Abstract
Open Source programs are often produced by groups of people who work collaboratively on the internet. The software built, becomes a property of the group and is distributed free of charge to anyone who desires to use it. Open Source collaborations have increased of late thus, becoming socially and economically vibrant venture. Therefore, a big question emerges, what contributes to success or failure of Open Source Projects?
By embracing a Greenstone Software, a product of Open Source Initiative, the writer finds out that; physical and community characteristics, use, longevity, standard economic factors and security and functionality, and institutions contributes to the success of an Open Source Project.
However, factors such as; support, poor documentation, issues of proprietary software’s and legal challenges have noted as major problems affecting the operations and success of Open Source Project
Introduction
The term “Open Source” is a common word in the world of Information Technology, particularly, in the area of Software Engineering. Open Source is a software development strategy that simplifies the work of software developers across the world by collaboratively downloading, refining and improving the source code by using internet technology, as a key communication platform.
Pioneered by Richard Stallman and Erick Raymond, during the 1990’s, movement of “Open Source” was envisioned as a choice to create software’s by programmers and academicians in their own spare time, the culture has endeavored to stand present (DiBona & Ockman, 1999).
Open Source has received broad confirmation by a majority of programmers as an alternative procedure in Software Engineering. It has achieved success in coming up with projects that include; Apache Web Server, Linux Operating system, Mozilla Firefox among others
However, despite successful factors, linked to Open Source projects, many projects developed using these approaches have failed. Several researches have been conducted to determine the cause of this failure.
Khosrow-Pour (2006) notes that, majority of failure has indicated lack of dedicated and interested programmers in the spirit of the project, it is viewed that, Open Source projects requires a high level of technical skills, the prevailing ad hoc development archetype that inclined majorly in building features and fixing bugs and others have failed to recognize this concept.
Therefore, fresh and innovative methodologies need to be instituted to instill success and survival of Open Source projects.
The new methodologies have to be implemented by assessing the success factors present, so that they can be enforced by Open Source programmers and other project members during the initial development phase (Khosrow-Pour, 2006); little has been done to understand how developers in these communities integrate software development across a heterogeneous environment.
In other words, what software procedures, work practices and firms contexts are critical to their success or failure.
Research Context
Open Source software’s are type of software’s which are produced and are available freely over the internet. Thousands of these projects exist; hence they range from applications to business solutions. Because of their size, complexity and control, Apache Web Server and Linux operating system are commonly known. However, hundreds of other projects still exists and in use across the internet.
The measures of success of these projects are important for two major reasons. First, measures aid project leaders in evaluating their projects, Sometimes, open source projects are funded by third parties, and thus, measures are important to assist third parties comprehend return on their resources.
Secondly, Open Source projects are progressively distinct and duplicated during system or software development. Many users rely on systems such as internet and Linux which are heavily dependent on Open Source tools According to Koranne (2010),
Research in the Open Source projects has been done overtime to determine the key factors contributing to Open Source Software projects. Feller (2005) notes that, one major advance has been researching on complex but successful projects such as; GNU/Linux, Apache Webserver and FreeBSD among others.
Similarly, other studies have tried to fix the similarities existing in Open Source software’s in areas such as; the study of Mozilla and Apache, Arla and Mozila projects. Other studies embracing comparative have been conducted to determine the differences existing between software engineering practices such as; development pattern, software progression, requirement management, and structure of re-use.
According to Feller (2005), however, small software projects have been considered to achieve success because of their small size and easier management practices. Moreover, Open source software’s are significantly embracing web portals such as; lauchpad.net, sourceforge.net and freshmeat.net.
This site provides the free hosting services and supportive instruments such as Concurrent Versioning System (CVS), wiki, error handling and mailing lists for software’s developed hence simplifying development costs (Feller, 2005).
Empirical Analysis of Greenstone Open Source Software
Greenstone is an Open Source application for building and implementing online digital libraries and management of digital information. The libraries include documents in various electronic formats. The Software was created in 1995 at the University of Waikato, New Zealand.
