans with higher interest rates than the HELOC rate may seem smart, leading to increased mortgage rates.
HELOC repayment functions similarly to credit cards, allowing one to withdraw funds up to the balance limit. One is usually expected to pay interest during withdrawal, lasting between 10 and 15 years. During the withdrawal period, one may make a payment back toward the principal. When you settle a portion of the principal, the money is added to one’s credit card line. As soon as the draw time is through, you enter the repayment schedule and repay the outstanding balance on your HELOC, money borrowed. Given that one can acquire more or little as they would desire, HELOCs can be helpful as a home remodeling loan. If it turns out that a customer requires additional funds, they can access them from their line of credit providing, there is still room instead of submitting a new home loan application.
References
Canner, G. B., Fergus, J. T., & Luckett, C. A. (2019). Home equity lines of credit. Federal Reserve Bulletin, 74(7), 361. Web.
Fontinelle, A. (2022). Home Equity Loan vs. HELOC: What’s the difference? Investopedia. Web.
Kim, J. (2020). Macroeconomic effects of the mortgage refinance and the home equity lines of credit. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 121(121), 104021. Web.
Robertson, C. (2022). HELOC rates expected to rise another 2% by early 2023. The truth about mortgage. Web.