Introduction
The initial attempts to make the mobile phone an electronic wallet can be traced to the efforts by Nokia around 1997 (Leavitt 2010). In that year the Company (Nokia) made attempts to allow people purchase soft drinks from vending machines through the use of Short Messaging Services (SMS). Soon after that initial effort another Finnish company, Merita Bank, offloaded the first mobile banking system based on SMS (Leavitt 2010).
A mobile payment system is one that facilitates transfer of funds securely for purchase of goods through a mobile phone-based application (Quigley 2008). However, mobile payment systems did not make the expected impact owing to the fact that the use of wireless devices was still not widespread and the GUI’s for most of these initial devices were poorly designed (Leavitt 2010).
Technological advancement has seen the production of smartphones with many capabilities and significant changes in the capacity and bandwidth on the cellular networks around the world. Further dissatisfaction associated with credit card fees has worked to further increase the propensity towards mobile payment options.
Currently, through the use of smartphones, there are applications to make purchases such as music and videos possible online. It is in light of this that an innovation such as a comprehensive mobile payment system may go a long way in reducing the complexities associated with transfer of cash in Abu Dhabi. Such a system could be useful in activities such as the collection of charitable donations, purchase of air time, utility bill payment, and mobile banking.
In this project, the objective is the creation of a mobile payment system for use in Abu Dhabi. The proposed system could be used to pay for services such as taxi fares, make purchases, and pay utility bills. The system could be especially useful for visitors as the region is typically inhabited by an Arab-speaking population (Middle East Hub).
Factors in Favor of the Innovation
Prior to making a decision on the innovation, it was essential to establish the viability of the project. In this regard, it was noted that the revenue fro telecommunications in UAE rose from $ 2.7 to $3.1 million between 2000 and 2004 (Shirazi & Rogers 2008). This data suggests that there has been an increase in the usage of telecommunication in the period and it is likely that the increase is bound to be sustained over time with the emergence of new technology in cellular networks.
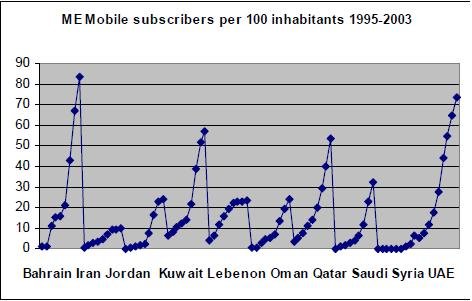
In addition to that it was observed that the number that the number of mobile phone subscribers rose from below 10 per 100 people to almost 80 per 100 people over the duration between 1995 and 2003. Based on this it is possible to conclude that the penetration of mobile phones within the Abu Dhabi area is very widespread given that it is the largest of the emirates.
Another factor that may favor the innovation of a mobile phone-passed payment application in Abu Dhabi is based on the fact the region has a high number of immigrant workers. According to Kapeszweski, the Gulf region is among the largest job markets for Asian and Arab job seekers (2006). In light of this the UAE has a population of foreigners that constitutes almost 80% of the overall population (Kapeszweski 2006).
Due to this fact, there is a very large percentage of the population that may not be very fluent in Arabic, the local language. This portion of the population could greatly benefit from such an innovation which will significantly reduce the hassles involved with payment of services. Due to the above contributing factors it would appear that such an innovation may be successful in the region. This is based on the high penetration and large population that may benefit from such an innovation.
Potential Benefits
The use of a mobile phone to make payments can allow the user several potential advantages. For example, the mobile device can be linked to a credit or debit card thus granting the user access to essential services even in the absence of credit card verification machines (Leavitt 2010). This access to services when needed is very beneficial for users and has been reported to create much additional revenue for merchants whose markets are expanded to include areas prior to inaccessible.
In addition to that these payments options allow the users to take maximum advantage of social networking forums (Leavitt 2010). Social networks are already being widely used and these options can provide an avenue to maximize on the opportunities available in the forums. It is hoped that through the creation of a similar system the residents of Abu Dhabi can benefit from the increased efficiency it will ensure.
Cases Studies in Mobile Payment Systems
Among the examples of successful mobile payment schemes in other parts of the world is the system known as BOKU. This company was launched in 2009 and has grown through the acquisition of mobile vendors, namely, Mobilcash and Paymo (Leavitt 2010). The BOKU system relies on its relationships with several mobile carriers around the world to serve both merchants ad publishers in 65 countries around the world (Leavitt 2010).
The company mainly performs transactions and offers assistance for purchasing gaming products and other virtual goods. The product does not focus on money transfer. The system basically asks a user to authenticate a transaction whenever they intend to make a purchase. After calculation of the purchase totals the system will then reflect the same on the users wireless phone bill (Leavitt 2010).