Presently, the software is available under the GPL. The present version of the software is 2.42. According to Koch (2005), Greenstone can be installed on Windows, Solaris, Linux, macOS and UNIX; it also functions well with Apache, a Webserver.
Features of Greenstone software
- It has a browser supported access.
- It contains both full text and detailed field searching options.
- Comprehensive browseable lists of titles, dates, classification numbers, and authors among others.
- Uses Dublin Core and other kind of metadata schema.
- Advanced and comprehensive data density methods that decrease response times when users search huge volumes of data.
- A customized interface mimicking a configuration file.
- A multi-lingual interface in; Maori, German, English, Portuguese Arabic, Chinese, Dutch and French.
- Plug-ins to boost conversions of documents into different formats i.e. HTML, email, MS Word and PDF.
- Administrative functions which support user activity account and access control.
Greenstone employs the use of Unicode as a pattern to its interfaces thus simplifying its use in any language. The documentation of Greenstone software includes installation instructions, technical manual, an online FAQ and a user guide for tailoring the Greenstone interface. The Greenstone software is available at SourceForge for free downloading.
The website for Greenstone it has a lists online digital libraries built using this software. Several organizations have adopted this program to increase access to their digital data. Koch (2005), gives samples of these countries as; India, United Kingdom, India, Germany, United States, China and Russia.
The success of Greenstone software can be attributed to a number of factors which will be clearly elaborated under literature study. Though the Greenstone project proved successful, a number of factors can be attributed to a test that applies to it and the wider Open source Projects.
Literature Review
As Open Source is a form of system development, we can be better placed to begin our analysis for success measures in this field. The author will not exhaustively explore this extensive literature, but, will attempt to distinguish success measures attributed to Open Source framework.
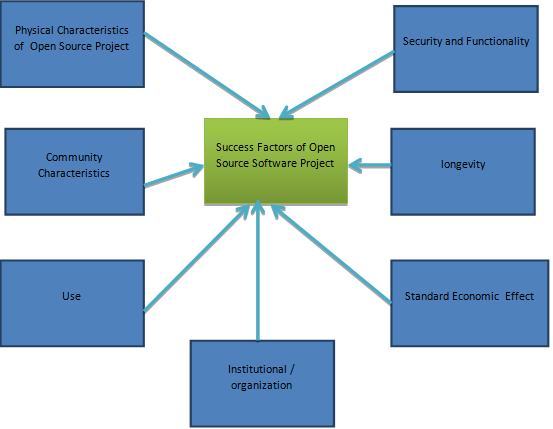
The author will review documentation relating to; physical characteristics of open source project, community characteristics, use, standard economic effects, longevity, security and functionality and institutions or organizations.
Physical characteristics of Open Source Project
Physical characteristics of Open Source projects refer to a set of variables linked to the software produced or to technological plan required for team coordination. According to Remenyi (2005), variables that obviously command Open Source Project success includes; collaborative platform, modularity, competition, software requirement, product effectiveness and code quality.
Software requirements primarily refer to all the processes that what intention of the result will gain or accomplish. It is believed that clear and vision defined projects perform well compared to ones without a clear vision (Remenyi, 2005).
Modularity affects the design of the program, and whether it can be easily decomposed into separate units or stand-alone components. Within some limits, modular design simplifies the work of contributors to “carve off chunks” in regard to the project on which they intend to embark on (Fogel, 2006).
Product utility enhances the project success if the program being developed encompasses the needs of the people or if it is a refinement of the previous one.
Competition designates whether a potential competitor would encourage organizations or potential people to connect with any specific project as noted by Remenyi (2005). Additionally, competitions seize the situation where a competitive technology exists thus, decreasing people’s enthusiasm to the software being created.
Khosrow-Pour (2006) asserts that, collaborative platform designates different types of technologies embraced to assist in coordination of the collaborative team.
