Introduction
One of the significant traits of the 21st century is the increasing internationalization of trade, production, investment, finance, technology, communication, politics, society, and almost any conceivable sphere. The world is shrinking towards a truly global village. Does globalization lead to equality as anticipated or brings about grave inequalities in its wake? The neoliberal ideology and the Washington consensus hold that globalization with its free trade and market competition is inbuilt to foster economic growth. However, there is enough disturbing evidence that points toward discontents and impoverishment as impacts of globalization.
The work of Professor Joseph Stiglitz Globalization and Its Discontents (2001) is a powerful critique of globalization and all its attendant consequences. He outlines the origins of IMF and the World Bank in the opening chapter, The Promise of Global Institutions. The IMF and the World Bank have their roots in 1944 in the Bretton Woods, New Hampshire. The Allies laid out their plans for a new international economic world order to prevent the recurrence of a globally devastating depression. Adhering to a new post-Depression Keynesian philosophy, the architects of the new system created the IMF to maintain economic stability by helping countries avert crises and the World Bank to induce economic development in poor countries through targeted loans and grants. WTO, which came to existence in 1994 had its precursor in the Bretton Woods era GATT with a mandate to make available a level playing field for the rich and the poor nations (Stiglitz 11). The question is how far have these financial bodies fulfilled the ambitious mandates they set out to achieve? According to Nafeez M. Ahmed of Institute for Policy Research and Development, UK, “… the world capitalist economy has created a phenomenon that can be accurately described as the globalization of insecurity, by firstly generating conflict thus destabilizing nations and communities, and secondly escalating impoverishment, disease, and deprivation” (2004).
Globalization and China
Despite many historical antecedents to our current understanding of growth in China and its causes, the current growth will be traced back to the early 1980s, as the ideological between the superpowers was concluding after more than four decades of bitter ideological conflict and the eventual supremacy of democracy and neoliberalism as the dominant principles of the New World Order. Seeking to explore the Chinese growth and globalization phenomenon by looking back over the past twenty-odd years, this essay will analyze the important antecedents to Chinese growth today.
Neoliberalism and China
Globalization, as it exists today, rests largely on the shoulders of neoliberal economics and the global entrenchment of capitalism as the dominant economic system in the world. Neo-liberalism, the belief in laissez-faire economics, was best articulated by Margaret Thatcher in the United Kingdom and Ronald Reagan in the United States in the 1980s. US President Ronald Regan famously remarked, “government was not the solution but the problem” (Hobsbawm 1994). Neo-liberals put all of their faith in the distributive capabilities of the invisible hand of the free market, and believe that business was inherently good and that government was bad. The government was longer interested in the provision of welfare but existed to stimulate the capitalist economic market. The United States under Ronald Reagan was thus described as the “greatest of the neo-liberal regimes” (Hobsbawm 1994). Accordingly,
The essence of neo-liberalism, its pure form, is a more or less thoroughgoing adherence, in rhetoric if not in practice, to the virtues of a market economy, and, by extension, a market-oriented society. While some neo-liberals appear to assume that one can construct any kind of ‘society’ on any kind of economy, the position taken here is that the economy, the state, and civil society are, in fact, inextricably interrelated (Coburn, 2000).
Effects of globalization
The proponents of globalization do not find any problems with globalization per se. However, they would prefer appropriate governance for managing globalization. No one can deny that the availability of huge capital required for investment in China has done wonders in the forms of modernization of technology, raising productivity, accelerating growth, and creating employment. This is of course not to rule out the havoc capital can play upon China, for example in Mexico there was a rapid destabilizing reversal of capital flows. In the highly integrated market of today, such impacts can lead to spillover effects with adverse consequences for other nations (Michael Camdessus, 1996).
The cause of success or failure in globalization is seen in privatization-driven policies. They have received much criticism in China in terms of ineffective management of corporate ventures, lack of proper resources management, and political interventions. Most cases of privatization failures are linked to poor contract design, opaque processes with heavy state involvement, lack of re-regulation, and a poor corporate governance framework. (Gopal 2007:158).
The experience of China in globalization has gone on to improve over the years. During the initial globalizing days, there was a crucial doctrinal difference between China and the IMF, about the appropriate roles of the state and the private sector, the need for fiscal equilibrium, and the virtues of deregulation. According to the official UN view, the lesser the role of the state, the better are the gains derived from privatization. This view holds that when the state dominates the economy, resources are often misallocated. However, the governments have an important role to play as a facilitator of economic activities rather than occupying the position of private entrepreneurs’. In the case of China change in policies and performance can be attributed to two factors: the changing role of the state and the globalization of the international capital markets. Since the late 80s, China has witnessed drastic shift in the orientation of economic policy. The reform results were dramatic. Meanwhile, inflation declined and currently experiencing growth. On the external side, however, the region’s current account deficit has narrowed creating and economic giant. This was due in part to the relative weakness of domestic saving at a time of sharply increasing investment, including imports of capital goods needed for industrial modernization, which were facilitated by the increased access to international capital markets” (Michael Camdessus, 1996).