Another novel approach in the mobile payment systems market is known as Obopay. According to the company vice president, this service is suitable for funds transfer between people, payment for goods or services, purchase of mobile phone air time and making charitable donations (Leavitt 2010). However the service is not offered directly but through partners such as financial institutions, mobile carriers, merchants and other non profit organizations.
The system allows users to effect payment by sending an SMS to the company. Thorough the Obopay payment mechanism a consumer can access money for expenditure that is locked in a credit/debit card, bank account or even use the prepaid deposit (Leavitt 2010). After making an entry on details of the purchase the user selects the source from which they want to make the payment (Leavitt 2010). The payment process is secured through use of an authenticated phone and a user PIN to prevent fraud and other risks.
The last mobile payment system that was explored in considering this project is known as Zong. This company was established in the year 2000 and has established a network of various mobile carriers which it can rely on to charge the user. The company has managed to build an impressive following and boasts almost 3.5 million registered users serving almost 220 carriers in 50 countries across the globe (Leavitt 2010).
The company liaises with major digital goods company’s such as Facebook and is reported to be the mobile payment provider for Facebook credits (Leavitt 2010). They also provide virtual currency that can be used for games and other purposes. Payments are made on merchant websites and require the user to enter their phone numbers and a PIN for the transaction. The funds are then deducted through the user mobile carrier.
New Approaches in Mobile Payment Systems
In recent times the development of various apps that are used on smart phones to facilitate making payments. Some established online payment companies such as Papal are in the process of developing apps that can use the smart phone technology such as blue tooth to allow for funds transfer between phones (Leavitt 2010).
Another smart innovation worth consideration is the mobile application that allows transfer of a check to a Papal account by taking a picture of the check for submission in place of the check. These applications have been able to take and advantage of the fact that Papal stores both credit and debit card information securely on their servers thus reducing the complexity of creating such an application (Leavitt 2010).
However, among the more notable and potentially beneficial current trends is the use of near field communication technology in mobile payment systems. This technology allows the mobile phone to be fitted with a device that allows it to be identified within a specified proximity (Ondrus & Pigneur 2007).
In fact in some countries such as Japan and Korea mobile phones are already being mass produced with Radio Frequency Identification (Ondrus & Pigneur 2007). With this technological attachment in place the mobile phone can act as a contact less card and be used for financial transactions (Quigley 2008).
The NFC device embedded in the mobile phone despite having a shorter range can allow the phone to perform a large variety of functions. Fr example with such technology it is possible to create a smart poster with an embedded RFID tag. Upon waving the device close to the poster the phone can get more information about the poster.
Such applications have been found effective in ticketing and purchase of promotion products (Ondrus & Pigneur 2007). This technology offers much promise and may be considered as the option of choice for the proposed mobile payment system for Abu Dhabi.
Potential Success Factors
Mobile payment options have of recent began to gain acceptance across the world due to a variety of factors. First of all the success and interest in the options is due to the compatibility with the lifestyles of a large percentage of the population (Mallat 2007). In a study that observed the mobile phone use patterns across a cross section of user it was noted that among teens, students, young adults, parents and middle aged adults, all groups were conversant with use of the device and had used the device for mobile payment (Mallat 2007).
In addition to this some users suggested that such options seriously favored them as they reduced the hassle associated with queues at various POS. In addition to this convenience there is the fact that mobile devices are carried by almost all people almost all the time. This provides the user with the advantage of combining various functions in a single device.
Most of the users of these facilities have suggested that the main advantage with the mobile payment options is the simplicity of the SMS options (Mallat 2007). As the users have already become accustomed to the use of the mobile phone the SMS based procedure to carry out the transaction is especially well suited and easy to use (Mallat 2007).
The above points are among the factors that provide this proposal with motivation and suggest it will be successful if implemented. In addition to these it should be kept in mind that mobile phone penetration is quite high in Abu Dhabi and thus it should be successful.
References
Kapiszewski, A. (2006). Arab Versus Asian Migrant workers in the GCC countries. United Nations Expert Group Meeting on International Migration and Development in the Arab Region, 02, 1-21.
Leavitt, N. (2010). Payments Applications Make E-Commerce Mobile. Technology News, 19-22.
Mallat, N. (2007). Exploring Consumer Adoption of Mobile Payment Systems: A Qualitative Study. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 1-14.
Middle East Hub. (n.d.). Transportation in Abu Dhabi. Web.
Ondrus, J., & Pigneur, Y. (2007). An Assessment of NFC for Future Mobile Payment Systems. Management of Mobile Technology, 1-7.
Quigley, M. (2008). Encyclopedia of Information Ethics and Security. Hershey, PA: Information Science Reference.
Shirazi, F., & Rogers, T. (2008). The Contribution of ICT to Freedom and Democracy: An Empirical Analysis of Archival Data on the Middle East. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 35(6), 1-24.