The platform exists in a variety. According to Weber (2004), specific configuration is crucial in decreasing the length consumed by the project team members. For instance, a tradition that emphasize using questions and answers forum for support creates and a searchable credentials database
Code Quality, a prerequisite in software engineering has been extensively researched to ensure that it meets the necessary standards for the Open Source Project at hand to achieve its intended outcome.
According to Kamel (2006), measures of code quality in terms of completeness, conciseness, structuredness, understandability, portability, efficiency, reliability, usability, maintainability, stability and testability provides a core to the level of Open source project success.
Equally, system documentation also aids in ensuring the Open Source project succeeds. Code Quality, since it is available as a freeware, offers unique capabilities such as; having produced by a mix of talented programmers’ substantial set of developers and accurately tested (Kamel, 2006).
Community Characteristics
Weber (2004) notes that, community characteristics aid in appropriating variables linked to people. The “people” in this context refers to developers of the software and markers. These features need strong governance, social capital, involvement of the user and the group size among other facets,
User involvement in the Open Source Project is one significant variables contributing to the success of Open Source Project (Weber, 2004). Equally, leadership in Open Source projects teams either virtual or face to face contribute greatly to success of Open Source projects.
This is because, leadership consists of teams which are; well- structured, motivated and a shared vision of what goals have to be accomplished. The importance of User satisfaction is commonly used to determine the success of Open Source project.
Users can review the stakeholder’s response if the project was a success. Most OSP has data repository used to determine the user satisfaction with the OSP projects. According to Koranne (2010), the Freshmeat, a web enabled system, tracks the releases of OSP gathers user ratings of projects.
However, most of these ratings, unfortunately, are anchored on a non-random model for example, users who voluntarily take their time to reflect on the suitability and so on. Moreover, Mozilla is also another Open Source which can be used to measure user satisfaction. This Web browser contains a program that provides users with the help in reporting crashes and collecting other feedback
In other disciplines such as economics and political science, the nature of social capital is expressed. In political science and economics, the amount of social capital usually characterizes “trust” within the members of the community, accordingly, it is used enhance “healthy” or active community (Weber, 2004).
Similarly, other factors such as; creation and sustaining trust, reciprocal relationship, repeated interaction and face to face meetings have been used to describe a healthy community thus contributory factor in Open Source Project success.
Additionally, group heterogeneity influences the capacity of a team to serve cooperatively. Reijswoud (2008) sub-divided group heterogeneity into three broad categories interest, socio-cultural and resource heterogeneity. Socio-cultural heterogeneity embraces fundamentals such as; religion, cultural, semantic and ethnicity variances.
The common beliefs are that, groups having contrasting background will experience problems or difficulties working together because there is tiff and, equally, limited trust as noted by Reijswoud (2008). Interest’s heterogeneity seizes the inspiration people of who partake in the project.
Volunteers who contribute in Open Source project bring in new ideas, and this increases up to the already paid programmers involved in the project. Besides, stress heterogeneity help to attract the idea that some people may bring fresh ideas or resources in the project than those others in the team lacks. For example, the theory of political authority and prosperity, are some vital resources present in majority of Open Source.
Weber (2004) suggests that, the size of a group has also been attributed to the success of an Open Source Project. Thus, large groups demands huge costs to cater for coordination issues than smaller group. A larger group helps in minimizing the workload and brings in new ideas thus increasing time taken for project completion.
Lastly, marketing strategies and project financing plays a vital role in Open Source project success. Studies conducted in Open source projects shows that, finance is a critical aspect necessitating success.
Finance ensures that the project moves forward without stagnation or hitches. Besides, financing provides a source of confidence to stakeholders or sponsors to be sure that the project will be completed on allocated time and with the available resources.
Use
According to Muffatto (2006), system use plays an important role in assessing the success of Open Source software project. For software, in which its operation is done freely, as Open Source, use is used to indicate the relevancy of OSP success.
For example, Avery pennaruns Debian a famous popularity contest, gathers data on Linux machine using Debian distribution software (Muffatto, 2006). Thus, this software helps to determine its effectiveness and reliability.
