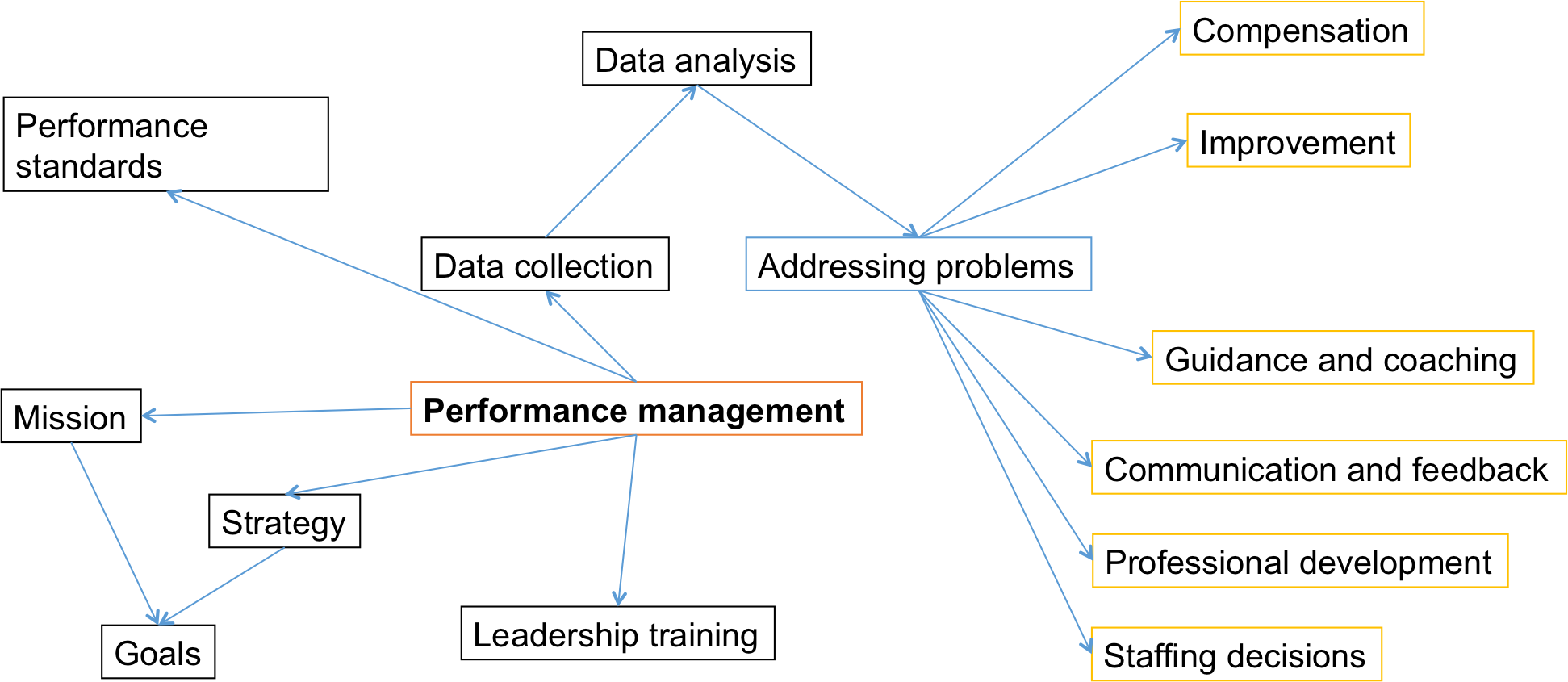
The concept map illustrated above shows key components of performance management that the Information Technology Department at DEWA can use for assessing its performance. The department’s goals should align with its strategy and mission in order to ensure that performance measurement answers questions that directly relate to established objectives. Through detailed data collection and analysis, the department can identify problems and subsequently address them.
They can include such issues as compensation, staffing decisions, employees’ professional development feedback, communication, coaching, guidance, and improvement. Other components of performance management can include leadership training and setting performance standards for achieving the department’s goals.
Department’s Vision and Strategic Goals
It was chosen to discuss the strategic vision of the Information technology Department (ITD) at DEWA. The department’s vision is creating a sustainable and innovative world-class utility. The vision is reinforced by the attention to such values as stakeholder satisfaction, technological innovation, sustainability, excellence, and good governance. In order to achieve the vision, the ITD at DEWA set out such strategies as learning and growth (e.g., retaining and attracting talent, workforce motivation), internal processes strategies (e.g., lean operations, services’ digitization, exponential project management), stakeholder satisfaction (ensuring stakeholder happiness), and triple bottom line (e.g., cost optimization, social responsibility, and minimized environmental footprint).
Through establishing key performance indicators for each strategy, the department is able to measure whether its vision is accomplished. Possible KPIs include talent retention rates, stakeholder satisfaction rates, cost reduction rates, and many more. For instance, in cases when retention rates were high, when the department’s spending decreased, and profits increased, or when stakeholders showed high rates of satisfaction with the department’s work, the goals were considered to be achieved. For managing the identified measures, the department defined tools and methods of measurement, made a plan of activities, defined resources available to it, and assigned people to conduct measurements.
Quality and Its Dimensions
Because of the complex nature of the concept of quality, eight dimensions have been developed to provide an in-depth explanation.
The eight dimensions of quality that companies around the world use to win customers’ preferences are the following:
- Performance: a product or service does everything mentioned in its specifications; e.g., a compass points to the North (Vrindavan, 2014).
- Features: a product or service has all specified features; e.g., a dish includes all ingredients mentioned on the menu.
- Reliability: are specifications performed consistently; e.g., a car’s airbags came out during an accident.
- Conformance: are specifications of a product or service perform as specified; e.g., a smartphone’s camera shoots 4k videos.
- Durability: does a product last for as long as specified; e.g., a washing machine surpasses a 10-year warranty.
- Serviceability: can a product be maintained or fixed quickly; e.g., are spare parts to an automobile readily available (Hilnbrand, 2017).
- Aesthetics: does a product has an aesthetic appeal and does it attract customers; e.g., a laptop has an ergonomic design.
- Perception: does customer perception align with the representation of a product; e.g., customers give a vacuum cleaner high ratings.
As seen from the list of quality dimensions above, a product or a service should possess a list of characteristics that can influence customer satisfaction. Quality is often associated with brand reputation and customer retention, which means that a process of quality management and control should be put in place in order to win customers’ attention.
References
Hilnbrand, J. (2017). Garvin’s 8 dimensions of quality in digital design. Web.
Vrindavan, M. (2014). What are the “dimensions of quality” – in total quality management? Web.