WTO and China
The matching of china into WTO opened new doors for growth and economic labialization. China has become the center of the world for services and external trade. Goods from China are available in the third world at a cheaper price than there before. This is because China is a developing country with a strong labor force that managed to produce goods at a cheaper price and currently they are a major international player in the trade and production of goods and services. They have diversified from the traditional form of production into the new modern technology. This has been made possible because of joining WTO. The country has also changed perceptions on how they treat foreign companies and this has made them a major direct investment country for multinationals. WTO made china open up most of its industries to be accessed by market players and this has lead to the increased growth that is being experienced currently. China started experiencing growth in the year 2000 at a faster rate than what they were experiencing initially. This is due to the growth of information technology, economic restructuring as demanded by WTO, and great growth opportunities brought by redistribution of wealth across the world due to multinationals. There is an improvement in economic growth since currently, the country is growing at the rate of 22%. Therefore WTO has brought the following positive economic effect. Increased economic growth, there is an increase in wages and salaries which are compensation to the members and this began in the year 1978. That’s when growth started being experienced in China. As growth has been experienced in china there has been increased investment geared to consumption and export. Below is a graph showing the growth of china between the years 1975 and 2008.
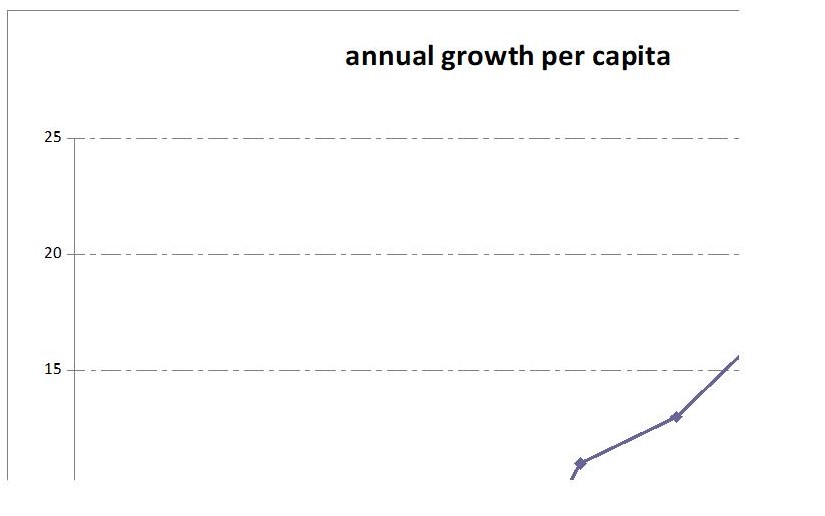
Globalization and democratic environment in China
There will be no growth without politics. Politics determine the direction of the country in terms of democratic growth. The benefit of a democratic environment in china has been experienced through the growth of democratic space and this has influenced economic growth at the same time. This can be observed because it can be noted that China has cooperated with United Nations as well as the United States and WTO. If one wants to have a look at the impact of democratic space in china one should be wise enough to look at the growth as influenced by organizations as WTO, United Nations, UNEP, and many organizations. Most Chinese non-governmental organizations have received donations from this organization and this has helped them improve their lives. You look at the unemployment rate, they are coming down for example, in the year 2003, the employment rate was 4.3 and it changes to 4.2 in the year 2004. Below is a graph showing the employment rate and their changes.
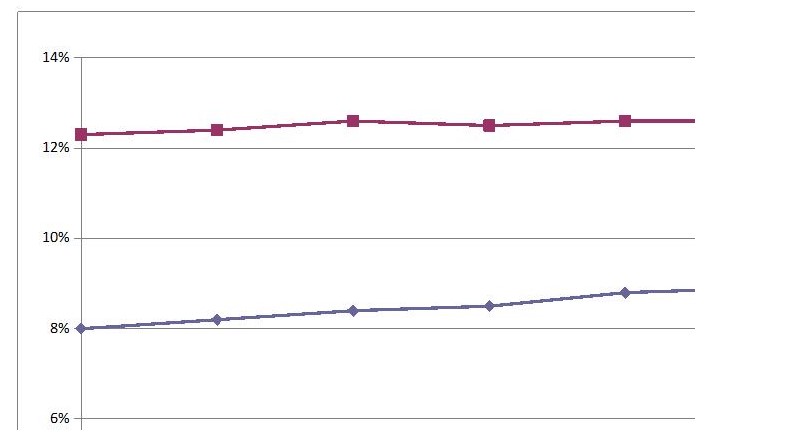
The graph above shows the level of unemployment and the rate of unemployment. As the graph indicates there is an upward trend in growth that is reducing the unemployment level as well as the rate of unemployment in china. This is because the growth has been influenced by foreign capital inflow to the country.