Users install this software on Linux platform and collects information on a daily basis, and the resulting data displays which package has been installed, and among the installed, which program has been used of late. The data are gathered from non-random machines on a Linux platform, thus, the results will show the use of the OSP (Muffatto, 2006).
It is equally relevant to determine the use from other perspectives rather than focusing on the user. The openness opportunity created by Open Source projects entails that; other programs can be assembled on top of it. Hence, the rule of one open Source project success can demonstrate that other projects utilize it.
Package reliance information in Open Source projects evident in software categorization by software distribution system. Golden (2005) suggests that, careful examination of the source code can reveal reengineering or reuse of code from one project to the other.
Standard Economic Effect
The Success of an Open Source Project is also influenced by economic factors, and especially the market influence. Deek & James (2007) notes that, questions such as, what can the product perform? Is it simple to use? Is it secure, portable or fast? The possible answers to these basic questions depend largely with the type of Open Source applications being developed and the anticipated Users.
For example, a consideration for an internet security or a Web server or a system administrators apparatus are specific to those, let’s say, for mass market tools such as Web browsers or accounting utilities. A common variable is the effect such as network effects, vendor-lock in and overall costs of use (Deek & James, 2007).
Vendor Lock-in provides a bigger success story for Open Source products. Vendor lock-in encourages “tying in” a user of a given brand if the direct or indirect budgets of shifting to a different brand is extremely repressive. This is sometimes known as Vendor lock-in. The shifting costs may seem pricey for example, in training, to facilitate understanding of the new system.
According to Deek & James (2007), most other software’s have this capability of locking in users in their system thus preventing them from accruing much benefits and flexibility. However, the success of Open Source products has been the results of being available freely.
According to Taylor (2004), network Effect has also contributed to the success of Open Source projects. A network implementation designates the increase in cost of service or product depending on the number of users.
For example, majority of people uses emails and other web services such as eBay, thus the more benefit this services grows because, it becomes a possible social connection for any user thus becoming popular. Consequently, the more the websites on the internet, the more value other internet users accrue from the internet (Deek & James, 2007).
Open Source has endeavored presence on the internet thus exploiting areas where the proprietary software’s have left a void. For instance, Netscape, an open source program, which was released by Netscape Inc., was a success because it utilized the market thus leading to its dominance in the market by exploiting the network effect.
Other Open source products such as adobe Reader have utilized Network effect strategy. Adobe is embraced by being a nifty utility. Adobe is required for efficient functioning of adobe product. Without this utility, documents prepared using this software is not easily readable (Deek & James, 2007). Besides, Firefox has also embraced this strategy.
Firefox spread rapidly across the internet during initial years of it’s a lunch. It attracted many enthusiastic users. This was a benefit of web effect. As the market share enlarged, the magnitude of distribution of Firefox, at that moment, aided it to be appealing thus attracting a larger number of users. Therefore, the network effect, contributes in ensuring the success of Open Source Products (Golden, 2005).
Longevity
Taylor (2004) asserts that longevity of a product refers to the measure of the duration of a product since its inception. It elaborates on project strength and probability of survival of a project that is beginning but has a lot of errors.
Thus, the owner the project becomes, the less likelihood of the developers not abandoning. An important technique to be factored when software is still new, is to consider whether we have a dynamic community around it (Taylor, 2004).
The activity and age level of project development are frequently linked. Thus, infant projects tend to have more activity level than projects that are old. Perhaps, is because, when a project has stabilized and meets the user’s needs, restricted forums are realized and releases are generally less, containing errors and security solutions.
To ensure all issues have been dealt with, longevity is better emphasized by embracing techniques such as; age of the product and version number (Taylor, 2004). The age of a project typically is the date of the first release thus if the project is old enough, it is noteworthy to determine the if it has redesigned or if it is a current project, it should be checked to verify the compatibility with the new technology.
