
Why Get Insured?
In 2017 harbor wealth survey stated that 60% of adults in the United Kingdom do not have any form of life insurance. Many people in the UK and worldwide think about saving their loved ones, especially when they have families. Elderly people think about life insurance or what they will bequeath to their family after death.
Nowadays, people get more educated, and even small families and people who work in dangerous fields think about leaving value when they pass away; it also depends on the personality whether they want to add value to their beneficiary after death or not. Ford et al. (2020) note that life insurance is not just a way to protect yourself and your family from financial losses in unforeseen situations but also an opportunity to provide for old age and even earn money. Nevertheless, there is a problem of understanding the need and functions of life insurance among the population, which becomes an obstacle to the registration of such services.
Life Insurance Industry in the UK
The United Kingdom, as one of the world’s largest financial centers, is the leader of the European life insurance industry. According to Rudden (2022), as of 2019, UK life insurance companies had over 70% of the total UK insurance market, providing a wide range of insurance and financial investment products. In 2020, the top three UK life insurers were Legal & General, Aviva, and Scottish Widows (Rudden, 2022). Such growth is associated with the onset of a global pandemic and greater attention to health among the population.
Types of Insurance
There are many types of life insurance policies out there; in this blog post, I will focus on the two main types, whole-life insurance, and term life insurance.
Whole life insurance is insurance that charges higher (premium) payments and its maturity due on death date. On the other hand, Term Life insurance charges lower prices, but it is restricted to a pre-agreed period. Whole life insurance, unlike term insurance, does not end until a person makes constant premium contributions and also offers the same sash value, which can be a source of additional funds. Term life insurance, on the contrary, is concluded for a fixed period, and benefits are paid only if death occurs within this period. This type of insurance does not offer additional cash value.
Whole Life Insurance
Pros

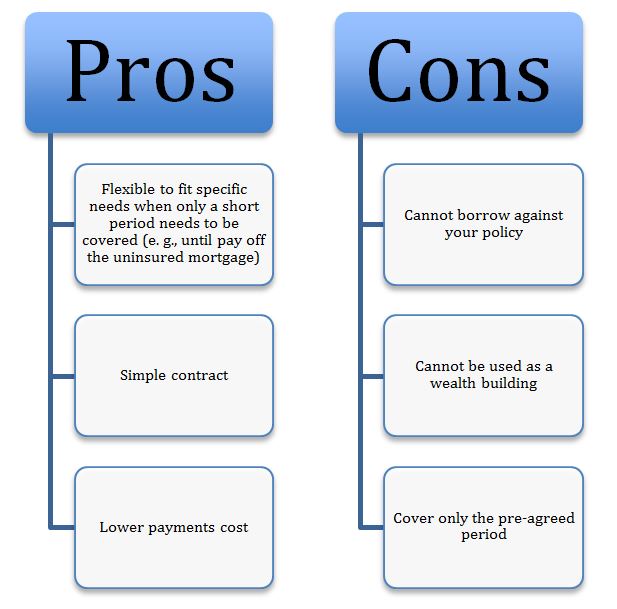
- Death date is the maturity date (no expiry date).
- People are able to borrow against their insurance.
- Can build up cash value depending on the policy and claim date period.
- Tax-free.
Cons

- Higher payments cost.
- Less return if compared with potential investment.
- Benefits will be lower if there is current debt or mortgage.
Term Life Insurance
Direct and Indirect Financing
Nowadays, life insurance is used not only for protection, but for investment and collateral. It has created new debate and much confusion about the effectiveness of dividends and the benefits of indirect recognition versus life insurance with direct recognition.

First, it is necessary to consider the features of each of them. Insurance companies use two different methods to process loanable cash value – direct recognition and indirect recognition. In an indirect recognition company, the rate of return on cash value is completely independent of any borrowing against the cash value. In a direct recognition company, rates of return on loanable cash value are affected both positively and negatively when the cash value is used as collateral.
As part of insurance financing, indirect recognition is the preferred option. Indirect recognition is the most preferred for long-term loans, as it provides more stable, albeit lower margins. As part of life insurance, where interest rates are low and fixed, one does not have to worry about their increase, which makes indirect recognition highly risk tolerable. Additionally, indirect recognition provides faster monetary value growth than the direct variant. At the same time, life insurance offers rather low dividends, which may result in lower margins than expected. Thus, indirect recognition offers the best conditions in the long term, providing better liquidity and minimizing risks. On the other hand, for higher and shorter margins, direct recognition is more suitable, which is irrelevant within life insurance options.
Challenges in the UK Insurance Industry
Life insurance has three causes of problems in the industry, dictated by the three factors described below (3 reasons why the life insurance industry is struggling, n.d.):
New Technologies

Many insurance companies have not implemented technology into their existing ecosystems, so they are losing potential customers. However, filling this gap can help improve both internal and client processes through cost reduction, efficiency gains, simplified management, simpler products, and the ability to assess risk better.
Changing Customer Expectations

The Internet and the transition of businesses to it have led to a change in customer expectations. Customers now expect companies to respond quickly and deliver flawlessly. Clients, especially well-connected urban populations, want information exactly when they need it. They also expect more personalization as companies collect data about their visitors. In addition, people’s financial situations are unique and require unique solutions.
Financial Situation of the Client
The high cost of living is a major barrier, and real incomes have not changed over the past decade. From 2012 to 2017, household debt and unsecured consumer debt increased (Deloitte, n.d.). With such a large portion of income going into debt, it is not surprise that any savings or investment in life insurance falls by the wayside. Finally, people with pre-existing medical conditions must go through the lengthy and painful process of getting insurance. This acts as a huge deterrent.