Globalization and outsourcing
One of the positive effects of globalization to the public of china is the issue of outsourcing. The western countries have fewer laborers as compared to china. Therefore the Chinese have provided laborers for some sectors to the west industries. This earns the employees help in generating foreign income which has helped in spurring growth for the country.
Current economic growth
The current economic growth being experienced in China is due to globalization. Globalization has provided the market for Chinese growth, provided jobs to the Chinese people, and helped in influencing foreign inflow of income thus helping in economic growth. China is currently viewed by many nations as one of the best and stable economies in the world. This is because:
- Of increased market prices for goods manufactured in china,
- Increased industrial growth and agricultural development.
- Stable market prices for goods and services
- Reduction in export and increase of imports
- Increase in foreign direct investment
It can be summarized that in the long term as well as medium-term china has experienced growth that has never been experienced before.
Globalization and Chinese’s agriculture
Industrialization provides a philosophical change where people develop a different attitude towards their perception of nature. Intensified agriculture can be said to be operating as a cultural-ecological system because as a result of improved technology in agriculture, the available crop production resources are now utilized well without damage or wastage (Cowdrey, Albert E 1996).
This shows that sustainable land use should not target preserving and maintaining the ecological stand for occupation and improvement but also as developing the community and environment. This will enable it to adopt the increase and also maintenance of the options present or available as well as in the face of a natural and social world in an unending conversion.
For China to be able to produce food that will assist the country to experience faster economic growth, the use of land must be sustainable. That is involving social-economic and ecological options that will assist in reducing susceptibility and increasing options for the use of land. The country needs to adopt high technology in the use of land to improve productivity. Apart from the use of technology, crop rotation has been adapted as a viable way of improving production but it is implemented with the assistance of government-trained agriculture officers. (Cowdrey, Albert E 1996).
The use of technology and crop rotation is intended to improve production as well as make life more comfortable for the people of China. It also ensures that there is enough food for the people of China. Applicable technology involves the use of the machine, the use of irrigation in arid and semi-arid areas as well as encouraging large-scale farming for economies of scale. Agriculture in China has been made impossible because of global warming which has reduced food production thus leading to increased food prices. This is observed by the increase in food prices although the government has subsidies some farms from some farming activities as well as increased drought-resistant food crops to increase production of food.
In the era that we are today, technology has been found not only including research, design, and crafts but also it is said to be a multifaceted communal project involving maintenance, marketing, labor, management, manufacturing, and finance. As a result of industrialization through technology, in the broadest sense, it improves our abilities to change the world, since research clearly shows that a higher percentage of the world’s economy depends on agriculture (Cowdrey, Albert E 1996).
As a result of the introduction of technology, the naturally available resources can now be completely utilized. Examples include; the introduction of machines that can be used in irrigation to ensure better utilization of water whereby water can be drawn from rivers and spread to larger farms by the use of water pipes.
However, intensive agriculture and industrialization also have some things to do with demography. Though in this type of agriculture especially the large scale one is adversely affected by increased land pressure due to the rapidly growing population, there are advantages on both sides, that is, to the agricultural sector and the local people or residents whereby, the agricultural sector benefits from the availability of labor whereas the local people benefit from employment when they are picked by the farmers and given different responsibilities hence it becomes of great importance to the community by providing employment opportunities.
Social relations have some significance in the agricultural sector whereby it ensures collective responsibilities in resource management. Better relationships between different people or countries high standards of farming hence steady food supply. For example, China is one of the most industrialized countries and also densely populated thus making it enjoy good farming technologies and reliable labor supply, for this matter, the international community has established a good relationship with China by amending its grain policy to enable the international community access China’s grain market (Berry, Wendell 1998).
Culture as a factor also has something to do with intensive agriculture whereby the environment to where the type of agriculture is done should be favorable. The community should embrace it no matter what so long as it is of importance. For instance, the United States of America amended its policies which were barriers in 1990. Intensive agriculture as well depends on the way it is carried out, either large scale or small, and also the types of inputs.
Inflation
Inflation is one of the problems or negative effects that china has experienced due to globalization. There has been a flow of capital into China from the west and this capital was coming from companies that are currently experiencing financial crisis making them spread the crisis to China.