Moreover, Version numbers do not actually reveal the whole truth about projects. For example, some projects might upgrade from version 1.0.1 to 2.0.0 with a similar amount of change that another pretty similar project has gone i.e. 1.0 to 1.1 (Taylor, 2004).
Security and Functionality
According to Still (2007), when referring to Open Source software, security encompasses two sides. First, are people who believe that protection by anonymity is essential, implying, the inner operations of the software are protected in a closed source, however, this is not the case with Open Source.
Still (2007) notes that, the proponents of security by obscurity view that openness associated with Open Source programs as a security threat. On the other hand, others see it as safe because vulnerability linked to the codes are easily noticed.
Open Source programs therefore provides both the defenders and attackers authority over system security. Consequently, the security relies on the attention the developers put in the project i.e. code quality has more to do with security (DiBona & Ockman, 1999).
Open Source Projects uses the method described as “release early and often” (Still, 2007). This method simplifies error corrections (Weber, 2004) by sustaining the software. Moreover, it also plays an important aspect by encouraging people to positively contribute before they see their contributions within the shortest time possible i.e. during the next release.
Institutions or Organization
DiBona and Ockman (1999) argue that, institutions or organization contributes largely to success or failure of Open Source Software project. Institution is made up of characteristics which are related to management systems and governance employed in the development of Open Source projects.
It also contains rules and regulations which plays a key role in guiding the morals of the team or participants. According DiBona and Ockman (1999), organizations contributes to the success of open source particularly in areas of provision of natural resources that limit or protect resources from being wasted and overuse.
Reijswoud (2008) points out that, researchers have, of recent theorized and examining empirically organizations designs in an open source environment. One of the reasons for this lack of priority may be because of some stringed rules and processes which have been believed to exhibit a disincentive for taking part in Open Source.
Reijswoud (2008) notes that, besides, Open Source projects contents versions and control systems have replaced the requirements of rules by safeguarding the Open Source software from inadvertent destruction through configuration control and rollback capabilities.
Nevertheless, the increasing role of governments, firms and non-profit organization in Open Source software project collaboration include increased institutional designs. This has prompted the success factor in Open Source projects.
Institutional framework which is organized into; operational, constitutions and collective decision levels ensure that each level contributes independently to the success of the task at hand. In a more comprehensive platform; operational level entails the traditions and rules that oversee the daily activities taking place in a project.
Collective and control backs in defining and elaborating on how, an event alters in functioning and effect the desired changes in the development process. Constitutional levels assist in specifying the eligibility or a person who has authority to amend collective decision, it also delineate procedures for affecting such kind of changes.
Constitutional levels back to formalize rules that establish a check or stipulate principles that anchor collaboration. Constitutional level has enhanced Open Source license thus creating a success factor in Open Source projects.
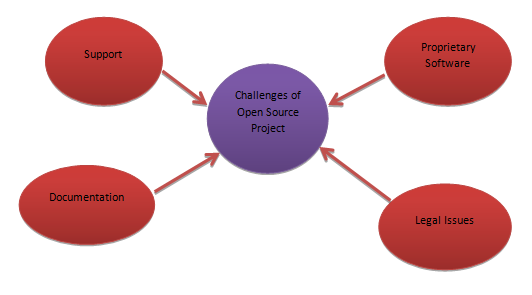
Challenges/ Problems with Open Source Software
Though Open Source software contributes to minimizing cost compared to proprietary software’s, issues relating to level of support present and role of technical proficiency needed to install and efficiently use it are common.
Thus, with no responsible vendor for the software, most support for the Open Source Software vary, and largely depends on the developer or the user’s community’s dedication and commitment to the project. Feller and Fitzgerald (2005) explain that, Open Source Software can be challenging to use, install and maintain as this can be verified by numerous postings in blogs, forums of Open Source.
The degree of technical knowledge required to install and maintain an Open Source Software can be hindrance to its usage. According to Feller and Fitzgerald (2005), some Open Source software developers chooses some proprietary software libraries, because, they don’t possess the necessary technical abilities to support the Open Source Software in-house.