Based on the above, three strategies can be identified to create new opportunities by extending existing challenges:
- Personalization of every aspect of customer interaction.
- Development of flexible product solutions suitable for complex regulatory and percentage environments.
- Rethinking skills and capabilities.
Opportunities in the UK Insurance Industry
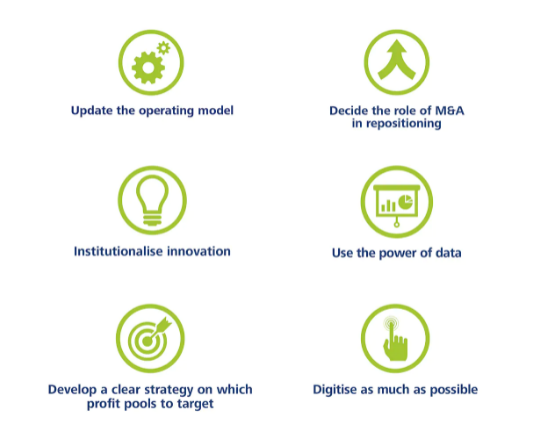
Several trends are encouraging for the life insurance industry in the next decade. According to Deloitte (n.d.), customer demand is at an all-time high. The COVID-19 pandemic has forced people to pay attention to their health and take life risks more seriously. Moreover, the global middle class is expanding, bringing with it higher incomes, growing financial prosperity, and increased risks.
Thus, the life insurance industry faces a key, dual opportunity: the chance to meet the growing needs of customers, returning to profitability and growth. According to Deloitte (n.d.), life insurers can use the described levers below to achieve these goals.
Risks and Decisions
Bernard et al. (2020) provided an industry outlook for the UK life insurance market. The pension risk reduction market is expected to pick up in 2022 and 2023, supported by strong structural demand from corporations to reduce risk on their balance sheets. It is facilitated by the improvement in the level of funding for pension schemes and, consequently, the increase in the number of schemes seeking to reduce risks.

British life insurers continue to be exposed to low-interest rate risk, mainly due to the impact of low-interest rates on their bottom line. They are expected to have limited exposure to rising inflation, due primarily to hedging of inflation-related liabilities and the limited impact of growth in the cost base.
UK life insurers’ investments remain subject to some degree of asset risk affecting sectors struggling post-pandemic. This risk is mitigated by high portfolio diversification, which also means that such risks are usually limited in size. However, insurers’ exposure to credit risk is expected to remain moderate and corporate defaults low and manageable.
Cyber risks are another area of growing concern for regulators, even if life insurers do not directly sign cyber insurance policies. Regulators are certainly paying more attention to this. A study by Ford et al. (2020) shows that most cybersecurity incidents where data and/or systems are potentially compromised are the result of employee actions such as opening phishing emails or insecure data transfers. Thus, much of the work in this area involves working closely with HR peers and organizational consultants to improve safeguards through tougher work practices and staff training.

My View
Life insurance is still a responsible step for every person and has a lot of subjective reasons for and against. As reported by Reassured, insurance companies rate of payout is 97.4% regards to term life insurance, and the percentage goes higher to whole life insurance with a payout rate of 99.99% (Life insurance payout rates: Do life insurance providers pay, n.d.). That sounds protected for risk-averse people, which means they prefer to secure the capital over earning a high return. People who are more prone to risk can invest their capital with the possibility of further earnings. However, in such a case there are no guarantees and mechanisms for risk mitigation – most insured events are still undesirable for clients.
In modern conditions, the life insurance market expects gradual growth. The experience of the pandemic has changed people’s attitudes towards health, and the restrictions associated with the spread of the virus have forced us to rethink the value of life. The main risk in this situation is the instability of the market, as well as rising inflation. The opportunity is greater customer dispute over various types of short-term insurance due to the threat of loss of property and funds. Investment and returns strategies in the industry are also affected by increasing uncertainty, so companies need to take a more informed approach through the integration of data analysis and forecast techniques. To mitigate existing risks, companies should expand the options for providing temporary insurance to minimize long-term losses. The main recommendation for improving the risk management model in the industry is the need for better customer demand research and modification of insurance products in accordance with it.
References
3 reasons why the life insurance industry is struggling (n.d.). SPIXII. Web.
60% of UK adults don’t have any form of life insurance. (2021). Harbour Wealth Limited. Web.
Bernard, P.-I., Ellingrud, K., Godsall, J., Kotanko, B. & Reich, A. (2020). The future of life insurance: Reimagining the industry for the decade ahead. McKinsey & Company. Web.
Deloitte. (n.d.). UK life insurance futures: Growing the retirement opportunity. Deloitte. Web.
Ford, M., Ring, B., & Narker, W. (2020). The UK life insurance market 2019-2020: A snapshot.Wtw. Web.
Life insurance payout rates: Do life insurance providers pay? (n.d.). Reassured. Web.
Rudden, J. (2022). Life insurance industry in the United Kingdom (UK) – statistics & facts. Statista. Web.