Runaway Inflation which is caused by oil prices has caused food prices to go up and other consumable goods have become very expensive although the government has responded with the increased supply of food to try to reduce the shortage and ensure prices are affordable to the community. It has been complicated further by climatic changes. It is feared that global warming has had a negative impact on the production of food which has contributed to runaway inflation. Inflation in China is causing a lot of problems since life is becoming difficult for the citizens of the country. For the first time in ten years, consumer price index was at 5.6% which was higher than what the government has anticipated in the year.
Inflation in other parts of the world complicates strategies to be adopted by the Chinese government to fight run-away inflation. For example, if the government wanted to fight food prices, the option of reducing the prices of food was imported from foreign countries but it is not possible since inflation has taken a toll in most countries. For example, inflation in the United States has affected the dollar which is accepted in the national currency meaning that even imports to China will be expensive.
The government has responded with a monetary policy to ease inflation and increase economic development as well as increase employment opportunities for the citizens of the country. Using the producer price index in china which has been on the increase the government has predicted the future consumer price index through the use of these statistics a monetary policy has been designed to reduce dependence on outside importations. This has helped to create a balance in economic growth as well as inflationary tendencies and this is how they have managed to maintain their growth at 22%. The financial crisis which began as a subprime crisis in the united states has had a negative impact and added to inflation in the economy of China. The Chinese economy has been affected due to the devaluation of the dollar, strong economic growth in India, an increase in oil prices between the month of august and November 2008, the increase in food prices, and the collapse of major international banks. These factors although not directly involved they are the main causes of inflation in China.
Concluding Remarks
Globalization has been propelled by capitalism and the internationalization of the capitalist economic system. The main effect of globalization on china is the spread of neo-liberalism and the entrenchment of some capitalism– some would say the sole – viable economic system for the China economy. This essay has traced the antecedents to the current wave of globalization in china with an emphasis on key events associated with the arrival of neoliberalism in the 1980s, followed by Communist collapse and the emergence of authoritarian capitalism in China. Enthusiastically promoted by the Reagan and Thatcher regimes in America and Britain, neo-liberalism was given a huge boost following the collapse of the Berlin Wall and the fall of communism in Eastern Europe in the late 1980s. Entrenched as the dominant economic ideology across china, neo-liberalism is the underlying force behind the current wave of globalization. Despite numerous detractors on all corners of the globe, globalization remains an important force in modern society and a key component of continued and sustained economic growth on a global scale (Harvey 2007).
References
- Ahmed, Nafeez Mosaddeq (2004); The Globalization of Insecurity. Institute for Policy Research & Development, United Kingdom, p.113-126
- Bhagwati J.N. (2004); In Defense of Globalization, Oxford University Press. 2004
- Berry, Wendell. (1998)The Unsettling of America: Culture and Agriculture. San Francisco: Sierra Club Books.
- Camdessus M. (1996); Argentina and the Challenge of Globalization; International Monetary Fund.
- Clark, G.L. & W. B. Kim 1995. Asian NIEs & the Global Economy: Industrial Restructuring & Corporate Strategy in the 1990s. Johns Hopkins University Press, New York.
- Clark J. (2002); Globalization and the Poor: Exploitation or Equalizer. IDEA.
- Coburn, D. 2000. “Income inequality, social cohesion and the health status of populations: the role of neo-liberalism”, Social Science & Medicine, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 135-146.
- Cowdrey, Albert E. (1996) This Land, This South: An Environmental History. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky
- Gopal R. (2007); Dynamics of International Trade and Economy. Nova Publishers.
- Hale, W. & E. Kienle. 1997. After the Cold War: Security and Democracy in Africa and Asia. I.B.Tauris, London.
- Harvey, D. 2007. A Brief History of Neoliberalism. Oxford University Press, London.
- Herman, Edward S. (1999);The Threat of Globalization, New Politics, vol. 7, no. 2 (new series), whole no. 26.
- Hobsbawm, E.1994. Age of Extremes: The Short History of the Twentieth Century: 1914-1991. Abacus, London.
- Mamman. A and Liu K (2008); The Interpretation Of Globalization Amongst Chinese Business Leaders: A Managerial And Organizational Cognition Approach, Brooks World Poverty Institute (The University Of Manchester )
- Roland R. and White K. E. (2004); Critical Concepts in Sociology. Routledge.
- Stiglitz, J. (2002); Globalization and Its Discontents. New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
- Strayer, R. W. 1998. Why Did the Soviet Union Collapse?: Understanding Historical Change. I. E. Sharpe, New York.