Feller and Fitzgerald (2005) also, admit the sudden knowledge arc for implementing library for Linux Operating System, if users or staffs have no prior experience. Besides, technical support also has been a challenge to Open Source Software.
Technical support depends on a dedicated person or team in responding to lists of appeal which can be handled when help is invoked. For Open Source software, this has been an inherent barrier as noted by Koch (2005). Although Open Source communities respond quickly in consideration for advice or assistance, with respond to questions dispatched within minutes despite taking more days.
Documentation plays an important aspect in any software development. It aids in program, upgrade, maintenance, installation among other things.
Poor quality in the documentation is cited as an impediment to open source Software’s. They have inconsistent documentation which is either incomplete or poor developed documentation. Perhaps, this can be a result of no dedicated and dedicated team for the project (Meeker, 2008).
According to Meeker (2008), proprietary software gives more authority to the user thus simplifying the user navigation through complex tasks. However, in Open Source software, a user has to comprehensively grasp what the program intends to do to accomplish the task at hand successfully.
Moreover, Open Source consists of wizard type kind of user interface, hence, when this wizard does not have room to enable a user make the changes regarding the responsibility anticipated, the wizard type of interface can cause more challenges such as; changing values or actions to unexpected places. Software which has familiar and elaborate interface makes it simple to direct actions and aptitude to identify and fix a problem.
According to Woods and Guliani (2005), legal issues have also affected the success of Open Source software. Companies involved in Open Source software development have failed to adequately locate the appropriate license which fits their brand. This has resulted in many legal suits.
Besides, most Open Source software companies have failed to manage their developed software hence leading to violation of Open Source license in possession; the possession of a program license is a direct violation of the copyright act and establishes a liability for risky damages.
Woods and Guliani (2005) points out that, Open Source developers have faced the issue of combining Open Source license with that of proprietary software license. The legal challenges that have ensued with Open Source software’s includes; the scope of license, automatic termination, conflicting licenses and demands for transparency (Woods and Guliani, 2005)
The scope of License
In spite of the surge in regard to the use of Open Source software, the Open Source license has not been fully interpreted in the courts and primary disputes in relation to their range are still pending. The GPL (General Public License), popularly used as Open Source License, spans to “derived works” of software that has been licensed under GPL and “collective works” (Woods and Guliani, 2005).
Both derived and collective works are regarded as expressions of art and copyright law. They therefore encompasses the following broad interpretation; a derivative work is typically work done based on one or more work pre-existing i.e. in translations, art reproduction or abridgement.
A collective work on the other hand designate works in fields such as in; anthology or encyclopedia as noted by Woods and Guliani (2005). Copyright law therefore fails to fit into this context and possess difficulty in interpreting noting the context in which computer software operate.
The GPL has only been involved in United States cases, though, it has not been comprehensively been interpreted. However, other Open Source licenses such as; Apache and Mozilla Public Licenses have not been fully addressed by the law (Dixon, 2004).
Automatic Termination has also been a challenge to Open Source software’s. Many of the commonly used licenses such as; Apache Public License and GPL are “provisional licenses”. This implies that, they do not have conventional period of notice.
Failing to conform to its stipulations leads to its termination (Woods and Guliani, 2005). Because the software is secured with copyright (owners privileges such as; modifying, distributing, reproducing, publicly displaying and publicly performing) the license reserves the rights for using the software, this means that, terminating the license whereas continuing using the software leads to copyright infringement.
Also, conflicting licenses have continued to challenge the usefulness of Open Source software. Dixon (2004) points out that, the Open Source Initiative (OSI), has of recent approved fifty eight licenses as “Open Source”. However, vendors have found more than 600 types of software licenses; a variation of OSI certified licenses.
These issues of multiplication of licenses that may on occasion include the difference in terms suggest that it is challenging to amalgamate some software’s, even when they have been licensed under “Open Source” (Dixon, 2004).
Though, majority of Open Source projects uses about eight of these licenses, they are still opposed. For instance, software parts licensed with GPL license cannot be dispensed with software module licensed to Mozilla Public license.
According to Dixon (2004), demands of clarity and understanding the product being purchased by consumers has been too demanding. Customers have been relentless in wanting to know if the products being purchased are fully compliant with the appropriate licenses.
This has posed a challenge to open Source software’s. In light with these uncertainties’ (Dixon, 2004), Open Source developer’s needs to address the potential threats linked to their Open source Software. It is not simple to avoid all these threats, but, by developing and adhering to Open Source policy will assist in enhancing smooth Open source projects.
Conclusion
Open Source software projects like any other projects are infamous for being delivered behind the scheduled time, approving budgets and below expectation. With technologies evolving at a faster pace, Open Source is seen to contribute largely to innovation and streamlined online collaboration. Identifying, essential success factors to successfully accomplish substantial progress are achieved, prior planning is important.
This paper has explored the Open Source software project in greater details. It has explained the Open Source Software project and pointed out the Greenstone Open Source project as one of the software project which has achieved success by enhancing key project practices.
By embracing Greenstone software, the paper has extensively elaborated success factors basing on literature review which contributes to success of open Source project. Factors which have been identified includes; physical characteristics, community characteristics, use, standard economic effects, longevity, security and functionality and institutions.
Though the aim of any project is geared towards success, challenges are inevitable. Open Source software experiences problems thus a need arises of how this challenges can be averted and contribute to effective project development. This paper has identified; lack of support, poor documentation, availability of proprietary software’s and legal issues have the major challenges in realizing the full potential of Open Source software’s.
References
Deek, F., P., and James A., M., 2007. Open Source: Technology and Policy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
DiBona, C., Ockman, S., 1999. Open Sources: Voices from The Open Source Revolution O’Reilly Media, Inc., California.
Dixon, R., 2004. Open Source Software Law, Artech House, New York.
Feller, J. and Fitzgerald, B., 2002. Understanding Open Source Software Development, Addison- Wesley, Cambridge.
Feller, J., 2005. Perspectives on Free and Open Source Software, MIT Press, Massachusetts.
Golden, B., 2005. Succeeding With Open Source, Addison-Wesley, Cambridge.
Kamel, S., 2006. Electronic Business in Developing Countries: Opportunities And Challenges, Idea Group Inc (IGI), Pennsylvania.
Khosrow-Pour, M., 2006. Emerging Trends and Challenges In Information Technology Management Idea Group Inc (IGI), Pennsylvania.
Koch, S., 2005. Free/Open Source Software Development, Idea Group Inc (IGI), Pennsylvania Fogel, K., 2006. Producing Open Source Software: How to Run A Successful Free Software Project O’Reilly Media, Inc., California.
Koranne, S., 2010. Handbook of Open Source Tools, Springer, Berlin.
Lindberg, V., 2008. Intellectual Property And Open Source, O’Reilly Media, Inc., California xxx.
Meeker, H., J., 2008. The Open Source Alternative: Understanding Risks and Leveraging Opportunities, John Wiley and Sons, New Jersey.
Muffatto, M., 2006. Open Source: A Multidisciplinary Approach, Imperial College Press, London.
Reijswoud, V., V., 2008. Free and Open Source Software for Development: Exploring Expectations, Achievements and the Future, Polimetrica s.a.s., Milan.
Remenyi, D., 2005. Proceedings of the International Conference on E-Government, Academic Conferences Limited, Reading.
Still, B., 2007. Handbook of Research on Open Source Software: Technological, Economic, And Social Perspectives, Idea Group Inc (IGI), Pennsylvania.
Taylor, J., 2004. Managing Information Technology Projects Applying Project Management Strategies To Software, Hardware, And Integration Initiatives. American Management Association, New York.
Weber, S., 2004. The Success of Open Source, Harvard University Press, Massachusetts.
Woods, D., and Guliani, G., 2005. Open Source for The Enterprise: Managing Risks, Reaping Rewards, O’Reilly Media, Inc., California.